Abstract
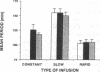
Ultradian "oscillations" or "pulses" of insulin secretion with periods around 120 min occur in man. It is not known whether glucose plays an active role in generating these oscillations, or if an intrapancreatic pacemaker generates oscillations in insulin secretion that entrain glucose passively. To determine if the frequency of pulses of insulin secretion could be modified by oscillatory glucose infusion, seven normal men were studied on three separate occasions. The first study involved a constant glucose infusion administered at a rate of 6 mg/kg per min for 28 h. During the two subsequent studies, the subjects received an oscillatory glucose infusion for 28 h with the same mean rate, an amplitude of 33% above and below the mean infusion rate, a sinusoidal waveshape and a period either 20% longer ("slow oscillatory infusion") or 20% shorter ("rapid oscillatory infusion") than the periodicity observed during constant glucose infusion. Samples for insulin, C-peptide, and glucose were drawn at 10-min intervals during the last 24 h of each study. Insulin secretion rates were calculated by deconvolution of C-peptide levels. During constant glucose infusion, the respective periods of oscillation of glucose and insulin secretion averaged 126 +/- 5 min and 118 +/- 3 min (mean +/- SEM). During the slow oscillatory infusion, the period of infusion was 155 +/- 7 min and the periods of insulin secretion and glucose were, respectively, 155 +/- 7 min and 150 +/- 5 min. During rapid oscillatory infusion, the period of infusion was 103 +/- 5 min and the period of both insulin secretion and glucose was 105 +/- 5 min. Thus the periodicity of both insulin secretion and plasma glucose changed in parallel with the exogenous periodicity, indicating complete entrainment of the secretory oscillations. These results suggest that the ultradian oscillations of insulin secretion are caused by the feedback loop linking glucose and insulin.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowden C. R., Bergman R. N., Marsh D. J. Cause of glucose oscillations during glucose infusion: periodic variation in glucose uptake. Am J Physiol. 1980 Apr;238(4):E395–E407. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.4.E395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou H. F., Ipp E. Pulsatile insulin secretion in isolated rat islets. Diabetes. 1990 Jan;39(1):112–117. doi: 10.2337/diacare.39.1.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton R. P., Allen R. C., Schade D. S., Erickson K. M., Standefer J. Prehepatic insulin production in man: kinetic analysis using peripheral connecting peptide behavior. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Sep;51(3):520–528. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-3-520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. S., Faria A. C., Christiansen E., Ho K. Y., Weiss J., Rogol A. D., Johnson M. L., Blizzard R. M., Veldhuis J. D., Thorner M. O. Impact of intensive venous sampling on characterization of pulsatile GH release. Am J Physiol. 1987 Apr;252(4 Pt 1):E549–E556. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.252.4.E549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber O. K., Binder C., Markussen J., Heding L. G., Naithani V. K., Kuzuya H., Blix P., Horwitz D. L., Rubenstein A. H. Characterization of seven C-peptide antisera. Diabetes. 1978;27 (Suppl 1):170–177. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.1.s170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen B. C., Schielke G. P., Jen K. L., Wolfe R. A., Movahed H., Pek S. B. Rapid fluctuations in plasma catecholamines in monkeys under undisturbed conditions. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jan;242(1):E40–E46. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.242.1.E40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. A., Matthews D. R., Peto J., Turner R. C. Cyclic oscillations of basal plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in human beings. N Engl J Med. 1979 Nov 8;301(19):1023–1027. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197911083011903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh B. D., Marsh D. J., Bergman R. N. Oscillations enhance the efficiency and stability of glucose disposal. Am J Physiol. 1986 May;250(5 Pt 1):E576–E582. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.250.5.E576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. R., Lang D. A., Burnett M. A., Turner R. C. Control of pulsatile insulin secretion in man. Diabetologia. 1983 Apr;24(4):231–237. doi: 10.1007/BF00282705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ookhtens M., Marsh D. J., Smith S. W., Bergman R. N., Yates F. E. Fluctuations of plasma glucose and insulin in conscious dogs receiving glucose infusions. Am J Physiol. 1974 Apr;226(4):910–919. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.4.910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky K. S., Given B. D., Hirsch L. J., Tillil H., Shapiro E. T., Beebe C., Frank B. H., Galloway J. A., Van Cauter E. Abnormal patterns of insulin secretion in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 12;318(19):1231–1239. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805123181903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky K. S., Given B. D., Van Cauter E. Twenty-four-hour profiles and pulsatile patterns of insulin secretion in normal and obese subjects. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):442–448. doi: 10.1172/JCI113339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky K. S., Licinio-Paixao J., Given B. D., Pugh W., Rue P., Galloway J., Karrison T., Frank B. Use of biosynthetic human C-peptide in the measurement of insulin secretion rates in normal volunteers and type I diabetic patients. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):98–105. doi: 10.1172/JCI112308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prager R., Wallace P., Olefsky J. M. In vivo kinetics of insulin action on peripheral glucose disposal and hepatic glucose output in normal and obese subjects. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):472–481. doi: 10.1172/JCI112599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro E. T., Tillil H., Polonsky K. S., Fang V. S., Rubenstein A. H., Van Cauter E. Oscillations in insulin secretion during constant glucose infusion in normal man: relationship to changes in plasma glucose. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Aug;67(2):307–314. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-2-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon C., Brandenberger G., Follenius M. Ultradian oscillations of plasma glucose, insulin, and C-peptide in man during continuous enteral nutrition. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Apr;64(4):669–674. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-4-669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon C., Follenius M., Brandenberger G. Postprandial oscillations of plasma glucose, insulin and C-peptide in man. Diabetologia. 1987 Oct;30(10):769–773. doi: 10.1007/BF00275742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagner J. I., Samols E., Weir G. C. Sustained oscillations of insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin from the isolated canine pancreas during exposure to a constant glucose concentration. J Clin Invest. 1980 Apr;65(4):939–942. doi: 10.1172/JCI109750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Cauter E., Désir D., Decoster C., Féry F., Balasse E. O. Nocturnal decrease in glucose tolerance during constant glucose infusion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Sep;69(3):604–611. doi: 10.1210/jcem-69-3-604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Cauter E. Estimating false-positive and false-negative errors in analyses of hormonal pulsatility. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jun;254(6 Pt 1):E786–E794. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.6.E786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldhuis J. D., Evans W. S., Rogol A. D., Drake C. R., Thorner M. O., Merriam G. R., Johnson M. L. Intensified rates of venous sampling unmask the presence of spontaneous, high-frequency pulsations of luteinizing hormone in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Jul;59(1):96–102. doi: 10.1210/jcem-59-1-96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. J., Hope I. D., Ader M., Bergman R. N. Insulin transport across capillaries is rate limiting for insulin action in dogs. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1620–1628. doi: 10.1172/JCI114339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]