Abstract
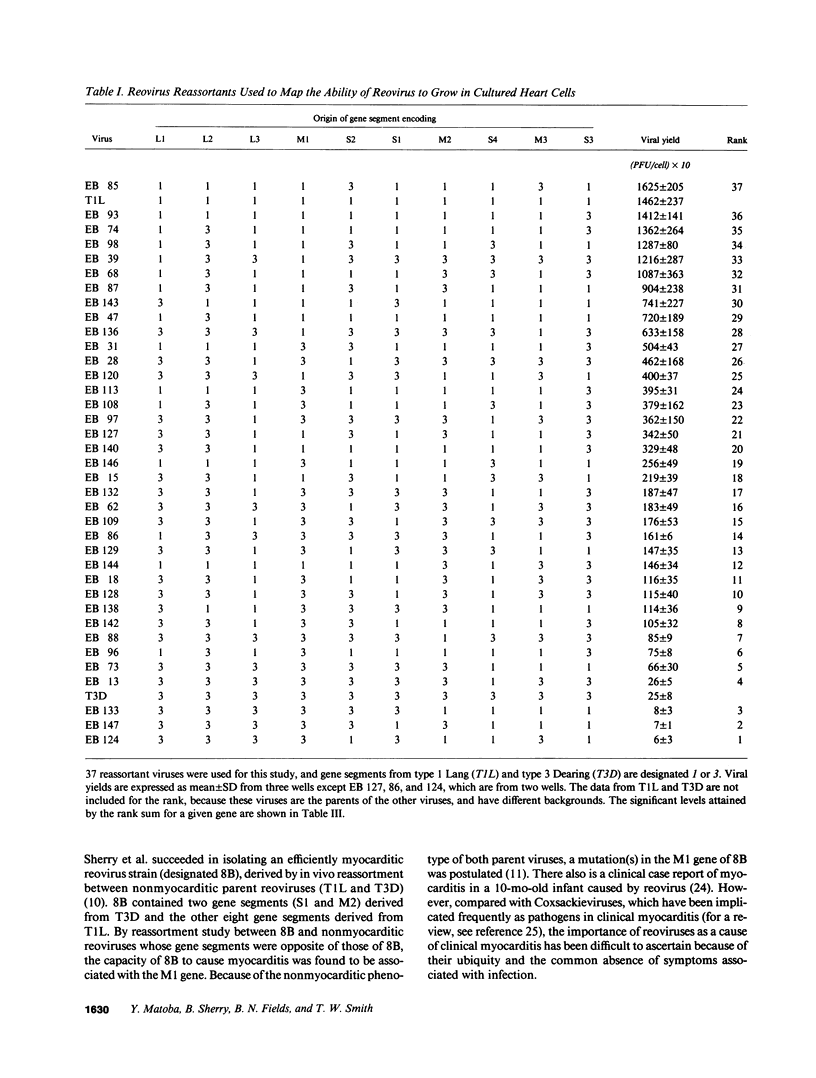
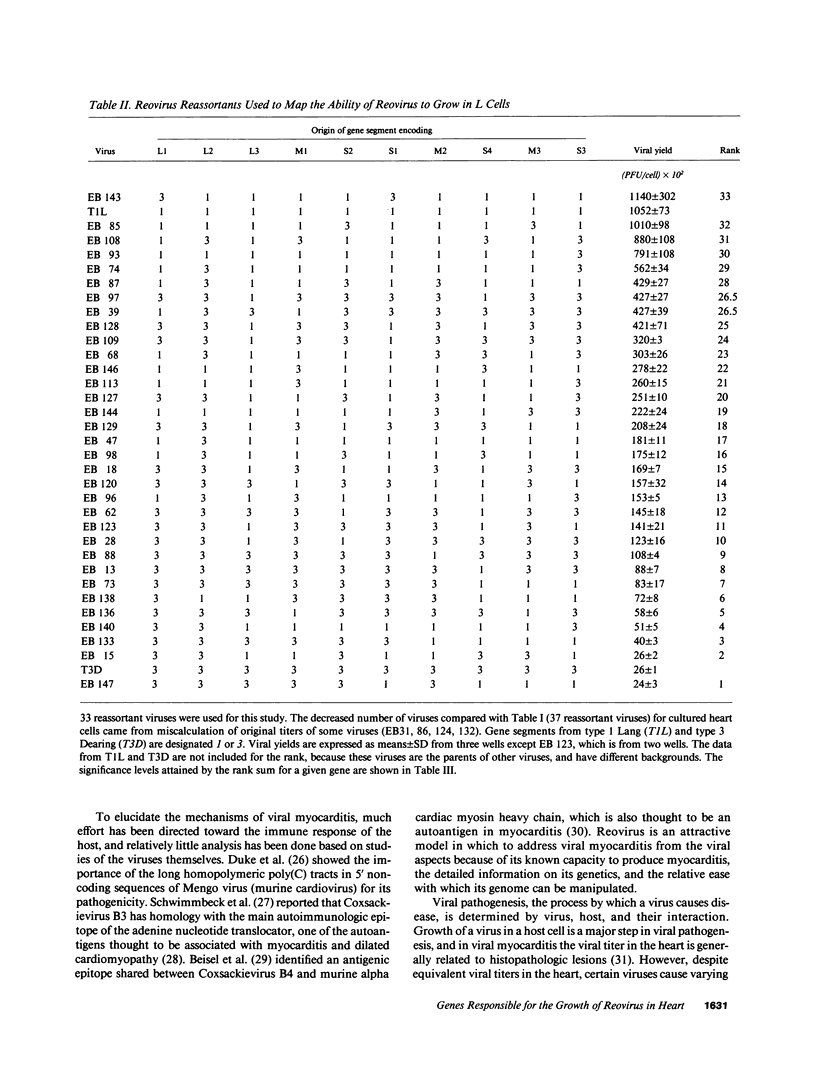
Viral growth in specific tissue is usually required in order to lead to pathology. Two reovirus isolates (type 1 Lang and type 3 Dearing) differ in their capacity to grow in cultured mouse heart cells. The mammalian reoviruses contain a genome of 10 double-stranded RNA gene segments. By the use of 37 reassortant viruses (consisting of viruses with different combinations of genes derived from the two parents), difference in capacity of different strains to grow in heart cells was mapped to three different genes, all of which encode viral core proteins: the M1 gene (P less than 0.000044); the L1 gene (P = 0.00094); and the L3 gene (P = 0.019). Using the same set of reassortant viruses, the L1 (P = 0.00015) and L3 (P = 0.0065) genes were involved in differences of the ability of viral strains to grow in mouse L cells (fibroblasts), but the M1 gene (P = 0.12) was not. These findings suggest that the M1 gene plays an important and specific role in determining the relative capacity of certain viral strains to grow in the heart. Thus, we have identified viral genes responsible for differing growth capacity in heart muscle cells in culture. These findings provide a novel system for studies of viral myocarditis at a molecular genetic level.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed R., Fields B. N. Role of the S4 gene in the establishment of persistent reovirus infection in L cells. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):605–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch K. D., Seidman J. G., Naftilan J. D., Fallon J. T., Seidman C. E. Neonatal atria and ventricles secrete atrial natriuretic factor via tissue-specific secretory pathways. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):695–702. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90512-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodkin D. K., Fields B. N. Growth and survival of reovirus in intestinal tissue: role of the L2 and S1 genes. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1188–1193. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1188-1193.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichter M. A., Weiner H. L. Infection of neuronal cell cultures with reovirus mimics in vitro patterns of neurotropism. Ann Neurol. 1984 Nov;16(5):603–610. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., Fields B. N. Activation and characterization of the reovirus transcriptase: genetic analysis. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):110–118. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.110-118.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., Fields B. N. Genetic studies on the mechanism of chemical and physical inactivation of reovirus. J Gen Virol. 1982 Nov;63(Pt 1):149–159. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-63-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke G. M., Osorio J. E., Palmenberg A. C. Attenuation of Mengo virus through genetic engineering of the 5' noncoding poly(C) tract. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):474–476. doi: 10.1038/343474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göller T., Galle J., Eggers H. J., Bültmann B. Experimental reovirus myocarditis in newborn mice. Electron microscopic observations. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1986;50(4):373–386. doi: 10.1007/BF02889915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASSAN S. A., RABIN E. R., MELNICK J. L. REOVIRUS MYOCARDITIS IN MICE: AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC, IMMUNOFLUORESCENT, AND VIRUS ASSAY STUDY. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Feb;76:66–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrdy D. B., Rubin D. H., Fields B. N. Molecular basis of reovirus neurovirulence: role of the M2 gene in avirulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1298–1302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. A., Lodge P. A. Coxsackievirus B-3 myocarditis. Identification of different pathogenic mechanisms in DBA/2 and Balb/c mice. Am J Pathol. 1986 Feb;122(2):284–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOSKE R. A., KEALL D. D., LEAK P. J., STANLEY N. F., WALTERS M. N. HEPATITIS-ENCEPHALITIS IN HUMANS WITH REOVIRUS INFECTION. Arch Intern Med. 1964 Jun;113:811–816. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1964.00280120011003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maratos-Flier E., Goodman M. J., Fields B. N., Kahn C. R. Differential effects of viral infection on islet and pituitary cell lines. Endocrinology. 1985 Jun;116(6):2430–2437. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-6-2430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morkin E., Ashford T. P. Myocardial DNA synthesis in experimental cardiac hypertrophy. Am J Physiol. 1968 Dec;215(6):1409–1413. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.6.1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morozov S. Y. A possible relationship of reovirus putative RNA polymerase to polymerases of positive-strand RNA viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5394–5394. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu N., Beisel K. W., Traystman M. D., Rose N. R., Craig S. W. Autoantibodies specific for the cardiac myosin isoform are found in mice susceptible to Coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2488–2492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paque R. E., Gauntt C. J., Nealon T. J., Trousdale M. D. Assessment of cell-mediated hypersensitivity against coxsackievirus B3 viral-induced myocarditis utilizing hypertonic salt extracts of cardiac tissue. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1672–1678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramig R. F., Cross R. K., Fields B. N. Genome RNAs and polypeptides of reovirus serotypes 1, 2, and 3. J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):726–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.726-733.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. H., Fields B. N. Reovirus inhibition of cellular RNA and protein synthesis: role of the S4 gene. Virology. 1982 Oct 30;122(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. H., Ramig R. F., Mustoe T. A., Fields B. N. A genetic map of reovirus. 1. Correlation of genome RNAs between serotypes 1, 2, and 3. Virology. 1978 Jan;84(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90218-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Fields B. N. The reovirus M1 gene, encoding a viral core protein, is associated with the myocarditic phenotype of a reovirus variant. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4850–4856. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4850-4856.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Schoen F. J., Wenske E., Fields B. N. Derivation and characterization of an efficiently myocarditic reovirus variant. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4840–4849. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4840-4849.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler K. L., Bronson R. T., Byers K. B., Fields B. Molecular basis of viral neurotropism: experimental reovirus infection. Neurology. 1985 Jan;35(1):88–92. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.1.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virgin H. W., 4th, Bassel-Duby R., Fields B. N., Tyler K. L. Antibody protects against lethal infection with the neurally spreading reovirus type 3 (Dearing). J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4594–4604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4594-4604.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALTERS M. N., JOSKE R. A., LEAK P. J., STANLEY N. F. MURINE INFECTION WITH REOVIRUS: I. PATHOLOGY OF THE ACUTE PHASE. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Aug;44:427–436. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALTERS M. N., LEAK P. J., JOSKE R. A., STANLEY N. F., PERRET D. H. MURINE INFECTION WITH REOVIRUS. 3. PATHOLOGY OF INFECTION WITH TYPES 1 AND 2. Br J Exp Pathol. 1965 Apr;46:200–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Ault K. A., Fields B. N. Interaction of reovirus with cell surface receptors. I. Murine and human lymphocytes have a receptor for the hemagglutinin of reovirus type 3. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2143–2148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Drayna D., Averill D. R., Jr, Fields B. N. Molecular basis of reovirus virulence: role of the S1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5744–5748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Powers M. L., Fields B. N. Absolute linkage of virulence and central nervous system cell tropism of reoviruses to viral hemagglutinin. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):609–616. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfgram L. J., Beisel K. W., Herskowitz A., Rose N. R. Variations in the susceptibility to Coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis among different strains of mice. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1846–1852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zak R. Cell proliferation during cardiac growth. Am J Cardiol. 1973 Feb;31(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(73)91034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



