Abstract
The Finnish type of familial amyloidosis is a systemic disease characterized by progressive cranial neuropathy, corneal lattice dystrophy, and distal sensimotor neuropathy. Amyloid fibrils were isolated from the kidney and heart of a patient with Finnish amyloidosis. After solubilization, the amyloid proteins were fractionated by gel filtration and purified by reverse-phase HPLC. Complete amino acid sequence analyses show that the two amyloid components obtained are fragments of gelsolin, an actin-modulating protein occurring in plasma and the cytoskeleton. The larger component represents residues 173-243 and the minor component residues 173-225, respectively, of mature gelsolin. When compared with the predicted primary structure of human gelsolin a single amino acid substitution is present in amyloid: at position 15 of the amyloid proteins an asparagine is found instead of an aspartic acid residue at the corresponding position (187) in gelsolin. Antibodies to a dodecapeptide of the amyloidogenic region of gelsolin specifically stain the tissue amyloid deposits in Finnish hereditary amyloidosis. The results show that the amyloid subunit protein in Finnish hereditary amyloidosis represents a new type of amyloid that is derived from an actin filament-binding region of a variant gelsolin molecule by limited proteolysis.
Full text
PDF


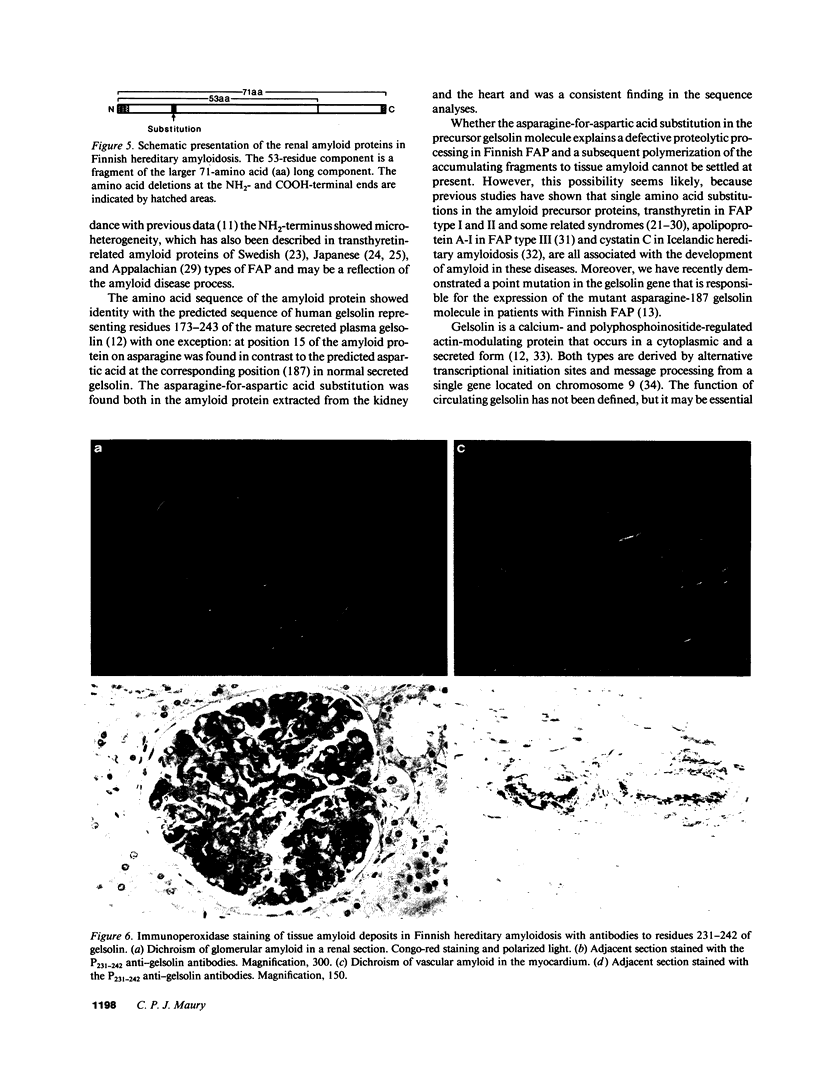

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ampe C., Vandekerckhove J. The F-actin capping proteins of Physarum polycephalum: cap42(a) is very similar, if not identical, to fragmin and is structurally and functionally very homologous to gelsolin; cap42(b) is Physarum actin. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4149–4157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02761.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- André E., Lottspeich F., Schleicher M., Noegel A. Severin, gelsolin, and villin share a homologous sequence in regions presumed to contain F-actin severing domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):722–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arpin M., Pringault E., Finidori J., Garcia A., Jeltsch J. M., Vandekerckhove J., Louvard D. Sequence of human villin: a large duplicated domain homologous with other actin-severing proteins and a unique small carboxy-terminal domain related to villin specificity. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1759–1766. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. D. Partial amino acid sequence homology between an heredofamilial amyloid protein and human plasma prealbumin. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):1035–1041. doi: 10.1172/JCI110114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boysen G., Galassi G., Kamieniecka Z., Schlaeger J., Trojaborg W. Familial amyloidosis with cranial neuropathy and corneal lattice dystrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1979 Nov;42(11):1020–1030. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.42.11.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J. Gelsolin has three actin-binding sites. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1553–1562. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa P. P., Figueira A. S., Bravo F. R. Amyloid fibril protein related to prealbumin in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4499–4503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darras B. T., Adelman L. S., Mora J. S., Bodziner R. A., Munsat T. L. Familial amyloidosis with cranial neuropathy and corneal lattice dystrophy. Neurology. 1986 Mar;36(3):432–435. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.3.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwulet F. E., Benson M. D. Characterization of a transthyretin (prealbumin) variant associated with familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy type II (Indiana/Swiss). J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):880–886. doi: 10.1172/JCI112675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwulet F. E., Benson M. D. Primary structure of an amyloid prealbumin and its plasma precursor in a heredofamilial polyneuropathy of Swedish origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):694–698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gejyo F., Yamada T., Odani S., Nakagawa Y., Arakawa M., Kunitomo T., Kataoka H., Suzuki M., Hirasawa Y., Shirahama T. A new form of amyloid protein associated with chronic hemodialysis was identified as beta 2-microglobulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jun 28;129(3):701–706. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91948-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G. Amyloid deposits and amyloidosis. The beta-fibrilloses (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 5;302(23):1283–1292. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006053022305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltia M., Prelli F., Ghiso J., Kiuru S., Somer H., Palo J., Frangione B. Amyloid protein in familial amyloidosis (Finnish type) is homologous to gelsolin, an actin-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 30;167(3):927–932. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90612-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kametani F., Tonoike H., Hoshi A., Shinoda T., Kito S. A variant prealbumin-related low molecular weight amyloid fibril protein in familial amyloid polyneuropathy of Japanese origin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 14;125(2):622–628. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90584-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Janmey P. A., Yin H. L. Identification of critical functional and regulatory domains in gelsolin. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1717–1726. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Stossel T. P., Orkin S. H., Mole J. E., Colten H. R., Yin H. L. Plasma and cytoplasmic gelsolins are encoded by a single gene and contain a duplicated actin-binding domain. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):455–458. doi: 10.1038/323455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Westbrook C. A., Bruns G. A., Morton C. C. Localization of gelsolin proximal to ABL on chromosome 9. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Apr;42(4):565–572. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Lopez-Otin C., Ghiso J., Geltner D., Frangione B. Stroke in Icelandic patients with hereditary amyloid angiopathy is related to a mutation in the cystatin C gene, an inhibitor of cysteine proteases. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1771–1778. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maury C. P., Alli K., Baumann M. Finnish hereditary amyloidosis. Amino acid sequence homology between the amyloid fibril protein and human plasma gelsoline. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jan 15;260(1):85–87. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80072-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maury C. P., Baumann M. Isolation and characterization of cardiac amyloid in familial amyloid polyneuropathy type IV (Finnish): relation of the amyloid protein to variant gelsolin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Nov 14;1096(1):84–86. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(90)90016-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maury C. P., Kere J., Tolvanen R., de la Chapelle A. Finnish hereditary amyloidosis is caused by a single nucleotide substitution in the gelsolin gene. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 10;276(1-2):75–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80510-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meretoja J. Familial systemic paramyloidosis with lattice dystrophy of the cornea, progressive cranial neuropathy, skin changes and various internal symptoms. A previously unrecognized heritable syndrome. Ann Clin Res. 1969 Dec;1(4):314–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meretoja J. Genetic aspects of familial amyloidosis with corneal lattice dystrophy and cranial neuropathy. Clin Genet. 1973;4(3):173–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1973.tb01140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meretoja J., Hollmén T., Meretoja T., Penttinen R. Partial characterization of amyloid proteins in inherited amyloidosis with lattice corneal dystrophy and in secondary amyloidosis. Med Biol. 1978 Feb;56(1):17–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazato M., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Tawara S., Matsuo H., Araki S. Revised analysis of amino acid replacement in a prealbumin variant (SKO-III) associated with familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy of Jewish origin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 28;123(3):921–928. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80222-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols W. C., Dwulet F. E., Liepnieks J., Benson M. D. Variant apolipoprotein AI as a major constituent of a human hereditary amyloid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 31;156(2):762–768. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80909-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Franklin E. C., Prelli F., Frangione B. A variant of prealbumin from amyloid fibrils in familial polyneuropathy of Jewish origin. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):989–993. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell J. J., Jr, Rodrigues M., Chishti M. I., Riner R. N., Dooley J. M. Lattice corneal dystrophy associated with familial systemic amyloidosis (Meretoja's syndrome). Ophthalmology. 1983 Dec;90(12):1512–1517. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(83)34369-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack G. H., Jr, Dumars K. W., Gummerson K. S., Law A., McKusick V. A. Three forms of dominant amyloid neuropathy. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1981 Dec;149(6):239–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraiva M. J., Birken S., Costa P. P., Goodman D. S. Amyloid fibril protein in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy, Portuguese type. Definition of molecular abnormality in transthyretin (prealbumin). J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):104–119. doi: 10.1172/JCI111390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M., Cohen A. S. The prealbumin nature of the amyloid protein in familial amyloid polyneuropathy (FAP)-swedish variety. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 30;99(4):1326–1332. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90764-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawara S., Nakazato M., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Araki S. Identification of amyloid prealbumin variant in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (Japanese type). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 15;116(3):880–888. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. R., Dwulet F. E., Conneally P. M., Benson M. D. Biochemical and molecular genetic characterization of a new variant prealbumin associated with hereditary amyloidosis. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):6–12. doi: 10.1172/JCI112573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way M., Gooch J., Pope B., Weeds A. G. Expression of human plasma gelsolin in Escherichia coli and dissection of actin binding sites by segmental deletion mutagenesis. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):593–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelman J. E., Delleman J. W., Ansink B. J. Ein hereditäres Syndrom, bestehend aus peripherer Polyneuopatie, Hauveränderungen und gittriger Dystrophie der Hornhaut. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1971 Nov;159(5):618–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Iida K., Janmey P. A. Identification of a polyphosphoinositide-modulated domain in gelsolin which binds to the sides of actin filaments. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):805–812. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Kwiatkowski D. J., Mole J. E., Cole F. S. Structure and biosynthesis of cytoplasmic and secreted variants of gelsolin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5271–5276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]