Abstract
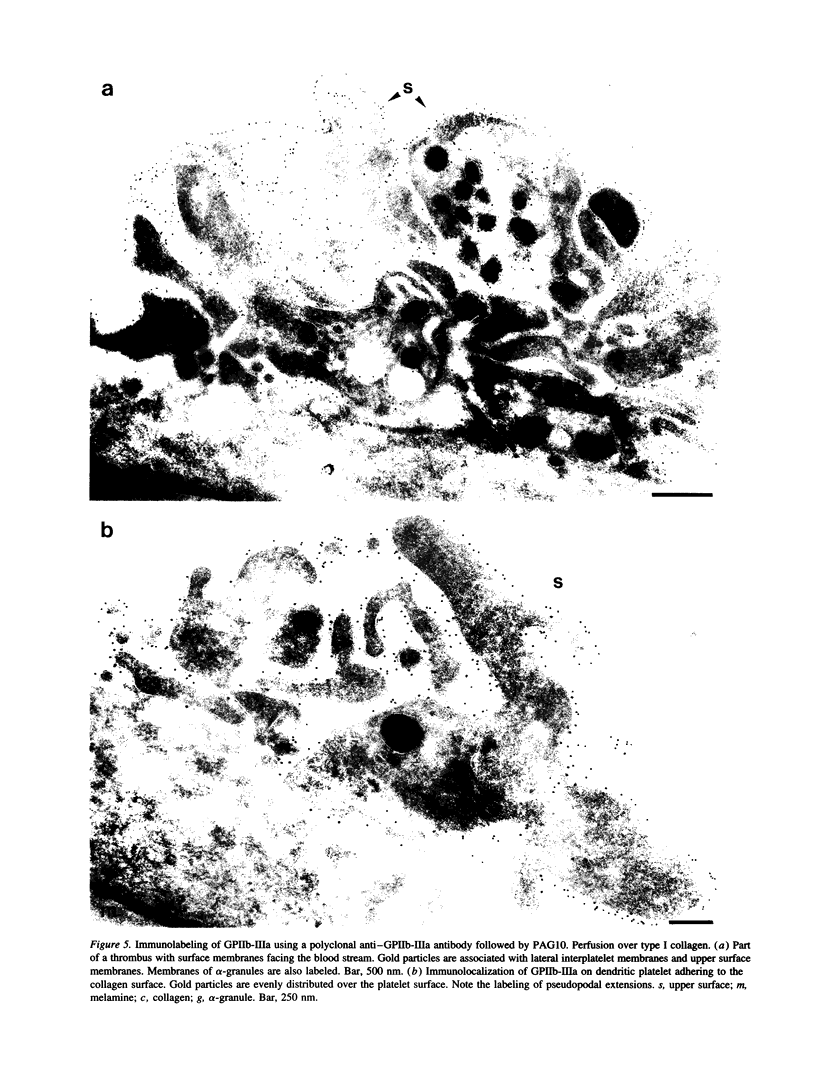
We examined the distribution of glycoprotein IIb-IIIa (GPIIb-IIIa) and its ligands fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor (vWf) on platelets which had adhered under flow conditions. Immunoelectron microscopy was performed on whole mounts and frozen thin sections of adhering platelets. GPIIb-IIIa was homogeneously distributed on dendritic platelets and on interplatelet membranes of formed thrombi. Fibrinogen and vWf were predominantly associated with interplatelet membranes and membranes facing the substrate. On whole mounts, vWf appeared in clumps and linear arrays, representing the tangled or extended forms of the multimeric molecule. From semiquantitative analysis, it appeared that fibrinogen and vWf were, respectively, nine- and fourfold higher on interplatelet membranes than on surface membranes facing the blood stream, while GPIIb-IIIa was evenly distributed over all platelet plasma membranes. Ligand-induced binding sites (LIBS) of GPIIb-IIIa, as measured with conformation specific monoclonal antibodies RUU 2.41 and LIBS-1, were present on the surface of adhered platelets and thrombi. A redistribution of LIBS-positive forms of GPIIb-IIIa towards interplatelet membranes was not observed. Our data support the hypothesis that, under flow conditions, ligands have first bound to activated GPIIb-IIIa but this binding is reversed on the upper surface of adhering platelets. This relative absence of ligands on the exposed surface of thrombi may play a role in limiting their size.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asch E., Podack E. Vitronectin binds to activated human platelets and plays a role in platelet aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1372–1378. doi: 10.1172/JCI114581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner H. R., Tschopp T. B., Meyer D. Shear rate dependent inhibition of platelet adhesion and aggregation on collagenous surfaces by antibodies to human factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. Br J Haematol. 1980 Jan;44(1):127–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1980.tb01190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouma B. N., van Mourik J. A., de Graaf S., Hordijk-Hos J. M., Sixma J. J. Immunologic studies on human factor VIII (anti-hemophilic factor A, AHF) components produced by low-ionic-strength dialysis. Blood. 1976 Feb;47(2):253–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S. A new murine monoclonal antibody reports an activation-dependent change in the conformation and/or microenvironment of the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):101–108. doi: 10.1172/JCI111931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S. Interaction of normal, thrombasthenic, and Bernard-Soulier platelets with immobilized fibrinogen: defective platelet-fibrinogen interaction in thrombasthenia. Blood. 1980 Feb;55(2):169–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S., Peerschke E. I., Scudder L. E., Sullivan C. A. Studies with a murine monoclonal antibody that abolishes ristocetin-induced binding of von Willebrand factor to platelets: additional evidence in support of GPIb as a platelet receptor for von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1983 Jan;61(1):99–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer E. M., Savidge G. F., Vainchenker W., Berndt M. C., Pidard D., Caen J. P., Massé J. M., Breton-Gorius J. Alpha-granule pool of glycoprotein IIb-IIIa in normal and pathologic platelets and megakaryocytes. Blood. 1990 Mar 15;75(6):1220–1227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler W. E., Fretto L. J., Hamilton K. K., Erickson H. P., McKee P. A. Substructure of human von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1491–1500. doi: 10.1172/JCI112129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelinger A. L., 3rd, Cohen I., Plow E. F., Smith M. A., Roberts J., Lam S. C., Ginsberg M. H. Selective inhibition of integrin function by antibodies specific for ligand-occupied receptor conformers. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6346–6352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelinger A. L., 3rd, Du X. P., Plow E. F., Ginsberg M. H. Monoclonal antibodies to ligand-occupied conformers of integrin alpha IIb beta 3 (glycoprotein IIb-IIIa) alter receptor affinity, specificity, and function. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17106–17111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawaz M. P., Loftus J. C., Bajt M. L., Frojmovic M. M., Plow E. F., Ginsberg M. H. Ligand bridging mediates integrin alpha IIb beta 3 (platelet GPIIB-IIIA) dependent homotypic and heterotypic cell-cell interactions. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1128–1134. doi: 10.1172/JCI115412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heijnen H. F., Koedam J. A., Sandberg H., Beeser-Visser N. H., Slot J. W., Sixma J. J. Characterization of human factor VIII and interaction with von Willebrand factor. An electron microscopic study. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 12;194(2):491–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilmann E., Hourdillé P., Pruvost A., Paponneau A., Nurden A. T. Thrombin-induced platelet aggregates have a dynamic structure. Time-dependent redistribution of glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complexes and secreted adhesive proteins. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 May-Jun;11(3):704–718. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.3.704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houdijk W. P., Sakariassen K. S., Nievelstein P. F., Sixma J. J. Role of factor VIII-von Willebrand factor and fibronectin in the interaction of platelets in flowing blood with monomeric and fibrillar human collagen types I and III. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):531–540. doi: 10.1172/JCI111729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houdijk W. P., de Groot P. G., Nievelstein P. F., Sakariassen K. S., Sixma J. J. Subendothelial proteins and platelet adhesion. von Willebrand factor and fibronectin, not thrombospondin, are involved in platelet adhesion to extracellular matrix of human vascular endothelial cells. Arteriosclerosis. 1986 Jan-Feb;6(1):24–33. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.6.1.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourdille P., Benabdallah S., Belloc F., Nurden A. T. Distribution of glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complexes in the surface membranes of human platelets and megakaryocytes. Br J Haematol. 1985 Jan;59(1):171–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb02977.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg W. M., McEver R. P., Phillips D. R., Shuman M. A., Bainton D. F. Immunogold-surface replica study of ADP-induced ligand binding and fibrinogen receptor clustering in human platelets. Am J Anat. 1989 Jun-Jul;185(2-3):142–148. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001850207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg W. M., McEver R. P., Phillips D. R., Shuman M. A., Bainton D. F. The platelet fibrinogen receptor: an immunogold-surface replica study of agonist-induced ligand binding and receptor clustering. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1655–1663. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer N., Guichard J., Breton-Gorius J. Dynamic redistribution of major platelet surface receptors after contact-induced platelet activation and spreading. An immunoelectron microscopy study. Am J Pathol. 1992 Jan;140(1):57–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Packham M. A., Mustard J. F. Vessel injury, platelet adherence, and platelet survival. Arteriosclerosis. 1983 Nov-Dec;3(6):529–546. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.3.6.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leistikow E. A., Barnhart M. I., Escolar G., White J. G. Receptor-ligand complexes are cleared to the open canalicular system of surface-activated platelets. Br J Haematol. 1990 Jan;74(1):93–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb02544.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. C., Hantgan R. R., Stevenson S. C., Thornburg T., Kieffer N., Guichard J., Breton-Gorius J. Fibrinogen and glycoprotein IIb/IIIa localization during platelet adhesion. Localization to the granulomere and at sites of platelet interaction. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jan;136(1):239–252. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. C., Johnson C., Ramsamooj P., Hantgan R. R. Orientation and specificity of fibrin protofibril binding to ADP-stimulated platelets. Blood. 1988 Dec;72(6):1992–2000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loftus J. C., Albrecht R. M. Redistribution of the fibrinogen receptor of human platelets after surface activation. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):822–829. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher E. F., Weber S. The formation of the haemostatic plug--a special case of platelet aggregation. An experiment and a survey of the literature. Thromb Haemost. 1993 Aug 2;70(2):234–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzelaar M. J., Sixma J. J., Nieuwenhuis H. K. Detection of platelet activation using activation specific monoclonal antibodies. Blood Cells. 1990;16(1):85–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern E., Reimers H. J., Miyashita C. Ultrastructural studies on the binding sites of fibrinogen on platelet surface during aggregation. Acta Histochem Suppl. 1984;29:183–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muggli R., Baumgartner H. R., Tschopp T. B., Keller H. Automated microdensitometry and protein assays as a measure for platelet adhesion and aggregation on collagen-coated slides under controlled flow conditions. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Feb;95(2):195–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pareti F. I., Niiya K., McPherson J. M., Ruggeri Z. M. Isolation and characterization of two domains of human von Willebrand factor that interact with fibrillar collagen types I and III. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13835–13841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. I., Gralnick H. R. Identification of platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa as the major binding site for released platelet-von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1986 Sep;68(3):732–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Charo I. F., Parise L. V., Fitzgerald L. A. The platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex. Blood. 1988 Apr;71(4):831–843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piétu G., Cherel G., Marguerie G., Meyer D. Inhibition of von Willebrand factor-platelet interaction by fibrinogen. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):648–649. doi: 10.1038/308648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E., Marguerie G. A., Ginsberg M. H. The effect of Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptides on fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor binding to platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8057–8061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakariassen K. S., Aarts P. A., de Groot P. G., Houdijk W. P., Sixma J. J. A perfusion chamber developed to investigate platelet interaction in flowing blood with human vessel wall cells, their extracellular matrix, and purified components. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Oct;102(4):522–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage B., Ruggeri Z. M. Selective recognition of adhesive sites in surface-bound fibrinogen by glycoprotein IIb-IIIa on nonactivated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11227–11233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., Hoxie J. A., Cunningham M., Brass L. F. Changes in the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb.IIIa complex during platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11107–11114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixma J. J., Pronk A., Nievelstein P. N., Zwaginga J. J., Hindriks G., Tijburg P., Banga J. D., De Groot P. G. Platelet adhesion to extracellular matrices of cultured cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;614:181–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb43702.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J. A new method of preparing gold probes for multiple-labeling cytochemistry. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;38(1):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stel H. V., Sakariassen K. S., de Groot P. G., van Mourik J. A., Sixma J. J. Von Willebrand factor in the vessel wall mediates platelet adherence. Blood. 1985 Jan;65(1):85–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Packham M. A., Tanoue K., Yamazaki H., Mustard J. F. Immunocytochemical localization of fibrinogen during thrombin-induced aggregation of washed human platelets. Blood. 1988 May;71(5):1310–1320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tetteroo P. A., Lansdorp P. M., Leeksma O. C., von dem Borne A. E. Monoclonal antibodies against human platelet glycoprotein IIIa. Br J Haematol. 1983 Nov;55(3):509–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb02166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Baumgartner H. R., Tschopp T. B., Turitto V. T., Cohen D. Correction by factor VIII of the impaired platelet adhesion to subendothelium in von Willebrand disease. Blood. 1978 Feb;51(2):267–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Turitto V. T., Baumgartner H. R. Platelet adhesion and thrombus formation on subendothelium in platelets deficient in glycoproteins IIb-IIIa, Ib, and storage granules. Blood. 1986 Feb;67(2):322–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wencel-Drake J. D. Plasma membrane GPIIb/IIIa. Evidence for a cycling receptor pool. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jan;136(1):61–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal C., Hörler H., Pentz S., Frösch D. A new method for cell culture on an electron-transparent melamine foil suitable for successive LM, TEM and SEM studies of whole cells. J Microsc. 1988 Jun;150(Pt 3):225–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1988.tb04641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Escolar G. Fibrinogen receptors do not undergo spontaneous redistribution on surface-activated platelets. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Sep-Oct;10(5):738–744. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.5.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Induction of patching and its reversal on surface-activated human platelets. Br J Haematol. 1990 Sep;76(1):108–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb07844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Leistikow E. L., Escolar G. Platelet membrane responses to surface and suspension activation. Blood Cells. 1990;16(1):43–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Separate and combined interactions of fibrinogen-gold and latex with surface-activated platelets. Am J Pathol. 1990 Oct;137(4):989–998. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods V. L., Jr, Wolff L. E., Keller D. M. Resting platelets contain a substantial centrally located pool of glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex which may be accessible to some but not other extracellular proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15242–15251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Willigen G., Akkerman J. W. Protein kinase C and cyclic AMP regulate reversible exposure of binding sites for fibrinogen on the glycoprotein IIB-IIIA complex of human platelets. Biochem J. 1991 Jan 1;273(Pt 1):115–120. doi: 10.1042/bj2730115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]