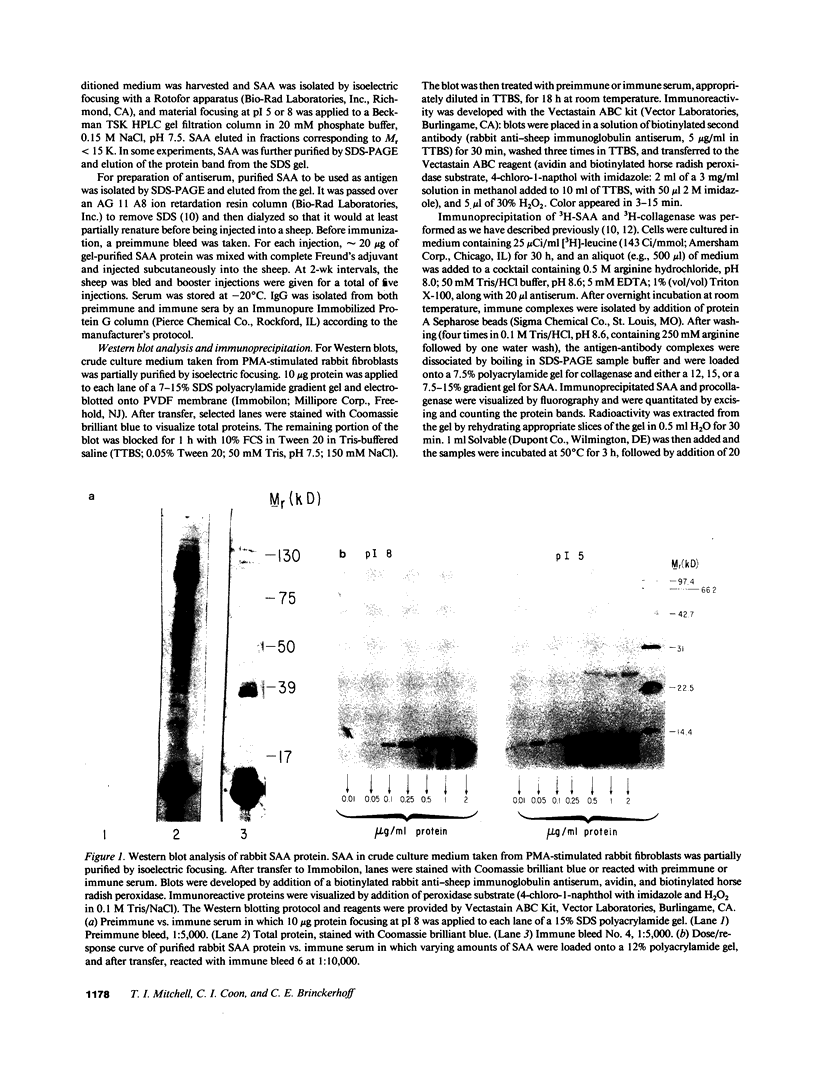
Abstract
We report that nucleic acid sequence analysis of a full-length cDNA clone for a rabbit serum amyloid A (SAA)-like protein has identified this protein as more closely related to SAA3 than to SAA1. SAA3 induced collagenase synthesis in rabbit synovial fibroblasts, and immune IgG raised against this SAA protein abrogated the induction. Using antisera to immunoprecipitate biosynthetically labeled 3H-SAA and 3H-collagenase from culture medium, we compared the levels of SAA and collagenase synthesized by cultures of rabbit fibroblasts at early passage (passages 3-6) with those synthesized by late passage cells (passage 16). Comparatively high levels of both proteins were produced constitutively by fibroblasts at low passage. With increasing passage, levels of both proteins drop so that by passage 16, constitutive production of SAA and collagenase was only approximately 15-20% that of passage 3 cells. Cells at low passage could be readily stimulated with phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) or interleukin 1 (IL-1) to synthesize increased amounts of both SAA and collagenase. In passage 5 cells treated with PMA, we detected increased SAA mRNA by 1.5 h and collagenase mRNA by 5 h. However, older passage cells were more refractory to stimulation and required longer induction times. We suggest that SAA3 may be expressed by fibroblasts at sites of acute inflammation or injury, and that elevated levels of SAA3 may signify "activated" fibroblasts which are already producing increased amounts of collagenase constitutively and which are predisposed to further stimulation.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Baumann I., Stein B., Delius H., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate induction of the human collagenase gene is mediated by an inducible enhancer element located in the 5'-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2256–2266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. A., O'Hara M., Angel P., Chojkier M., Karin M. Prolonged activation of jun and collagenase genes by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):661–663. doi: 10.1038/337661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinckerhoff C. E., Mitchell T. I. Autocrine control of collagenase synthesis by synovial fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Jul;136(1):72–80. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041360109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinckerhoff C. E., Mitchell T. I., Karmilowicz M. J., Kluve-Beckerman B., Benson M. D. Autocrine induction of collagenase by serum amyloid A-like and beta 2-microglobulin-like proteins. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):655–657. doi: 10.1126/science.2536953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinckerhoff C. E., Plucinska I. M., Sheldon L. A., O'Connor G. T. Half-life of synovial cell collagenase mRNA is modulated by phorbol myristate acetate but not by all-trans-retinoic acid or dexamethasone. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 21;25(21):6378–6384. doi: 10.1021/bi00369a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Boyle W. J., Meek J., Smeal T., Hunter T., Karin M. The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conca W., Kaplan P. B., Krane S. M. Increases in levels of procollagenase messenger RNA in cultured fibroblasts induced by human recombinant interleukin 1 beta or serum follow c-jun expression and are dependent on new protein synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1753–1757. doi: 10.1172/JCI114077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fini M. E., Karmilowicz M. J., Ruby P. L., Beeman A. M., Borges K. A., Brinckerhoff C. E. Cloning of a complementary DNA for rabbit proactivator. A metalloproteinase that activates synovial cell collagenase, shares homology with stromelysin and transin, and is coordinately regulated with collagenase. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Nov;30(11):1254–1264. doi: 10.1002/art.1780301108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. H., Sheldon L. A., Fletcher C. F., Brinckerhoff C. E. Isolation of a collagenase cDNA clone and measurement of changing collagenase mRNA levels during induction in rabbit synovial fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1981–1985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. D., Holt J. T., Matrisian L. M. Growth factors regulate transin gene expression by c-fos-dependent and c-fos-independent pathways. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1424–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.2462278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluve-Beckerman B., Dwulet F. E., DiBartola S. P., Benson M. D. Primary structures of dog and cat amyloid A proteins: comparison to human AA. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1989;94(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(89)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluve-Beckerman B., Long G. L., Benson M. D. DNA sequence evidence for polymorphic forms of human serum amyloid A (SAA). Biochem Genet. 1986 Dec;24(11-12):795–803. doi: 10.1007/BF00554519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner I., Ganapathi M., Schultz D. The acute phase response is mediated by heterogeneous mechanisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;557:19–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb23996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner I. The phenomenon of the acute phase response. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:39–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowell C. A., Potter D. A., Stearman R. S., Morrow J. F. Structure of the murine serum amyloid A gene family. Gene conversion. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8442–8452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowell C. A., Stearman R. S., Morrow J. F. Transcriptional regulation of serum amyloid A gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8453–8461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek R. L., Benditt E. P. Rat tissues express serum amyloid A protein-related mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1890–1894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmelee D. C., Titani K., Ericsson L. H., Eriksen N., Benditt E. P., Walsh K. A. Amino acid sequence of amyloid-related apoprotein (apoSAA1) from human high-density lipoprotein. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 6;21(14):3298–3303. doi: 10.1021/bi00257a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramadori G., Sipe J. D., Colten H. R. Expression and regulation of the murine serum amyloid A (SAA) gene in extrahepatic sites. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3645–3647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack G. H., Jr, Talbot C. C., Jr The human serum amyloid A (SAA)-encoding gene GSAA1: nucleotide sequence and possible autocrine-collagenase-inducer function. Gene. 1989 Dec 14;84(2):509–515. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90528-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönthal A., Herrlich P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Ponta H. Requirement for fos gene expression in the transcriptional activation of collagenase by other oncogenes and phorbol esters. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):325–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90195-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. D., Colten H. R., Goldberger G., Edge M. D., Tack B. F., Cohen A. S., Whitehead A. S. Human serum amyloid A (SAA): biosynthesis and postsynthetic processing of preSAA and structural variants defined by complementary DNA. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 4;24(12):2931–2936. doi: 10.1021/bi00333a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiemeier D. C., Tilghman S. M., Leder P. Purification and cloning of a mouse ribosomal gene fragment in coliphage lambda. Gene. 1977;2(3-4):173–191. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb C. F., Tucker P. W., Dowton S. B. Expression and sequence analyses of serum amyloid A in the Syrian hamster. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4785–4790. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo P., Sipe J., Dinarello C. A., Colten H. R. Structure of a human serum amyloid A gene and modulation of its expression in transfected L cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15790–15795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]