Abstract
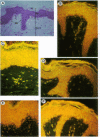
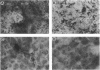
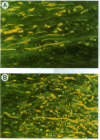
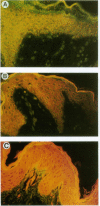
The pathogenic gram-positive bacterium Streptococcus pyogenes (group A streptococcus) causes numerous diseases of cutaneous tissue, each of which is initiated after the interaction of the bacterium with the cells of the epidermis. In this study, we show that different surface proteins of S. pyogenes play important roles in determining the cell-specific tropism of the bacterium in skin. Using streptococcal strains with defined mutations in the genes which encode surface proteins in combination with primary cultures of human skin and an in situ adherence assay which uses histological sections of human skin, we show that the M protein of S. pyogenes mediates the binding of the bacterium to keratinocytes, while a second streptococcal surface protein, protein F, directs the adherence of the organism to Langerhans' cells. Characterization of binding revealed that adherence was inhibited by purified streptococcal proteins and pretreatment of both host cells with the protease trypsin. Adherence was only slightly affected by the state of keratinocyte differentiation in vitro, but was considerably modulated in response to environmental conditions known to regulate expression of M protein and protein F, suggesting that the interaction between these bacterial cell-surface structures/adhesins and keratinocytes and Langerhans' cells may play an important role in streptococcal skin disease.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björck L., Kastern W., Lindahl G., Widebäck K. Streptococcal protein G, expressed by streptococci or by Escherichia coli, has separate binding sites for human albumin and IgG. Mol Immunol. 1987 Oct;24(10):1113–1122. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caparon M. G., Geist R. T., Perez-Casal J., Scott J. R. Environmental regulation of virulence in group A streptococci: transcription of the gene encoding M protein is stimulated by carbon dioxide. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(17):5693–5701. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.17.5693-5701.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caparon M. G., Stephens D. S., Olsén A., Scott J. R. Role of M protein in adherence of group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1811–1817. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1811-1817.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRita V. J., Mekalanos J. J. Genetic regulation of bacterial virulence. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:455–482. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk P., Roth K. A., Borén T., Westblom T. U., Gordon J. I., Normark S. An in vitro adherence assay reveals that Helicobacter pylori exhibits cell lineage-specific tropism in the human gastric epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):2035–2039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Jones K. F., Manjula B. N., Scott J. R. Streptococcal M6 protein expressed in Escherichia coli. Localization, purification, and comparison with streptococcal-derived M protein. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):1083–1095. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A. Streptococcal M protein: molecular design and biological behavior. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jul;2(3):285–314. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fithian E., Kung P., Goldstein G., Rubenfeld M., Fenoglio C., Edelson R. Reactivity of Langerhans cells with hybridoma antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2541–2544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E. Epidermal differentiation: the bare essentials. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):2807–2814. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanski E., Caparon M. Protein F, a fibronectin-binding protein, is an adhesin of the group A streptococcus Streptococcus pyogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6172–6176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanski E., Horwitz P. A., Caparon M. G. Expression of protein F, the fibronectin-binding protein of Streptococcus pyogenes JRS4, in heterologous streptococcal and enterococcal strains promotes their adherence to respiratory epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):5119–5125. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.5119-5125.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasty D. L., Ofek I., Courtney H. S., Doyle R. J. Multiple adhesins of streptococci. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2147–2152. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2147-2152.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath D. G., Cleary P. P. Fc-receptor and M-protein genes of group A streptococci are products of gene duplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4741–4745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges S., Svensson M., Svanborg C. Interleukin-6 response of epithelial cell lines to bacterial stimulation in vitro. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1295–1301. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1295-1301.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingshead S. K., Fischetti V. A., Scott J. R. Complete nucleotide sequence of type 6 M protein of the group A Streptococcus. Repetitive structure and membrane anchor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1677–1686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ike Y., Craig R. A., White B. A., Yagi Y., Clewell D. B. Modification of Streptococcus faecalis sex pheromones after acquisition of plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5369–5373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kripke M. L., Munn C. G., Jeevan A., Tang J. M., Bucana C. Evidence that cutaneous antigen-presenting cells migrate to regional lymph nodes during contact sensitization. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):2833–2838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupper T. S. Immune and inflammatory processes in cutaneous tissues. Mechanisms and speculations. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1783–1789. doi: 10.1172/JCI114907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Current knowledge of type-specific M antigens of group A streptococci. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder H., Engberg I., Baltzer I. M., Jann K., Svanborg-Edén C. Induction of inflammation by Escherichia coli on the mucosal level: requirement for adherence and endotoxin. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1309–1313. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1309-1313.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lottenberg R., Broder C. C., Boyle M. D., Kain S. J., Schroeder B. L., Curtiss R., 3rd Cloning, sequence analysis, and expression in Escherichia coli of a streptococcal plasmin receptor. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(16):5204–5210. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.16.5204-5210.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Proctor R. A. Binding and factor XIIIa-mediated cross-linking of a 27-kilodalton fragment of fibronectin to Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1980 Aug 22;209(4459):927–929. doi: 10.1126/science.7403857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Stern D. M. Modulation of endothelial cell hemostatic properties by tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):740–745. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole P. W., O'Toole P., Stenberg L., Rissler M., Lindahl G. Two major classes in the M protein family in group A streptococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8661–8665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Geist R. T., Caparon M. G. Positive transcriptional control of mry regulates virulence in the group A streptococcus. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Mar;7(6):893–903. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens R. J., Baralle F. E. Mapping the collagen-binding site of human fibronectin by expression in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2825–2830. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04575.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pancholi V., Fischetti V. A. A major surface protein on group A streptococci is a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase with multiple binding activity. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):415–426. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentland A. P., Mahoney M., Jacobs S. C., Holtzman M. J. Enhanced prostaglandin synthesis after ultraviolet injury is mediated by endogenous histamine stimulation. A mechanism for irradiation erythema. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):566–574. doi: 10.1172/JCI114746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Casal J., Caparon M. G., Scott J. R. Introduction of the emm6 gene into an emm-deleted strain of Streptococcus pyogenes restores its ability to resist phagocytosis. Res Microbiol. 1992 Jul-Aug;143(6):549–558. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90112-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Casal J., Caparon M. G., Scott J. R. Mry, a trans-acting positive regulator of the M protein gene of Streptococcus pyogenes with similarity to the receptor proteins of two-component regulatory systems. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(8):2617–2624. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.8.2617-2624.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riesenfeld-Orn I., Wolpe S., Garcia-Bustos J. F., Hoffmann M. K., Tuomanen E. Production of interleukin-1 but not tumor necrosis factor by human monocytes stimulated with pneumococcal cell surface components. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1890–1893. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1890-1893.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Fibronectin and its receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:375–413. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Courtney H. S., Ofek I. Interactions of fibronectin with streptococci: the role of fibronectin as a receptor for Streptococcus pyogenes. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jul-Aug;9 (Suppl 4):S351–S359. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.supplement_4.s351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speziale P., Hök M., Switalski L. M., Wadström T. Fibronectin binding to a Streptococcus pyogenes strain. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):420–427. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.420-427.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L. Invasive group A streptococcus infections. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;14(1):2–11. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stingl G., Katz S. I., Clement L., Green I., Shevach E. M. Immunologic functions of Ia-bearing epidermal Langerhans cells. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2005–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stingl G., Wolff-Schreiner E. C., Pichler W. J., Gschnait F., Knapp W., Wolff K. Epidermal Langerhans cells bear Fc and C3 receptors. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):245–246. doi: 10.1038/268245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strömberg N., Marklund B. I., Lund B., Ilver D., Hamers A., Gaastra W., Karlsson K. A., Normark S. Host-specificity of uropathogenic Escherichia coli depends on differences in binding specificity to Gal alpha 1-4Gal-containing isoreceptors. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):2001–2010. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08328.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strömberg N., Nyholm P. G., Pascher I., Normark S. Saccharide orientation at the cell surface affects glycolipid receptor function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9340–9344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanHeyningen T., Fogg G., Yates D., Hanski E., Caparon M. Adherence and fibronectin binding are environmentally regulated in the group A streptococci. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Sep;9(6):1213–1222. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01250.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler D. E., Chenoweth D. E., Cleary P. P. Mechanism of action of the group A streptococcal C5a inactivator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8144–8148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Lipoteichoic acids: a new class of bacterial antigen. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1161–1167. doi: 10.1126/science.46620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward M. P., Young W. W., Jr, Bloodgood R. A. Detection of monoclonal antibodies specific for carbohydrate epitopes using periodate oxidation. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Apr 8;78(1):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Man P., van Kooten C., Aarden L., Engberg I., Linder H., Svanborg Edén C. Interleukin-6 induced at mucosal surfaces by gram-negative bacterial infection. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3383–3388. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3383-3388.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]