Abstract
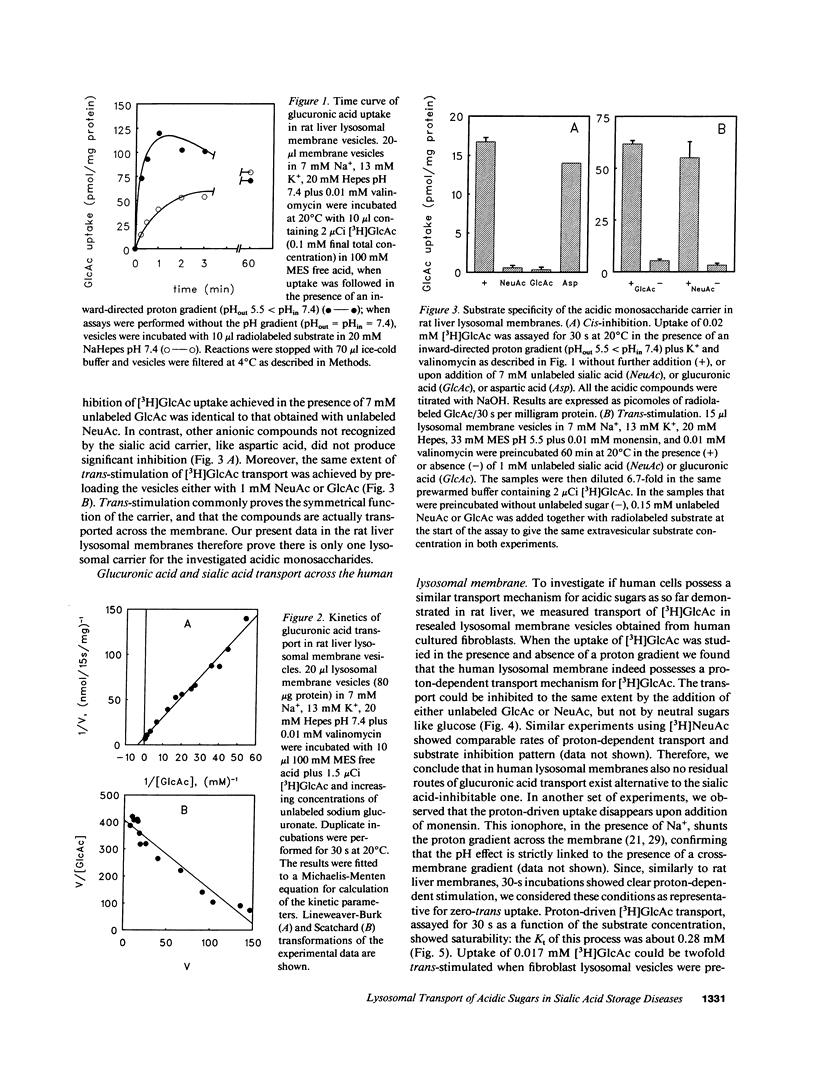
A defective efflux of free sialic acid from the lysosomal compartment has been found in the clinically heterogeneous group of sialic acid storage disorders. Using radiolabeled sialic acid (NeuAc) as a substrate, we have recently detected and characterized a proton-driven carrier for sialic acid in the lysosomal membrane from rat liver. This carrier also recognizes and transports other acidic monosaccharides, among which are uronic acids. If no alternative routes of glucuronic acid transport exist, the disposal of uronic acids can be affected in the sialic acid storage disorders. In this study we excluded the existence of more than one acidic monosaccharide carrier by measuring uptake kinetics of labeled glucuronic acid [( 3H]GlcAc) in rat lysosomal membrane vesicles. [3H]GlcAc uptake was carrier-mediated with an affinity constant of transport (Kt) of 0.3 mM and the transport could be cis-inhibited or trans-stimulated to the same extent by sialic acid or glucuronic acid. Human lysosomal membrane vesicles isolated from cultured fibroblasts showed the existence of a similar proton-driven transporter with the same properties as the rat liver system (Kt of [3H]GlcAc uptake 0.28 mM). Uptake studies with [3H]NeuAc and [3H]GlcAc in resealed lysosome membrane vesicles from cultured fibroblasts of patients with different clinical presentation of sialic acid storage showed defective carrier-mediated transport for both sugars. Further evidence that the defective transport of acidic sugars represents the primary genetic defect in sialic acid storage diseases was provided by the observation of reduced, half-normal transport rates in lymphoblast-derived lysosomal membrane vesicles from five unrelated obligate heterozygotes. This study reports the first observation of a human lysosomal transport defect for multiple physiological compounds.
Full text
PDF

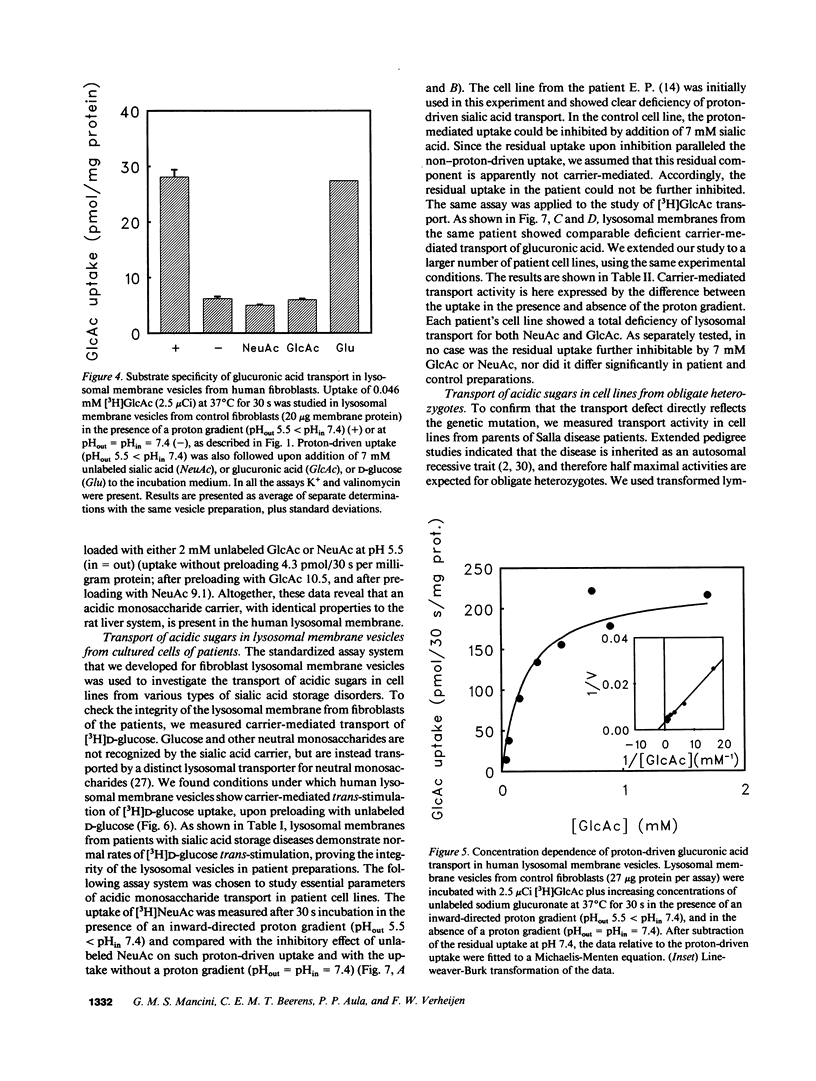


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aula P., Autio S., Raivio K. O., Rapola J., Thodén C. J., Koskela S. L., Yamashina I. "Salla disease": a new lysosomal storage disorder. Arch Neurol. 1979 Feb;36(2):88–94. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1979.00500380058006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bame K. J., Rome L. H. Genetic evidence for transmembrane acetylation by lysosomes. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1087–1089. doi: 10.1126/science.3090688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumkötter J., Cantz M., Mendla K., Baumann W., Friebolin H., Gehler J., Spranger J. N-Acetylneuraminic acid storage disease. Hum Genet. 1985;71(2):155–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00283373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blom H. J., Andersson H. C., Seppala R., Tietze F., Gahl W. A. Defective glucuronic acid transport from lysosomes of infantile free sialic acid storage disease fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 15;268(3):621–625. doi: 10.1042/bj2680621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
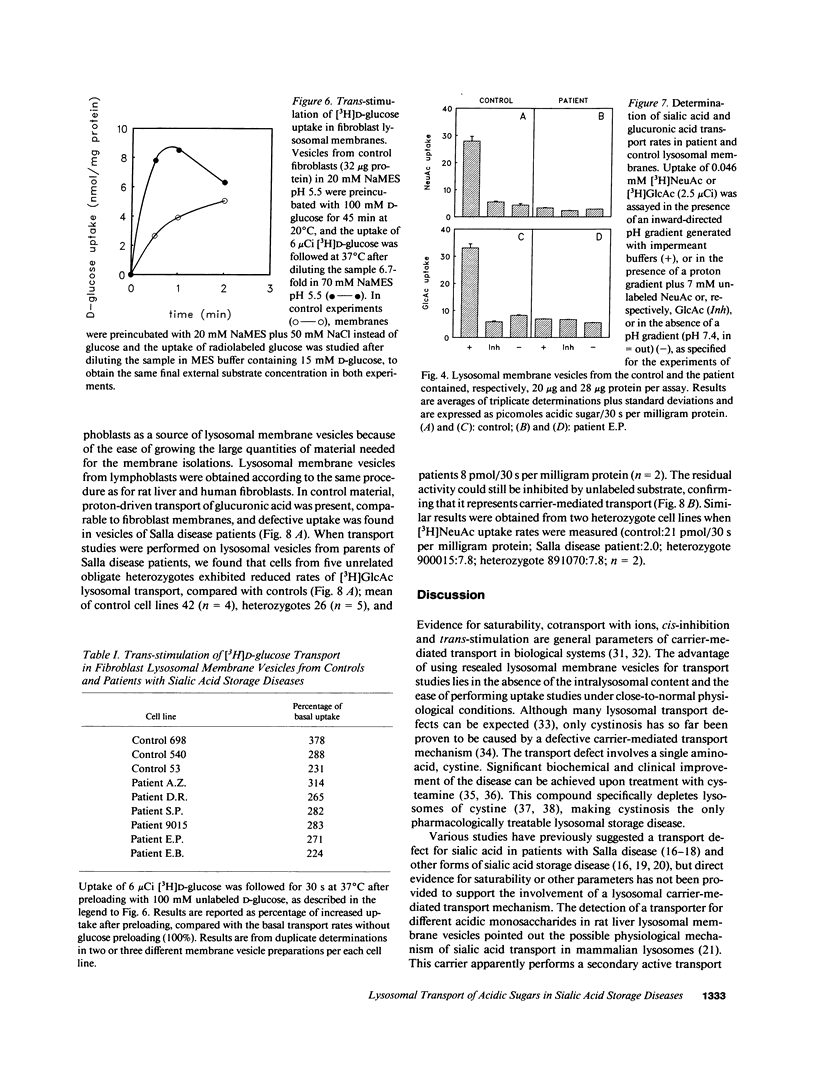
- Cameron P. D., Dubowitz V., Besley G. T., Fensom A. H. Sialic acid storage disease. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Mar;65(3):314–315. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.3.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N. Amino acid transport systems of lysosomes: possible substitute utility of a surviving transport system for one congenitally defective or absent. Biosci Rep. 1988 Apr;8(2):121–129. doi: 10.1007/BF01116456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N. What are the requisites for a model transport analog? Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):40–42. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A., Sardharwalla I. B., Thornley M., Ward K. P. Infantile sialic acid storage disease in two siblings. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1988;11 (Suppl 2):259–262. doi: 10.1007/BF01804252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echenne B., Vidal M., Maire I., Michalski J. C., Baldet P., Astruc J. Salla disease in one non-Finnish patient. Eur J Pediatr. 1986 Sep;145(4):320–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00439413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fois A., Balestri P., Farnetani M. A., Mancini G. M., Borgogni P., Margollicci M. A., Molinelli M., Alessandrini C., Gerli R. Free sialic acid storage disease. A new Italian case. Eur J Pediatr. 1987 Mar;146(2):195–198. doi: 10.1007/BF02343235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahl W. A., Bashan N., Tietze F., Bernardini I., Schulman J. D. Cystine transport is defective in isolated leukocyte lysosomes from patients with cystinosis. Science. 1982 Sep 24;217(4566):1263–1265. doi: 10.1126/science.7112129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahl W. A., Reed G. F., Thoene J. G., Schulman J. D., Rizzo W. B., Jonas A. J., Denman D. W., Schlesselman J. J., Corden B. J., Schneider J. A. Cysteamine therapy for children with nephropathic cystinosis. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 16;316(16):971–977. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704163161602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms E., Kartenbeck J., Darai G., Schneider J. Purification and characterization of human lysosomes from EB-virus transformed lymphoblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Feb;131(2):251–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas A. J. Studies of lysosomal sialic acid metabolism: retention of sialic acid by Salla disease lysosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 29;137(1):175–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91192-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G. M., Beerens C. E., Verheijen F. W. Glucose transport in lysosomal membrane vesicles. Kinetic demonstration of a carrier for neutral hexoses. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12380–12387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G. M., Verheijen F. W., Galjaard H. Free N-acetylneuraminic acid (NANA) storage disorders: evidence for defective NANA transport across the lysosomal membrane. Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;73(3):214–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00401229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G. M., de Jonge H. R., Galjaard H., Verheijen F. W. Characterization of a proton-driven carrier for sialic acid in the lysosomal membrane. Evidence for a group-specific transport system for acidic monosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15247–15254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendla K., Baumkötter J., Rosenau C., Ulrich-Bott B., Cantz M. Defective lysosomal release of glycoprotein-derived sialic acid in fibroblasts from patients with sialic acid storage disease. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 15;250(1):261–267. doi: 10.1042/bj2500261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollenhauer H. H., Morré D. J., Rowe L. D. Alteration of intracellular traffic by monensin; mechanism, specificity and relationship to toxicity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 7;1031(2):225–246. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(90)90008-Z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsumi Y., Ishikawa T., Kato K. A rapid and simplified method for the preparation of lysosomal membranes from rat liver. J Biochem. 1983 Feb;93(2):547–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paschke E., Trinkl G., Erwa W., Pavelka M., Mutz I., Roscher A. Infantile type of sialic acid storage disease with sialuria. Clin Genet. 1986 May;29(5):417–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb00514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisoni R. L., Flickinger K. S., Thoene J. G., Christensen H. N. Characterization of carrier-mediated transport systems for small neutral amino acids in human fibroblast lysosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6010–6017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisoni R. L., Thoene J. G., Christensen H. N. Detection and characterization of carrier-mediated cationic amino acid transport in lysosomes of normal and cystinotic human fibroblasts. Role in therapeutic cystine removal? J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4791–4798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renlund M., Aula P., Raivio K. O., Autio S., Sainio K., Rapola J., Koskela S. L. Salla disease: a new lysosomal storage disorder with disturbed sialic acid metabolism. Neurology. 1983 Jan;33(1):57–66. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renlund M. Clinical and laboratory diagnosis of Salla disease in infancy and childhood. J Pediatr. 1984 Feb;104(2):232–236. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80998-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renlund M., Tietze F., Gahl W. A. Defective sialic acid egress from isolated fibroblast lysosomes of patients with Salla disease. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):759–762. doi: 10.1126/science.3961501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCRIVER C. R., WILSON O. H. POSSIBLE LOCATIONS FOR A COMMON GENE PRODUCT IN MEMBRANE TRANSPORT OF IMINO-ACIDS AND GLYCINE. Nature. 1964 Apr 4;202:92–93. doi: 10.1038/202092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperl W., Gruber W., Quatacker J., Monnens L., Thoenes W., Fink F. M., Paschke E. Nephrosis in two siblings with infantile sialic acid storage disease. Eur J Pediatr. 1990 Apr;149(7):477–482. doi: 10.1007/BF01959399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson R. E., Lubinsky M., Taylor H. A., Wenger D. A., Schroer R. J., Olmstead P. M. Sialic acid storage disease with sialuria: clinical and biochemical features in the severe infantile type. Pediatrics. 1983 Oct;72(4):441–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart B. H., Collarini E. J., Pisoni R. L., Christensen H. N. Separate and shared lysosomal transport of branched and aromatic dipolar amino acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 28;987(2):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90537-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoene J. G., Oshima R. G., Crawhall J. C., Olson D. L., Schneider J. A. Cystinosis. Intracellular cystine depletion by aminothiols in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):180–189. doi: 10.1172/JCI108448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tietze F., Seppala R., Renlund M., Hopwood J. J., Harper G. S., Thomas G. H., Gahl W. A. Defective lysosomal egress of free sialic acid (N-acetylneuraminic acid) in fibroblasts of patients with infantile free sialic acid storage disease. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15316–15322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tondeur M., Libert J., Vamos E., Van Hoof F., Thomas G. H., Strecker G. Infantile form of sialic acid storage disorder: clinical, ultrastructural, and biochemical studies in two siblings. Eur J Pediatr. 1982 Oct;139(2):142–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00441499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss P., Tietze F., Gahl W. A., Seppala R., Ashwell G. Identification of the metabolic defect in sialuria. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17635–17636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolburg-Buchholz K., Schlote W., Baumkötter J., Cantz M., Holder H., Harzer K. Familial lysosomal storage disease with generalized vacuolization and sialic aciduria. Sporadic Salla disease. Neuropediatrics. 1985 May;16(2):67–75. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1052546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylitalo V., Hagberg B., Rapola J., Månsson J. E., Svennerholm L., Sanner G., Tonnby B. Salla disease variants. Sialoylaciduric encephalopathy with increased sialidase activity in two non-Finnish children. Neuropediatrics. 1986 Feb;17(1):44–47. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1052498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Silva V. A., Zurbrügg R. P., Lavanchy P., Blumberg A., Suter H., Wyss S. R., Lüthy C. M., Oetliker O. H. Long-term treatment of infantile nephropathic cystinosis with cysteamine. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 5;313(23):1460–1463. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512053132307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



