Abstract
The human insulin receptor has two isoforms derived from alternative splicing of exon 11 of the insulin receptor gene. The type B (containing exon 11, or exon 11+) isoform binds insulin with twofold lower affinity than the type A (lacking exon 11, or exon 11-) isoform. In efforts to resolve the controversy over whether altered splicing is involved in the development of insulin resistance and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM), the spontaneously obese diabetic rhesus monkey, a unique model that is extraordinarily similar to human NIDDM, was used. Cross-sectional studies of insulin receptor mRNA splicing variants in vastus lateralis muscle were performed on 19 rhesus monkeys. When monkeys were divided into four groups based upon the known stages of progression to NIDDM: normal (normoglycemic/normoinsulinemic), prediabetic (normoglycemic/hyperinsulinemic), early NIDDM (hyperglycemic/hyperinsulinemic), and late NIDDM (hyperglycemic/hypoinsulinemic), both hyperinsulinemic groups had significantly higher percentages of the exon 11- mRNA splicing variant compared to the normal (74.8 +/- 1.7 vs 59.0 +/- 2.3%; P < 0.005) and late NIDDM groups (74.8 +/- 1.7 vs 64.2 +/- 3.9%; P < 0.05). Our findings provide the first direct evidence linking hyperinsulinemia to alterations in insulin receptor mRNA splicing, and suggest that alterations of insulin receptor mRNA splicing in muscle is an early molecular marker that may play an important role in NIDDM.
Full text
PDF

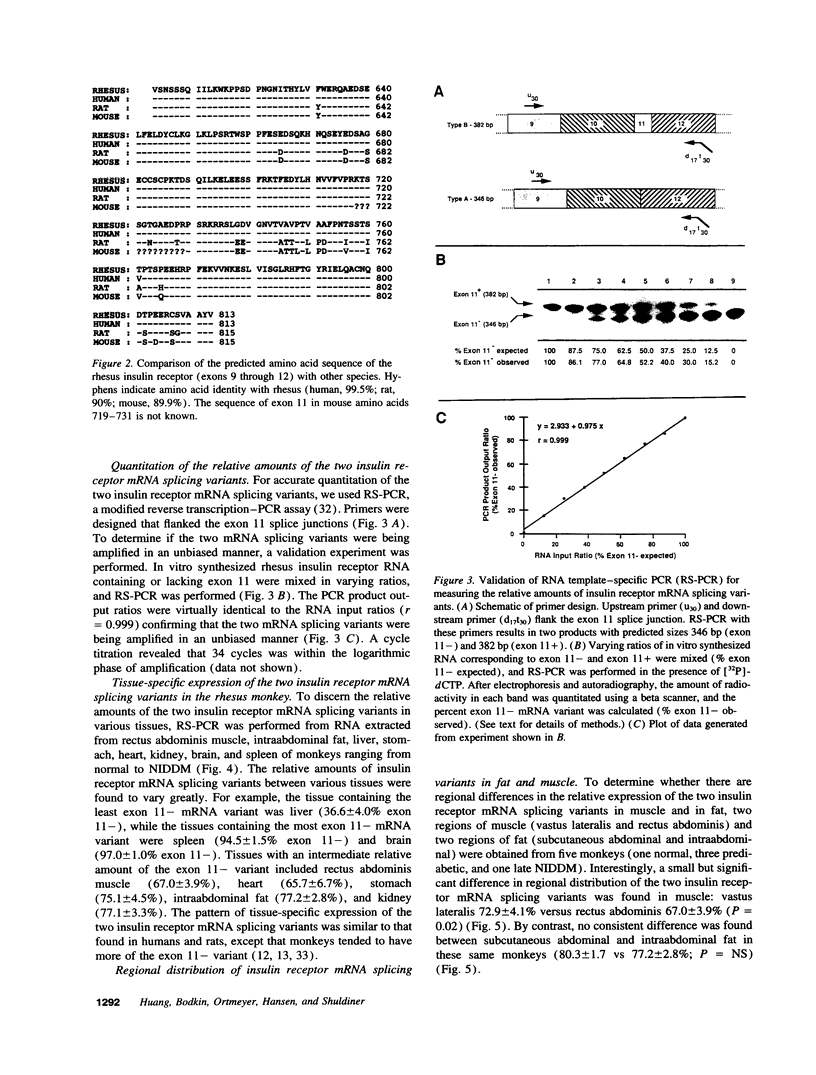
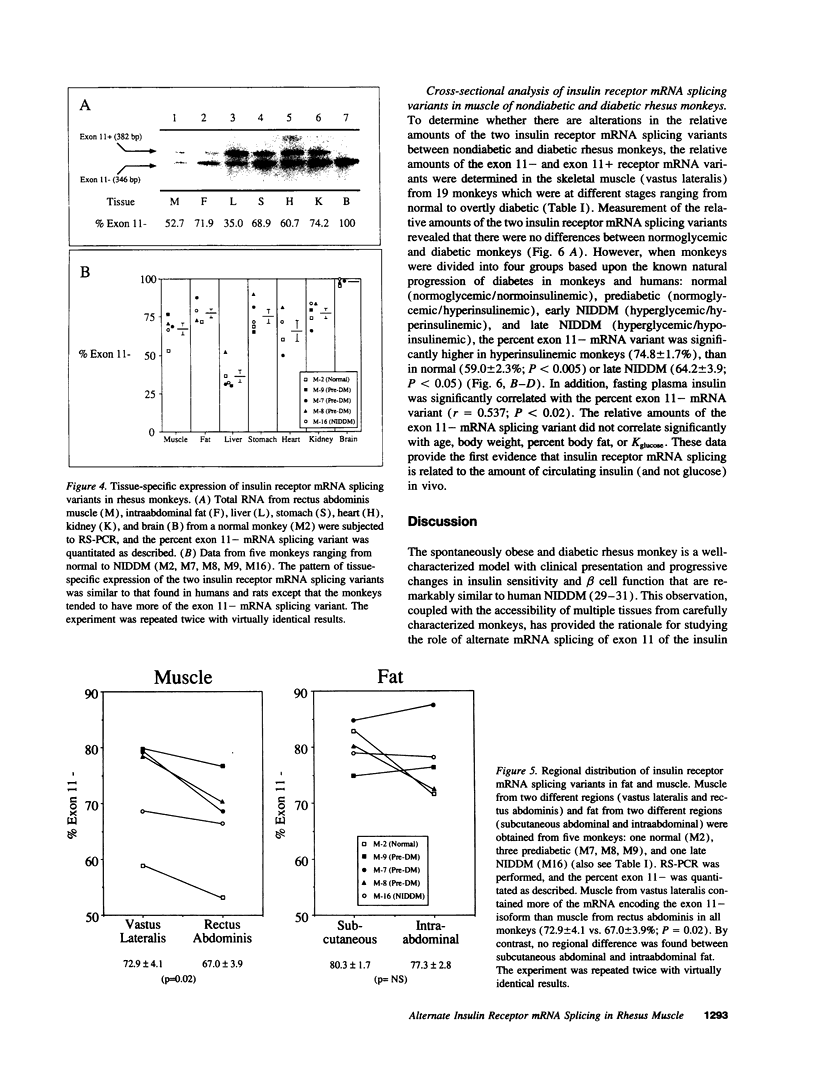
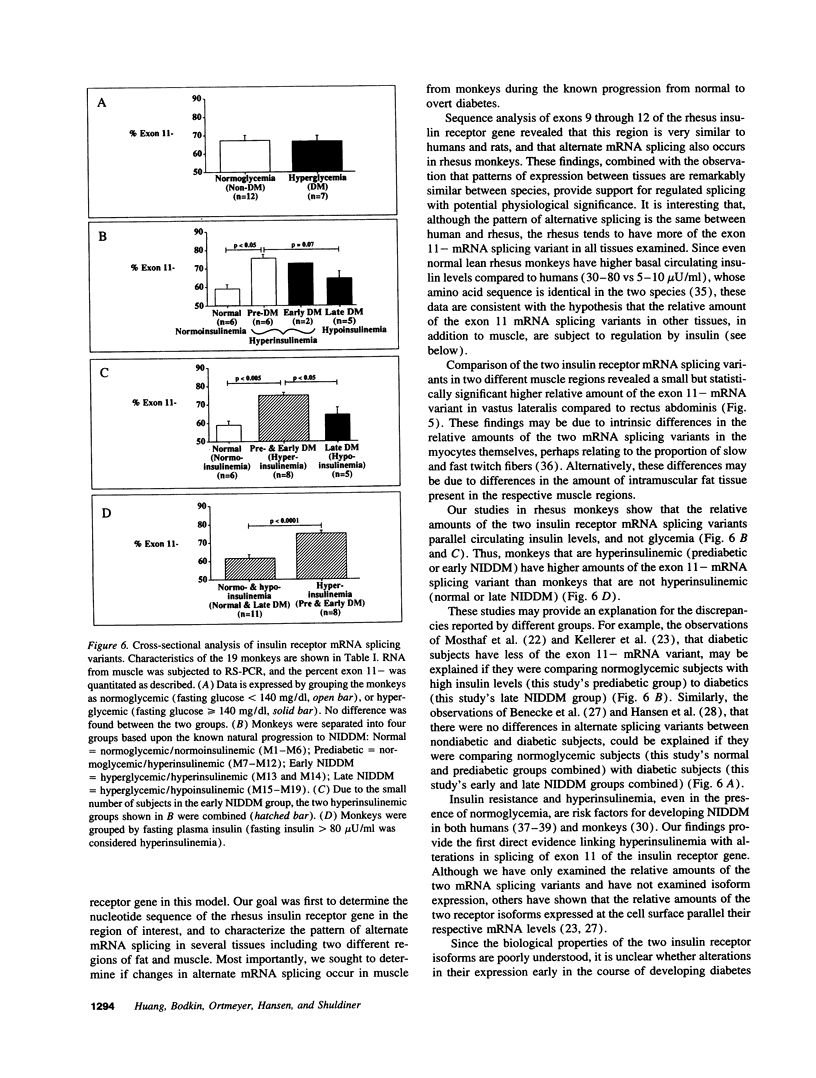


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benecke H., Flier J. S., Moller D. E. Alternatively spliced variants of the insulin receptor protein. Expression in normal and diabetic human tissues. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jun;89(6):2066–2070. doi: 10.1172/JCI115819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodkin N. L., Metzger B. L., Hansen B. C. Hepatic glucose production and insulin sensitivity preceding diabetes in monkeys. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 1):E676–E681. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.256.5.E676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. M., Vogt B., Ullrich A., Häring H. U. Activation of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase by insulin is mediated by both A and B human insulin receptor types. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 15;174(1):123–127. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90494-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J. E., Tavaré J. M., Ellis L., Roth R. A. Evidence for hybrid rodent and human insulin receptors in transfected cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15587–15590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Bonadonna R. C., Ferrannini E. Pathogenesis of NIDDM. A balanced overview. Diabetes Care. 1992 Mar;15(3):318–368. doi: 10.2337/diacare.15.3.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Riveros J. R., Sibley E., Kastelic T., Lane M. D. Substrate phosphorylation catalyzed by the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. Kinetic correlation to autophosphorylation of specific sites in the beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21557–21572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frattali A. L., Treadway J. L., Pessin J. E. Transmembrane signaling by the human insulin receptor kinase. Relationship between intramolecular beta subunit trans- and cis-autophosphorylation and substrate kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19521–19528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein B. J., Dudley A. L. The rat insulin receptor: primary structure and conservation of tissue-specific alternative messenger RNA splicing. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Feb;4(2):235–244. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-2-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granner D. K., O'Brien R. M. Molecular physiology and genetics of NIDDM. Importance of metabolic staging. Diabetes Care. 1992 Mar;15(3):369–395. doi: 10.2337/diacare.15.3.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffner S. M., Stern M. P., Mitchell B. D., Hazuda H. P., Patterson J. K. Incidence of type II diabetes in Mexican Americans predicted by fasting insulin and glucose levels, obesity, and body-fat distribution. Diabetes. 1990 Mar;39(3):283–288. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen B. C., Bodkin N. L. Beta-cell hyperresponsiveness: earliest event in development of diabetes in monkeys. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 2):R612–R617. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1990.259.3.R612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen T., Bjørbaek C., Vestergaard H., Grønskov K., Bak J. F., Pedersen O. Expression of insulin receptor spliced variants and their functional correlates in muscle from patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Dec;77(6):1500–1505. doi: 10.1210/jcem.77.6.8263133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häring H. U., Mehnert H. Pathogenesis of type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus: candidates for a signal transmitter defect causing insulin resistance of the skeletal muscle. Diabetologia. 1993 Mar;36(3):176–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00399946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. A., Polgar J., Weightman D., Appleton D. Data on the distribution of fibre types in thirty-six human muscles. An autopsy study. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Jan;18(1):111–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Miyake Y., Hagura R., Akanuma Y., Kajinuma H., Kuzuya N., Takaku F., Kosaka K. Risk factors for worsening to diabetes in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetologia. 1984 Jan;26(1):44–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00252262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Folli F. Molecular determinants of insulin action. Horm Res. 1993;39 (Suppl 3):93–101. doi: 10.1159/000182793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellerer M., Lammers R., Ermel B., Tippmer S., Vogt B., Obermaier-Kusser B., Ullrich A., Häring H. U. Distinct alpha-subunit structures of human insulin receptor A and B variants determine differences in tyrosine kinase activities. Biochemistry. 1992 May 19;31(19):4588–4596. doi: 10.1021/bi00134a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellerer M., Sesti G., Seffer E., Obermaier-Kusser B., Pongratz D. E., Mosthaf L., Häring H. U. Altered pattern of insulin receptor isotypes in skeletal muscle membranes of type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetic subjects. Diabetologia. 1993 Jul;36(7):628–632. doi: 10.1007/BF00404072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaki A., Webster N. J. Effect of dexamethasone on the alternative splicing of the insulin receptor mRNA and insulin action in HepG2 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21990–21996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D. A. Different ligand affinities of the two human insulin receptor splice variants are reflected in parallel changes in sensitivity for insulin action. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 May;5(5):734–739. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-5-734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller D. E., Flier J. S. Insulin resistance--mechanisms, syndromes, and implications. N Engl J Med. 1991 Sep 26;325(13):938–948. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199109263251307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller D. E., Yokota A., Caro J. F., Flier J. S. Tissue-specific expression of two alternatively spliced insulin receptor mRNAs in man. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Aug;3(8):1263–1269. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-8-1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller D. E., Yokota A., Flier J. S. Normal insulin-receptor cDNA sequence in Pima Indians with NIDDM. Diabetes. 1989 Nov;38(11):1496–1500. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.11.1496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosthaf L., Eriksson J., Häring H. U., Groop L., Widen E., Ullrich A. Insulin receptor isotype expression correlates with risk of non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2633–2635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosthaf L., Grako K., Dull T. J., Coussens L., Ullrich A., McClain D. A. Functionally distinct insulin receptors generated by tissue-specific alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2409–2413. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07416.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosthaf L., Vogt B., Häring H. U., Ullrich A. Altered expression of insulin receptor types A and B in the skeletal muscle of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4728–4730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naithani V. K., Steffens G. J., Tager H. S., Buse G., Rubenstein A. H., Steiner D. F. Isolation and amino-acid sequence determination of monkey insulin and proinsulin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1984 May;365(5):571–575. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1984.365.1.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgren S., Zierath J., Galuska D., Wallberg-Henriksson H., Luthman H. Differences in the ratio of RNA encoding two isoforms of the insulin receptor between control and NIDDM patients. The RNA variant without Exon 11 predominates in both groups. Diabetes. 1993 May;42(5):675–681. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.5.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M. After insulin binds. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1452–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.2442814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saad M. F., Knowler W. C., Pettitt D. J., Nelson R. G., Mott D. M., Bennett P. H. The natural history of impaired glucose tolerance in the Pima Indians. N Engl J Med. 1988 Dec 8;319(23):1500–1506. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198812083192302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seino S., Bell G. I. Alternative splicing of human insulin receptor messenger RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Feb 28;159(1):312–316. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92439-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seino S., Seino M., Bell G. I. Human insulin-receptor gene. Partial sequence and amplification of exons by polymerase chain reaction. Diabetes. 1990 Jan;39(1):123–128. doi: 10.2337/diacare.39.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sesti G., Marini M. A., Tullio A. N., Montemurro A., Borboni P., Fusco A., Accili D., Lauro R. Altered expression of the two naturally occurring human insulin receptor variants in isolated adipocytes of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 31;181(3):1419–1424. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)92097-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. I., Cama A., Accili D., Barbetti F., Quon M. J., de la Luz Sierra M., Suzuki Y., Koller E., Levy-Toledano R., Wertheimer E. Mutations in the insulin receptor gene. Endocr Rev. 1992 Aug;13(3):566–595. doi: 10.1210/edrv-13-3-566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treadway J. L., Morrison B. D., Soos M. A., Siddle K., Olefsky J., Ullrich A., McClain D. A., Pessin J. E. Transdominant inhibition of tyrosine kinase activity in mutant insulin/insulin-like growth factor I hybrid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):214–218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt B., Carrascosa J. M., Ermel B., Ullrich A., Häring H. U. The two isotypes of the human insulin receptor (HIR-A and HIR-B) follow different internalization kinetics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jun 28;177(3):1013–1018. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90639-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi Y., Flier J. S., Benecke H., Ransil B. J., Moller D. E. Ligand-binding properties of the two isoforms of the human insulin receptor. Endocrinology. 1993 Mar;132(3):1132–1138. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.3.8440175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi Y., Flier J. S., Yokota A., Benecke H., Backer J. M., Moller D. E. Functional properties of two naturally occurring isoforms of the human insulin receptor in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Endocrinology. 1991 Oct;129(4):2058–2066. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-4-2058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]