Abstract
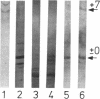
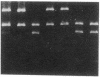
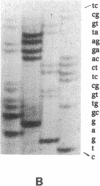
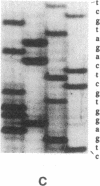
Epidemiologic data of recent years have identified an important role of HDL deficiency in the etiology of atherosclerosis. Biochemical data suggest that some of these deficiencies may be a consequence of defects in the structural genes of HDL apolipoproteins or of plasma enzymes that modify HDL. We analyzed the genetic defect in a 42-yr-old patient suffering from corneal opacities and complete absence of HDL cholesterol but not of coronary artery disease, thus clinically resembling fish eye disease. The observation of an abnormal immunoblot banding pattern of apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) and of reduced lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) activity in plasma led to sequence analysis of the genes for apo A-I and LCAT in this patient and his family. Direct sequencing of polymerase chain reaction amplified DNA segments containing the exons of the candidate genes, resulted in the identification of a frameshift mutation in apo A-I while the LCAT sequence was identical to the wild type. The apo A-I mutation was predictive for an extensive alteration of the COOH-terminal sequence of the encoded protein. Evidence for the release of this mutant protein into the plasma compartment and for the absence of normal apo A-I was derived from ultraviolet laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry analysis. Our results suggest that a defective apo A-I is the causative defect in this case of HDL deficiency with corneal opacities.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers J. J., Adolphson J. L., Chen C. H. Radioimmunoassay of human plasma lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):141–148. doi: 10.1172/JCI110006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobiásová M. Lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase and the regulation of endogenous cholesterol transport. Adv Lipid Res. 1983;20:107–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidge N. H., Nestel P. J. Identification of apolipoproteins involved in the interaction of human high density lipoprotein3 with receptors on cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3570–3575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte T. M., Nichols A. V., Krauss R. M., Norum R. A. Familial apolipoprotein AI and apolipoprotein CIII deficiency. Subclass distribution, composition, and morphology of lipoproteins in a disorder associated with premature atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1601–1613. doi: 10.1172/JCI111576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franceschini G., Sirtori C. R., Capurso A., 2nd, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. A-IMilano apoprotein. Decreased high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels with significant lipoprotein modifications and without clinical atherosclerosis in an Italian family. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):892–900. doi: 10.1172/JCI109956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedewald W. T., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 1972 Jun;18(6):499–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohlich J., Hoag G., McLeod R., Hayden M., Godin D. V., Wadsworth L. D., Critchley J. D., Pritchard P. H. Hypoalphalipoproteinemia resembling fish eye disease. Acta Med Scand. 1987;221(3):291–298. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1987.tb00896.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohlich J., McLeod R., Pritchard P. H., Fesmire J., McConathy W. Plasma lipoprotein abnormalities in heterozygotes for familial lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency. Metabolism. 1988 Jan;37(1):3–8. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(88)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A. The plasma lecithins:cholesterol acyltransferase reaction. J Lipid Res. 1968 Mar;9(2):155–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson A., McConathy W. J., Alaupovic P., Curry M. D., Persson B. Identification of lipoprotein families in a variant of human plasma apolipoprotein A deficiency. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1979 Jun;39(4):377–387. doi: 10.3109/00365517909106122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W., Weisgraber K. H., Bersot T. P. Apoprotein (E--A-II) complex of human plasma lipoproteins. II. Receptor binding activity of a high density lipoprotein subfraction modulated by the apo(E--A-II) complex. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6289–6295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs H. U., Assmann G., Greifendorf D., Benninghoven A. High performance liquid chromatography and time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry: a new dimension in structural analysis of apolipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1986 Jun;27(6):613–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., Ferris E., Haddad I. A. DNA inversion within the apolipoproteins AI/CIII/AIV-encoding gene cluster of certain patients with premature atherosclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7198–7202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Isolation and characterization of the human apolipoprotein A-I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6147–6151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J., Wion K., Drayna D., Fielding C., Lawn R. Human lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase gene: complete gene sequence and sites of expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 9;14(23):9397–9406. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.23.9397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel H. J., Kladetzky R. G., Assmann G. One-step screening method for the polymorphism of apolipoproteins A-I, A-II, and A-IV. J Lipid Res. 1982 Aug;23(6):915–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norum R. A., Lakier J. B., Goldstein S., Angel A., Goldberg R. B., Block W. D., Noffze D. K., Dolphin P. J., Edelglass J., Bogorad D. D. Familial deficiency of apolipoproteins A-I and C-III and precocious coronary-artery disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jun 24;306(25):1513–1519. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198206243062503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordovas J. M., Cassidy D. K., Civeira F., Bisgaier C. L., Schaefer E. J. Familial apolipoprotein A-I, C-III, and A-IV deficiency and premature atherosclerosis due to deletion of a gene complex on chromosome 11. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16339–16342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Protter A. A., Levy-Wilson B., Miller J., Bencen G., White T., Seilhamer J. J. Isolation and sequence analysis of the human apolipoprotein CIII gene and the intergenic region between the apo AI and apo CIII genes. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):449–456. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandkamp M., Tambyrajah B., Schriewer H., Assmann G. Simplified turbidimetric determination of apolipoproteins A-I, A-II and B using a microtitre method. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1988 Nov;26(11):685–688. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1988.26.11.685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Ordovas J. M., Law S. W., Ghiselli G., Kashyap M. L., Srivastava L. S., Heaton W. H., Albers J. J., Connor W. E., Lindgren F. T. Familial apolipoprotein A-I and C-III deficiency, variant II. J Lipid Res. 1985 Sep;26(9):1089–1101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz G., Robenek H., Lohmann U., Assmann G. Interaction of high density lipoproteins with cholesteryl ester-laden macrophages: biochemical and morphological characterization of cell surface receptor binding, endocytosis and resecretion of high density lipoproteins by macrophages. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):613–622. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03674.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe C. R., Sidoli A., Shelley C. S., Lucero M. A., Shoulders C. C., Baralle F. E. Human apolipoproteins AI, AII, CII and CIII. cDNA sequences and mRNA abundance. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3917–3932. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slotte J. P., Oram J. F., Bierman E. L. Binding of high density lipoproteins to cell receptors promotes translocation of cholesterol from intracellular membranes to the cell surface. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):12904–12907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Eckardstein A., Funke H., Henke A., Altland K., Benninghoven A., Assmann G. Apolipoprotein A-I variants. Naturally occurring substitutions of proline residues affect plasma concentration of apolipoprotein A-I. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1722–1730. doi: 10.1172/JCI114355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Eckardstein A., Funke H., Walter M., Altland K., Benninghoven A., Assmann G. Structural analysis of human apolipoprotein A-I variants. Amino acid substitutions are nonrandomly distributed throughout the apolipoprotein A-I primary structure. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8610–8617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]