Abstract
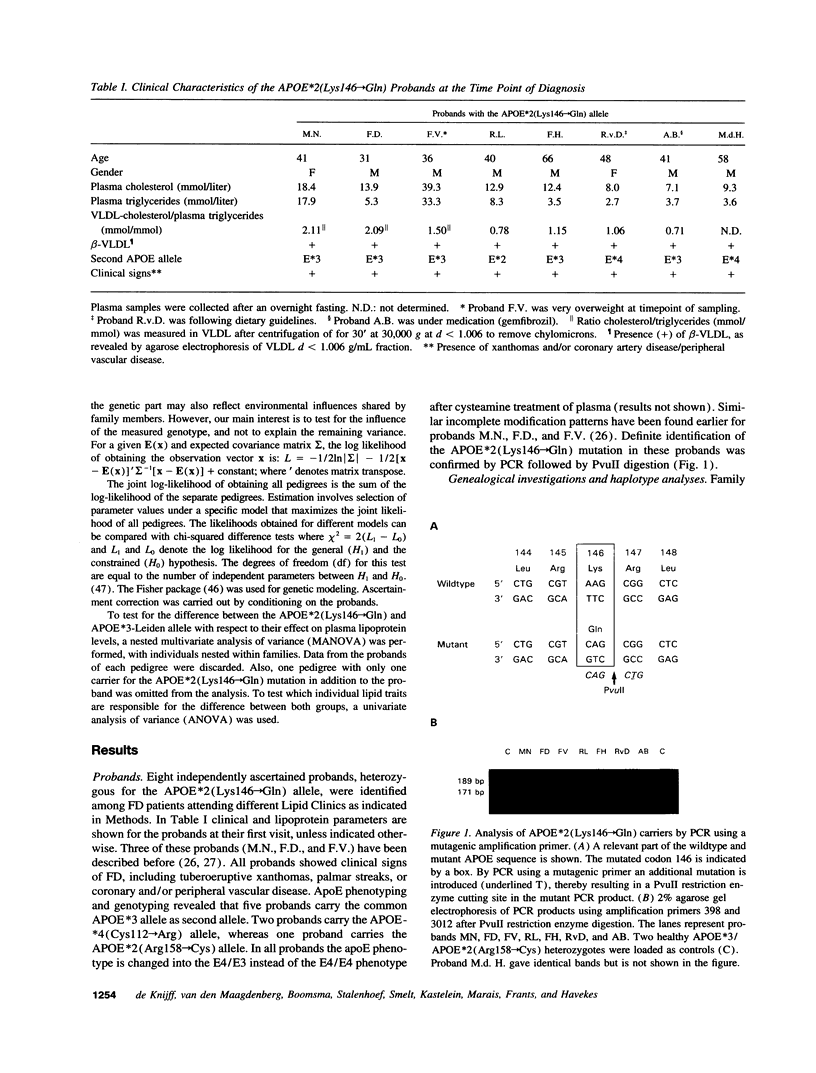
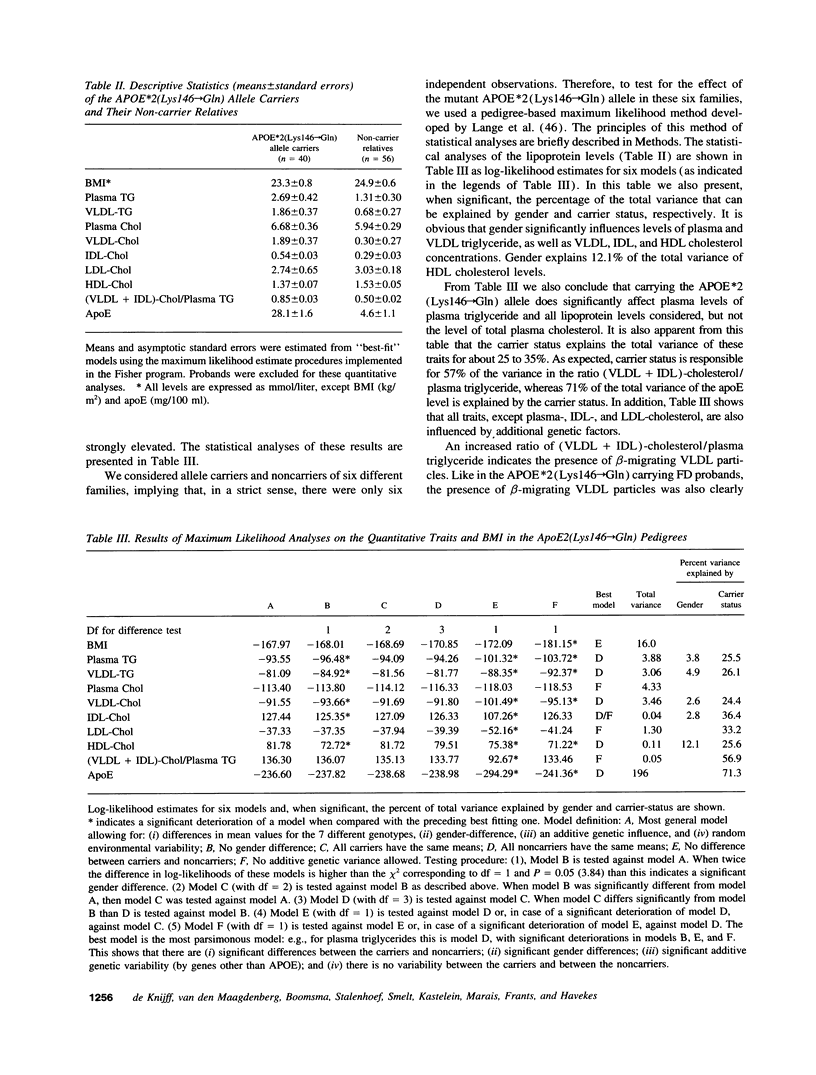
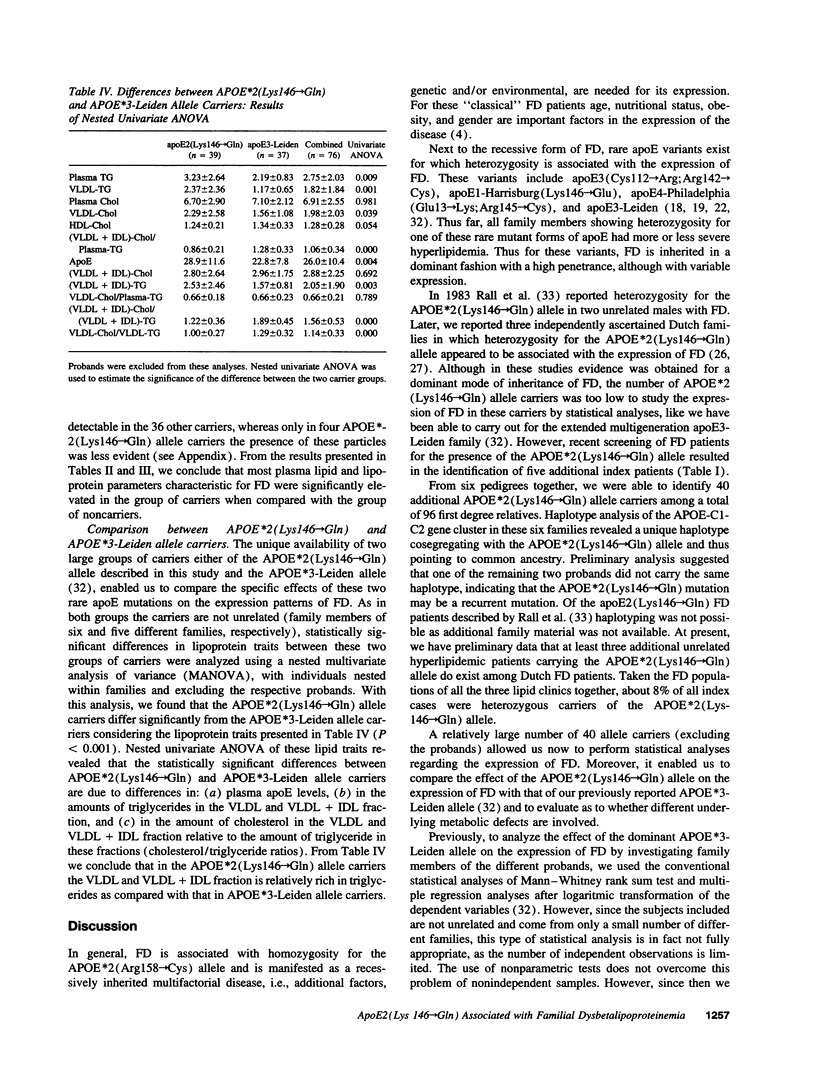
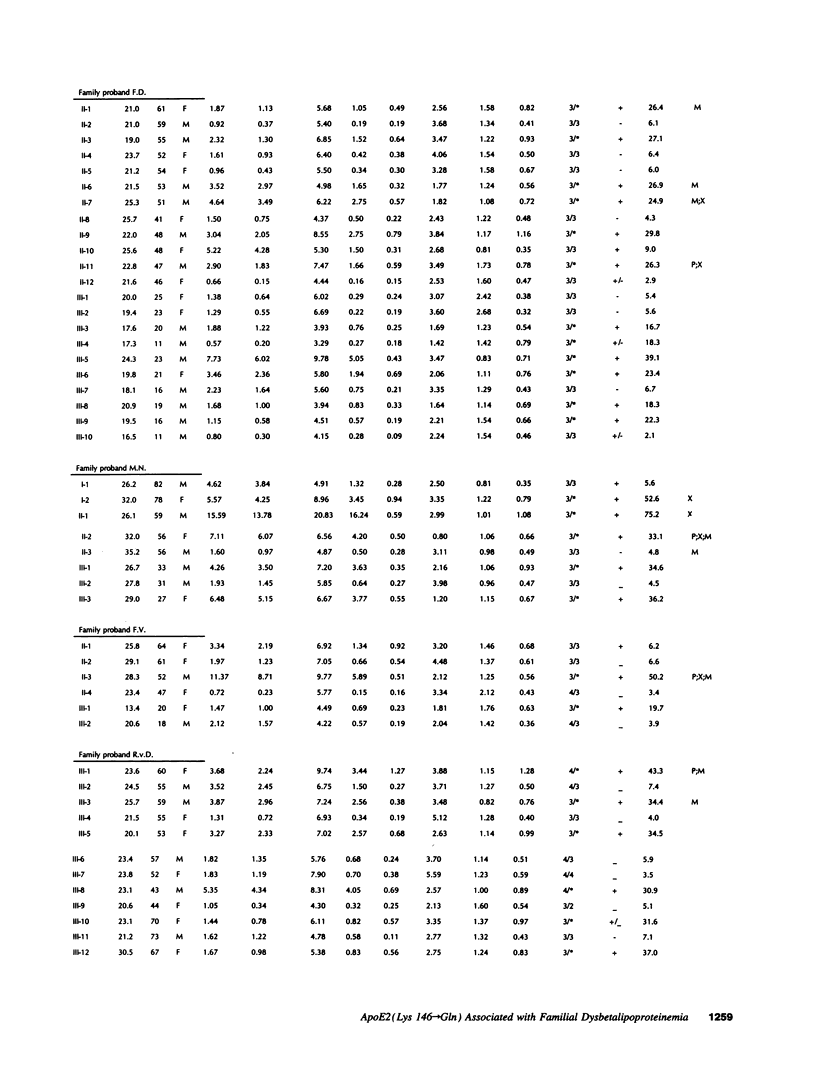
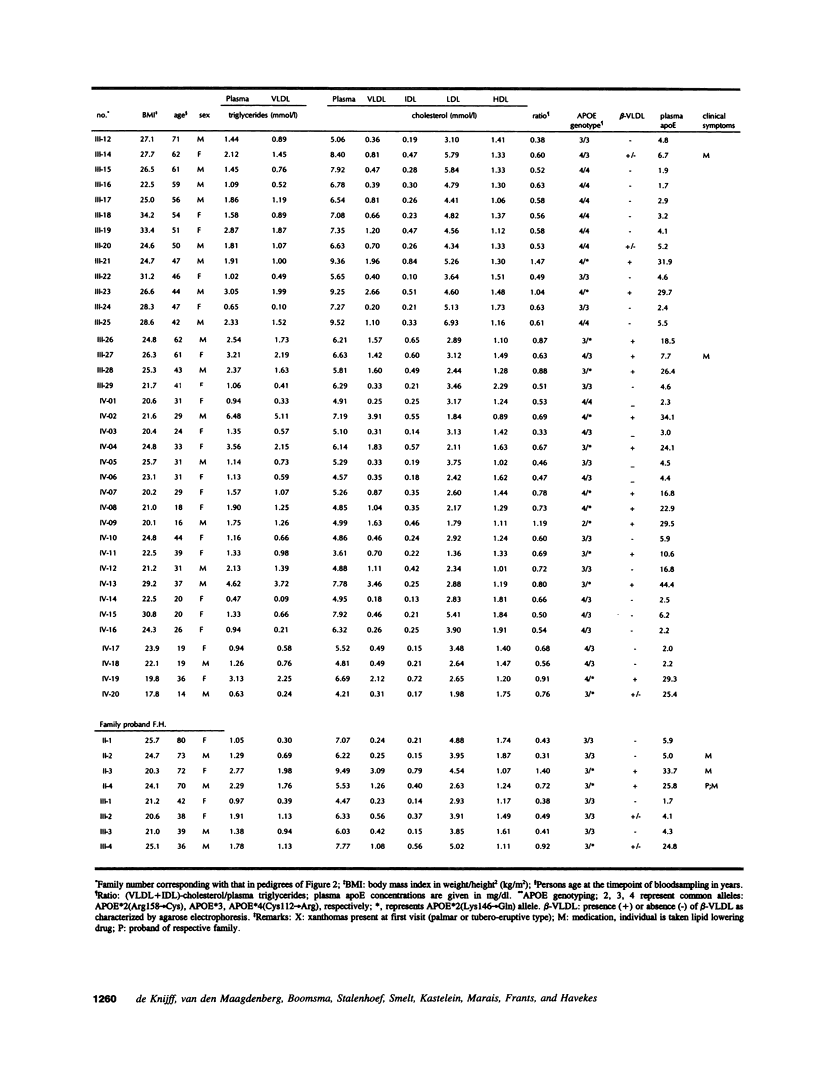
Genetic and biochemical studies were carried out in 96 relatives of six independently ascertained probands with familial dysbetalipoproteinemia (FD) carrying the APOE*2 (Lys146-->Gln) allele. Compared to noncarriers, the 40 heterozygous APOE*2 (Lys146-->Gln) allele carriers exhibited markedly increased mean levels of cholesterol and triglyceride in the very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) (1.89 +/- 0.37 vs 0.30 +/- 0.27 and 1.86 +/- 0.37 vs 0.68 +/- 0.27 mmol/liter, respectively) and plasma apolipoprotein (apo) E levels (28.1 +/- 1.6 vs 4.6 +/- 1.1 mg/dl), which is characteristic for FD. By means of a pedigree-based maximum likelihood method we calculated that carrier-status accounted for 57% and 71%, respectively, of the total variance of the ratio (VLDL + IDL)-cholesterol/plasma triglyceride and plasma apoE levels. APOE*2 (Lys146-->Gln) and APOE*3-Leiden allele carriers were found to differ significantly in: (a) plasma apoE levels, (b) in the amounts of triglycerides in the VLDL and VLDL + IDL fraction, and (c) in the amount of cholesterol in the VLDL and VLDL + IDL fraction relative to the amount of triglyceride in these fractions. In the APOE*2 (Lys146-->Gln) allele carriers the VLDL and VLDL + IDL fraction is relatively rich in triglycerides as compared with that in APOE*3-Leiden carriers. We hypothesize that these two rare mutations of apoE both lead to dominantly inherited forms of FD along different underlying metabolic defects.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Demacker P. N., Vos-Janssen H. E., van 't Laar A., Jansen A. P. A descriptive study of the different electrophoretic patterns on agarose of human serum very-low-density lipoproteins. Clin Chem. 1978 Sep;24(9):1439–1444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emi M., Wu L. L., Robertson M. A., Myers R. L., Hegele R. A., Williams R. R., White R., Lalouel J. M. Genotyping and sequence analysis of apolipoprotein E isoforms. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):373–379. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazio S., Horie Y., Weisgraber K. H., Havekes L. M., Rall S. C., Jr Preferential association of apolipoprotein E Leiden with very low density lipoproteins of human plasma. J Lipid Res. 1993 Mar;34(3):447–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornage M., Chan L., Siest G., Boerwinkle E. Allele frequency distribution of the (TG)n(AG)m microsatellite in the apolipoprotein C-II gene. Genomics. 1992 Jan;12(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90407-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frossard P. M., Coleman R. T., Malloy M. J., Kane J. P., Levy-Wilson B., Appleby V. A. Human apolipoprotein CI (apoC1) gene locus: DraI dimorphic site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1884–1884. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havekes L. M., Gevers Leuven J. A., van Corven E., de Wit E., Emeis J. J. Functionally inactive apolipoprotein E3 in a type III hyperlipoproteinaemic patient. Eur J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;14(1):7–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1984.tb00696.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havekes L., de Wit E., Leuven J. G., Klasen E., Utermann G., Weber W., Beisiegel U. Apolipoprotein E3-Leiden. A new variant of human apolipoprotein E associated with familial type III hyperlipoproteinemia. Hum Genet. 1986 Jun;73(2):157–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00291607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Chao Y., Windler E. E., Kotite L., Guo L. S. Isoprotein specificity in the hepatic uptake of apolipoprotein E and the pathogenesis of familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4349–4353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kotite L., Kane J. P., Tun P., Bersot T. Atypical familial dysbetalipoproteinemia associated with apolipoprotein phenotype E3/3. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):379–387. doi: 10.1172/JCI110978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixson J. E., Vernier D. T. Restriction isotyping of human apolipoprotein E by gene amplification and cleavage with HhaI. J Lipid Res. 1990 Mar;31(3):545–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horie Y., Fazio S., Westerlund J. R., Weisgraber K. H., Rall S. C., Jr The functional characteristics of a human apolipoprotein E variant (cysteine at residue 142) may explain its association with dominant expression of type III hyperlipoproteinemia. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1962–1968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Friedlander E. J., Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. The receptor-binding domain of human apolipoprotein E. Binding of apolipoprotein E fragments. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12341–12347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalazar A., Mahley R. W. Human apolipoprotein E. Receptor binding activity of truncated variants with carboxyl-terminal deletions. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8447–8450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalazar A., Weisgraber K. H., Rall S. C., Jr, Giladi H., Innerarity T. L., Levanon A. Z., Boyles J. K., Amit B., Gorecki M., Mahley R. W. Site-specific mutagenesis of human apolipoprotein E. Receptor binding activity of variants with single amino acid substitutions. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3542–3545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K., Weeks D., Boehnke M. Programs for Pedigree Analysis: MENDEL, FISHER, and dGENE. Genet Epidemiol. 1988;5(6):471–472. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370050611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K., Westlake J., Spence M. A. Extensions to pedigree analysis. III. Variance components by the scoring method. Ann Hum Genet. 1976 May;39(4):485–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1976.tb00156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse P., Mann W. A., Stein E. A., Brewer H. B., Jr Apolipoprotein E-4Philadelphia (Glu13----Lys,Arg145----Cys). Homozygosity for two rare point mutations in the apolipoprotein E gene combined with severe type III hyperlipoproteinemia. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10479–10484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse P., Rader D. J., Brewer H. B., Jr Heterozygosity for apolipoprotein E-4Philadelphia(Glu13----Lys, Arg145----Cys) is associated with incomplete dominance of type III hyperlipoproteinemia. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13642–13646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes-Virella M. F., Stone P., Ellis S., Colwell J. A. Cholesterol determination in high-density lipoproteins separated by three different methods. Clin Chem. 1977 May;23(5):882–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie A. E., MacLeod H. L., Leblond S. C., Monteith N., Lahey D., Korneluk R. G. DNA polymorphism and linkage disequilibrium within the apolipoprotein CII locus on human chromosome 19. Hum Hered. 1991;41(3):188–194. doi: 10.1159/000153999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Angelin B. Type III hyperlipoproteinemia: recent insights into the genetic defect of familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. Adv Intern Med. 1984;29:385–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann W. A., Gregg R. E., Sprecher D. L., Brewer H. B., Jr Apolipoprotein E-1Harrisburg: a new variant of apolipoprotein E dominantly associated with type III hyperlipoproteinemia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Oct 17;1005(3):239–244. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90043-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama K., Sasaki J., Matsunaga A., Arakawa F., Takada Y., Araki K., Kaneko S., Arakawa K. Apolipoprotein E1 Lys-146----Glu with type III hyperlipoproteinemia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Sep 22;1128(1):58–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90257-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nillesen W. M., Smeets H. J., van Oost B. A. Human ApoCI HpaI restriction site polymorphism revealed by the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3428–3428. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3428-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paik Y. K., Chang D. J., Reardon C. A., Davies G. E., Mahley R. W., Taylor J. M. Nucleotide sequence and structure of the human apolipoprotein E gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3445–3449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Bersot T. P., Mahley R. W., Blum C. B. Identification of a new structural variant of human apolipoprotein E, E2(Lys146 leads to Gln), in a type III hyperlipoproteinemic subject with the E3/2 phenotype. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1288–1297. doi: 10.1172/JCI111085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Structural basis for receptor binding heterogeneity of apolipoprotein E from type III hyperlipoproteinemic subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4696–4700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Structural basis for receptor binding heterogeneity of apolipoprotein E from type III hyperlipoproteinemic subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4696–4700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. Human apolipoprotein E. The complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4171–4178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrill B. C., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Rapid hepatic clearance of the canine lipoproteins containing only the E apoprotein by a high affinity receptor. Identity with the chylomicron remnant transport process. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1804–1807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit M., de Knijff P., Frants R. R., Klasen E. C., Havekes L. M. Familial dysbetalipoproteinemic subjects with the E3/E2 phenotype exhibit an E2 isoform with only one cysteine residue. Clin Genet. 1987 Nov;32(5):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1987.tb03298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit M., de Knijff P., van der Kooij-Meijs E., Groenendijk C., van den Maagdenberg A. M., Gevers Leuven J. A., Stalenhoef A. F., Stuyt P. M., Frants R. R., Havekes L. M. Genetic heterogeneity in familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. The E2(lys146----gln) variant results in a dominant mode of inheritance. J Lipid Res. 1990 Jan;31(1):45–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit M., van der Kooij-Meijs E., Frants R. R., Havekes L., Klasen E. C. Apolipoprotein gene cluster on chromosome 19. Definite localization of the APOC2 gene and the polymorphic Hpa I site associated with type III hyperlipoproteinemia. Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;78(1):90–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00291243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit M., van der Kooij-Meijs E., Woudt L. P., Havekes L. M., Frants R. R. Exact localization of the familial dysbetalipoproteinemia associated HpaI restriction site in the promoter region of the APOC1 gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):1282–1288. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80424-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalenhoef A. F., Malloy M. J., Kane J. P., Havel R. J. Metabolism of apolipoproteins B-48 and B-100 of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in patients with familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):722–728. doi: 10.1172/JCI112632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Hees M., Steinmetz A. Polymorphism of apolipoprotein E and occurrence of dysbetalipoproteinaemia in man. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):604–607. doi: 10.1038/269604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Jaeschke M., Menzel J. Familial hyperlipoproteinemia type III: deficiency of a specific apolipoprotein (apo E-III) in the very-low-density lipoproteins. FEBS Lett. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):352–355. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Vogelberg K. H., Steinmetz A., Schoenborn W., Pruin N., Jaeschke M., Hees M., Canzler H. Polymorphism of apolipoprotein E. II. Genetics of hyperlipoproteinemia type III. Clin Genet. 1979 Jan;15(1):37–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardell M. R., Brennan S. O., Janus E. D., Fraser R., Carrell R. W. Apolipoprotein E2-Christchurch (136 Arg----Ser). New variant of human apolipoprotein E in a patient with type III hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):483–490. doi: 10.1172/JCI113096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardell M. R., Weisgraber K. H., Havekes L. M., Rall S. C., Jr Apolipoprotein E3-Leiden contains a seven-amino acid insertion that is a tandem repeat of residues 121-127. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21205–21210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Harder K. J., Mahley R. W., Milne R. W., Marcel Y. L., Sparrow J. T. The receptor-binding domain of human apolipoprotein E. Monoclonal antibody inhibition of binding. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12348–12354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Rall S. C., Jr, Mahley R. W. Human E apoprotein heterogeneity. Cysteine-arginine interchanges in the amino acid sequence of the apo-E isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9077–9083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Just P. W., Breslow J. L. Human apolipoprotein E isoprotein subclasses are genetically determined. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 Jan;33(1):11–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Knijff P., van den Maagdenberg A. M., Stalenhoef A. F., Leuven J. A., Demacker P. N., Kuyt L. P., Frants R. R., Havekes L. M. Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia associated with apolipoprotein E3-Leiden in an extended multigeneration pedigree. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):643–655. doi: 10.1172/JCI115349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Maagdenberg A. M., de Knijff P., Stalenhoef A. F., Gevers Leuven J. A., Havekes L. M., Frants R. R. Apolipoprotein E*3-Leiden allele results from a partial gene duplication in exon 4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 15;165(2):851–857. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




