Abstract
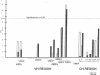
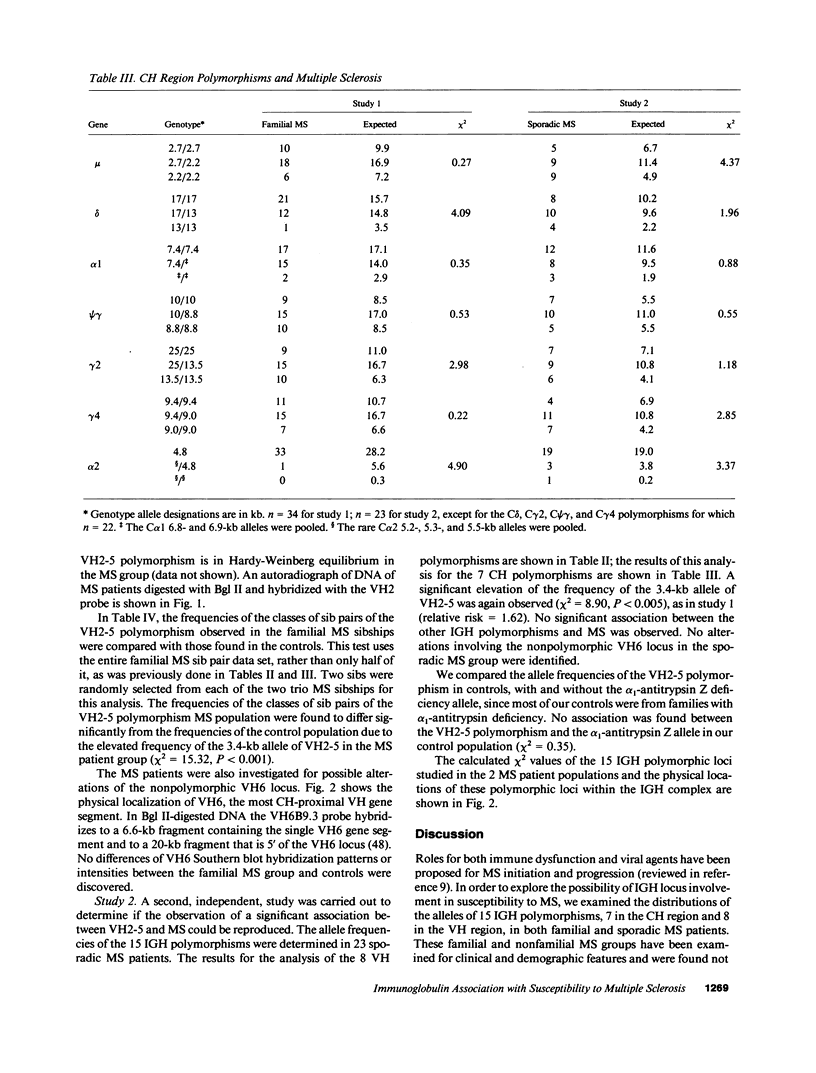
15 immunoglobulin heavy chain constant (CH) and variable region (VH) polymorphisms were selected to span the entire length of the heavy chain cluster. These polymorphisms were examined in 34 sib pairs concordant for multiple sclerosis (MS) and in 23 sporadic MS patients. Allele frequencies were calculated for the 2 MS patient groups and compared with those found in a control population from the same geographical location and of similar ethnic background. No significant association was found between MS and the 7 CH region polymorphisms examined. However, a significant correlation between the MS phenotype and a VH2 family polymorphism was observed in both MS patient populations (familial MS patients chi 2 = 8.16, P less than 0.005; sporadic MS patients chi 2 = 8.90, P less than 0.005). One allele of the VH2-5 gene segment was found to be over-represented in both MS groups. VH2-5 has recently been physically mapped close to the CH region, between 180 and 360 kb away. These results indicate that a locus near or within the CH-proximal VH region is associated with increased susceptibility to MS.
Full text
PDF
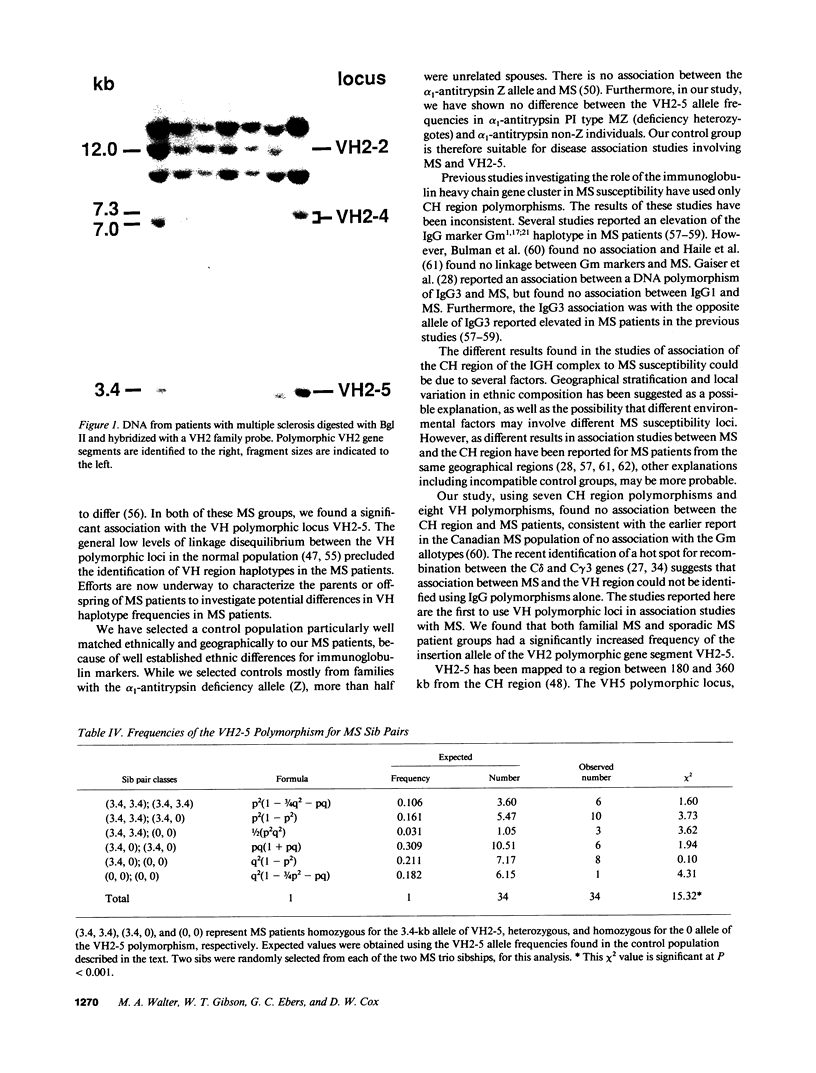
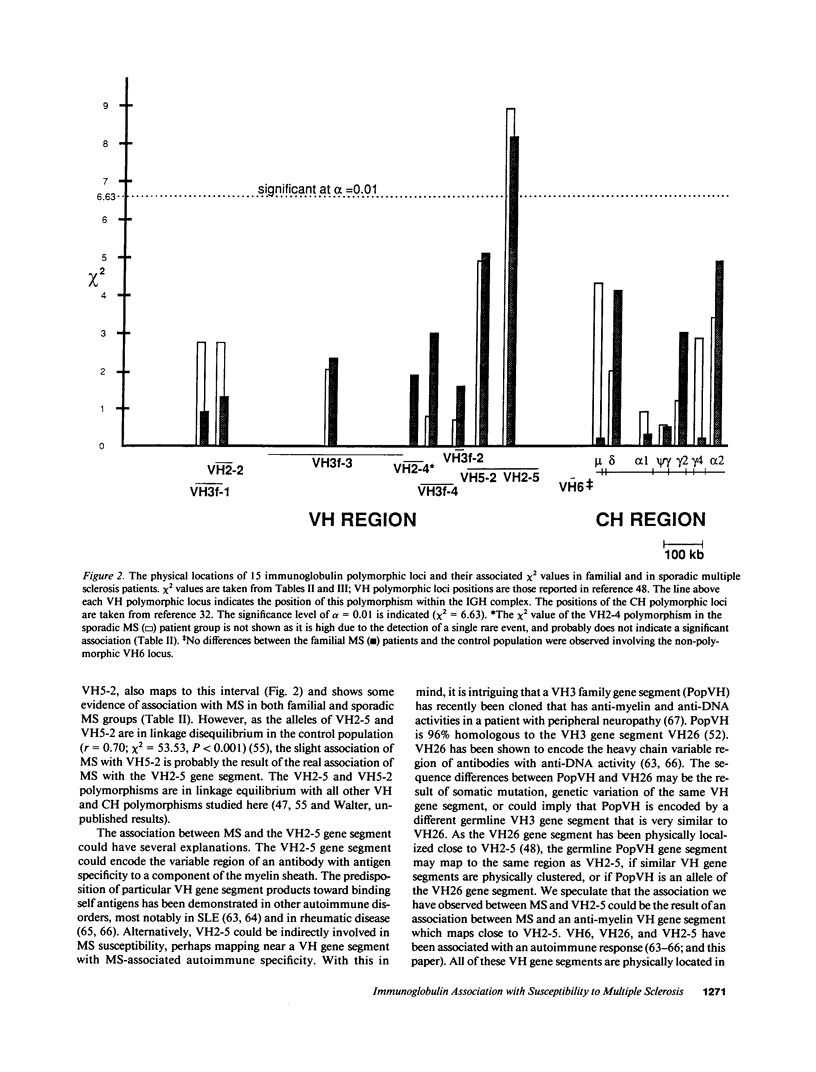


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beall S. S., Concannon P., Charmley P., McFarland H. F., Gatti R. A., Hood L. E., McFarlin D. E., Biddison W. E. The germline repertoire of T cell receptor beta-chain genes in patients with chronic progressive multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Jan;21(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bech-Hansen N. T., Linsley P. S., Cox D. W. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms associated with immunoglobulin C gamma genes reveal linkage disequilibrium and genomic organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6952–6956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benger J. C., Cox D. W. Polymorphisms of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain delta gene and association with other constant-region genes. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Oct;45(4):606–614. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman J. E., Mellis S. J., Pollock R., Smith C. L., Suh H., Heinke B., Kowal C., Surti U., Chess L., Cantor C. R. Content and organization of the human Ig VH locus: definition of three new VH families and linkage to the Ig CH locus. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):727–738. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02869.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottaro A., Gallina R., DeMarchi M., Carbonara A. O. Genetic analysis of new restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLP) in the human IgH constant gene locus. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Nov;19(11):2151–2157. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottaro A., de Marchi M., Migone N., Carbonara A. O. Pulsed-field gel analysis of human immunoglobulin heavy-chain constant region gene deletions reveals the extent of unmapped regions within the locus. Genomics. 1989 May;4(4):505–508. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90273-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder V., Owen S., Watson C., Feldmann M., Davison A. MS: a localized immune disease of the central nervous system. Immunol Today. 1989 Mar;10(3):99–103. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90235-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Liu M. F., Sinha S., Carson D. A. A 16/6 idiotype-positive anti-DNA antibody is encoded by a conserved VH gene with no somatic mutation. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Nov;31(11):1429–1431. doi: 10.1002/art.1780311113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Siminovitch K. A., Olsen N. J., Erger R. A., Carson D. A. A highly informative probe for two polymorphic Vh gene regions that contain one or more autoantibody-associated Vh genes. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):706–710. doi: 10.1172/JCI114218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley J. J., Mageed R. A., Silverman G. J., Chen P. P., Kozin F., Erger R. A., Jefferis R., Carson D. A. The incidence of a new human cross-reactive idiotype linked to subgroup VHIII heavy chains. Mol Immunol. 1990 Jan;27(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuisinier A. M., Guigou V., Boubli L., Fougereau M., Tonnelle C. Preferential expression of VH5 and VH6 immunoglobulin genes in early human B-cell ontogeny. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Oct;30(4):493–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb02455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dersimonian H., Schwartz R. S., Barrett K. J., Stollar B. D. Relationship of human variable region heavy chain germ-line genes to genes encoding anti-DNA autoantibodies. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2496–2501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebers G. C., Bulman D. E., Sadovnick A. D., Paty D. W., Warren S., Hader W., Murray T. J., Seland T. P., Duquette P., Grey T. A population-based study of multiple sclerosis in twins. N Engl J Med. 1986 Dec 25;315(26):1638–1642. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198612253152603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebers G. C. Genetic factors in multiple sclerosis. Neurol Clin. 1983 Aug;1(3):645–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebers G. C., Paty D. W., Stiller C. R., Nelson R. F., Seland T. P., Larsen B. HLA-typing in multiple sclerosis sibling pairs. Lancet. 1982 Jul 10;2(8289):88–90. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91702-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis D. A., Klouda P. T., Brazier D. M., Batchelor J. R., McDonald W. I., Hern J. E. Alpha-1-antitrypsin (Pi) types in multiple sclerosis and lack of interaction with immunoglobulin (Gm) markers. J Immunogenet. 1988 Oct-Dec;15(5-6):251–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1988.tb00428.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaiser C. N., Johnson M. J., de Lange G., Rassenti L., Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Steinman L. Susceptibility to multiple sclerosis associated with an immunoglobulin gamma 3 restriction fragment length polymorphism. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):309–313. doi: 10.1172/JCI112801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghanem N., Lefranc M. P., Lefranc G. Definition of the RFLP alleles in the human immunoglobulin IGHG gene locus. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jul;18(7):1059–1065. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hader W. J., Elliot M., Ebers G. C. Epidemiology of multiple sclerosis in London and Middlesex County, Ontario, Canada. Neurology. 1988 Apr;38(4):617–621. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.4.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafler D. A., Benjamin D. S., Burks J., Weiner H. L. Myelin basic protein and proteolipid protein reactivity of brain- and cerebrospinal fluid-derived T cell clones in multiple sclerosis and postinfectious encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):68–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafler D. A., Weiner H. L. MS: a CNS and systemic autoimmune disease. Immunol Today. 1989 Mar;10(3):104–107. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90236-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haile R. W., Goldstein A., Field L., Marazita M. L. A linkage analysis of the Gm locus and multiple sclerosis. Genet Epidemiol. 1985;2(1):29–34. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370020104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haile R. W., Hodge S. E., Iselius L. Genetic susceptibility to multiple sclerosis: a review. Int J Epidemiol. 1983 Mar;12(1):8–16. doi: 10.1093/ije/12.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., Walter M. A., Cox D. W. Complete physical map of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region gene complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5567–5571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeong H. D., Teale J. M. VH gene family repertoire of resting B cells. Preferential use of D-proximal families early in development may be due to distinct B cell subsets. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2752–2760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. J., Natali A. M., Cann H. M., Honjo T., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Polymorphisms of a human variable heavy chain gene show linkage with constant heavy chain genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7840–7844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnunen E., Koskenvuo M., Kaprio J., Aho K. Multiple sclerosis in a nationwide series of twins. Neurology. 1987 Oct;37(10):1627–1629. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.10.1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Kono D. H., Urban J. L., Hood L. The T-cell receptor repertoire and autoimmune diseases. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:657–682. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Matsuda F., Kinashi T., Kodaira M., Honjo T. A novel family of variable region genes of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):761–768. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90482-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linthicum D. S., Frelinger J. A. Acute autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. II. Susceptibility is controlled by the combination of H-2 and histamine sensitization genes. J Exp Med. 1982 Jul 1;156(1):31–40. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logtenberg T., Young F. M., Van Es J. H., Gmelig-Meyling F. H., Alt F. W. Autoantibodies encoded by the most Jh-proximal human immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1347–1355. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malynn B. A., Yancopoulos G. D., Barth J. E., Bona C. A., Alt F. W. Biased expression of JH-proximal VH genes occurs in the newly generated repertoire of neonatal and adult mice. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):843–859. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthyssens G., Rabbitts T. H. Structure and multiplicity of genes for the human immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6561–6565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald W. I. Multiple sclerosis: epidemiology and HLA associations. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;436:109–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb14781.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migone N., Feder J., Cann H., van West B., Hwang J., Takahashi N., Honjo T., Piazza A., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Multiple DNA fragment polymorphisms associated with immunoglobulin mu chain switch-like regions in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):467–471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oksenberg J. R., Sherritt M., Begovich A. B., Erlich H. A., Bernard C. C., Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Steinman L. T-cell receptor V alpha and C alpha alleles associated with multiple and myasthenia gravis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):988–992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oksenberg J. R., Stuart S., Begovich A. B., Bell R. B., Erlich H. A., Steinman L., Bernard C. C. Limited heterogeneity of rearranged T-cell receptor V alpha transcripts in brains of multiple sclerosis patients. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):344–346. doi: 10.1038/345344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson T., Baig S., Höjeberg B., Link H. Antimyelin basic protein and antimyelin antibody-producing cells in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1990 Feb;27(2):132–136. doi: 10.1002/ana.410270207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter C., Monestier M., Bonin B., Bona C. A. Functional and molecular studies of V genes expressed in autoantibodies. Immunol Rev. 1986 Dec;94:75–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey J. P., Goust J. M., Salier J. P., Fudenberg H. H. Immunoglobulin G heavy chain (Gm) allotypes in multiple sclerosis. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;67(6):1797–1800. doi: 10.1172/JCI110220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Propert D. N., Bernard C. C., Simons M. J. Gm allotypes and multiple sclerosis. J Immunogenet. 1982 Oct;9(5):359–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1982.tb00994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadovnick A. D., Macleod P. M. The familial nature of multiple sclerosis: empiric recurrence risks for first, second-, and third-degree relatives of patients. Neurology. 1981 Aug;31(8):1039–1041. doi: 10.1212/wnl.31.8.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sam M., Walter M. A., Cox D. W. RsaI polymorphism of a human immunoglobulin VH5 subclass locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8748–8748. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg-Wollheim M., Baird L. G., Schanfield M. S., Knoppers M. H., Youker K., Tachovsky T. G. Association of CSF IgG concentration and immunoglobulin allotype in multiple sclerosis and optic neuritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 May;31(2):212–221. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90241-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schluesener H. J., Sobel R. A., Linington C., Weiner H. L. A monoclonal antibody against a myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein induces relapses and demyelination in central nervous system autoimmune disease. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4016–4021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W., Jr, Hillson J. L., Perlmutter R. M. Early restriction of the human antibody repertoire. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):791–793. doi: 10.1126/science.3118465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W., Jr, Walter M. A., Hofker M. H., Ebens A., Willems van Dijk K., Liao L. C., Cox D. W., Milner E. C., Perlmutter R. M. Physical linkage of a human immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene segment to diversity and joining region elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8196–8200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seboun E., Robinson M. A., Doolittle T. H., Ciulla T. A., Kindt T. J., Hauser S. L. A susceptibility locus for multiple sclerosis is linked to the T cell receptor beta chain complex. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1095–1100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sesboü R., Daveau M., Degos J. D., Martin-Mondiere C., Goust J. M., Schuller E., Rivat-Peran L., Coquerel A., Dujardin M., Salier J. P. IgG (Gm) allotypes and multiple sclerosis in a French population: phenotype distribution and quantitative abnormalities in CSF with respect to sex, disease severity, and presence of intrathecal antibodies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 Nov;37(2):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(85)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen A., Humphries C., Tucker P., Blattner F. Human heavy-chain variable region gene family nonrandomly rearranged in familial chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8563–8567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. R., Steinberg A. D. Autoimmunity--a perspective. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:175–210. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souroujon M. C., Rubinstein D. B., Schwartz R. S., Barrett K. J. Polymorphisms in human H chain V region genes from the VHIII gene family. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 15;143(2):706–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spatz L. A., Wong K. K., Williams M., Desai R., Golier J., Berman J. E., Alt F. W., Latov N. Cloning and sequence analysis of the VH and VL regions of an anti-myelin/DNA antibody from a patient with peripheral neuropathy and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2821–2828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull I. F., Bernard O., Sriprakash K. S., Mathews J. D. Human immunoglobulin variable region genes: a new VH sequence used to detect polymorphism. Immunogenetics. 1987;25(3):184–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00344033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOLF B. On estimating the relation between blood group and disease. Ann Hum Genet. 1955 Jun;19(4):251–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1955.tb01348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman B. H. Autoimmunity in demyelinating diseases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;540:13–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb27047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
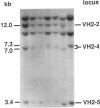
- Walter M. A., Cox D. W. Analysis of genetic variation reveals human immunoglobulin VH-region gene organization. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Mar;42(3):446–451. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter M. A., Linsley P. S., Cox D. W. Apa I polymorphism of a human immunoglobin VH3 subclass locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4697–4697. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter M. A., Surti U., Hofker M. H., Cox D. W. The physical organization of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain gene complex. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3303–3313. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07530.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. G., Catz I. Diagnostic value of cerebrospinal fluid anti-myelin basic protein in patients with multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jul;20(1):20–25. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinshenker B. G., Bass B., Rice G. P., Noseworthy J., Carriere W., Baskerville J., Ebers G. C. The natural history of multiple sclerosis: a geographically based study. I. Clinical course and disability. Brain. 1989 Feb;112(Pt 1):133–146. doi: 10.1093/brain/112.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinshenker B. G., Bulman D., Carriere W., Baskerville J., Ebers G. C. A comparison of sporadic and familial multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1990 Sep;40(9):1354–1358. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.9.1354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems van Dijk K., Schroeder H. W., Jr, Perlmutter R. M., Milner E. C. Heterogeneity in the human Ig VH locus. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2547–2554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]