Abstract
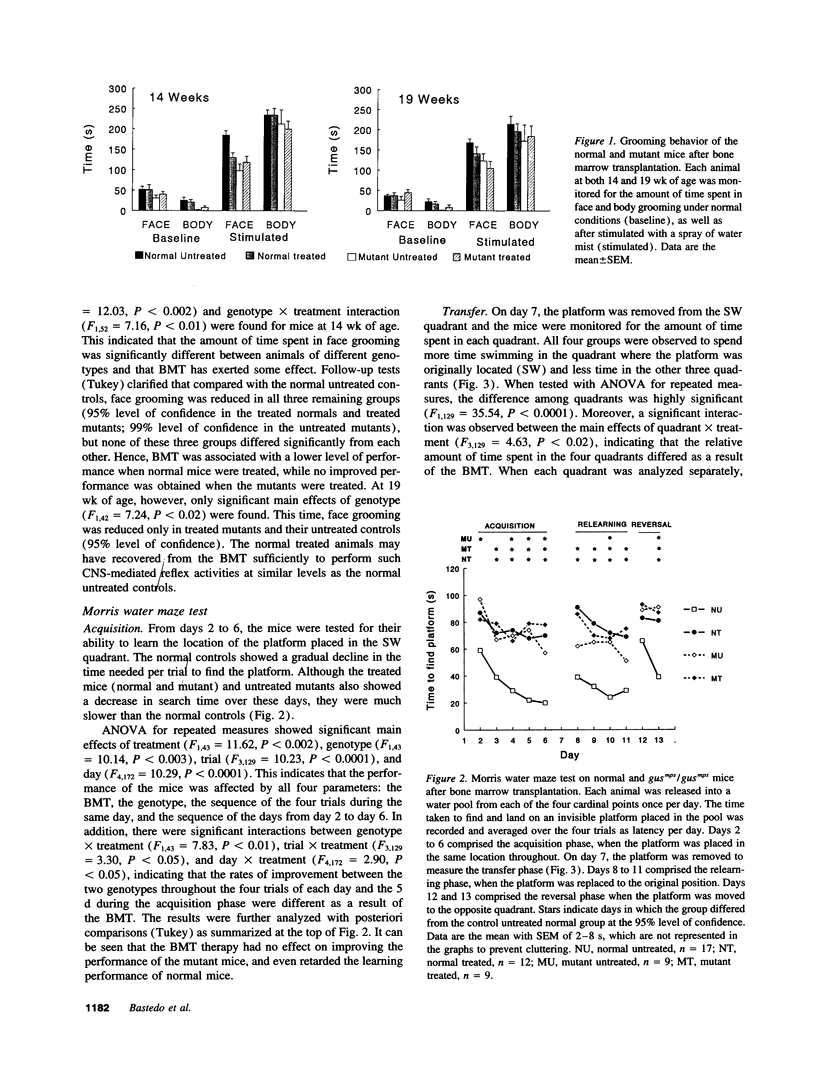
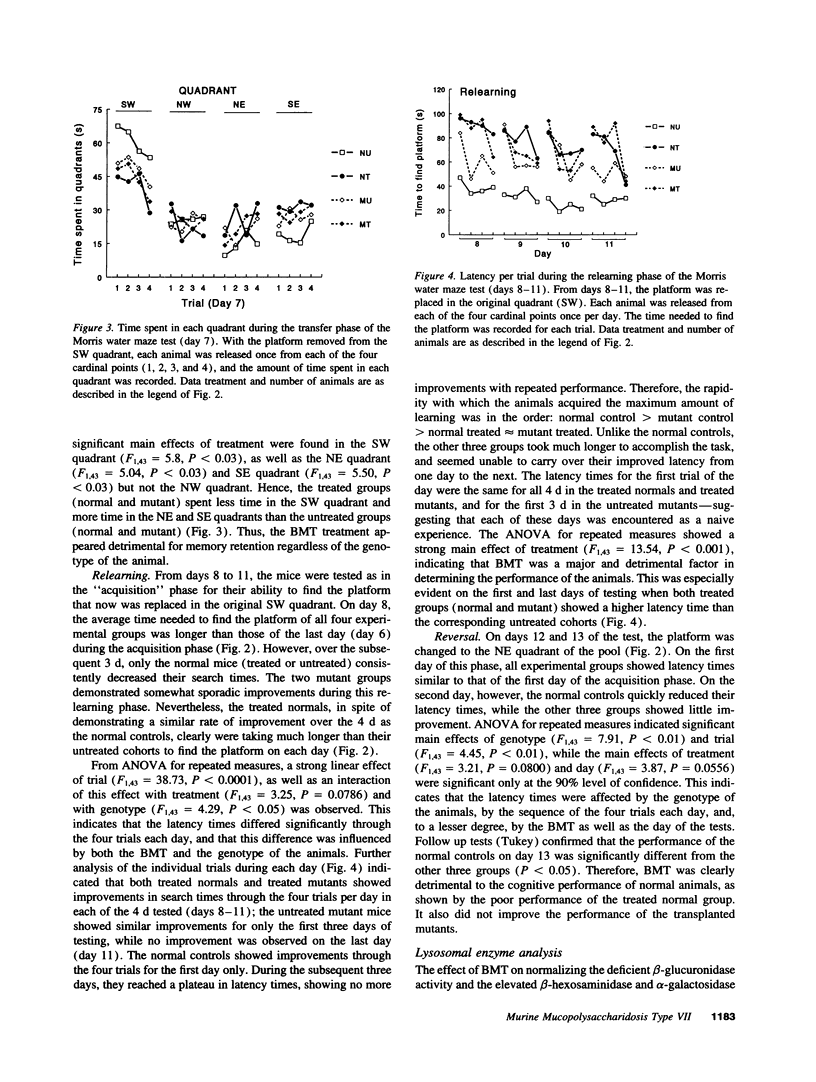
The gusmps/gusmps mouse is a model of the human lysosomal storage disease mucopolysaccharidosis type VII caused by deficient beta-glucuronidase activity. Bone marrow transplantation has been shown to correct some of their biochemical and pathological abnormalities but its efficacy in correcting their neurological functional deficits is unknown. We transplanted the neonatal gusmps/gusmps mice and their normal controls and evaluated their central nervous system function with two behavioral tests: the grooming test, a developmentally regulated and genetically based activity, and a Morris water maze test which assessed spatial learning abilities. The two transplanted groups groomed less than the normals, were unable to remember the location of an invisible platform from day to day, and were severely impaired at developing strategies to locate the platform in unfamiliar locations. The performance of both normal and mutant transplanted groups was clearly inferior to the untreated normals and, in some instances, close to or worse than the untreated mutants, even though the enzyme abnormalities of the mutants have been partially corrected. Hence, the behavioral deficits in the mutant mice were not restored to normal while similarly treated normal mice showed significant functional deterioration, indicating the detrimental consequence of this therapy in the neonatal period.
Full text
PDF

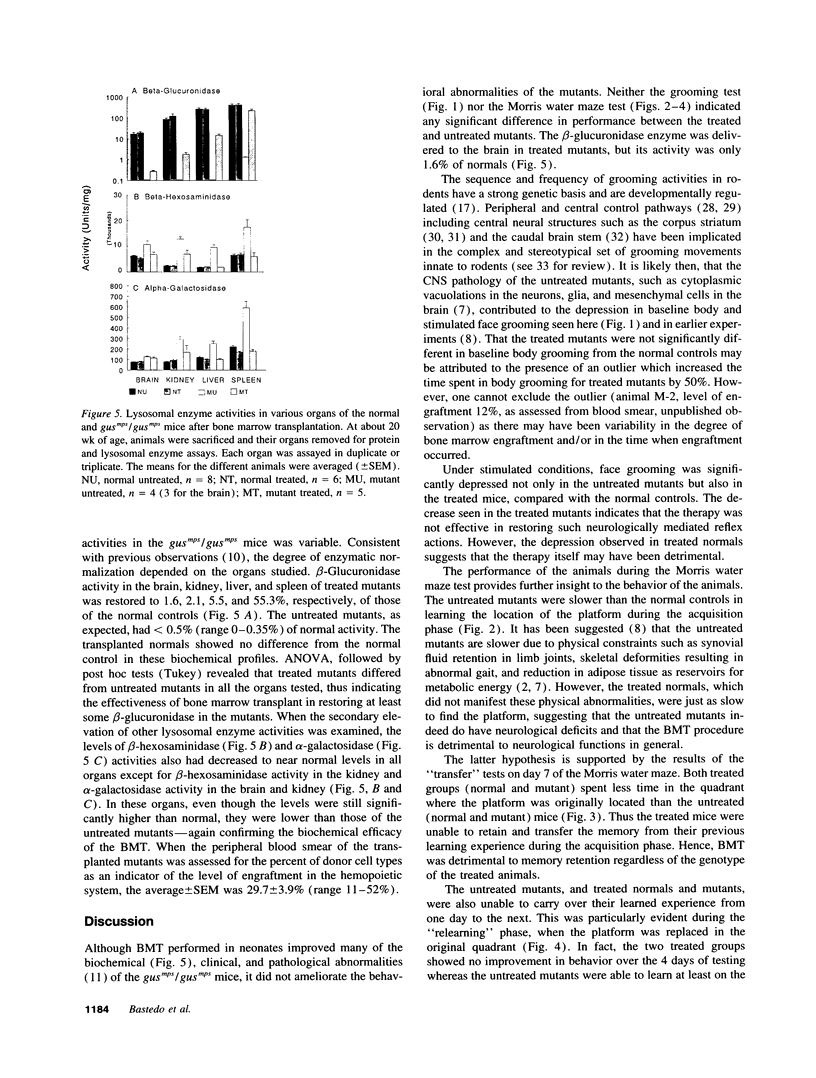


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge K. C., Fentress J. C. Contextual control of trigeminal sensorimotor function. J Neurosci. 1986 Feb;6(2):325–330. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-02-00325.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge K. C., Fentress J. C. Deafferentation does not disrupt natural rules of action syntax. Behav Brain Res. 1987 Jan;23(1):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(87)90243-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge K. C., Fentress J. C., Parr H. Natural syntax rules control action sequence of rats. Behav Brain Res. 1987 Jan;23(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(87)90242-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Barker J. E., Vogler C. A., Kyle J. W., Sly W. S., Gwynn B., Levy B., Pegors C. Increased life span and correction of metabolic defects in murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII after syngeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1991 Dec 1;78(11):3081–3092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Davisson M. T., Beamer W. G., Ganschow R. E., Vogler C. A., Gwynn B., Lyford K. A., Maltais L. M., Wawrzyniak C. J. Murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII. Characterization of a mouse with beta-glucuronidase deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1258–1266. doi: 10.1172/JCI114010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang P. L., Capone J. P., Brown G. M. Autologous fibroblast implantation. Feasibility and potential problems in gene replacement therapy. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Dec;7(6):461–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang P. L., Lambert D. T., Pisa M. A. Behavioural abnormalities in a murine model of a human lysosomal storage disease. Neuroreport. 1993 May;4(5):507–510. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199305000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang P. L., Shen N., Westcott A. J. Delivery of recombinant gene products with microencapsulated cells in vivo. Hum Gene Ther. 1993 Aug;4(4):433–440. doi: 10.1089/hum.1993.4.4-433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman S., Gray R. G., Constable T. J., Bundey S. Atypical radiological features of beta-glucuronidase deficiency (mucopolysaccharidosis VII) occurring in an elderly patient from an inbred kindred. Br J Radiol. 1989 May;62(737):491–494. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-62-737-491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnett S. B., Iversen S. D. Sensorimotor impairments following localized kainic acid and 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the neostriatum. Brain Res. 1982 Sep 23;248(1):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fentress J. C. Expressive contexts, fine structure, and central mediation of rodent grooming. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;525:18–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb38592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser J. H., Sly W. S. Beta-glucuronidase deficiency mucopolysaccharidosis: methods for enzymatic diagnosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Dec;82(6):969–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb B., Sutherland R. J., Whishaw I. Q. A comparison of the contributions of the frontal and parietal association cortex to spatial localization in rats. Behav Neurosci. 1983 Feb;97(1):13–27. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.97.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb B., Whishaw I. Q. Decortication of rats in infancy or adulthood produced comparable functional losses on learned and species-typical behaviors. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1981 Jun;95(3):468–483. doi: 10.1037/h0077784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krivit W., Whitley C. B. Bone marrow transplantation for genetic diseases. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 23;316(17):1085–1087. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704233161710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris R. G., Garrud P., Rawlins J. N., O'Keefe J. Place navigation impaired in rats with hippocampal lesions. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):681–683. doi: 10.1038/297681a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris R. Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods. 1984 May;11(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(84)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moullier P., Bohl D., Heard J. M., Danos O. Correction of lysosomal storage in the liver and spleen of MPS VII mice by implantation of genetically modified skin fibroblasts. Nat Genet. 1993 Jun;4(2):154–159. doi: 10.1038/ng0693-154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkman R. The application of bone marrow transplantation to the treatment of genetic diseases. Science. 1986 Jun 13;232(4756):1373–1378. doi: 10.1126/science.3520819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer R. A., Kresse H., Bäumer N., Sattinger E. Beta-glucuronidase deficiency in a girl with unusual clinical features. Eur J Pediatr. 1977 Oct 12;126(3):155–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00442197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands M. S., Barker J. E., Vogler C., Levy B., Gwynn B., Galvin N., Sly W. S., Birkenmeier E. Treatment of murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII by syngeneic bone marrow transplantation in neonates. Lab Invest. 1993 Jun;68(6):676–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands M. S., Birkenmeier E. H. A single-base-pair deletion in the beta-glucuronidase gene accounts for the phenotype of murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6567–6571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewell A. C., Gehler J., Mittermaier G., Meyer E. Mucopolysaccharidosis type VII (beta-glucuronidase deficiency): a report of a new case and a survey of those in the literature. Clin Genet. 1982 Jun;21(6):366–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1982.tb01389.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sly W. S., Quinton B. A., McAlister W. H., Rimoin D. L. Beta glucuronidase deficiency: report of clinical, radiologic, and biochemical features of a new mucopolysaccharidosis. J Pediatr. 1973 Feb;82(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland R. J., Whishaw I. Q., Kolb B. A behavioural analysis of spatial localization following electrolytic, kainate- or colchicine-induced damage to the hippocampal formation in the rat. Behav Brain Res. 1983 Feb;7(2):133–153. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(83)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogler C., Birkenmeier E. H., Sly W. S., Levy B., Pegors C., Kyle J. W., Beamer W. G. A murine model of mucopolysaccharidosis VII. Gross and microscopic findings in beta-glucuronidase-deficient mice. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jan;136(1):207–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogler C., Sands M., Higgins A., Levy B., Grubb J., Birkenmeier E. H., Sly W. S. Enzyme replacement with recombinant beta-glucuronidase in the newborn mucopolysaccharidosis type VII mouse. Pediatr Res. 1993 Dec;34(6):837–840. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199312000-00028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whishaw I. Q., Mittleman G., Bunch S. T., Dunnett S. B. Impairments in the acquisition, retention and selection of spatial navigation strategies after medial caudate-putamen lesions in rats. Behav Brain Res. 1987 May;24(2):125–138. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(87)90250-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whishaw I. Q., Tomie J. A. Cholinergic receptor blockade produces impairments in a sensorimotor subsystem for place navigation in the rat: evidence from sensory, motor, and acquisition tests in a swimming pool. Behav Neurosci. 1987 Oct;101(5):603–616. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.101.5.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe J. H., Deshmane S. L., Fraser N. W. Herpesvirus vector gene transfer and expression of beta-glucuronidase in the central nervous system of MPS VII mice. Nat Genet. 1992 Aug;1(5):379–384. doi: 10.1038/ng0892-379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe J. H., Sands M. S., Barker J. E., Gwynn B., Rowe L. B., Vogler C. A., Birkenmeier E. H. Reversal of pathology in murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII by somatic cell gene transfer. Nature. 1992 Dec 24;360(6406):749–753. doi: 10.1038/360749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]