Abstract
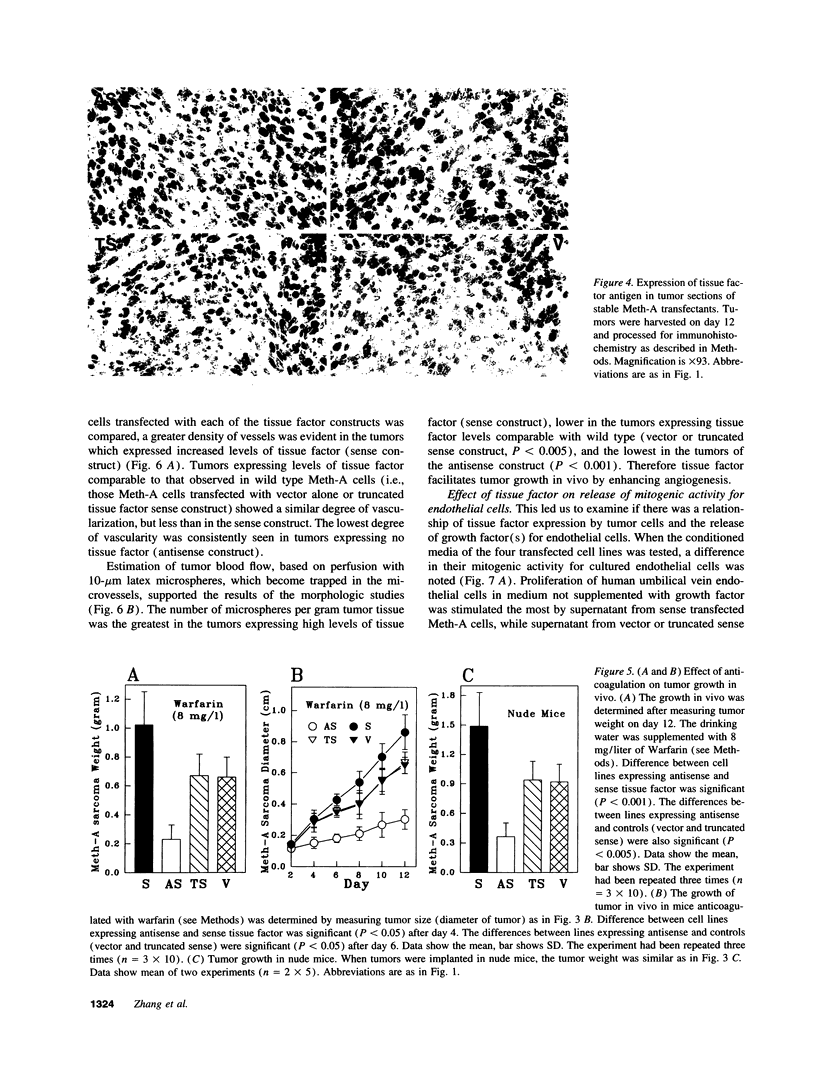
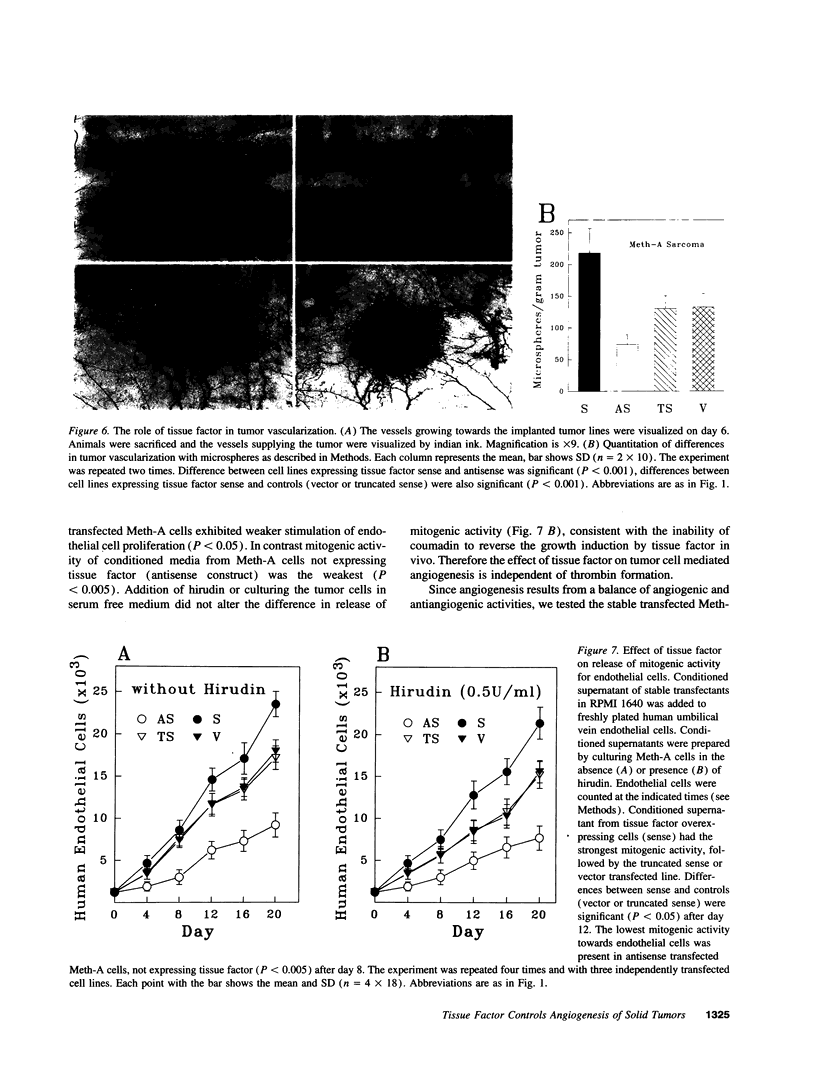
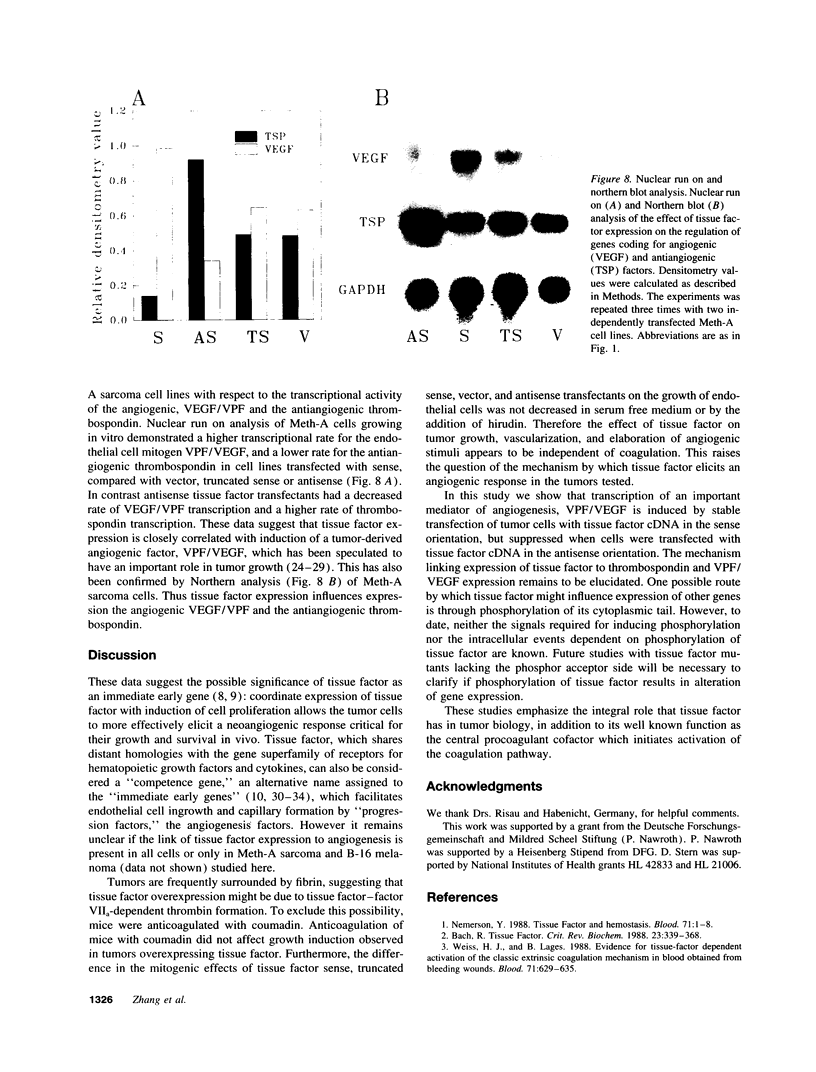
Meth-A sarcoma cells were stable transfected to overexpress (sense construct) or underexpress (antisense construct) tissue factor. In vitro, there was no difference in plating efficiency or growth between these cell lines. In vivo, tumor cells transfected to overexpress tissue factor grew more rapidly, and established larger and more vascularized tumors than control transfectants. Antisense transfectants grew the slowest and were the least vascularized. Anticoagulation of mice with warfarin did not alter the difference between these tumor lines. Tumor cells over-expressing tissue factor released more (compared with control transfectants) mitogenic activity for endothelial cells in parallel with enhanced transcription of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF/VPF), and diminished transcription of thrombospondin (TSP2), a molecule with anti-angiogenic properties. Antisense tissue factor transfectants, while releasing the lowest amount of mitogenic activity, had increased thrombospondin and decreased VEGF/VPF transcription compared with control transfectants or wild-type cells. Experiments with these sense, antisense, truncated sense, or vector tumor lines gave comparable results in complete medium, serum free medium or in the presence of hirudin, indicating that the activation of the coagulation mechanism was not likely to be responsible for changes in tumor cell properties. These results suggest that tissue factor regulates angiogenic properties of tumor cells by altering the production of growth regulatory molecules of endothelium by a mechanism distinct from tissue factor activation of the coagulation mechanism.
Full text
PDF

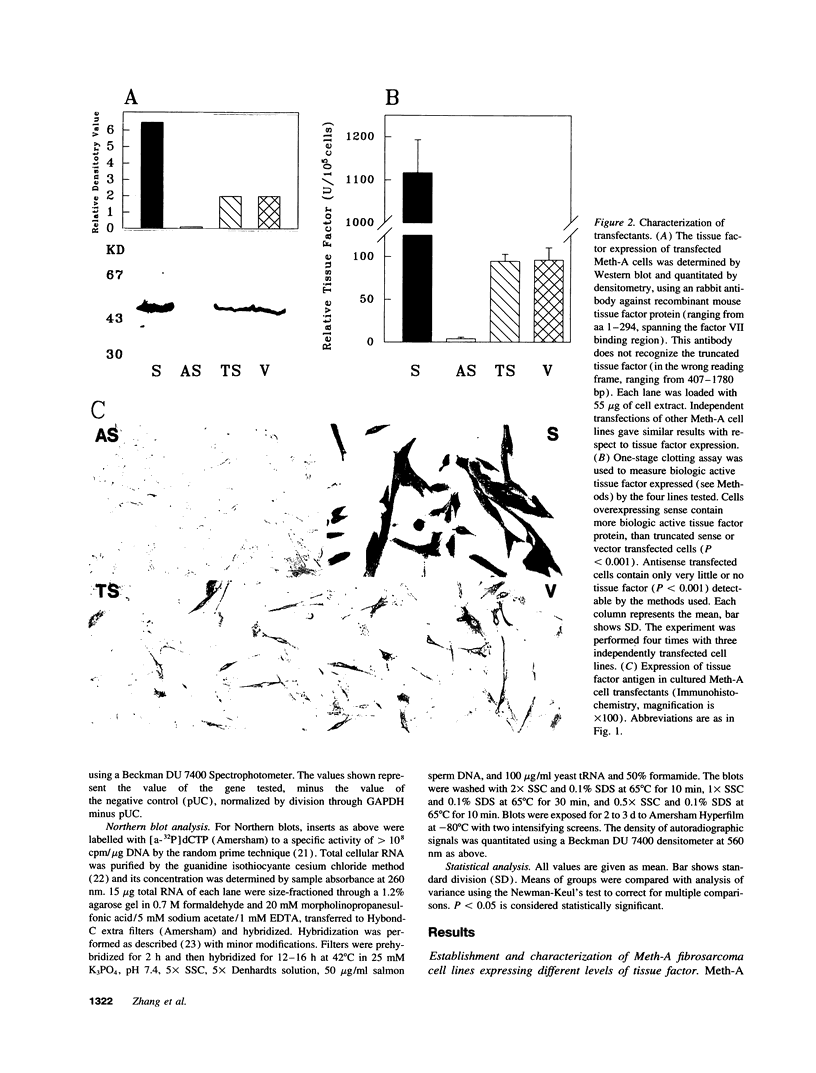
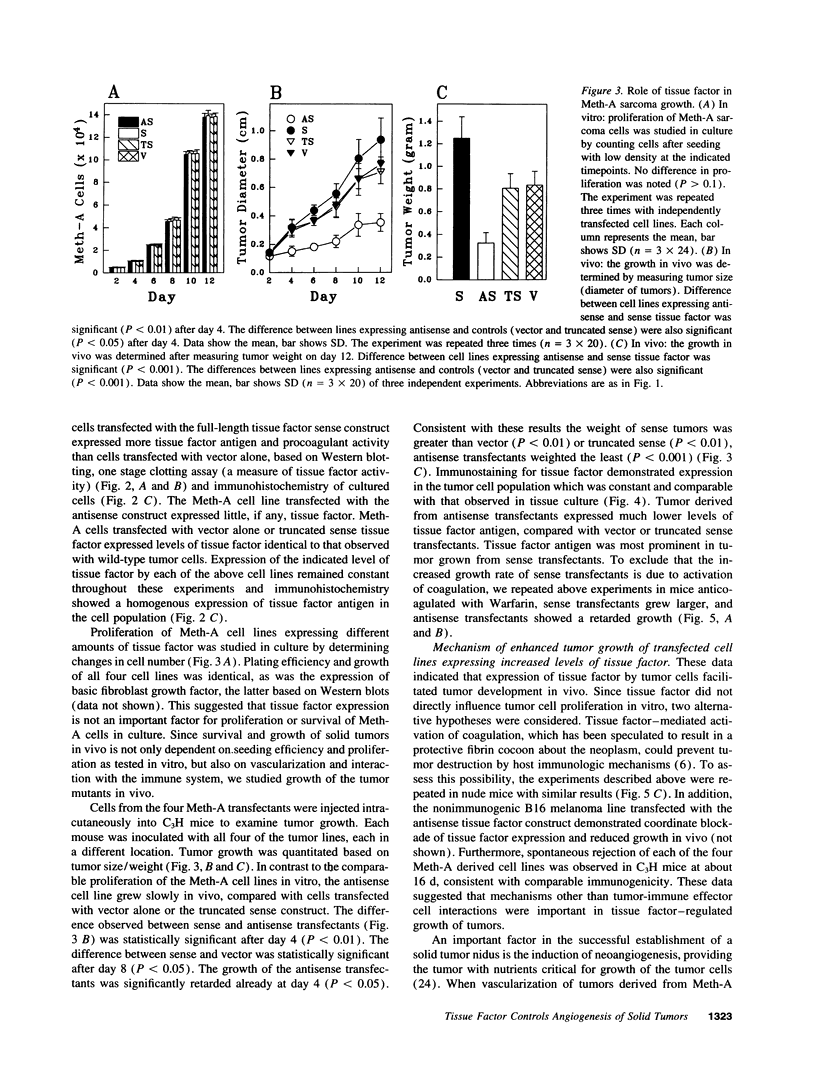

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almendral J. M., Sommer D., Macdonald-Bravo H., Burckhardt J., Perera J., Bravo R. Complexity of the early genetic response to growth factors in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2140–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach R. R. Initiation of coagulation by tissue factor. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1988;23(4):339–368. doi: 10.3109/10409238809082548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatti S. P., Foster D. N., Ranganathan G., Moses H. L., Getz M. J. Induction of fibronectin gene transcription and mRNA is a primary response to growth-factor stimulation of AKR-2B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1119–1123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter C. A., Wagner E. F. A universal retroviral vector for efficient constitutive expression of exogenous genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7194–7194. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breier G., Albrecht U., Sterrer S., Risau W. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor during embryonic angiogenesis and endothelial cell differentiation. Development. 1992 Feb;114(2):521–532. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.2.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran B. H., Reffel A. C., Stiles C. D. Molecular cloning of gene sequences regulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly D. T., Heuvelman D. M., Nelson R., Olander J. V., Eppley B. L., Delfino J. J., Siegel N. R., Leimgruber R. M., Feder J. Tumor vascular permeability factor stimulates endothelial cell growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1470–1478. doi: 10.1172/JCI114322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake T. A., Morrissey J. H., Edgington T. S. Selective cellular expression of tissue factor in human tissues. Implications for disorders of hemostasis and thrombosis. Am J Pathol. 1989 May;134(5):1087–1097. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Winer J., Burton T., Rowland A., Siegel M., Phillips H. S., Terrell T., Keller G. A., Levinson A. D. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor does not promote transformation but confers a growth advantage in vivo to Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):160–170. doi: 10.1172/JCI116166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Shing Y. Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):10931–10934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasso R. J., Buchanan J. M. Synthesis of early RNA in bacteriophage T4-infected Escherichia coli B. Nature. 1969 Nov 29;224(5222):882–885. doi: 10.1038/224882a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunji Y., Gorelik E. Role of fibrin coagulation in protection of murine tumor cells from destruction by cytotoxic cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Sep 15;48(18):5216–5221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell S., Ryder K., Lanahan A., Lau L. F., Nathan D. A growth factor-responsive gene of murine BALB/c 3T3 cells encodes a protein homologous to human tissue factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2567–2573. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplow I. S. Letter: Substitute for benzidine in myeloperoxidase stains. Am J Clin Pathol. 1975 Mar;63(3):451–451. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/63.3.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markus G. The role of hemostasis and fibrinolysis in the metastatic spread of cancer. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1984 Jan;10(1):61–70. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. C. Coagulation and cancer. Br J Cancer. 1991 Sep;64(3):422–424. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Bank I., Handley D., Cassimeris J., Chess L., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin interacts with endothelial cell receptors to induce release of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1363–1375. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Stern D. M. Modulation of endothelial cell hemostatic properties by tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):740–745. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P., Handley D., Matsueda G., De Waal R., Gerlach H., Blohm D., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin-induced intravascular fibrin formation in meth A fibrosarcomas. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):637–647. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y. Tissue factor and hemostasis. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate K. H., Breier G., Weich H. A., Risau W. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumour angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivo. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):845–848. doi: 10.1038/359845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pledger W. J., Stiles C. D., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. Induction of DNA synthesis in BALB/c 3T3 cells by serum components: reevaluation of the commitment process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4481–4485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W., Bolle A., Epstein R. Transcription during bacteriophage T4 development: a demonstration that distinct subclasses of the "early" RNA appear at different times and that some are "turned off" at late times. J Mol Biol. 1970 Apr 28;49(2):271–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90246-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawdey M., Podor T. J., Loskutoff D. J. Regulation of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene expression in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Induction by transforming growth factor-beta, lipopolysaccharide, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10396–10401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shweiki D., Itin A., Soffer D., Keshet E. Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):843–845. doi: 10.1038/359843a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D., Brett J., Harris K., Nawroth P. Participation of endothelial cells in the protein C-protein S anticoagulant pathway: the synthesis and release of protein S. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1971–1978. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. L., Vanek M., Wagner E. F. Expression of foreign genes from retroviral vectors in mouse teratocarcinoma chimaeras. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3701–3709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04138.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Lages B. Evidence for tissue factor-dependent activation of the classic extrinsic coagulation mechanism in blood obtained from bleeding time wounds. Blood. 1988 Mar;71(3):629–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zullo J. N., Cochran B. H., Huang A. S., Stiles C. D. Platelet-derived growth factor and double-stranded ribonucleic acids stimulate expression of the same genes in 3T3 cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):793–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90252-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]