Abstract
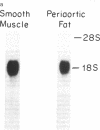
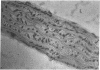
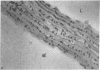
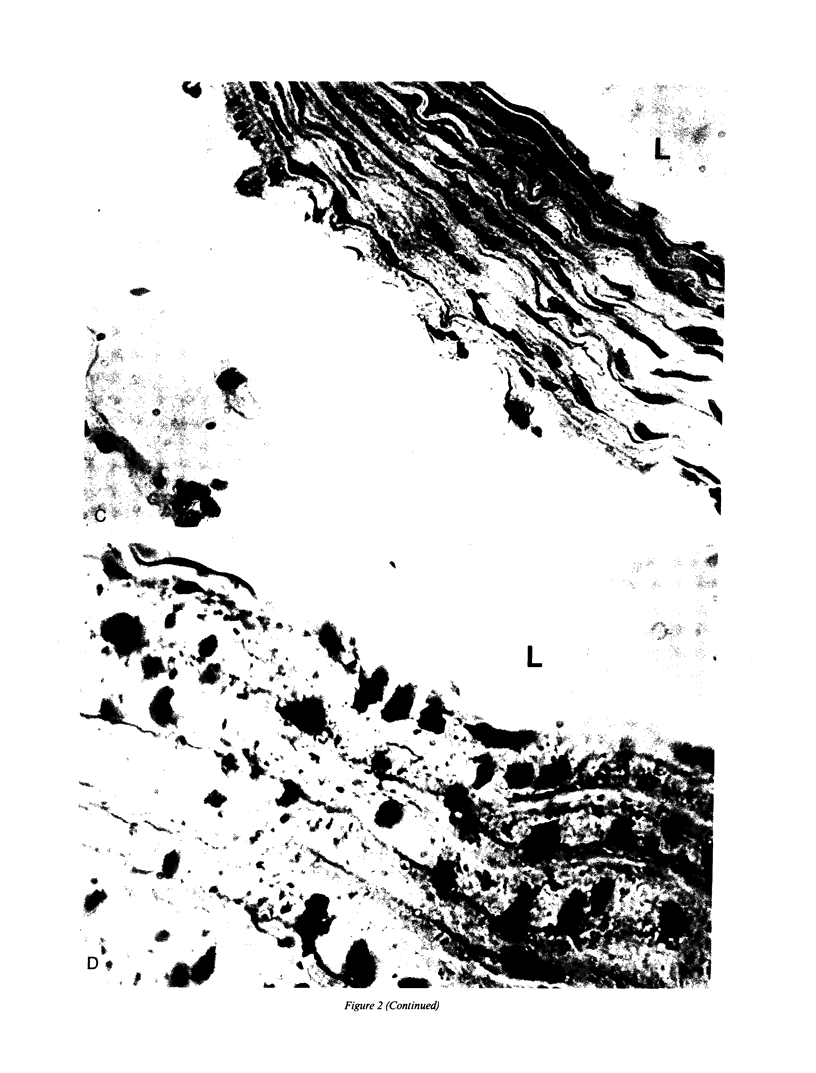
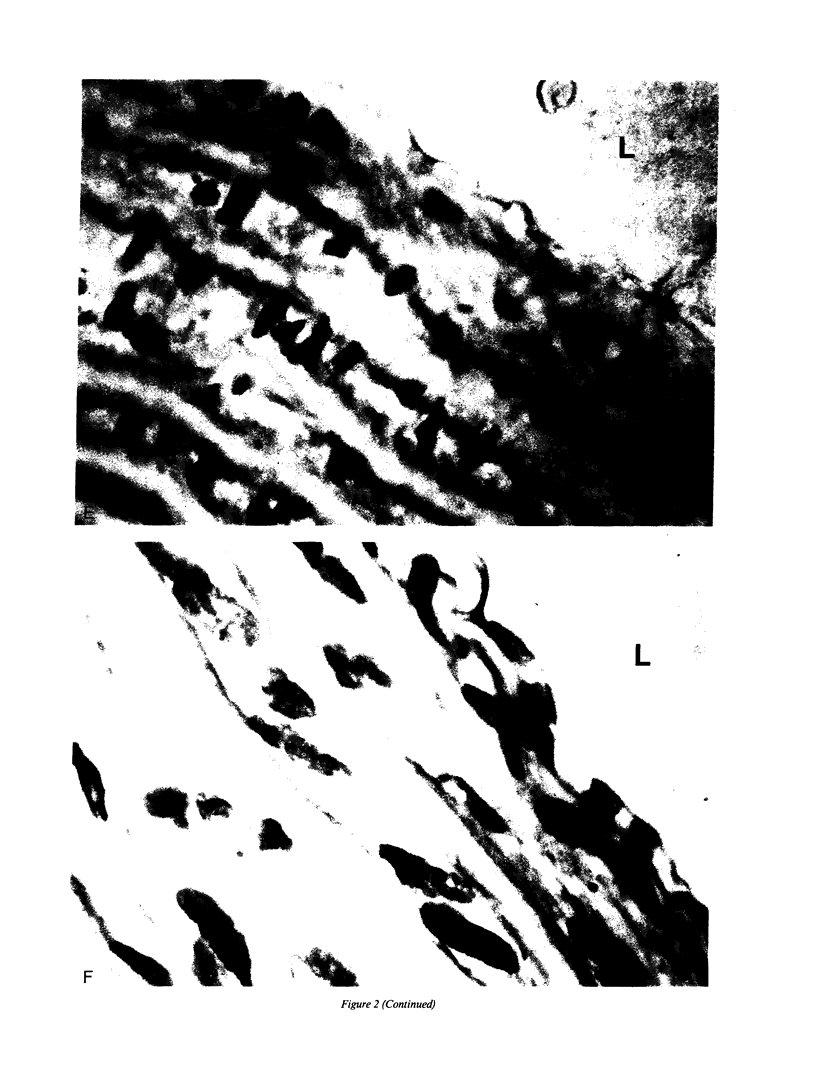
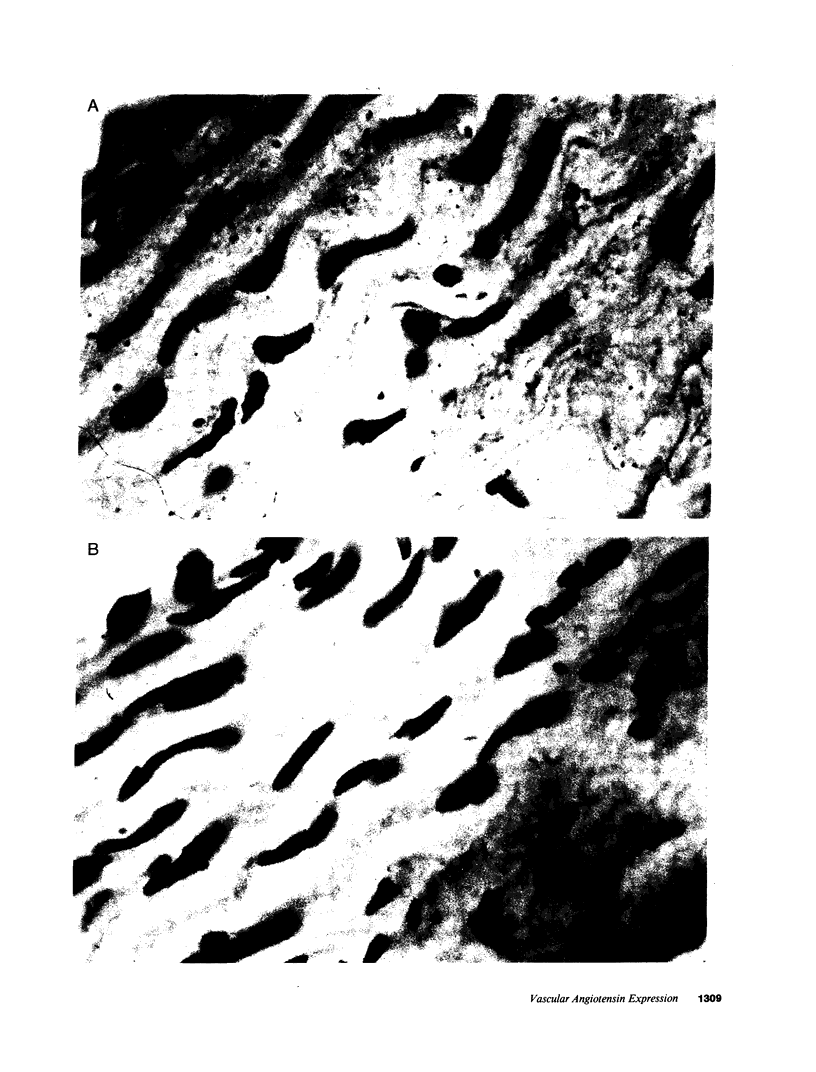
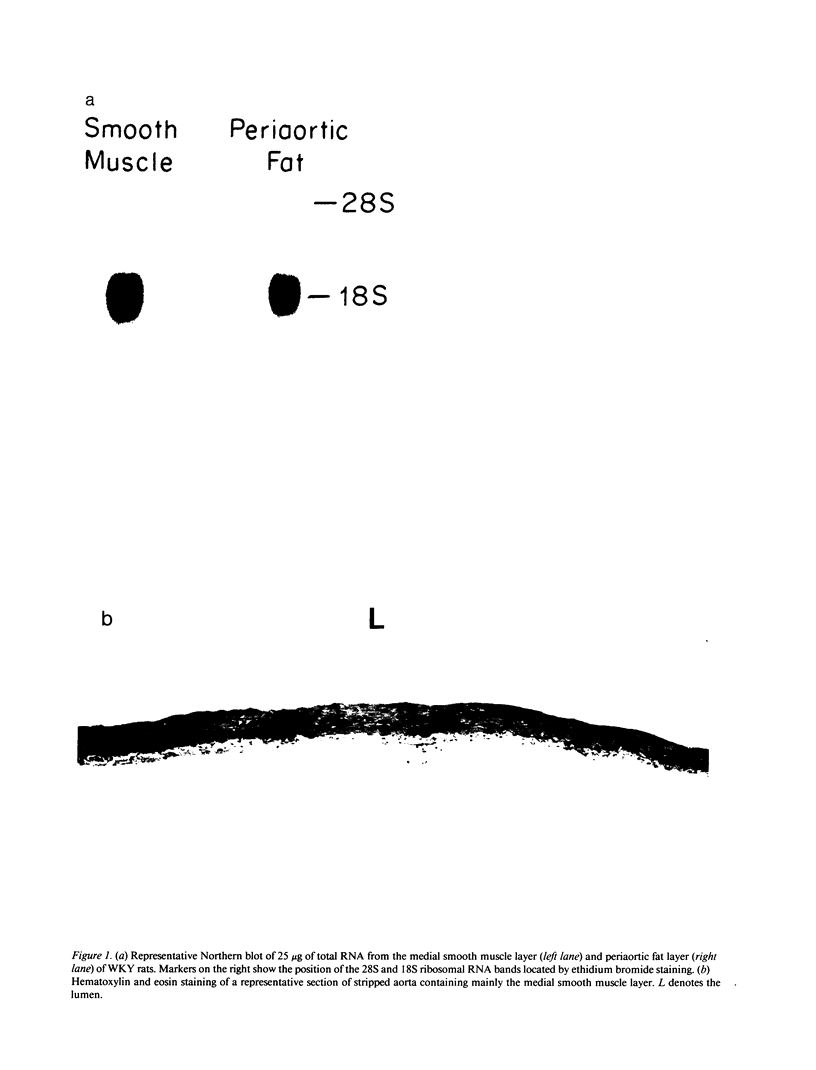
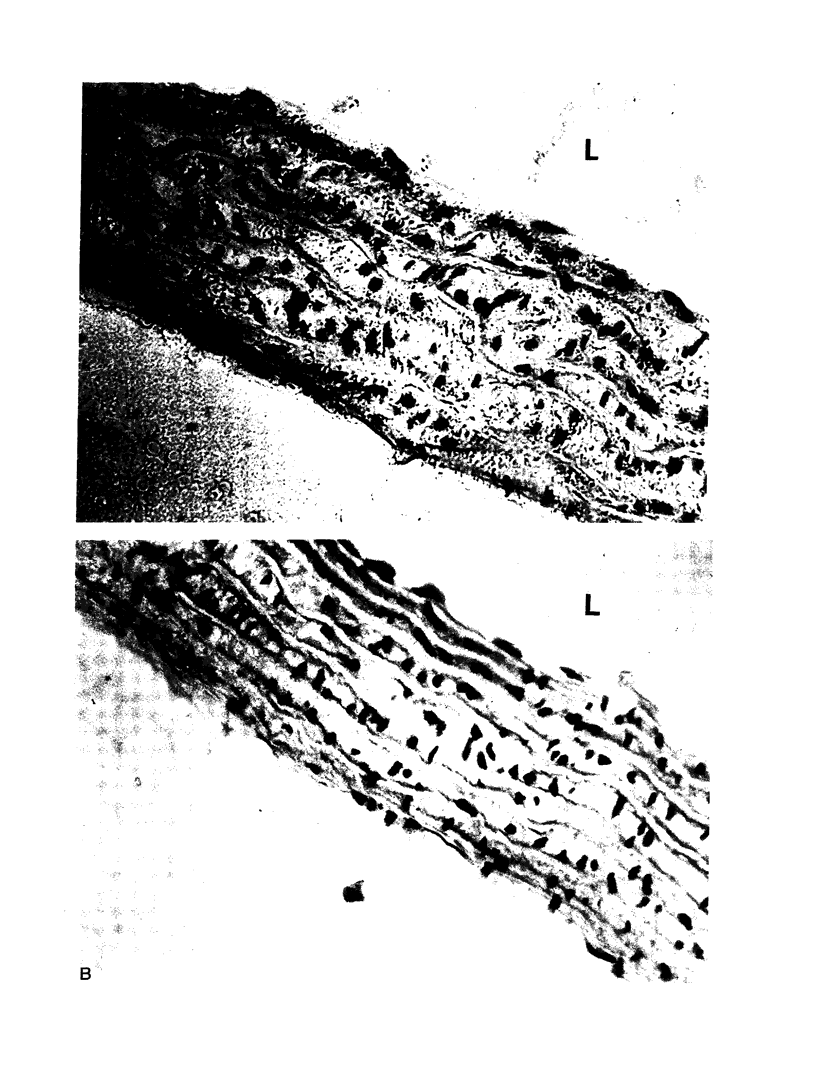
Recent data demonstrate the existence of a vascular renin angiotensin system. In this study we examine the localization of angiotensinogen mRNA in the blood vessel wall of two rat strains, the Wistar and Wistar Kyoto (WKY), as well as the regulation of vascular angiotensinogen mRNA expression by dietary sodium. Northern blot analysis and in situ hybridization histochemistry demonstrate that in both strains angiotensinogen mRNA is detected in the aortic medial smooth muscle layer as well as the periaortic fat. In WKY rats fed a 1.6% sodium diet, angiotensinogen mRNA concentration is 2.6-fold higher in the periaortic fat than in the smooth muscle, as analyzed by quantitative slot blot hybridization. Angiotensinogen mRNA expression in the medial smooth muscle layer is sodium regulated. After 5 d of a low (0.02%) sodium diet, smooth muscle angiotensinogen mRNA levels increase 3.2-fold (P less than 0.005) as compared with the 1.6% sodium diet. In contrast, angiotensinogen mRNA level in the periaortic fat is not influenced by sodium diet. In summary, our data demonstrate regional (smooth muscle vs. periaortic fat) differential regulation of angiotensinogen mRNA levels in the blood vessel wall by sodium. This regional differential regulation by sodium may have important physiological implications.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk B. C., Vekshtein V., Gordon H. M., Tsuda T. Angiotensin II-stimulated protein synthesis in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertension. 1989 Apr;13(4):305–314. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.13.4.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. J., Habener J. F. Angiotensinogen gene is expressed and differentially regulated in multiple tissues of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):31–39. doi: 10.1172/JCI112566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. J., Habener J. F. Cellular localization of angiotensinogen gene expression in brown adipose tissue and mesentery: quantification of messenger ribonucleic acid abundance using hybridization in situ. Endocrinology. 1987 Nov;121(5):1616–1626. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-5-1616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassis L. A., Lynch K. R., Peach M. J. Localization of angiotensinogen messenger RNA in rat aorta. Circ Res. 1988 Jun;62(6):1259–1262. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.6.1259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Kurz K. D. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition in tissues from spontaneously hypertensive rats after treatment with captopril or MK-421. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Jan;220(1):63–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzau V. J., Ellison K. E., Brody T., Ingelfinger J., Pratt R. E. A comparative study of the distributions of renin and angiotensinogen messenger ribonucleic acids in rat and mouse tissues. Endocrinology. 1987 Jun;120(6):2334–2338. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-6-2334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzau V. J., Ingelfinger J., Pratt R. E., Ellison K. E. Identification of renin and angiotensinogen messenger RNA sequences in mouse and rat brains. Hypertension. 1986 Jun;8(6):544–548. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.8.6.544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisterfer A. A., Peach M. J., Owens G. K. Angiotensin II induces hypertrophy, not hyperplasia, of cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1988 Apr;62(4):749–756. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.4.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loudon M., Bing R. F., Thurston H., Swales J. D. Arterial wall uptake of renal renin and blood pressure control. Hypertension. 1983 Sep-Oct;5(5):629–634. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.5.5.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch K. R., Simnad V. I., Ben-Ari E. T., Garrison J. C. Localization of preangiotensinogen messenger RNA sequences in the rat brain. Hypertension. 1986 Jun;8(6):540–543. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.8.6.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naftilan A. J., Pratt R. E., Dzau V. J. Induction of platelet-derived growth factor A-chain and c-myc gene expressions by angiotensin II in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1419–1424. doi: 10.1172/JCI114032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naftilan A. J., Pratt R. E., Eldridge C. S., Lin H. L., Dzau V. J. Angiotensin II induces c-fos expression in smooth muscle via transcriptional control. Hypertension. 1989 Jun;13(6 Pt 2):706–711. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.13.6.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo H., Nakayama K., Tanaka T., Nakanishi S. Tissue distribution of rat angiotensinogen mRNA and structural analysis of its heterogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):319–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura T., Miyazaki M., Inagami T., Toda N. Vascular renin-angiotensin system in two-kidney, one clip hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1986 Jul;8(7):560–565. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.8.7.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J. S., Clozel J. P., Müller R. K., Kuhn H., Hefti F., Hosang M., Baumgartner H. R. Inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme prevent myointimal proliferation after vascular injury. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):186–188. doi: 10.1126/science.2526370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt R. E., Zou W. M., Naftilan A. J., Ingelfinger J. R., Dzau V. J. Altered sodium regulation of renal angiotensinogen mRNA in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 2):F469–F474. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.3.F469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Re R. N., Vizard D. L., Brown J., Bryan S. E. Angiotensin II receptors in chromatin fragments generated by micrococcal nuclease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 29;119(1):220–227. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91641-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Re R., Parab M. Effect of angiotensin II on RNA synthesis by isolated nuclei. Life Sci. 1984 Feb 13;34(7):647–651. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90228-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger T., Ganten D., Lang R. E., Schölkens B. A. Persistent tissue converting enzyme inhibition following chronic treatment with Hoe498 and MK421 in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1985 Jan-Feb;7(1):36–41. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198501000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman B. G. Adrenergic facilitation by angiotensin: does it serve a physiological function? Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Apr;60(4):343–348. doi: 10.1042/cs0600343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]