Abstract
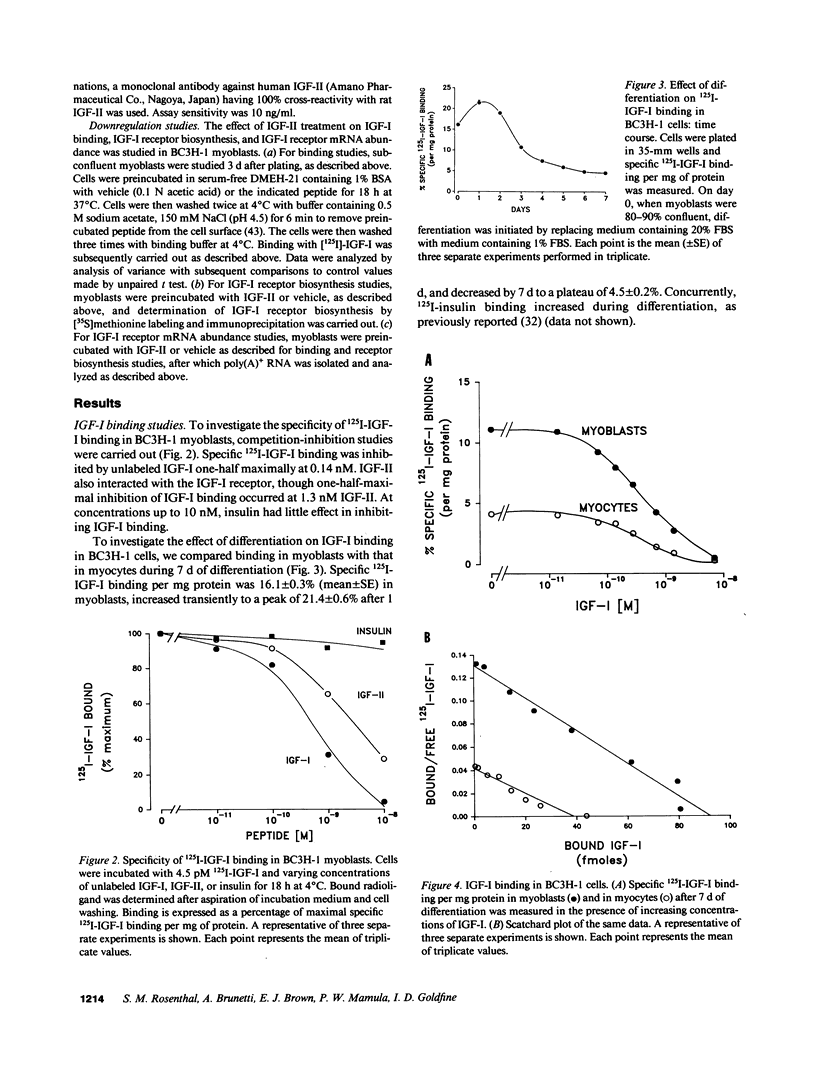
Muscle is an important target tissue for insulin-like growth factor (IGF) action. The presence of specific, high affinity IGF receptors, as well as the expression of IGF peptides and binding proteins by muscle suggest that a significant component of IGF action in this tissue is mediated through autocrine and/or paracrine mechanisms. To explore autocrine/paracrine action of IGFs in muscle, we studied the regulation of the IGF-I receptor and the expression of IGF peptides during differentiation of the mouse BC3H-1 muscle cell line. Differentiation from myoblasts to myocytes was associated with a 60% decrease in IGF-I receptor sites determined by Scatchard analysis. Analysis of mRNA abundance and protein labeling studies indicated that the decrease in IGF-I receptor sites was associated with similar reductions in IGF-I receptor gene expression and receptor biosynthesis. IGF-II peptide gene expression was detected in myoblasts and increased 15-fold with differentiation; the increase in IGF-II gene expression preceded the decrease in IGF-I receptor gene expression. In contrast, IGF-I peptide gene expression was low in myoblasts and decreased slightly with differentiation. To explore the potential role of endogenous IGF-II in the differentiation-associated decrease in IGF-I receptor expression, we investigated the effects of IGF-II treatment in myoblasts. The addition of IGF-II to undifferentiated myoblasts resulted in downregulation of the IGF-I receptor which was associated with decreased IGF-I receptor biosynthesis and decreased IGF-I receptor mRNA abundance. These studies suggest, therefore, that IGF-I receptor expression during muscle cell differentiation may be regulated, at least in part, through autocrine production of IGF-II.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexandrides T., Moses A. C., Smith R. J. Developmental expression of receptors for insulin, insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), and IGF-II in rat skeletal muscle. Endocrinology. 1989 Feb;124(2):1064–1076. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-2-1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beguinot F., Kahn C. R., Moses A. C., Smith R. J. Distinct biologically active receptors for insulin, insulin-like growth factor I, and insulin-like growth factor II in cultured skeletal muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15892–15898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowsher R. R., Lee W. H., Apathy J. M., O'Brien P. J., Ferguson A. L., Henry D. P. Measurement of insulin-like growth factor-II in physiological fluids and tissues. I. An improved extraction procedure and radioimmunoassay for human and rat fluids. Endocrinology. 1991 Feb;128(2):805–814. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-2-805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. L., Graham D. E., Nissley S. P., Hill D. J., Strain A. J., Rechler M. M. Developmental regulation of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA in different rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13144–13150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunetti A., Maddux B. A., Wong K. Y., Goldfine I. D. Muscle cell differentiation is associated with increased insulin receptor biosynthesis and messenger RNA levels. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):192–198. doi: 10.1172/JCI113858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casella S. J., Smith E. P., van Wyk J. J., Joseph D. R., Hynes M. A., Hoyt E. C., Lund P. K. Isolation of rat testis cDNAs encoding an insulin-like growth factor I precursor. DNA. 1987 Aug;6(4):325–330. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernausek S. D., Jacobs S., Van Wyk J. J. Structural similarities between human receptors for somatomedin C and insulin: analysis by affinity labeling. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 22;20(26):7345–7350. doi: 10.1021/bi00529a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Rotwein P. Insulin-like growth factors I and II. Peptide, messenger ribonucleic acid and gene structures, serum, and tissue concentrations. Endocr Rev. 1989 Feb;10(1):68–91. doi: 10.1210/edrv-10-1-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson M. V., Allen R. E., Hossner K. L. Ovine somatomedin, multiplication-stimulating activity, and insulin promote skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation in vitro. Endocrinology. 1985 Dec;117(6):2357–2363. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-6-2357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwall D., Schalling M., Jennische E., Norstedt G. Induction of insulin-like growth factor I messenger ribonucleic acid during regeneration of rat skeletal muscle. Endocrinology. 1989 Feb;124(2):820–825. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-2-820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewton D. Z., Falen S. L., Florini J. R. The type II insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor has low affinity for IGF-I analogs: pleiotypic actions of IGFs on myoblasts are apparently mediated by the type I receptor. Endocrinology. 1987 Jan;120(1):115–123. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-1-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewton D. Z., Florini J. R. Effects of the somatomedins and insulin on myoblast differentiation in vitro. Dev Biol. 1981 Aug;86(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90312-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewton D. Z., Florini J. R. Relative effects of the somatomedins, multiplication-stimulating activity, and growth hormone on myoblasts and myotubes in culture. Endocrinology. 1980 Feb;106(2):577–583. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-2-577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsayeth J., Maddux B., Goldfine I. D. Biosynthesis and processing of the human insulin receptor. Diabetes. 1986 Jul;35(7):837–846. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.7.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlanetto R. W., Underwood L. E., Van Wyk J. J., D'Ercole A. J. Estimation of somatomedin-C levels in normals and patients with pituitary disease by radioimmunoassay. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):648–657. doi: 10.1172/JCI108816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hari J., Pierce S. B., Morgan D. O., Sara V., Smith M. C., Roth R. A. The receptor for insulin-like growth factor II mediates an insulin-like response. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3367–3371. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02658.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B. Hybridization of oligo(dT) to RNA on nitrocellulose. Gene Anal Tech. 1987 Mar-Apr;4(2):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(87)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann K. K., Papa V., Brown E. J., Doerries U., Rosenthal S. M., Goldfine I. D. A rapid and simple one step method for isolation of poly(A)+ RNA from cells in monolayer. Endocrinology. 1990 Oct;127(4):2038–2040. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-4-2038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J., Crace C. J., Nissley S. P., Morrell D., Holder A. T., Milner R. D. Fetal rat myoblasts release both rat somatomedin-C (SM-C)/insulin-like growth factor I (IGF I) and multiplication-stimulating activity in vitro: partial characterization and biological activity of myoblast-derived SM-C/IGF I. Endocrinology. 1985 Nov;117(5):2061–2072. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-5-2061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L., Liu F., Chang D., Seegan G. A sensitive radioimmunoassay for somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth-factor I based on synthetic insulin-like growth factor 57-70. Horm Metab Res. 1988 Jun;20(6):344–347. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1010832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii D. N. Relationship of insulin-like growth factor II gene expression in muscle to synaptogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2898–2902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Kull F. C., Jr, Earp H. S., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Somatomedin-C stimulates the phosphorylation of the beta-subunit of its own receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9581–9584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keating M. T., Williams L. T. Autocrine stimulation of intracellular PDGF receptors in v-sis-transformed cells. Science. 1988 Feb 19;239(4842):914–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2829358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiess W., Haskell J. F., Lee L., Greenstein L. A., Miller B. E., Aarons A. L., Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P. An antibody that blocks insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding to the type II IGF receptor is neither an agonist nor an inhibitor of IGF-stimulated biologic responses in L6 myoblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12745–12751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. D., Hintz R. L., Rosenfeld R. G., Benitz W. E. Presence of insulinlike growth factor receptors and lack of insulin receptors on fetal bovine smooth muscle cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1988 Sep;24(9):921–926. doi: 10.1007/BF02623903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston N., Pollare T., Lithell H., Arner P. Characterisation of insulin-like growth factor I receptor in skeletal muscles of normal and insulin resistant subjects. Diabetologia. 1988 Dec;31(12):871–877. doi: 10.1007/BF00265369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCusker R. H., Camacho-Hübner C., Clemmons D. R. Identification of the types of insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins that are secreted by muscle cells in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7795–7800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald A. R., Maddux B. A., Okabayashi Y., Wong K. Y., Hawley D. M., Logsdon C. D., Goldfine I. D. Regulation of insulin-receptor mRNA levels by glucocorticoids. Diabetes. 1987 Jun;36(6):779–781. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.6.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy L. J., Bell G. I., Friesen H. G. Tissue distribution of insulin-like growth factor I and II messenger ribonucleic acid in the adult rat. Endocrinology. 1987 Apr;120(4):1279–1282. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-4-1279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Caldwell K. L., Gordon J. I., Glaser L. Regulation of creatine phosphokinase expression during differentiation of BC3H1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2644–2652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld R. G., Dollar L. A. Characterization of the somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor I (SM-C/IGF-I) receptor on cultured human fibroblast monolayers: regulation of receptor concentrations by SM-C/IGF-I and insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Sep;55(3):434–440. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-3-434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld R. G., Hintz R. L. Characterization of a specific receptor for somatomedin C (SM-C) on cultured human lymphocytes: evidence that SM-C modulates homologous receptor concentration. Endocrinology. 1980 Dec;107(6):1841–1848. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-6-1841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sbraccia P., Wong K. Y., Brunetti A., Rafaeloff R., Trischitta V., Hawley D. M., Goldfine I. D. Insulin down-regulates insulin receptor number and up-regulates insulin receptor affinity in cells expressing a tyrosine kinase-defective insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):4902–4907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Harris A. J., Devine C. E., Heinemann S. Characterization of a unique muscle cell line. J Cell Biol. 1974 May;61(2):398–413. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu M., Webster C., Morgan D. O., Blau H. M., Roth R. A. Insulin and insulinlike growth factor receptors and responses in cultured human muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Nov;251(5 Pt 1):E611–E615. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.251.5.E611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch A. R., Offord J. D., Chalkley R., Rubenstein P. A. Characterization of actin mRNA levels during BC3H1 cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):849–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally M., Li C. H., Hall K. IGF-2 stimulated growth mediated by the somatomedin type 2 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 29;148(2):811–816. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90948-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen S. E., Lajara R., McCusker R. H., Clemmons D. R., Rotwein P. Insulin-like growth factors (IGF) in muscle development. Expression of IGF-I, the IGF-I receptor, and an IGF binding protein during myoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13810–13817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen S. E., Sadow J. L., Rotwein P. Coordinate expression of insulin-like growth factor II and its receptor during muscle differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1543–1547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetter U., Zapf J., Heit W., Helbing G., Heinze E., Froesch E. R., Teller W. M. Human fetal and adult chondrocytes. Effect of insulinlike growth factors I and II, insulin, and growth hormone on clonal growth. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1903–1908. doi: 10.1172/JCI112518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner H., Woloschak M., Adamo M., Shen-Orr Z., Roberts C. T., Jr, LeRoith D. Developmental regulation of the rat insulin-like growth factor I receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7451–7455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield H. J., Bruni C. B., Frunzio R., Terrell J. E., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Isolation of a cDNA clone encoding rat insulin-like growth factor-II precursor. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):277–280. doi: 10.1038/312277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K. T., Czech M. P. The type I insulin-like growth factor receptor mediates the rapid effects of multiplication-stimulating activity on membrane transport systems in rat soleus muscle. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3090–3095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vroede M. A., Romanus J. A., Standaert M. L., Pollet R. J., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Interaction of insulin-like growth factors with a nonfusing mouse muscle cell line: binding, action, and receptor down-regulation. Endocrinology. 1984 May;114(5):1917–1929. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-5-1917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]










