Abstract
We provide an overview of the Kaiser Permanente Community Health Initiative—created in 2003 to promote obesity-prevention policy and environmental change in communities served by Kaiser Permanente—and describe the design for evaluating the initiative. The Initiative focuses on 3 ethnically diverse northern California communities that range in size from 37 000 to 52 000 residents. The evaluation assesses impact by measuring intermediate outcomes and conducting pre- and posttracking of population-level measures of physical activity, nutrition, and overweight.
The focus of public health practitioners on policy and environmental change in obesity- prevention efforts1–6 has led to the development of comprehensive community initiatives designed to produce a sustained effort by a broad range of community stakeholders.7,8 However, there are few credible studies demonstrating that comprehensive community initiatives are effective in lowering obesity rates,9,10 and therefore, evaluation of these initiatives is critical. This article gives an overview and describes the evaluation design of one such initiative—Kaiser Permanente's Community Health Initiative (CHI), created in 2003 to promote obesity-prevention policy and environmental change in communities served by Kaiser Permanente.
The core CHI principles encompass a place-based focus; an emphasis on interventions involving policy and environmental change; collaboratives with representatives of sectors such as health care, neighborhoods, schools, and work sites; community engagement and ownership; and systematic evaluation.11 Kaiser Permanente is sponsoring initiatives containing these elements in 30 sites. In this article, we concentrate on 3 northern California communities whose initiatives were implemented between 2005 and 2010.
METHODS
The northern California initiative (Healthy Eating, Active Living–Community Health Initiative or HEAL-CHI) is taking place in 3 largely ethnic minority communities with populations of between 37 000 and 52 000. The HEAL-CHI collaboratives convened a community-wide planning process that led to the adoption of community action plans providing a roadmap for interventions, such as implementing California's physical education and nutrition standards, constructing walking trails, increasing the availability of fresh produce, and working with city planning departments to incorporate health considerations (e.g., increasing walking) into general plans (Table 1).
TABLE 1.
Examples of Community Health Initiative Interventions: HEAL-CHI, Northern California, 2005–2010
| Category (Total No. of Strategies)a | Intervention Examples |
| Programs (n = 21) | Promote physical activities in after-school programs |
| Implement body mass index as a vital sign into well-visits and offer routine obesity counseling and referral | |
| Promote parents' and students' community awareness regarding healthy eating and active living at the targeted schools | |
| Organizational change (n = 23) | Implement California standards-based physical activity curriculum during school hours in local elementary schools |
| Implement breastfeeding policy in local clinics and educate patients and employees on the value of breastfeeding | |
| Work with employers to adopt and implement worksite wellness policies to promote physical activity among employees | |
| Environmental change (n = 10) | Install a lighted walking trail along canal banks to provide access to safe physical activity |
| Participate in Safe Routes to School Project to increase physical activity options in their neighborhoods | |
| Increase purchase or distribution points for fresh fruits and vegetables in the community | |
| Public policy (n = 2) | Work with city and county code enforcement to enforce existing laws and ordinances that govern the sale of alcohol to decrease the public nuisance associated with liquor stores |
| Affect the urban planning via the city general plans and explore other smart growth opportunities | |
| Community capacity building (n = 15) | Mobilize residents to create an ongoing grassroots effort to advocate for healthy eating and physical activity options in their neighborhoods |
| Build worksite sector leadership and infrastructure | |
| Recruit faith-based communities into the HEAL collaborative |
Note. HEAL-CHI = Healthy Eating, Active Living–Community Health Initiative.
Total number across all 3 communities = 71
The CHI evaluation uses a logic model approach to assessing impact that combines indicators of intermediate outcomes (e.g., environmental and policy changes) with more conventional pre- and posttracking of population-level measures of physical activity, nutrition, and overweight (e.g., via surveys). In assessing impact, the evaluators track intervention strategies using the Documentation of Community Change, a database that includes implementation status and the number or people reached by each strategy.
Two types of “reach” are being tracked for each intervention strategy: (1) the number exposed, which required estimating the number of people who potentially might encounter an environmental change on a regular basis, such as the number of people who live in a neighborhood being redeveloped to be more walkable, and (2) the number affected, i.e., an estimate of the number of people affected in a “significant” way by a program or environmental change. “Significant” is an approximation to “clinical significance” used in the medical literature, i.e., an effect large enough to see clinically measureable changes in health.12
Population-level change for adults is tracked through an automated telephone survey and, for youths, through a school-based survey and a statewide fitness test. The phone survey is being conducted among a random sample of adults identified through reverse telephone directories; the youth survey is being administered in a sample of schools within the target neighborhoods. Survey questions for both surveys are drawn from standard instruments whenever possible; for example the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System.13 The evaluation uses Kaiser Permanente clinical data to provide additional information, particularly for overweight and outcomes such as diabetes and hypertension. The results from the CHI communities will be compared with trends from state and national surveys, and, for the youth surveys and KP member data, with control communities.
RESULTS
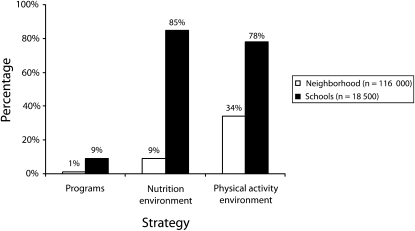
Figure 1 provides illustrative data on exposed reach: the percentage of neighborhood residents and school children potentially affected if 3 kinds of interventions were implemented successfully. In the school sector, for example, each community is working to implement districtwide healthy eating policies around vending machines and cafeteria food. The potential number of children exposed is significant: 85% across all 3 communities. In the neighborhood sector, the highest exposed reach is in the physical activity environment, where changes in the built environment—including street improvements to encourage walking, new parks, and bike trails—have the potential to reach 34% of the population.
FIGURE 1.
Kaiser Permanente's Community Health Initiative potential intervention penetration: HEAL-CHI, northern California, 2005–2010.
Note. HEAL-CHI = Healthy Eating, Active Living–Community Health Initiative. The figures shown are based on potential reach of the interventions, i.e., if all initiatives are implemented as planned. Currently, only a small number of the environmental interventions have been successfully implemented.
DISCUSSION
Our principal evaluation challenge has been the same one faced by other evaluators of comprehensive community initiatives: assessing the longer-term, population-level impact of the initiative.14,15 Population-level surveys, which are typically used to measure healthy eating and active living outcomes, are expensive16 and it is difficult to obtain response rates representative of an entire community.17,18 Moreover, measuring impact is challenging because interventions are typically small in relation to the array of factors that shape physical activity and diet.14,15 Our use of intermediate outcomes is in response to these challenges.
Despite the challenges, we believe that our multimethod approach to evaluating CHI is meeting the evaluation goals. The Documentation of Community Change system is providing rich qualitative and quantitative information and should provide a reasonably complete picture of the community changes brought about by CHI.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge and thank Kaiser Permanente for their financial support.
Human Participant Protection
The research was approved by the institutional review boards of Kaiser Permanente, Group Health Cooperative, and the University of California, Berkeley.
References
- 1.Doyle S, Kelly-Schwartz A, Schlossberg M, Stockard J. Active community environments and health: the relationship of walkable and safe communities to individual health. J Am Plann Assoc. 2006;72(1):19–31 [Google Scholar]
- 2.Glanz K, Hoelscher D. Increasing fruit and vegetable intake by changing environments, policy, and pricing: restaurant-based research, strategies, and recommendations. Prev Med. 2004;39(Suppl 2):88–93 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lake A, Townshend T. Obesogenic environments: exploring the built and food environments. J R Soc Promot Health. 2006;126(6):262–267 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Powell LM, Slater S, Mirtcheva D, Bao YJ, Chaloupka FJ. Food store availability and neighborhood characteristics in the United States. Prev Med. 2007;44(3):189–195 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sallis JF, Cervero RB, Ascher W, Henderson KA, Kraft MK, Kerr J. An ecological approach to creating active living communities. Annu Rev Public Health. 2006;27:297–322 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sallis JF, Glanz K. The role of built environments in physical activity, eating, and obesity in childhood. Future Child. 2006;16(1):89–108 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.WK Kellogg Foundation Food and Fitness Initiative Web site. Available at: http://www.wkkf.org/default.aspx?tabid=75&CID=383&NID=61&LanguageID=0. Accessed September 10, 2009.
- 8.Robert Wood Johnson Health Kids/Healthy Communities Initiative Web site. Available at: http://www.rwjf.org/childhoodobesity. Accessed September 10, 2009.
- 9.Economos CD, Hyatt RR, Goldberg JP, et al. A community intervention reduces BMI z-score in children: Shape Up Somerville first year results. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2007;15(5):1325–1336 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Institute of Medicine Bridging the Evidence Gap in Obesity Prevention: A Framework to Inform Decision Making. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2010 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kaiser Foundation Health Plans Kaiser Permanente's Framework for Community Health Initiatives Web site. September 2004. Available at: http://info.kp.org/communitybenefit/pdfs/CHIFramework.pdf. Accessed May1, 2008
- 12.Cheadle A, Samuels S, Rauzon S, et al. Approaches to measuring environmental change in community-level obesity prevention initiatives. Am J Public Health. 2010;100(11):2129–2136 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Survey Data. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2007 [Google Scholar]
- 14.Koepsell TD, Wagner EH, Cheadle AC, et al. Selected methodological issues in evaluating community-based health promotion and disease prevention programs. Annu Rev Public Health. 1992;13:31–57 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Merzel C, D'Afflitti JD. Reconsidering community-based health promotion: promise, performance, and potential. Am J Public Health. 2003;93(4):557–574 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Atienza AA, King AC. Community-based intervention trials: an overview of methodological issues. Epidemiol Rev. 2002;24(1):72–79 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Curtin R, Presser S, Singer E. Changes in telephone survey nonresponse over the past quarter century. Public Opinion Quarterly. 2005;69(1):87–98 [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bunin GR, Spector LG, Olshan AF, et al. Secular trends in response rates for controls selected by random digit dialing in childhood cancer studies: a report from the Children's Oncology Group. Am J Epidemiol. 2007;166(1)109–116 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]