Abstract
Psidium guajava L. leaves were subjected to extraction, fractionation and isolation of the flavonoidal compounds. Five flavonoidal compounds were isolated which are quercetin, quercetin-3-O-α-L-arabinofuranoside, quercetin-3-O-β-D-arabinopyranoside, quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucoside and quercetin-3-O-β-D-galactoside. Quercetin-3-O-β-D-arabinopyranoside was isolated for the first time from the leaves. Fractions together with the isolates were tested for their antimicrobial activity. The antimicrobial studies showed good activities for the extracts and the isolated compounds.
Keywords: Antimicrobial activity, guava leaves, Psidium guajava L, quercetin glycosides, quercetin, quercetin-3-O-β-D-arabinopyranoside
INTRODUCTION
Psidium guajava L. leaf (family Myrtaceae) has a long history of folk medicinal uses in Egypt and worldwide as a cough sedative, an anti-diarrheic, in the management of hypertension, obesity and in the control of diabetes mellitus.[1–7] The leaf extract was found to possess anticestodal,[8] analgesic, anti-inflammatory properties,[9] antimicrobial[10] hepatoprotective[11] and antioxidant activities.[12] In addition, the leaf extract is used in many pharmaceutical preparations as a cough sedative.
Guava leaf extract contains flavonoids, mainly quercetin derivatives, which are hydrolyzed in the body to give the aglycone quercetin which is responsible for the spasmolytic activity of the leaves.[4] Quercetin has several pharmacologic actions; it inhibits the intestinal movement, reduces capillary permeability in the abdominal cavity[13] and possesses dose-dependent antioxidant properties,[14] anti-inflammatory activity,[15–21] antiviral and antitumor activities.[22–27] It also inhibits the aldose reductase enzyme.[28] It should be noticed that most of the flavonoidal constituents of guava leaf are quercetin derivatives, namely, quercetin, avicularin, guaijaverin, isoquercetin, hyperin, quercitrin, quercetin 3-O-gentiobioside, quercetin 4’-glucuronoide.[4,29–33]
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant material
P. guajava L. leaf was collected from El tahrir (Alexandria-Cairo desert road) during spring while the fruits are premature. A specimen is deposited in the department of Pharmacognosy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Alexandria University, Egypt.
Reference materials
Quercetin, glucose, galactose, L-arabinose and d-arabinose were supplied by E. Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). Quercetin-3-β-D-glucoside and quercetin-3-β-D-galactoside were supplied by Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH (Steinheim, Germany).
Solvents
Petroleum ether (40-60°C), chloroform, ethyl acetate, n-butanol, methanol and ethanol were of analytical grade.
Chromatographic requirements
Precoated thin layer chromatography (TLC) plates (silica gel 60F-254) with the adsorbent layer thickness of 0.25 mm (E-Merck), silica gel (Merck) and kieselgel 60, 0.063-0.20 mm for column chromatography (E-Merck) were used.
Special apparatus
Melting points were determined using Sturat SMP heating stage microscope and were uncorrected. UV spectra were obtained on Pye Unicam SP8-100 UV/VIS spectrophotometer and Perkin-Elmer, Lambada 3B UV/VIS spectrophotometer. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analyses were recorded on JOEL 500 MHz and Bruker Avance 300 MHz spectrometers. Mass spectral analyses were recorded on VG 7070 E-HF.
Extraction, fractionation and isolation
The air-dried powdered P. guajava leaves (1 kg) were exhaustively extracted with 50% ethanol at room temperature. The extract was filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure at 60°C to about 0.5 l and then successively fractionated with petroleum ether, chloroform, ethyl acetate, and n-butanol. Each extract, as well as the interface formed between the chloroform and aqueous layer, were separately concentrated and freed from solvent. Six fractions were obtained: petroleum ether (0.6 g), chloroform (2.7 g), interface formed between chloroform and aqueous phase (10 g), ethyl acetate (9.7 g), n-butanol (22.8 g) and the remaining aqueous extract (9.5 g).
A portion of the ethyl acetate extract (3.5 g) was chromatographed on a 150-g silica gel column (3.5 cm diameter × 30 cm length).
Elution was started with chloroform:ethyl acetate mixture (8:2). Then, the polarity was increased using methanol gradually. Thirty-one fractions of 250 ml in each were collected, screened chromatographically using solvent system chloroform-ethyl acetate-methanol in the ratios (8:2:1) and (8:2:2).
Isolation of material “ A ”
Fractions 12-15 containing 4-6% methanol showed a major spot of Rf 0.46 [chloroform-ethyl acetate-methanol (8:2:1)] that gave a yellow color with ammonia. It was purified from the other minor spots by repeated crystallization from methanol, yielding yellow crystalline needles (21 mg). Rf 0.86 [ethyl acetate-methanol-water-acetic acid (100:2:1:4 drops)], m.p. 316-318°C, soluble in methanol, acetone, dilute alkali and gives a canary yellow color with AlCl3. The UV spectral data, γmax nm, are illustrated in Table 1; [M]+ m/z 302. 1H-NMR spectral data (300 MHz, CD3 COCD3 ) and 13C-NMR spectral data (75 MHz, CD3 COCD3 ) are shown in Table 2.
Table 1.
UV spectral data of the compounds “A”, “B” and “C”
| Spectrum | λmax (nm) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavonoid “A” |
Flavonoid “B” |
Flavonoid “C” |
|||||
| Band I | Band II | Band I | Band II | Band I | Band II | ||
| MeOH | 371 | 253 | 354.5 | 256 | 358 | 256 | |
| MeOH + NaOMe | 398.5, 318 sh | 271.5 | 408 | 272 | 411.5 | 272 | |
| MeOH + AlCl3 | 449.2 | 269 | 432 | 274 | 437 | 273.5 | |
| MeOH + AlCl3+HCl | 421.5, 358.1 sh | 266.9 | 402, 363.5 sh | 270.5 | 405, 365 sh | 268.5 | |
| MeOH + NaOAc | 398.4, 323.4 sh | 269.2 | 407 | 270 | 412 | 272 | |
sh: shoulder
Table 2.
NMR data of flavonoids A, B and C
| Flavonoid “A” |
Flavonoid “B” |
Flavonoid “C” |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (ppm) | δC (ppm) | δH (ppm) | δC (ppm) | δH (ppm) | δC (ppm) | |
| 2 | — | 147.2 | — | 157.7 | — | 157.4 |
| 3 | — | 137.2 | — | 133.3 | — | 134.3 |
| 4 | — | 177 | — | 178.4 | — | 178.2 |
| 5 | — | 162.7 | — | 161.5 | — | 161.7 |
| 6 | 6.13, d, J = 2.1 Hz | 99.5 | 6.21, d, J = 2.1 Hz | 98.3 | 6.21, d, J = 2.1 Hz | 100.3 |
| 7 | — | 165.3 | — | 164.5 | — | 164.8 |
| 8 | 6.4, d, J = 2.1 Hz | 94.8 | 6.41, d, J = 2.1 Hz | 93.2 | 6.41, d, J = 2.1 Hz | 95.1 |
| 9 | — | 158.2 | — | 156.9 | — | 157 |
| 10 | — | 104.5 | — | 104 | — | 104.3 |
| 1‘ | — | 124.1 | — | 121.2 | — | 121 |
| 2‘ | 7.71, d, J = 2.15 Hz | 116.2 | 7.53, d, J = 2.1 Hz | 115.2 | 7.76, d, J = 2.2 Hz | 116.2 |
| 3‘ | — | 146.2 | — | 144.8 | — | 144.7 |
| 4‘ | — | 148.7 | — | 148.2 | — | 148.7 |
| 5‘ | 6.86, d, J = 8.5 Hz | 116.6 | 6.92, d, J = 8.3 Hz | 114.8 | 6.88, d, J = 8.5 Hz | 114.9 |
| 6‘ | 7.57, dd, J = 2.15, 8.5 Hz | 121.8 | 7.51, dd, J = 2.1, 8.3 Hz | 121.4 | 7.58, dd, J = 2.2, 8.5 Hz | 121.7 |
| 1“ | — | — | 5.48, br s | 107.9 | 5.17, d, J = 6.5 Hz | 105 |
| 2“ | — | — | 81.7 | 73.3 | ||
| 3“ | — | — | 3.85-3.94 | 77.1 | 3.81-3.941 | 74.5 |
| 4“ | — | — | 86.4 | 69.5 | ||
| 5“ | — | — | 60.9 | 67.4 | ||
Isolation of material “B”
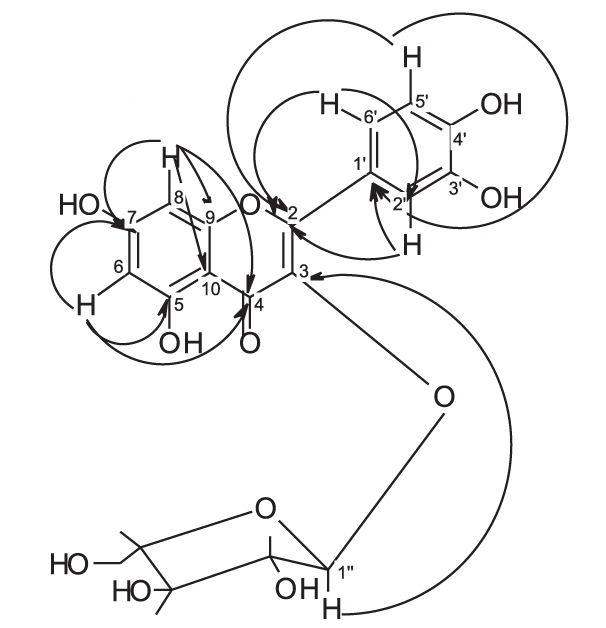
Fractions 18-20 containing 12-15% methanol showed a major spot of Rf 0.57 [chloroform-ethyl acetate-methanol (8:2:2)] that gave a yellow color with ammonia. It was purified by repeated crystallization (12 mg). Rf 0.55 [ethyl acetate-methanol-water-acetic acid (100:2:1:4 drops)], m.p. 209-211°C, soluble in methanol, acetone, dilute alkali and gives a canary yellow color with AlCl3, gives positive molisch’s test. The UV spectral data, γmax nm, are illustrated in Table 1.1 H-NMR spectral data (300 MHz CD3 OH) and 13 C-NMR spectral data (75 MHz, CD3 OH) are shown in Table 2. Long range 1H-13C correlation data as determined by HMBC experiments of flavonoid “B” are shown in Table 3.
Table 3.
Long range 1H-13C correlation data as determined by HMBC experiments of flavonoid “B”
| Carbon number | HMBC | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Flavonoid B | |||
 | |||
| 2 | 6.92 (H-5’) | 7.51(H-6’) | 7.53(H-2’) |
| 3 | 5.48(H-1") | — | — |
| 4 | 6.21(H-6) | 6.41(H-8) | — |
| 5 | 6.21(H-6) | — | — |
| 7 | 6.21(H-6) | 6.41(H-8) | — |
| 9 | 6.41(H-8) | — | — |
| 10 | 6.41(H-8) | — | — |
| 1’ | 7.53(H-2’) | 6.92(H-5’) | — |
| 2’ | 7.51(H-6’) | 6.92(H-5’) | — |
| 3’ | 7.51(H-6’) | 7.53(H-2’) | 6.92(H-5’) |
| 4’ | 7.51(H-6’) | 7.53(H-2’) | 6.92(H-5’) |
| 6’ | 7.53(H-2’) | 6.92(H-5’) | — |
Isolation of materials “C”, “D” and “E”
Fractions 23-29 (0.3 g) containing 17.5-20% methanol showed four spots (giving a yellow color with ammonia) of Rf values 0.61, 0.49, 0.4, 0.35 [ethyl acetate-formic acid-acetic acid-water (25:2:2:4)]. It was rechromatographed on 60 g silica gel column (2.5 cm diameter × 30 cm length). The column was eluted with chloroform, with increasing concentrations of ethyl acetate (0-50%) and then increasing concentrations of methanol. Fractions 13 (chloroform-ethyl acetate (1:1) containing 4% methanol) was crystallized to give 8 mg. Meanwhile, fraction containing 6% methanol in chloroform-ethyl acetate (1:1) was purified by crystallization to give compound “C” (19 mg).
Material “C”: Rf 0.41 [ethyl acetate-methanol-water-acetic acid (100:2:1:4 drops)], m.p. 264-267C, soluble in methanol, acetone, dilute alkali and gives a canary yellow color with AlCl3, gives positive molisch’s test. The UV spectral data, λmax nm, are illustrated in Table 1. 1H-NMR spectral data (300 MHz CD3 OH) and 13C-NMR spectral data (75 MHz, CD3 OH) are shown in Table 2.
Crystallization of fraction containing 10% methanol in chloroform-ethyl acetate (1:1) yielded a mixture of two compounds which were separated by preparative TLC using ethyl acetate-formic acid-acetic acid-water (25:2:2:4) with double run to give compound “D“ (10 mg) and compound “E” (11 mg).
Material “D”: Rf 0.31 [ethyl acetate-methanol-water-acetic acid (100:2:1:4 drops)], m.p. 240-243°C, soluble in methanol, acetone, dilute alkali and gives a canary yellow color with AlCl3, gives positive molisch’s test.
Material “E”: Rf 0.24 [ethyl acetate-methanol-water-acetic acid (100:2:1:4 drops)], m.p. 237-239°C, soluble in methanol, acetone, dilute alkali and gives a canary yellow color with AlCl3, gives positive molisch’s test.
Acid hydrolysis of flavonoids “B”, “C”, “D” and “E”
Three milligrams of each compound was separately dissolved in a mixture of 0.5 ml methanol and 1 ml 2N hydrochloric acid. The solutions were then heated under reflux for 2 h, cooled, diluted with 1 ml water and the aglycones were extracted with ethyl acetate. The aglycones of “B”, “C”, “D” and “E” were identified to be quercetin by co-chromatography using reference compounds and chromatographic system chloroform-ethyl acetate-methanol (8:2:1). The aqueous solutions were neutralized with 5% Na2 CO3 solution and concentrated. The sugar moieties of “B”, “C”, “D” and “E” were identified by TLC in comparison with authentic reference materials, using chloroform-methanol (6:4) and visualized by methanol/H2 SO4 spray reagent. The structures of the isolated compounds are given in Table 4.
Table 4.
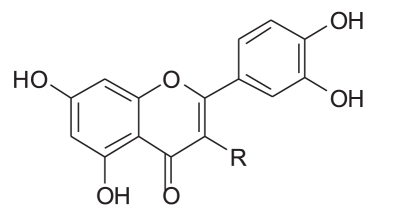
The structures of the isolated compounds
 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Isolated compound | R | Notes |
| Quercetin | -OH | |
| Quercetin-3-O-α-l-arabinofuranoside | 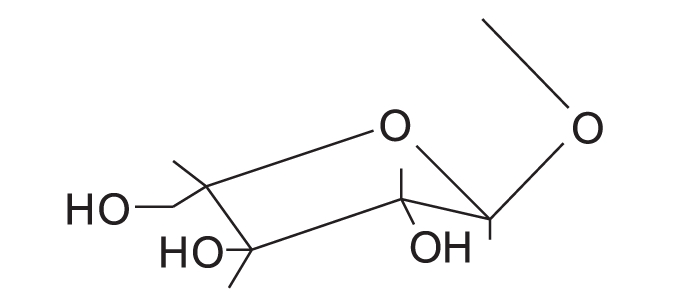 |
Avicularin |
| Quercetin-3-O-β-D-arabinopyranoside | 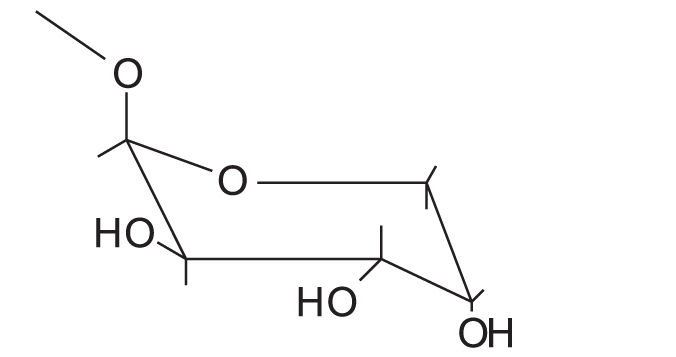 |
First report of its isolation from guava leaves |
| Quercetin 3-O-β-D-glucoside | 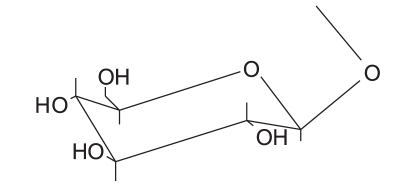 |
Isoquercetin |
| Quercetin 3-O-β-D-galactoside | 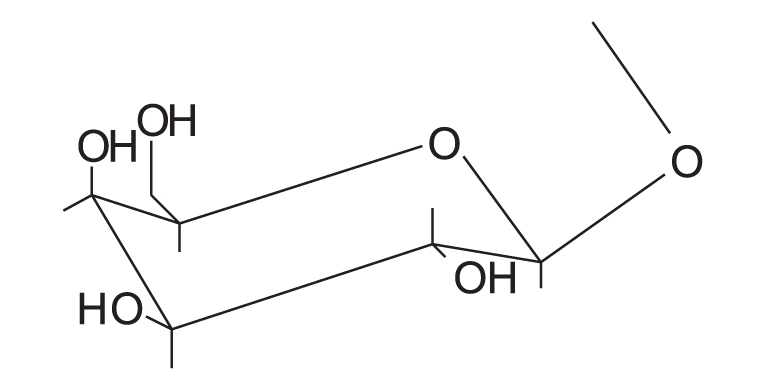 |
Hyperin |
Antimicrobial activity
Antibacterial and antifungal activities were determined using the agar diffusion technique[34] against the gram-positive bacterium Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), two gram-negative bacteria, Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa), and the fungus Candida albicans (C. albicans). The used organisms are local isolates provided from the Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Alexandria.
One milliliter of 24-h broth culture of each of the tested organisms was separately inoculated into 100 ml of sterile molten nutrient agar maintained at 45°C. The inoculated medium was mixed well and poured into sterile 10-cmdiameter petri dishes, receiving 15 ml. After setting, 10 cups, each of 8 mm diameter, were cut in the agar medium (Oxoid, Cambridge, England). Twelve milligrams of each extract or fraction or 3 mg of each isolate, accurately weighed, was dissolved in 1 ml dimethyl formamide (DMF). The solutions were inserted in the cups and incubated at 37°C for 24 h. The results of antimicrobial activity are shown in Table 5 and 6.
Table 5.
Results of antibacterial and antifungal screening of different isolates from P. guajava L. leaf
| Dry extract/isolate | Inhibition zone (IZ) in mm |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria |
Fungi | |||
| Gram positive |
Gram negative |
C. albicans | ||
| S. aureus | E. coli | P. aeruginosea | ||
| Aq. ext. | 19 | 16 | 15 | 17 |
| 16% ethan. | 22 | 17 | 15 | 16 |
| 50% ethan. | 25 | 17 | 16 | 18 |
| 95% ethan. | 26 | 17 | 15 | 18 |
| P.E. | 24 | 19 | — | 16 |
| Chloroform. | 25 | 20 | — | 17 |
| Et. Ac. | 16 | 15 | — | 20 |
| But. | 24 | — | — | 17 |
| Quercetin | 28 | 17 | 18 | 17 |
| Quercetin-3-O-α-L-arabinofuranoside | — | 17 | — | 17 |
| Quercetin-3-O-β-D-arabinopyranoside | — | 20 | — | 18 |
| Ampicillin (10 µg/disk) | 35 | 11 | — | — |
| Clotrimazole (10 mg/ml) | — | — | — | 24 |
Aq. ext., aqueous extract; 16% ethan., ethanolic (16%) extract; 50% ethan., ethanolic (50%) extract; 95% ethan., ethanolic (95%) extract; P.E., petroleum ether fraction of the 50% alcoholic extract; chloroform, chloroform fraction of the 50% alcoholic extract; Et. Ac., ethyl acetate fraction of the 50% alcoholic extract; but., butanol fraction of the 50% alcoholic extract
Table 6.
MIC of different isolates from P. guajava L. leaf
| Dry extract/isolate | MIC (µg/ml) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. coli | C. albicans | |
| Aq. ext. | 5.25 | 10.5 | 5.25 |
| 16% ethan. | 10.5 | 10.5 | 5.25 |
| 50% ethan. | 5.25 | 10.5 | 10.5 |
| 95% ethan. | 5.25 | 10.5 | 5.25 |
| P.E. | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 |
| Chloroform. | 0.78125 (this was least tested concentration) | 3.125 | 6.25 |
| Et. Ac. | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| But. | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Quercetin | 1.25 | 1.25 | 1.25 |
| Quercetin-3-O-α-L-arabinopyranoside | 0.09375 | 0.1875 | 0.375 |
| Quercetin-3-O-β-D-arabinopyranoside | 0.1875 | 0.09375 | 0.1875 |
Aq. ext., aqueous extract; 16% ethan., ethanolic (16%) extract; 50% ethan., ethanolic (50%) extract; 95% ethan., ethanolic (95%) extract; P.E., petroleum ether fraction of the 50% alcoholic extract; chloroform., chloroform fraction of the 50% alcoholic extract; Et. Ac., ethyl acetate fraction of the 50% alcoholic extract; but, butanol fraction of the 50% alcoholic extract.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The UV spectra of flavonoid “A” [Table 1] in different shift reagents showed the pattern of 5,7,3’,4’-tetrahydroxy flavonol aglycone, where the presence of free 5- hydroxy and 3’,4’-ortho dihydroxy groups was deduced from NaOMe spectrum, AlCl 3 and AlCl 3 /HCl spectra, while the presence of a free 7-hydroxy group was found from the NaOAc spectrum.[35] The electron impact-mass spectrometry (EI-MS) of flavonoid “A” illustrated the presence of molecular ion peak [M]+ at m/z 302, suggesting the presence of five hydroxyl groups.
1H-NMR spectra [Table 2] showed two meta coupled aromatic protons at δ 6.13 and δ 6.4 (d, J = 2.1 Hz), assigned for H-6 and H-8, respectively, confirming a 5,7-disubstituted ring A. 3’,4’-disubstituted ring B was deduced by the appearance of three protons at δ 7.71 (d, J = 2.15 Hz,), 6.86 (d, J = 8.5 Hz) and 7.57 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.15 Hz) assigned for H-2’, H-5’ and H-6’, respectively. The 13C-NMR spectrum [Table 2] indicated the presence of 15 signals corresponding to 15 carbons. Thorough study of the homonuclear correlation spectroscopy (COSY) and the heteronuclear multiple quantum coherence (HMQC) spectra helped in the full assignment of all protons to their carbon signals. All the spectral data of flavonoid “A” were found to be identical to those reported for quercetin.[31,36] The identification of the flavonoid was further confirmed by direct comparison with reference sample through mixed melting point (m.m.p.) and co-chromatography.
NMR spectra of flavonoids “B and C” [Table 2] showed similar pattern to those of flavonoid “A”, whereas they showed in addition, the appearance of five additional signals in the 13C-NMR spectra matching those of arabinose,[36,37] along with the appearance of signals of one sugar moiety in 1H-NMR spectra. Therefore, flavonoid “A” was probably the flavonol aglycone and flavonoids “B and C ”were its arabinosides. These data were further supported by the results of the acid hydolysis through comparison of flavonoid “A” and the aglycones resulting from the acid hydrolysis of flavonoids “B and C” with a reference quercetin sample by co-chromatography. Similarly, the sugar moieties were established to be arabinose by comparison with reference sample.
The anomeric proton of flavonoid “B” was observed at δ 5.48 (1H, br s) with its corresponding carbon atom at δ 107.9, while the anomeric proton of flavonoid “C” was observed at δ 5.17 (1H, d, J = 6.5 Hz) with its corresponding carbon atom at δ 105, indicating that the arabinose moiety possessed α-configuration inflavonoid “B” and β-configuration in flavonoid “C”. The ring size of the sugar moiety in both flavonoids was deduced from inspection of the chemical shift values for C-1" and C-4" where they appeared at δ 107.9 and 86.4 for flavonoid “B” and at δ 105 and 69.5 for flavonoid “C”, thus revealing the presence of α-arabinofuranoside and β-arabinopyranoside moieties in flavonoids “B” and “C”, respectively.[36,37]
3-O-glycosylation was confirmed from the study of the HMBC spectrum of flavonoid “B” [Table 3], which showed the correlation between the carbon at δ 133.3 (C-3) and the proton at δ 5.48 (H-1"). 2D HMQC, 2D HMBC and 2D COSY allowed the assignment of all protons to their carbons. Also, the UV absorption of band I at 354.5 and 358 nm (371 nm for quercetin aglycone) indicates the absence of free 3-OH.
From the previous discussion, the structure of flavonoids “B” and “C” could be identified as quercetin-3-O-α-L-arabinofuranoside and quercetin-3-O-β-D-arabinopyranoside, respectively. The observed data were found to be similar to those published for these materials.[36,37]
It is worth mentioning that this is the first report for the isolation of quercetin-3-O-β-D-arabinopyranoside from the species P. guajava L.
Flavonoids “D” and “E” were identified to be quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucoside and quercetin-3-O-β-D-galactoside through comparison with reference compounds using m.m.p. and co-chromatography using ethyl acetate-formic acid-acetic acid-water (25:2:2:4) as the mobile phase.
The results of antibacterial and antifungal screening [Table 5 and 6] showed that quercetin and its glycosides have strong antibacterial activity against the gram positive S. aureus, and the gram negative E. coli and P. aeruginosa. They also showed antifungal activity against C. albicans. It is worth mentioning that the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of quercetin-3-O-β-D-arabinopyranoside and that of quercetin-3-O-α-L-arabinofuranoside glycosides against the tested organisms were even lower than quercetin itself.
All the extracts showed antibacterial and antifungal activities, whereas the chloroformic fraction of the aqueous-alcoholic extract possessed a strong activity against S. aureus.
CONCLUSION
The above results revealed that quercetin is the main flavonoidal nucleus of guava glycosides. Meanwhile, the antimicrobial testing showed that the extracts and the isolated compounds possess antibacterial and antifungal activities. These findings explain the folkloric use of the extracts as bactericide, in cough, diarrhea, gargles to relieve oral ulcers and inflamed gums wound.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.Karawya MS, Abdel Wahab SM, Hifnawy MS, Azzam SM, El Gohary HM. Essential oil of egyptian guajava leaves. Egypt J Biomed Sci. 1999;40:209–16. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Abdelrahim SI, Almagboul AZ, Omer ME, Elegami A. Antimicrobial activity of Psidium guajava L. Fitoterapia. 2002;73:713–5. doi: 10.1016/s0367-326x(02)00243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Begum S, Hassan S, Ali S, Siddiqui B. Chemical constituents from the leaves of Psidium guajava. Nat Prod Res. 2004;18:135–40. doi: 10.1080/14786410310001608019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lozoya X, Meckes M, Abou-Zaid M, Tortoriello J, Nozzolillo C, Arnason JT. Calcium-antagonist effect of quercetin and its relation with the spasmolytic properties of Psidium guajava L. Arch Med Res. 1994;25:11–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ishihara T, Han R. Manufacture of guava leaf extracts. Japanese Kokai Tokkyo Koho Patency number JP 10202002, Kind A2, Date 19980804, Application number JP 1997-46858, Date. 1997;01:23–4. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sunagawa M, Shimada S, Zhang Z, Oonishi A, Nakamura M, Kosugi T. Plasma Insulin concentration was increased by long-term ingestion of guava juice in spontaneous non-insulin-dependant diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) rats. J Health Sci. 2004;50:674–8. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tanaka T, Ishida N, Ishimatsu M, Nonaka G, Nishioka I. Six new complex tannins, guajavins, psidins and psiguavin from the bark of Psidium guajava L. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1992;40:2092–8. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tangpu TV, Yadav AK. Anticestodal efficacy of Psidium guajava against experimental Hymenolepis diminuta infection in rats. Indian J Pharmacol. 2006;38:29–32. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ojewole JA. Anti-Inflammatory and analgesic effects of Psidium guajava Linn.(Myrtaceae) leaf aqueous extracts in rats and mice. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2006;28:441–6. doi: 10.1358/mf.2006.28.7.1003578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nair R, Chanda S. In-vitro antimicrobial activity of Psidium guajava L leaf extracts against clinically important pathogenic microbial strains. Braz J Microbiol. 2007;38:452–8. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Roy K, Kamath V, Asad M. Hepatoprotective activity of Psidium guajava L leaf extract. Indian J Exp Biol. 2006;44:305–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hui-Yin Chen, Gow-Chin Yen. Antioxidant activity and free radical-scavenging capacity of extracts from guava (Psidium guajava L.) leaves. Food Chem. 2007;101:686–94. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhang W, Chen B, Wang C, Zhu Q, Mo Z. Mechanism of quercetin as antidiarrheal agent. Di Yi Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao. 2003;23:1029–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nakamura Y, Ishimitsu S, Tonogai Y. Effects of quercetin and rutin on serum and hepatic lipid concentrations, fecal steroid excretion and serum antioxidant properties. J Health Sci. 2000;46:229–40. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Havsteen B. Flavonoids, A class of natural products of high pharmacological potency. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983;32:1141–8. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90262-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Middleton E, Drzewieki G. Flavonoid inhibition of human basophil histamine release stimulated by various agents. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984;33:3333–8. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90102-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Middleton E, Drzewieki G. Naturalty occurring flavonoids and human basophil histamine release. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;77:155–7. doi: 10.1159/000233771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Amella M, Bronner C, Briancon F, Haag M, Anton R, Landry Y. Inhibition of mast cell histamine release by flavonoids and bioflavonoids. Planta Med. 1985;51:16–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pearce F, Befus AD, Bienenstock J. Mucosal mast cells: III Etfect of quercetin and other flavonoids on antigen-induced histamine secretion from rat intestinal mast cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984;73:819–23. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(84)90453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Busse WW, Kopp DE, Middleton E. Flavonoid modulation of human neutrophil function. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984;73:801–9. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(84)90450-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yoshimoto T, Furukawa M, Yamamoto S, Horie T, Watanabe-Kohno S. Flavonoids Potent inhibitors of arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983;116:612–8. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90568-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Murray MT, Pizzorno JE. Flavonoids-Quercetin, citrus favonoids, and HERs (hydroxylethylrutosides) London: Harcourt Brace and company Ltd; 1999. Text book of Natural Medicine 2nd ed; pp. 745–50. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mucsi I, Pragai BM. Inhibition of virus multiplication and alteration of cyclic AMP level in cell cultures by flavonoids. Experientia. 1985;41:930–1. doi: 10.1007/BF01970018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kaul T, Middleton E, Ogra P. Antiviral effects of flavonoids on human viruses. J Med Virol. 1985;15:71–9. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890150110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Farkas L, Gabor M, kallay F, Wagner HI. New York: Elsevier; 1982. Flavonoids and Bioflavonoids; pp. 443–50. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Guttner J, Veckenstedt A, Heinecke H, Pusztai R. Effect of quercetin on the course of mengo virus infection in immunodeficient and normal mice. A histological study Acta Virol. 1982;26:148–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kaneuchi M, Sasaki M, Tanaka Y, Sakuragi N, Fujimoto S, Dahiya R. Quercetin regulates growth of Ishikawa cells through the suppression of EGF and cyclin D1. Int J Oncol. 2003;22:159–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chaundry PS, Cabrera J, Juliana HR, Varma SD. Inhibition of human lens aldose reductase by flavonoids, sulindac and indomethacin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983;32:1995–8. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90417-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Abdel Wahab SM, Hifawy MS, El Gohary HM, Isak M. Study of carbohydrates, lipids, protein, flavonoids, vitamin C and biological activity of Psidium guajava L growing in Egypt. Egypt J Biomed Sci. 2004;16:35–52. [Google Scholar]
- 30.El Khadem H, Mohamed YS. Constituents of the leaves of Psidium guajava L: Part II: Quercetin, avicularin, and guajaverin. J Chem Soc. 1958;32:3320–3. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Arima H, Danno G. Isolation of antimicrobial compounds from guava (Psidium guajava L.) and their structural elucidation. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2002;66:1727–30. doi: 10.1271/bbb.66.1727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Seshadri T, Vasishta K. Polyphenols of the leaves of Psidium guava; quercetin, guaijaverin, leucocyanidin, amritoside. Phytochemistry. 1965;4:989–92. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kandil FE, El-Sayed NH, Micheal HN, Ishak MS, Mabry TJ. Flavonoids from Psidium guajava. Asian J Chem. 1997;9:871–2. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jian FR, Kar A. The antibacterial activity of some essensial oils and their combinations. Planta Med. 1971;20:118–22. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1099675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Harbone JB, Mabry TJ. London: Chapman and Hall; 1982. The Flavonoids: Advances in research. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Agrawal PK. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1989. Carbon-13 NMR of flavonoids. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Markhan KR, Terani B, Stanley R, Geiger H, Mabry TJ. Carbon-13 NMR studies of flavonoid glycosides and their acylated derivatives. Tetrahedron. 1978;34:1389–97. [Google Scholar]


