Abstract
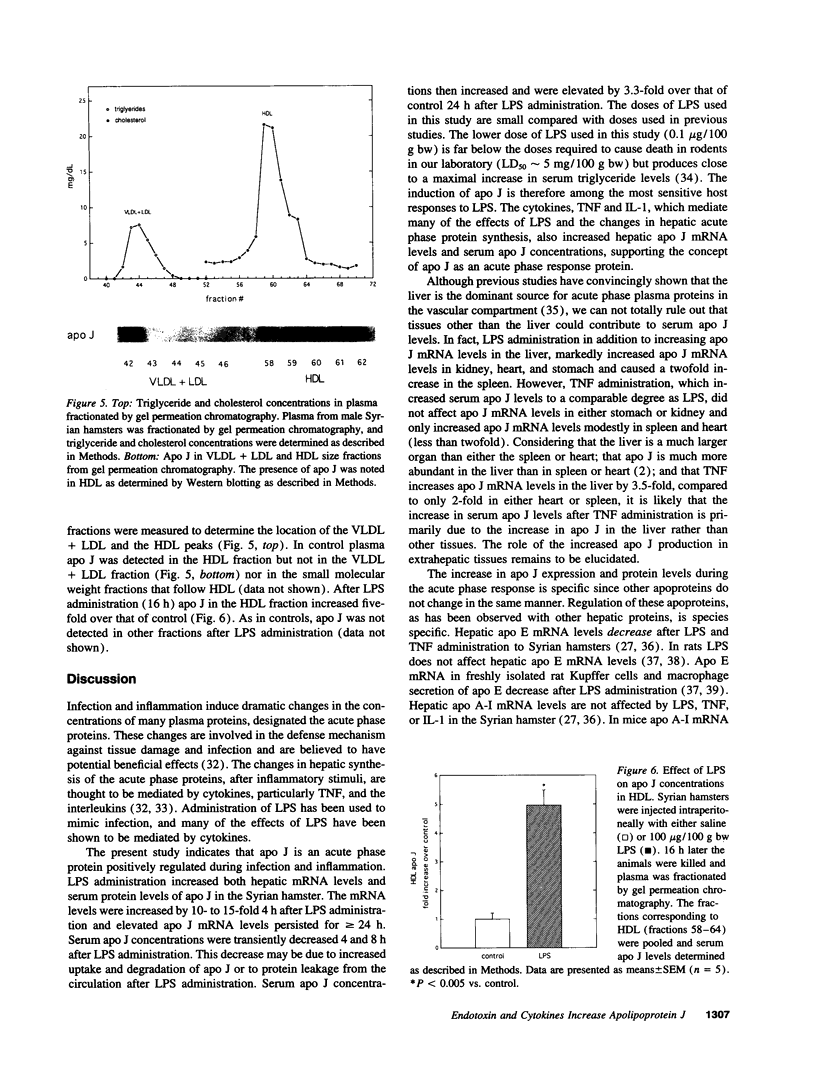
Infection and inflammation induce alterations in hepatic synthesis and plasma concentrations of the acute phase proteins. Our results show that apolipoprotein (apo) J is a positive acute phase protein. Endotoxin (LPS), tumor necrosis factor (TNF), and interleukin (IL)-1 increased hepatic mRNA and serum protein levels of apo J in Syrian hamsters. Hepatic apo J mRNA levels increased 10- to 15-fold with doses of LPS from 0.1 to 100 micrograms/100 g body weight within 4 h and were elevated for > or = 24 h. Serum apo J concentrations were significantly increased by 16 h and further elevated to 3.3 times that of control, 24 h after LPS administration. Serum apo J was associated with high density lipoprotein and increased fivefold in this fraction, after LPS administration. Hepatic apo J mRNA levels increased 3.5- and 4.6-fold, with TNF and IL-1, respectively, and 8.2-fold with a combination of TNF and IL-1. Serum apo J concentrations were increased 2.3-fold by TNF, 79% by IL-1, and 2.9-fold with a combination of TNF and IL-1. These results demonstrate that apo J is a positive acute phase protein.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bandyk M. G., Sawczuk I. S., Olsson C. A., Katz A. E., Buttyan R. Characterization of the products of a gene expressed during androgen-programmed cell death and their potential use as a marker of urogenital injury. J Urol. 1990 Feb;143(2):407–413. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)39975-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P., Eriksen N. Amyloid protein SAA is associated with high density lipoprotein from human serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4025–4028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P., Eriksen N., Hanson R. H. Amyloid protein SAA is an apoprotein of mouse plasma high density lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4092–4096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkey B. F., Stuart W. D., Harmony J. A. Hepatic apolipoprotein J is secreted as a lipoprotein. J Lipid Res. 1992 Oct;33(10):1517–1526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttyan R., Olsson C. A., Pintar J., Chang C., Bandyk M., Ng P. Y., Sawczuk I. S. Induction of the TRPM-2 gene in cells undergoing programmed death. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3473–3481. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabana V. G., Gewurz H., Siegel J. N. Interaction of very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) with rabbit C-reactive protein. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2342–2348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabana V. G., Siegel J. N., Sabesin S. M. Effects of the acute phase response on the concentration and density distribution of plasma lipids and apolipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1989 Jan;30(1):39–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke C. F., Edwards P. A., Lan S. F., Tanaka R. D., Fogelman A. M. Regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase mRNA levels in rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3305–3308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collard M. W., Griswold M. D. Biosynthesis and molecular cloning of sulfated glycoprotein 2 secreted by rat Sertoli cells. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 16;26(12):3297–3303. doi: 10.1021/bi00386a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa-Rotter R., Hostetter T. H., Manivel J. C., Eddy A. A., Rosenberg M. E. Intrarenal distribution of clusterin following reduction of renal mass. Kidney Int. 1992 Apr;41(4):938–950. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson P. A., Lukaszewski L. M., Ells P. F., Malbon C. C., Williams D. L. Quantification and regulation of apolipoprotein E expression in rat Kupffer cells. J Lipid Res. 1989 Mar;30(3):403–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delers F., Mangeney M., Raffa D., Vallet-Colom I., Daveau M., Tran-Quang N., Davrinches C., Chambaz J. Changes in rat liver mRNA for alpha-1-acid-glycoprotein, apolipoprotein E, apolipoprotein B and beta-actin after mouse recombinant tumor necrosis factor injection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 May 30;161(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91563-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowton S. B., Peters C. N., Jestus J. J. Regulation of serum amyloid A gene expression in Syrian hamsters by cytokines. Inflammation. 1991 Oct;15(5):391–397. doi: 10.1007/BF00917355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehnholm C., Bozas S. E., Tenkanen H., Kirszbaum L., Metso J., Murphy B., Walker I. D. The apolipoprotein A-I binding protein of placenta and the SP-40,40 protein of human blood are different proteins which both bind to apolipoprotein A-I. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Nov 27;1086(3):255–260. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(91)90167-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold K. R., Hardardottir I., Memon R., Krul E. J., Moser A. H., Taylor J. M., Grunfeld C. Effect of endotoxin on cholesterol biosynthesis and distribution in serum lipoproteins in Syrian hamsters. J Lipid Res. 1993 Dec;34(12):2147–2158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold K. R., Soued M., Serio M. K., Moser A. H., Dinarello C. A., Grunfeld C. Multiple cytokines stimulate hepatic lipid synthesis in vivo. Endocrinology. 1989 Jul;125(1):267–274. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-1-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold K. R., Staprans I., Memon R. A., Moser A. H., Shigenaga J. K., Doerrler W., Dinarello C. A., Grunfeld C. Endotoxin rapidly induces changes in lipid metabolism that produce hypertriglyceridemia: low doses stimulate hepatic triglyceride production while high doses inhibit clearance. J Lipid Res. 1992 Dec;33(12):1765–1776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz I. B., Burdzy K. Novel action of carnitine: inhibition of aggregation of dispersed cells elicited by clusterin in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jul;140(1):18–28. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041400104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunfeld C., Feingold K. R. Tumor necrosis factor, interleukin, and interferon induced changes in lipid metabolism as part of host defense. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1992 Jun;200(2):224–227. doi: 10.3181/00379727-200-43424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajduk S. L., Moore D. R., Vasudevacharya J., Siqueira H., Torri A. F., Tytler E. M., Esko J. D. Lysis of Trypanosoma brucei by a toxic subspecies of human high density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5210–5217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardardóttir I., Moser A. H., Memon R., Grünfeld C., Feingold K. R. Effects of TNF, IL-1, and the combination of both cytokines on cholesterol metabolism in Syrian hamsters. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1994 Jun;13(3):161–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H. W., Grunfeld C., Feingold K. R., Rapp J. H. Human very low density lipoproteins and chylomicrons can protect against endotoxin-induced death in mice. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):696–702. doi: 10.1172/JCI114765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herault Y., Chatelain G., Brun G., Michel D. V-src-induced-transcription of the avian clusterin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6377–6383. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. S., Benditt E. P. Changes in high density lipoprotein content following endotoxin administration in the mouse. Formation of serum amyloid protein-rich subfractions. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10510–10517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huemer H. P., Menzel H. J., Potratz D., Brake B., Falke D., Utermann G., Dierich M. P. Herpes simplex virus binds to human serum lipoprotein. Intervirology. 1988;29(2):68–76. doi: 10.1159/000150031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James R. W., Hochstrasser A. C., Borghini I., Martin B., Pometta D., Hochstrasser D. Characterization of a human high density lipoprotein-associated protein, NA1/NA2. Identity with SP-40,40, an inhibitor of complement-mediated cytolysis. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 May-Jun;11(3):645–652. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.3.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D. E., Lowin B., Peitsch M. C., Böttcher A., Schmitz G., Tschopp J. Clusterin (complement lysis inhibitor) forms a high density lipoprotein complex with apolipoprotein A-I in human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11030–11036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D. E., Tschopp J. Molecular structure and functional characterization of a human complement cytolysis inhibitor found in blood and seminal plasma: identity to sulfated glycoprotein 2, a constituent of rat testis fluid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7123–7127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirszbaum L., Sharpe J. A., Murphy B., d'Apice A. J., Classon B., Hudson P., Walker I. D. Molecular cloning and characterization of the novel, human complement-associated protein, SP-40,40: a link between the complement and reproductive systems. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):711–718. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisilevsky R. Serum amyloid A (SAA), a protein without a function: some suggestions with reference to cholesterol metabolism. Med Hypotheses. 1991 Aug;35(4):337–341. doi: 10.1016/0306-9877(91)90280-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner I. The acute phase response: from Hippocrates to cytokine biology. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1991 Mar-Apr;2(2):75–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyprianou N., Alexander R. B., Isaacs J. T. Activation of programmed cell death by recombinant human tumor necrosis factor plus topoisomerase II-targeted drugs in L929 tumor cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1991 Mar 6;83(5):346–350. doi: 10.1093/jnci/83.5.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J. C., Kane J. P., Oleszko O., Levy J. A. Antigen-specific nonimmunoglobulin factor that neutralizes xenotropic virus is associated with mouse serum lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):276–280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowell C. A., Stearman R. S., Morrow J. F. Transcriptional regulation of serum amyloid A gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8453–8461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow J. F., Stearman R. S., Peltzman C. G., Potter D. A. Induction of hepatic synthesis of serum amyloid A protein and actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4718–4722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. F., Saunders J. R., O'Bryan M. K., Kirszbaum L., Walker I. D., d'Apice A. J. SP-40,40 is an inhibitor of C5b-6-initiated haemolysis. Int Immunol. 1989;1(5):551–554. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.5.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewold T. A., Gruys E., Arakawa T., Shirahama T., Kisilevsky R. Recombinant human tumour necrosis factor-alpha (rhTNF-alpha) and rhTNF-alpha analogue enhance amyloid deposition in the Syrian hamster. Scand J Immunol. 1993 Jan;37(1):29–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1993.tb01660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Bryan M. K., Baker H. W., Saunders J. R., Kirszbaum L., Walker I. D., Hudson P., Liu D. Y., Glew M. D., d'Apice A. J., Murphy B. F. Human seminal clusterin (SP-40,40). Isolation and characterization. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1477–1486. doi: 10.1172/JCI114594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Rowe I. F., Baltz M. L. C-reactive protein: binding to lipids and lipoproteins. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1985;27:83–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C., Gauldie J., Baumann H. Cytokine control of acute phase protein expression. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1991 Mar-Apr;2(2):89–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin M. R. Identification of the trypanocidal factor in normal human serum: high density lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3450–3454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi S. Metabolic disorders of serum lipoproteins in endotoxin-poisoned mice: the role of high density lipoprotein (HDL) and triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. Microbiol Immunol. 1982;26(11):1017–1034. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1982.tb00251.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seganti L., Grassi M., Mastromarino P., Panà A., Superti F., Orsi N. Activity of human serum lipoproteins on the infectivity of rhabdoviruses. Microbiologica. 1983 Apr;6(2):91–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sernatinger J., Hoffman A., Hardman D., Kane J. P., Levy J. A. Neutralization of mouse xenotropic virus by lipoproteins involves binding to the virions. J Gen Virol. 1988 Oct;69(Pt 10):2657–2661. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-10-2657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortridge K. F., Ho W. K., Oya A., Kobayashi M. Studies on the inhibitory activities of human serum lipoproteins for Japanese encephalitis virus. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1975 Dec;6(4):461–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegenka U. M., Buschmann J., Lütticken C., Heinrich P. C., Horn F. Acute-phase response factor, a nuclear factor binding to acute-phase response elements, is rapidly activated by interleukin-6 at the posttranslational level. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):276–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Chin J. R. Apoprotein E is synthesized and secreted by resident and thioglycollate-elicited macrophages but not by pyran copolymer- or bacillus Calmette-Guerin-activated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1272–1293. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P., Pineault J., Lakins J., Taillefer D., Léger J., Wang C., Tenniswood M. Genomic organization and expression of the rat TRPM-2 (clusterin) gene, a gene implicated in apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):5021–5031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada N., Shames D. M., Havel R. J. Effect of low density lipoprotein receptor deficiency on the metabolism of apolipoprotein B-100 in blood plasma. Kinetic studies in normal and Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):507–515. doi: 10.1172/JCI113099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto K., Okamoto S., Mukaida N., Murakami S., Mai M., Matsushima K. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interferon gamma synergistically induce interleukin 8 production in a human gastric cancer cell line through acting concurrently on AP-1 and NF-kB-like binding sites of the interleukin 8 gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22506–22511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Silva H. V., Harmony J. A., Stuart W. D., Gil C. M., Robbins J. Apolipoprotein J: structure and tissue distribution. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 5;29(22):5380–5389. doi: 10.1021/bi00474a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Silva H. V., Stuart W. D., Duvic C. R., Wetterau J. R., Ray M. J., Ferguson D. G., Albers H. W., Smith W. R., Harmony J. A. A 70-kDa apolipoprotein designated ApoJ is a marker for subclasses of human plasma high density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13240–13247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Silva H. V., Stuart W. D., Park Y. B., Mao S. J., Gil C. M., Wetterau J. R., Busch S. J., Harmony J. A. Purification and characterization of apolipoprotein J. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14292–14297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








