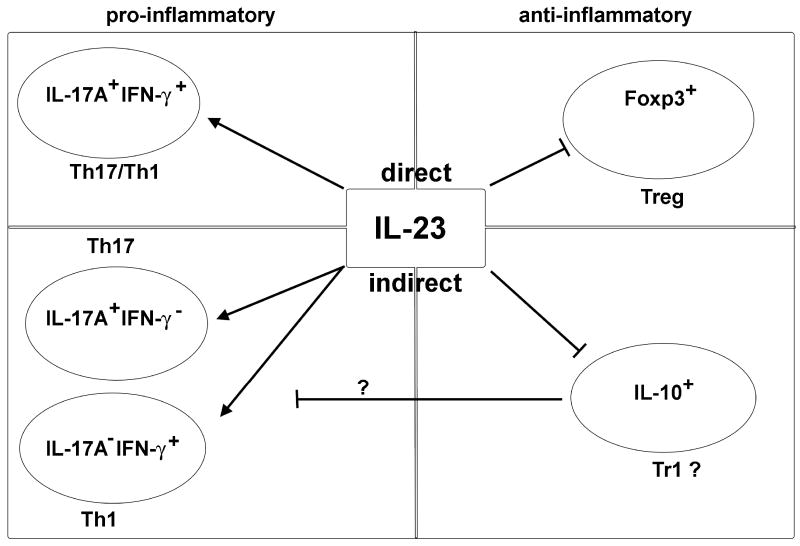
Figure 1. Direct and indirect effects of IL-23 on T cell subsets in the colon.
IL-23R signaling in CD4+ T cells is crucial for the accumulation of effector CD4+ T cells in the intestine. It directly promotes IL-17A+IFN-γ+ CD4+ T cells, while it inhibits Foxp3+ Treg cells. In contrast, IL-23 has an indirect inhibitory effect on IL-10 producing cells (which might be Tr1 cells) via an unidentified mediator. Additionally, IL-23 is indirectly promoting Th17 and Th1 cells, which might be mediated by suppression of IL-10 production by CD4+ T cells. Therefore IL-23 shifts the balance from an anti-inflammatory to a pro-inflammatory milieu in the intestine via direct and indirect effects on CD4+ T cell subsets.