Abstract
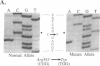
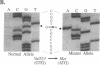
Type IIB von Willebrand Disease (vWD) is characterized by the selective loss of large von Willebrand Factor (vWF) multimers from plasma, presumably due to their increased reactivity with platelets and subsequent clearance from the circulation. Using the PCR, one of a panel of four potential missense mutations was identified in each of the 14 patients studied from 11 unrelated families. None of these substitutions was encountered in a large panel of normal DNAs. These changes all represent C----T transitions at CpG dinucleotides, proposed "hot spots" for mutation in the human genome. The four resulting amino acid substitutions, Arg543----Trp, Arg545----Cys, Val553----Met, and Arg578----Gln, are all clustered within the GpIb binding domain of vWF. Disruption of this latter functional domain may explain the pathogenesis of Type IIB vWD. By sequence polymorphism analysis, the Arg543----Trp substitution was shown to have occurred as at least two independent mutational events. This latter observation, along with the identification of mutations in all 14 patients studied and their localization to the GpIb binding domain, all strongly suggest that these substitutions represent the authentic defects responsible for Type IIB vWD. This panel of mutations may provide a useful diagnostic tool for the majority of patients with Type IIB vWD.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker D., Schafer M., White R. Restriction sites containing CpG show a higher frequency of polymorphism in human DNA. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonthron D. T., Handin R. I., Kaufman R. J., Wasley L. C., Orr E. C., Mitsock L. M., Ewenstein B., Loscalzo J., Ginsburg D., Orkin S. H. Structure of pre-pro-von Willebrand factor and its expression in heterologous cells. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):270–273. doi: 10.1038/324270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonthron D., Orr E. C., Mitsock L. M., Ginsburg D., Handin R. I., Orkin S. H. Nucleotide sequence of pre-pro-von Willebrand factor cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7125–7127. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco L., Girolami A., Zimmerman T. S., Ruggeri Z. M. Interaction of purified type IIB von Willebrand factor with the platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib induces fibrinogen binding to the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex and initiates aggregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7424–7428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J. A., Berkowitz S. D., Ware J., Kasper C. K., Ruggeri Z. M. Identification of a cleavage site directing the immunochemical detection of molecular abnormalities in type IIA von Willebrand factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6306–6310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Titani K., Holland L. Z., Roberts J. R., Kostel P., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. A heparin-binding domain of human von Willebrand factor. Characterization and localization to a tryptic fragment extending from amino acid residue Val-449 to Lys-728. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1734–1739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Titani K., Holland L. Z., Russell S. R., Roberts J. R., Elder J. H., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. von Willebrand factor. A reduced and alkylated 52/48-kDa fragment beginning at amino acid residue 449 contains the domain interacting with platelet glycoprotein Ib. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):381–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles A. R., Hoogendoorn H., Benford K. Type IIB von Willebrand's disease presenting as thrombocytopenia during pregnancy. Br J Haematol. 1987 Nov;67(3):349–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1987.tb02356.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg D., Handin R. I., Bonthron D. T., Donlon T. A., Bruns G. A., Latt S. A., Orkin S. H. Human von Willebrand factor (vWF): isolation of complementary DNA (cDNA) clones and chromosomal localization. Science. 1985 Jun 21;228(4706):1401–1406. doi: 10.1126/science.3874428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg D., Konkle B. A., Gill J. C., Montgomery R. R., Bockenstedt P. L., Johnson T. A., Yang A. Y. Molecular basis of human von Willebrand disease: analysis of platelet von Willebrand factor mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3723–3727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grainick H. R., Williams S. B., McKeown L. P., Rick M. E., Maisonneuve P., Jenneau C., Sultan Y. Von Willebrand's disease with spontaneous platelet aggregation induced by an abnormal plasma von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1522–1529. doi: 10.1172/JCI112132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handin R. I., Wagner D. D. Molecular and cellular biology of von Willebrand factor. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1989;9:233–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg L., Nilsson I. M., Borge L., Gunnarsson M., Sjörin E. Platelet aggregation induced by 1-desamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin (DDAVP) in Type IIB von Willebrand's disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Oct 6;309(14):816–821. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198310063091402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultin M. B., Sussman I. I. Postoperative thrombocytopenia in type IIB von Willebrand disease. Am J Hematol. 1990 Jan;33(1):64–68. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830330113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konkle B. A., Ginsburg D. The addition of endothelial cell growth factor and heparin to human umbilical vein endothelial cell cultures decreases plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):579–585. doi: 10.1172/JCI113635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso D. J., Tuley E. A., Westfield L. A., Worrall N. K., Shelton-Inloes B. B., Sorace J. M., Alevy Y. G., Sadler J. E. Structure of the gene for human von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19514–19527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marti T., Rösselet S. J., Titani K., Walsh K. A. Identification of disulfide-bridged substructures within human von Willebrand factor. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8099–8109. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurier C., Parquet-Gernez A., Goudemand J., Taillefer M. F., Goudemand M. Investigation of a large kindred with type IIB von Willebrand's disease, dominant inheritance and age-dependent thrombocytopenia. Br J Haematol. 1988 Aug;69(4):499–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1988.tb02406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohri H., Fujimura Y., Shima M., Yoshioka A., Houghten R. A., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Structure of the von Willebrand factor domain interacting with glycoprotein Ib. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):17901–17904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohri H., Yoshioka A., Zimmerman T. S., Ruggeri Z. M. Isolation of the von Willebrand factor domain interacting with platelet glycoprotein Ib, heparin, and collagen and characterization of its three distinct functional sites. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17361–17367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngo K. Y., Glotz V. T., Koziol J. A., Lynch D. C., Gitschier J., Ranieri P., Ciavarella N., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Homozygous and heterozygous deletions of the von Willebrand factor gene in patients and carriers of severe von Willebrand disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2753–2757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols W. C., Liepnieks J. J., McKusick V. A., Benson M. D. Direct sequencing of the gene for Maryland/German familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy type II and genotyping by allele-specific enzymatic amplification. Genomics. 1989 Oct;5(3):535–540. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Curiel D. T., Brantly M. L., Holmes M. D., Crystal R. G. Rapid, nonradioactive detection of mutations in the human genome by allele-specific amplification. J Lab Clin Med. 1989 Aug;114(2):105–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pareti F. I., Fujimura Y., Dent J. A., Holland L. Z., Zimmerman T. S., Ruggeri Z. M. Isolation and characterization of a collagen binding domain in human von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15310–15315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peake I. R., Liddell M. B., Moodie P., Standen G., Mancuso D. J., Tuley E. A., Westfield L. A., Sorace J. M., Sadler J. E., Verweij C. L. Severe type III von Willebrand's disease caused by deletion of exon 42 of the von Willebrand factor gene: family studies that identify carriers of the condition and a compound heterozygous individual. Blood. 1990 Feb 1;75(3):654–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rick M. E., Williams S. B., Sacher R. A., McKeown L. P. Thrombocytopenia associated with pregnancy in a patient with type IIB von Willebrand's disease. Blood. 1987 Mar;69(3):786–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodeghiero F., Castaman G., Dini E. Epidemiological investigation of the prevalence of von Willebrand's disease. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):454–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth G. J., Titani K., Hoyer L. W., Hickey M. J. Localization of binding sites within human von Willebrand factor for monomeric type III collagen. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 30;25(26):8357–8361. doi: 10.1021/bi00374a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. S., Antin J. H., Bingham E. L., Ginsburg D. Use of polymerase chain reaction-detected sequence polymorphisms to document engraftment following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation. 1990 Apr;49(4):714–720. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199004000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. S., Weiner G. J., Allen E. A., Terry V. H., Harnden C. E., Boehnke M., Kaminski M. S., Ginsburg D. Molecular characterization of anti-idiotype antibody-resistant variants of a murine B cell lymphoma. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):768–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Lombardi R., Gatti L., Bader R., Valsecchi C., Zimmerman T. S. Type IIB von Willebrand's disease: differential clearance of endogenous versus transfused large multimer von willebrand factor. Blood. 1982 Dec;60(6):1453–1456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Pareti F. I., Mannucci P. M., Ciavarella N., Zimmerman T. S. Heightened interaction between platelets and factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in a new subtype of von Willebrand's disease. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 8;302(19):1047–1051. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005083021902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. von Willebrand factor and von Willebrand disease. Blood. 1987 Oct;70(4):895–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba H. I., Fujimura Y., Saba S. R., Bruce A. C., Morelli G. A., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Spontaneous platelet aggregation in type IIB Tampa von Willebrand disease is inhibited by the 52/48-kDa fragment of normal von Willebrand factor, which contains the GPIb binding domain. Am J Hematol. 1989 Mar;30(3):150–153. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830300306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton-Inloes B. B., Chehab F. F., Mannucci P. M., Federici A. B., Sadler J. E. Gene deletions correlate with the development of alloantibodies in von Willebrand disease. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1459–1465. doi: 10.1172/JCI112974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton-Inloes B. B., Titani K., Sadler J. E. cDNA sequences for human von Willebrand factor reveal five types of repeated domains and five possible protein sequence polymorphisms. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3164–3171. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot P. G., Federici A. B., de Boer H. C., d'Alessio P., Mannucci P. M., Sixma J. J. von Willebrand factor synthesized by endothelial cells from a patient with type IIB von Willebrand disease supports platelet adhesion normally but has an increased affinity for platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3793–3797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]