Abstract
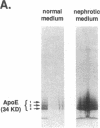
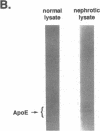
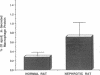
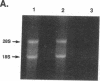
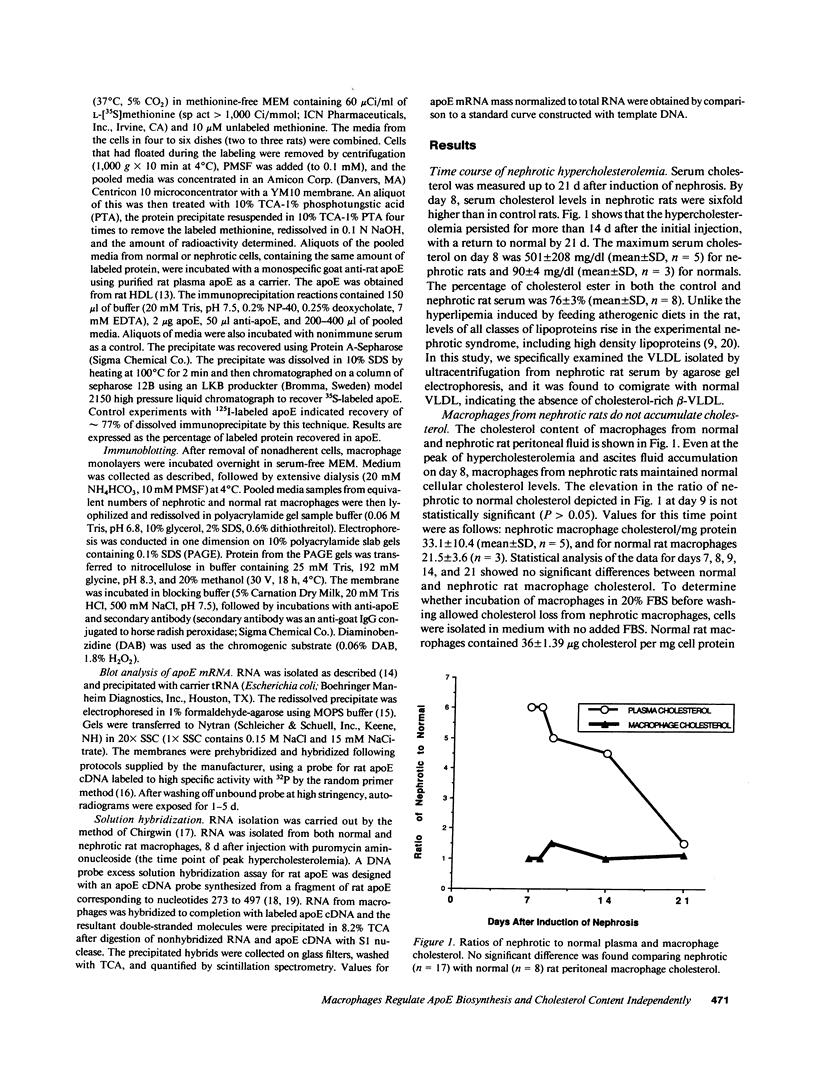
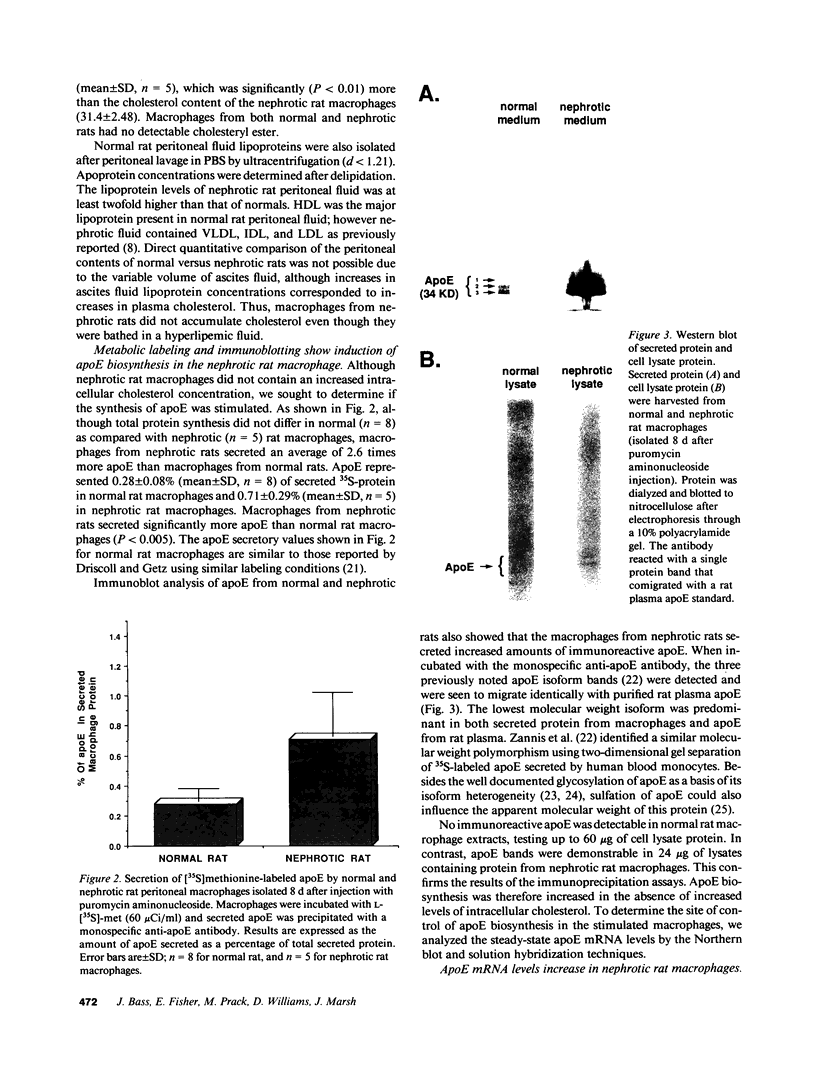
The effects of the nephrotic syndrome in rats on the cholesterol content and the biosynthesis of apolipoprotein E (apoE) by resident peritoneal macrophages have been investigated. Since the nephrotic syndrome has been associated with an increased risk of coronary atherosclerosis, we hypothesized that macrophages from nephrotic rats would accumulate cholesterol and undergo transformation into foam cells, with a concomitant increase in apoE biosynthesis. The nephrotic syndrome was induced in rats with puromycin aminonucleoside. Peritoneal macrophages exposed in vivo for 7-21 d to ascites fluid derived from plasma containing sixfold elevations of lipoproteins did not accumulate unesterified or esterified cholesterol. Nevertheless, immunoprecipitation assays after incubation of the isolated cells with [35S]methionine, or immunoblot analysis of the incubation medium demonstrated a 2.6-fold increase in apoE secretion compared with normal macrophages. This increase was accompanied by 5- to 10-fold increases in cellular apoE messenger RNA as determined by quantitative solution hybridization assay. Peritoneal macrophages cultured from nephrotic rats during the period of hypercholesterolemia also showed distinct and highly reproducible morphologic changes. The dissociation between apoE biosynthesis and macrophage cholesterol content provides new insight into the response of peritoneal macrophages in vivo to endogenous hyperlipemia.
Full text
PDF



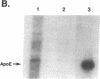
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auwerx J. H., Deeb S., Brunzell J. D., Peng R., Chait A. Transcriptional activation of the lipoprotein lipase and apolipoprotein E genes accompanies differentiation in some human macrophage-like cell lines. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2651–2655. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basheeruddin K., Stein P., Strickland S., Williams D. L. Expression of the murine apolipoprotein E gene is coupled to the differentiated state of F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):709–713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu S. K., Brown M. S., Ho Y. K., Havel R. J., Goldstein J. L. Mouse macrophages synthesize and secrete a protein resembling apolipoprotein E. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7545–7549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu S. K., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Independent pathways for secretion of cholesterol and apolipoprotein E by macrophages. Science. 1983 Feb 18;219(4586):871–873. doi: 10.1126/science.6823554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard D. B. Extrarenal complications of the nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int. 1988 Jun;33(6):1184–1202. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. W., Sholley M. M., Miller G. A. Macrophage heterogeneity in tumor resistance: cytostatic and cytotoxic activity of Corynebacterium parvum-activated and proteose peptone-elicited rat macrophages against Moloney sarcoma tumor cells. Cell Immunol. 1980 Mar 1;50(1):153–168. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson P. A., Lukaszewski L. M., Ells P. F., Malbon C. C., Williams D. L. Quantification and regulation of apolipoprotein E expression in rat Kupffer cells. J Lipid Res. 1989 Mar;30(3):403–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson P. A., Schechter N., Williams D. L. Induction of rat E and chicken A-I apolipoproteins and mRNAs during optic nerve degeneration. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5681–5684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. R., Pesek I., McCarter M. D., Karnovsky M. J. Altered functional characteristics of rat macrophages during nephrosis. Synergistic effects of hypercholesterolemia. Am J Pathol. 1989 Oct;135(4):711–718. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll D. M., Getz G. S. Extrahepatic synthesis of apolipoprotein E. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 1;25(12):1368–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feo F., Canuto R. A., Torrielli M. V., Garcea R., Dianzani M. U. Effect of a cholesterol-rich diet on cholesterol content and phagocytic activity of rat macrophages. Agents Actions. 1976 Feb;6(1-3):135–142. doi: 10.1007/BF01972197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber D. W., Marsh J. B. Ascites fluid lipoproteins in experimental nephrotic syndrome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 15;959(3):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebicke-Haerter P. J., Shooter E. M. Sulfation of rat apolipoprotein E. J Neurochem. 1989 Sep;53(3):912–916. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb11791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick J. M., Adelman S. J., Phillips M. C., Rothblat G. H. Cellular cholesteryl ester clearance. Relationship to the physical state of cholesteryl ester inclusions. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13425–13430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M. Rapid and quantitative preparation of cytoplasmic RNA from small numbers of cells. Anal Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;173(1):93–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignatius M. J., Gebicke-Härter P. J., Skene J. H., Schilling J. W., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Shooter E. M. Expression of apolipoprotein E during nerve degeneration and regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1125–1129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klahr S., Schreiner G., Ichikawa I. The progression of renal disease. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 23;318(25):1657–1666. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806233182505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSH J. B., DRABKIN D. L. Experimental reconstruction of metabolic pattern of lipid nephrosis: key role of hepatic protein synthesis in hyperlipemia. Metabolism. 1960 Oct;9:946–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):622–630. doi: 10.1126/science.3283935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Cellular and molecular biology of lipoprotein metabolism in atherosclerosis. Diabetes. 1981;30(Suppl 2):60–65. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.2.s60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. B. Lipoprotein metabolism in experimental nephrosis. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 15;25(13):1619–1623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzone T., Basheeruddin K., Poulos C. Regulation of macrophage apolipoprotein E gene expression by cholesterol. J Lipid Res. 1989 Jul;30(7):1055–1064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzone T., Gump H., Diller P., Getz G. S. Macrophage free cholesterol content regulates apolipoprotein E synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11657–11662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. E., Tsukada T., Gown A. M., Ross R. Fatty streak initiation in Watanabe Heritable Hyperlipemic and comparably hypercholesterolemic fat-fed rabbits. Arteriosclerosis. 1987 Jan-Feb;7(1):9–23. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.7.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snipes G. J., McGuire C. B., Norden J. J., Freeman J. A. Nerve injury stimulates the secretion of apolipoprotein E by nonneuronal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1130–1134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Chin J. R. Apoprotein E is synthesized and secreted by resident and thioglycollate-elicited macrophages but not by pyran copolymer- or bacillus Calmette-Guerin-activated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1272–1293. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Chin J. R. Endotoxin suppresses expression of apoprotein E by mouse macrophages in vivo and in culture. A biochemical and genetic study. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10642–10648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Chin J. R. Onset of apoprotein E secretion during differentiation of mouse bone marrow-derived mononuclear phagocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;97(4):1113–1118. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.4.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernette-Hammond M. E., Lauer S. J., Corsini A., Walker D., Taylor J. M., Rall S. C., Jr Glycosylation of human apolipoprotein E. The carbohydrate attachment site is threonine 194. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9094–9101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. L., Newman T. C., Shelness G. S., Gordon D. A. Measurement of apolipoprotein mRNA by DNA-excess solution hybridization with single-stranded probes. Methods Enzymol. 1986;128:671–689. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)28099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler K. E., Marsh J. B. Characterization of nascent high density lipoprotein subfractions from perfusates of rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1989 Jul;30(7):979–987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyne K. L., Schreiber J. R., Larsen A. L., Getz G. S. Regulation of apolipoprotein E biosynthesis by cAMP and phorbol ester in rat ovarian granulosa cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):981–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Human very low density lipoprotein apolipoprotein E isoprotein polymorphism is explained by genetic variation and posttranslational modification. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):1033–1041. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., vanderSpek J., Silverman D. Intracellular modifications of human apolipoprotein E. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13415–13421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]