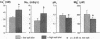Abstract
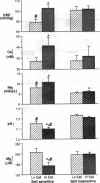
To study the ionic basis of salt sensitivity in hypertension, 19F-, 13P-, and 23Na-nuclear magnetic resonance techniques were used to measure cytosolic free calcium (Cai), pH (pHi), free magnesium (Mgi), and sodium (Nai) in erythrocytes of essential hypertensive subjects (n = 19). Individuals were studied for 2 mo each on low- (UNaV < 50 meq/d) and high- (UNaV > 200 meq/d) salt diets, with the concomitant administration of nifedipine (10 mg t.i.d.) or placebo tablets for 1 mo of each diet. Salt loading elevated Cai and Nai while suppressing Mgi and pHi; these changes occurred predominantly in salt-sensitive subjects (n = 9). Nifedipine blunted the pressor response to salt loading > 50% (delta diastolic BP [high-low salt vs placebo] = 5 +/- 2 vs 14 +/- 2 mmHg, P < 0.05) and reversed salt-induced ionic changes, lowering Cai and elevating Mgi and pHi. Regardless of the definition of salt sensitivity, continuous relationships were observed between the pressure response to salt loading, the levels of Cai (r = 0.726, P < 0.001), Nai (r = 0.747, P < 0.001), and pHi (r = -0.754, P < 0.001), and the salt-induced change in Mgi (r = -0.757, P < 0.001). Altogether, these results emphasize the reciprocal and coordinate nature of intracellular ionic changes in response to dietary salt loading and calcium channel blockade in essential hypertension. They suggest that salt sensitivity is mediated by cellular calcium accumulation from the extracellular space, in association with magnesium depletion and acidification. Lastly, interpretation of intracellular ion measurements in the future will require concurrent assessment of dietary salt intake.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altura B. M., Altura B. T., Gebrewold A., Ising H., Günther T. Magnesium deficiency and hypertension: correlation between magnesium-deficient diets and microcirculatory changes in situ. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1315–1317. doi: 10.1126/science.6701524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altura B. M., Altura B. T. Magnesium ions and contraction of vascular smooth muscles: relationship to some vascular diseases. Fed Proc. 1981 Oct;40(12):2672–2679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Leefmans F. J., Giraldez F., Gamiño S. M. Intracellular free magnesium in excitable cells: its measurement and its biologic significance. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1987 May;65(5):915–925. doi: 10.1139/y87-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batlle D. C., Saleh A., Rombola G. Reduced intracellular pH in lymphocytes from the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Hypertension. 1990 Jan;15(1):97–103. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.15.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batlle D. C., Sharma A. M., Alsheikha M. W., Sobrero M., Saleh A., Gutterman C. Renal acid excretion and intracellular pH in salt-sensitive genetic hypertension. J Clin Invest. 1993 May;91(5):2178–2184. doi: 10.1172/JCI116444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. Sodium ions, calcium ions, blood pressure regulation, and hypertension: a reassessment and a hypothesis. Am J Physiol. 1977 May;232(5):C165–C173. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1977.232.5.C165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campese V. M. Calcium, parathyroid hormone, and sympathoadrenal system. Am J Nephrol. 1986;6 (Suppl 1):29–32. doi: 10.1159/000167212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa M., Laski C., Falkner B. Red blood cell Na+ transport as a predictor of blood pressure response to Na+ load in young blacks and whites. Hypertension. 1990 Nov;16(5):508–514. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.16.5.508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erne P., Bolli P., Bürgisser E., Bühler F. R. Correlation of platelet calcium with blood pressure. Effect of antihypertensive therapy. N Engl J Med. 1984 Apr 26;310(17):1084–1088. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198404263101705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golowasch J., Kirkwood A., Miller C. Allosteric effects of Mg2+ on the gating of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from mammalian skeletal muscle. J Exp Biol. 1986 Sep;124:5–13. doi: 10.1242/jeb.124.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. K., Benovic J. L., Rose Z. B. The determination of the free magnesium level in the human red blood cell by 31P NMR. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6172–6176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. K., Gupta P., Moore R. D. NMR studies of intracellular metal ions in intact cells and tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1984;13:221–246. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.13.060184.001253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. E., Hungerford S. Prevention of DOCA-salt hypertension with the calcium blocker nitrendipine. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1983;5(5):721–728. doi: 10.3109/10641968309081803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iriuchijima J. Effect of calcium antagonist, nifedipine, on blood pressure of various hypertensive rats. Hiroshima J Med Sci. 1980 Mar;29(1):15–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelicks L. A., Weaver J., Pollack S., Gupta R. K. NMR studies of intracellular free calcium, free magnesium and sodium in the guinea pig reticulocyte and mature red cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Aug 15;1012(3):261–266. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90106-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kainouchi M., Matsuura H., Shingu T., Inoue I., Ishida T., Ozono R., Fujii T., Yuasa A., Oshima T., Kajiyama G. Time-course of changes in intracellular cations and blood pressure with salt loading in patients with essential hypertension. J Hypertens Suppl. 1991 Dec;9(6):S302–S303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama H., Ito Y., Suzuki H., Kitamura K., Itoh T. Factors modifying contraction-relaxation cycle in vascular smooth muscles. Am J Physiol. 1982 Nov;243(5):H641–H662. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1982.243.5.H641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L., Tsien R. Y., Miner C., Bookchin R. M. Physiological [Ca2+]i level and pump-leak turnover in intact red cells measured using an incorporated Ca chelator. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):478–481. doi: 10.1038/298478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewanczuk R. Z., Resnick L. M., Blumenfeld J. D., Laragh J. H., Pang P. K. A new circulating hypertensive factor in the plasma of essential hypertensive subjects. J Hypertens. 1990 Feb;8(2):105–108. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199002000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon R. B., Richards J. H. Determination of intracellular pH by 31P magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7276–7278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E., Berkowitz L. R., Orringer E., Levy L., Gabel S. A., London R. E. Cytosolic free calcium levels in sickle red blood cells. Blood. 1987 May;69(5):1469–1474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E., Levy L., Berkowitz L. R., Orringer E. P., Gabel S. A., London R. E. Nuclear magnetic resonance measurement of cytosolic free calcium levels in human red blood cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):C496–C504. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.4.C496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson J. P., Resnick L. M., Cigarroa J., Marion D., Vaughan E. D., Jr, Laragh J. H. The pressor effect of sodium-volume expansion is calcium mediated. Am J Hypertens. 1991 Nov;4(11):904–908. doi: 10.1093/ajh/4.11.904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima T., Matsuura H., Matsumoto K., Kido K., Kajiyama G. Role of cellular calcium in salt sensitivity of patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension. 1988 Jun;11(6 Pt 2):703–707. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.11.6.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima T., Young E. W., Hermsmeyer K., McCarron D. A. Modification of platelet and lymphocyte calcium handling and blood pressure by dietary sodium and calcium in genetically hypertensive rats. J Lab Clin Med. 1992 Feb;119(2):151–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K. E., Jest P., Klitgaard N. A., Rokkedal Nielsen J., Johansen T. Effect of oral salt loading on blood pressure and lymphocyte sodium metabolism in borderline hypertension. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1986;714:81–85. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1986.tb08973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick L. M., Gupta R. K., Bhargava K. K., Gruenspan H., Alderman M. H., Laragh J. H. Cellular ions in hypertension, diabetes, and obesity. A nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic study. Hypertension. 1991 Jun;17(6 Pt 2):951–957. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.17.6.951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick L. M., Gupta R. K., Laragh J. H. Intracellular free magnesium in erythrocytes of essential hypertension: relation to blood pressure and serum divalent cations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6511–6515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick L. M., Gupta R. K., Sosa R. E., Corbett M. L., Laragh J. H. Intracellular pH in human and experimental hypertension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7663–7667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick L. M., Laragh J. H., Sealey J. E., Alderman M. H. Divalent cations in essential hypertension. Relations between serum ionized calcium, magnesium, and plasma renin activity. N Engl J Med. 1983 Oct 13;309(15):888–891. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198310133091504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick L. M., Nicholson J. P., Laragh J. H. Alterations in calcium metabolism mediate dietary salt sensitivity in essential hypertension. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1985;98:313–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick L. M., Nicholson J. P., Laragh J. H. Calcium, the renin-aldosterone system, and the hypotensive response to nifedipine. Hypertension. 1987 Sep;10(3):254–258. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.10.3.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick L. M., Nicholson J. P., Laragh J. H. The effects of calcium channel blockade on blood pressure and calcium metabolism. Am J Hypertens. 1989 Dec;2(12 Pt 1):927–930. doi: 10.1093/ajh/2.12.927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick L. M. Uniformity and diversity of calcium metabolism in hypertension. A conceptual framework. Am J Med. 1987 Jan 26;82(1B):16–26. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey J. E., Blumenfeld J. D., Bell G. M., Pecker M. S., Sommers S. C., Laragh J. H. On the renal basis for essential hypertension: nephron heterogeneity with discordant renin secretion and sodium excretion causing a hypertensive vasoconstriction-volume relationship. J Hypertens. 1988 Oct;6(10):763–777. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198811000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shingu T., Matsuura H., Kusaka M., Inoue I., Yuasa A., Shingu T., Ishida T., Kajiyama G. Significance of intracellular free calcium and magnesium and calcium-regulating hormones with sodium chloride loading in patients with essential hypertension. J Hypertens. 1991 Nov;9(11):1021–1028. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199111000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squire L. G., Petersen O. H. Modulation of Ca2+- and voltage-activated K+ channels by internal Mg2+ in salivary acinar cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 May 29;899(2):171–175. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90397-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trieschmann U., Isenberg G. Ca2+-activated K+ channels contribute to the resting potential of vascular myocytes. Ca2+-sensitivity is increased by intracellular Mg2+-ions. Pflugers Arch. 1989;414 (Suppl 1):S183–S184. doi: 10.1007/BF00582296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. D., Drakenberg T., Thulin E., Forsén S. Is the binding of magnesium (II) to calmodulin significant? An investigation by magnesium-25 nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 16;26(12):3635–3643. doi: 10.1021/bi00386a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turlapaty P. D., Altura B. M. Extracellular magnesium ions control calcium exchange and content of vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Dec 1;52(3-4):421–423. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90303-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Törnquist K., Tashjian A. H., Jr pH homeostasis in pituitary GH4C1 cells: basal intracellular pH is regulated by cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration. Endocrinology. 1992 Feb;130(2):717–725. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.2.1733720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan-Jones R. D., Lederer W. J., Eisner D. A. Ca2+ ions can affect intracellular pH in mammalian cardiac muscle. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):522–524. doi: 10.1038/301522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawada E. T., Jr, Johnson M. Calcium chelation and calcium-channel blockade in anesthetized acute renovascular hypertensive dogs. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1984;10(6):366–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemel M. B., Kraniak J., Standley P. R., Sowers J. R. Erythrocyte cation metabolism in salt-sensitive hypertensive blacks as affected by dietary sodium and calcium. Am J Hypertens. 1988 Oct;1(4 Pt 1):386–392. doi: 10.1093/ajh/1.4.386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wardener H. E., MacGregor G. A. Dahl's hypothesis that a saluretic substance may be responsible for a sustained rise in arterial pressure: its possible role in essential hypertension. Kidney Int. 1980 Jul;18(1):1–9. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]