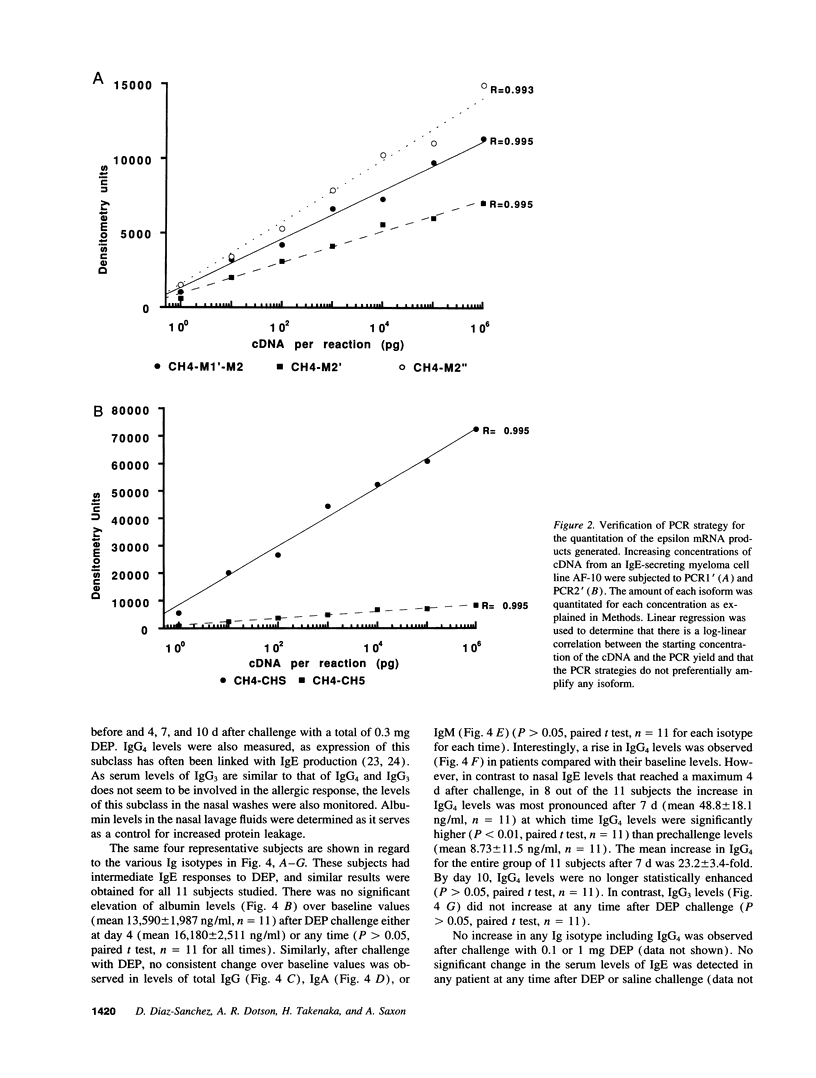
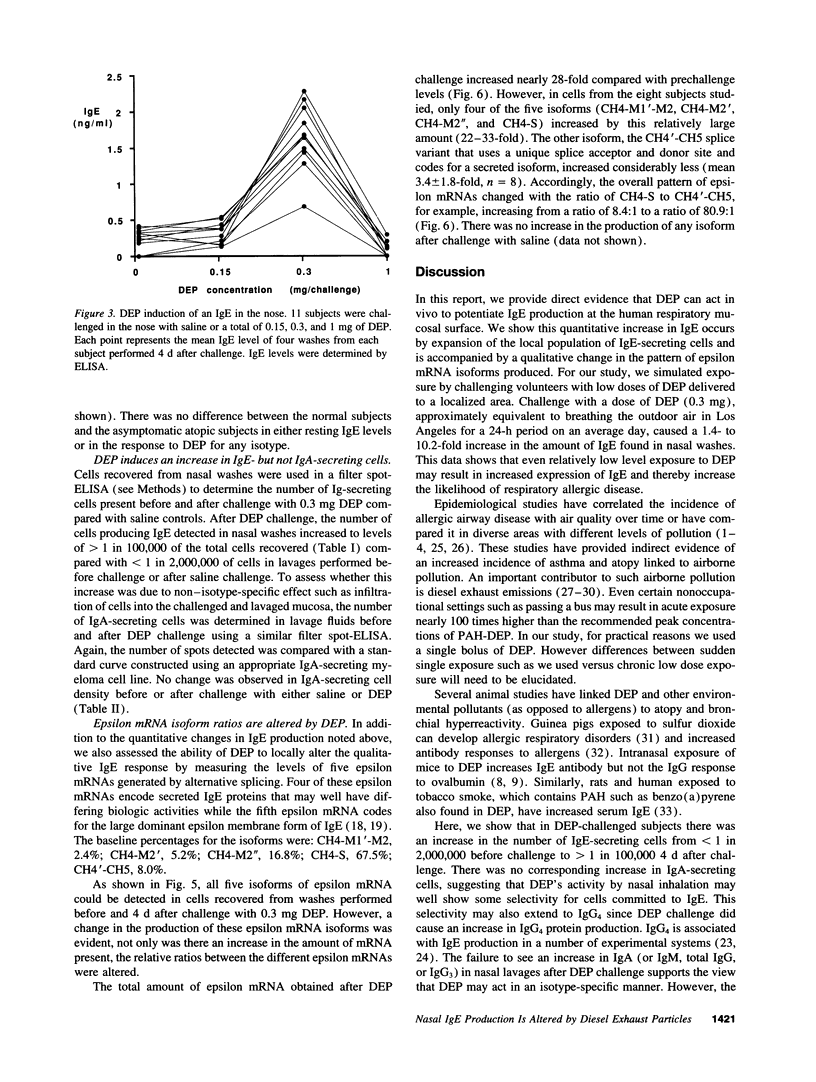
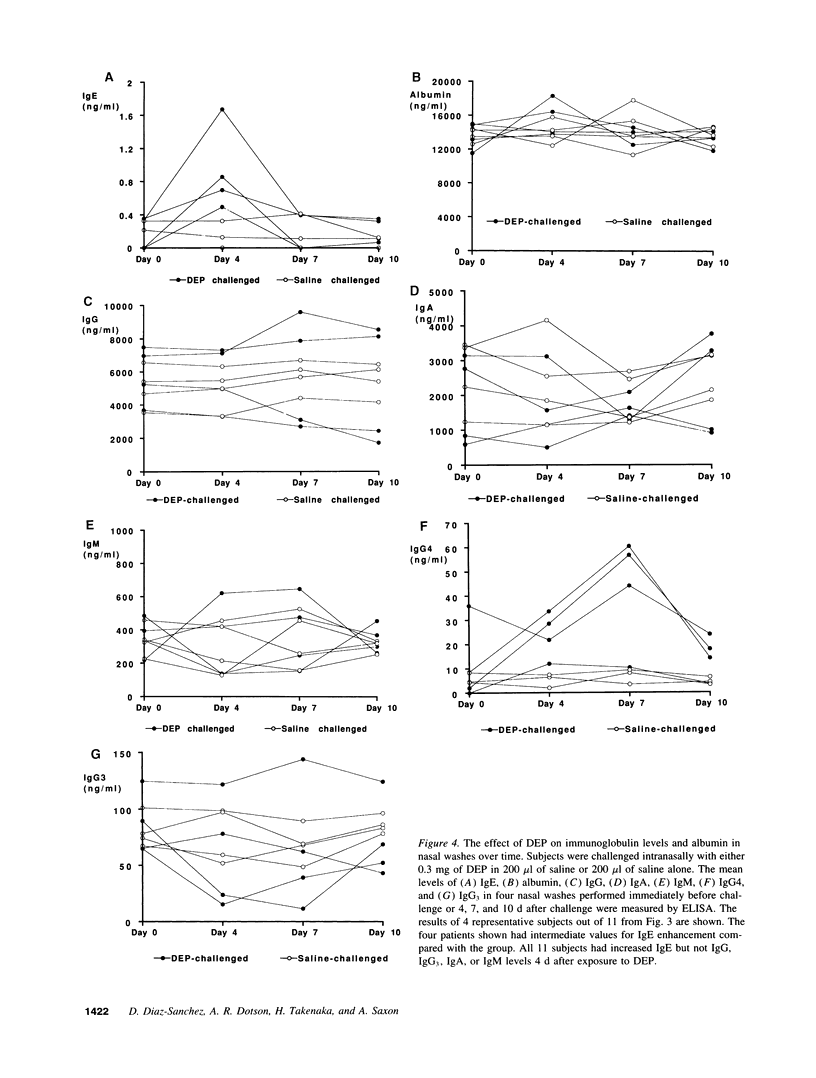
Abstract
Diesel exhaust particles (DEP) have been implicated in the increased incidence of allergic airway disorders. We investigated the effects of DEP on localized immunoglobulin production by performing nasal challenges with varying doses of DEP and analyzing the local immune response in nasal lavages obtained before and after. A significant rise in nasal IgE but not IgG, IgA, IgM, or albumin was observed in subjects 4 d after challenge with 0.30 mg DEP, equivalent to exposure on an average Los Angeles day. Direct evidence for DEP-enhanced local production of IgE was that challenge increased the number of IgE-secreting cells in lavage fluid from < 1 in 2,000,000 to > 1 in 100,000 but did not alter the number of IgA-secreting cells. There was a concomitant increase in epsilon mRNA production in the lavage cells. Additionally, DEP altered the relative amounts of five different epsilon mRNAs generated by alternative splicing, mRNAs that code for different IgE proteins. These results show that DEP exposure in vivo causes both quantitative and qualitative changes in local IgE production. The implication is that natural exposure to DEP may result in increased expression of respiratory allergic disease.
Full text
PDF


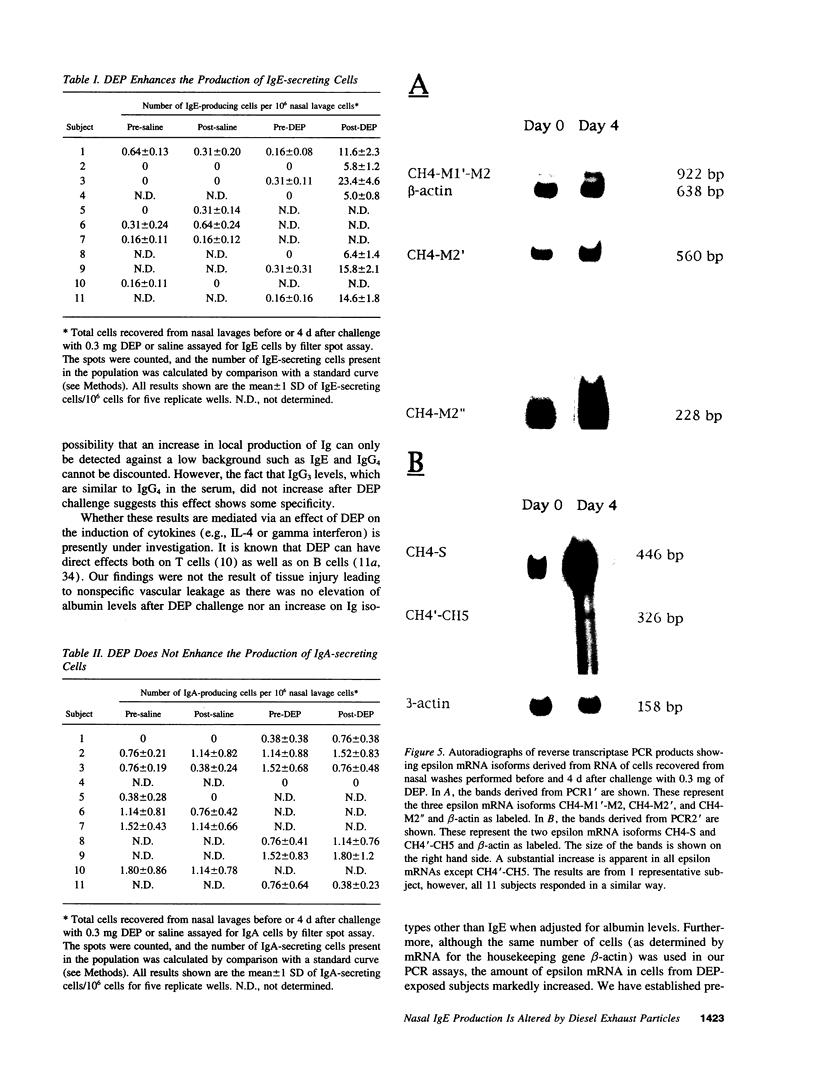
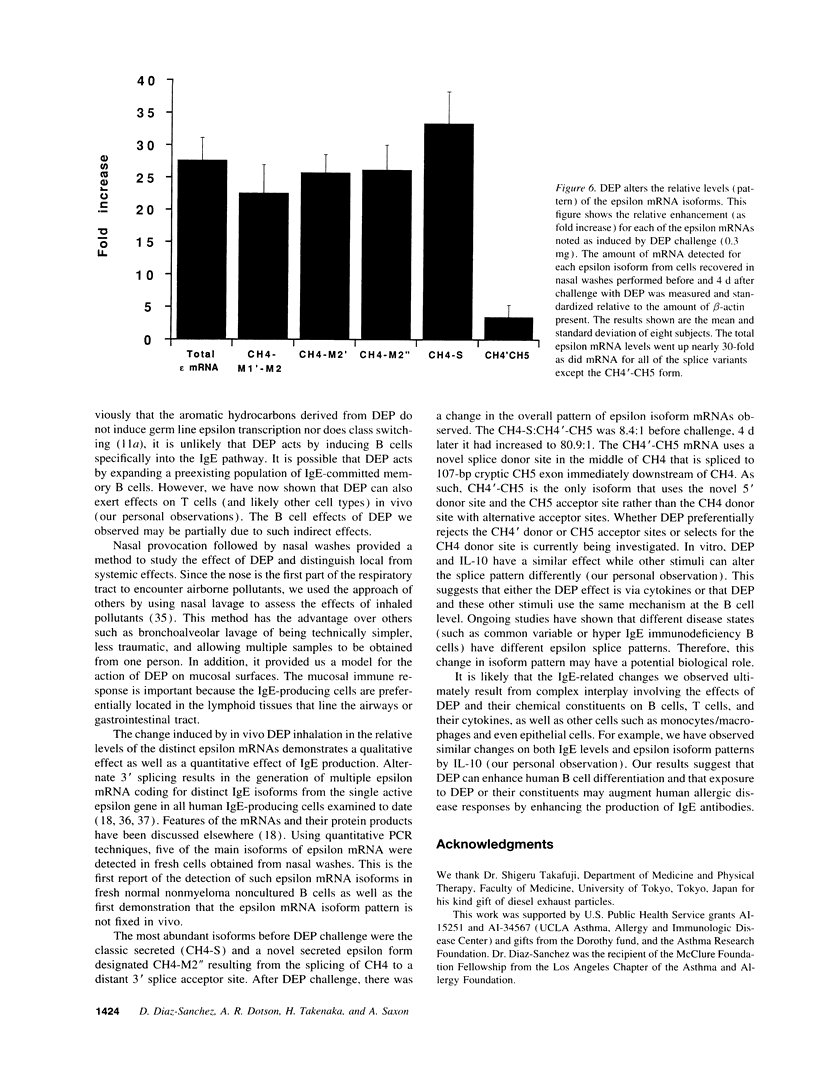

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armitage R. J., Macduff B. M., Spriggs M. K., Fanslow W. C. Human B cell proliferation and Ig secretion induced by recombinant CD40 ligand are modulated by soluble cytokines. J Immunol. 1993 May 1;150(9):3671–3680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bascom R., Kulle T., Kagey-Sobotka A., Proud D. Upper respiratory tract environmental tobacco smoke sensitivity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Jun;143(6):1304–1311. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/143.6.1304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbo G. M., Forastiere F., Dell'Orco V., Pistelli R., Agabiti N., De Stefanis B., Ciappi G., Perucci C. A. Effects of environment on atopic status and respiratory disorders in children. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993 Oct;92(4):616–623. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(93)90086-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel M. B. Hay fever, a post industrial revolution epidemic: a history of its growth during the 19th century. Clin Allergy. 1988 May;18(3):295–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1988.tb02872.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassner A., Saxon A. Isotype-specific human suppressor T cells for IgE synthesis activated by IgE-anti-IgE immune complexes. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2844–2849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman L. Characterization of four novel epsilon chain mRNA and a comparative analysis of genes for immunoglobulin E in rodents and man. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jan;23(1):159–167. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki T., Koizumi K., Ikemori R., Ishiyama Y., Kushibiki E. Studies of prevalence of Japanese cedar pollinosis among the residents in a densely cultivated area. Ann Allergy. 1987 Apr;58(4):265–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabara H. H., Fu S. M., Geha R. S., Vercelli D. CD40 and IgE: synergism between anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody and interleukin 4 in the induction of IgE synthesis by highly purified human B cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1861–1864. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. J., Pedersen B., Schmidt E., Dahl R. Serum IgE in nonatopic smokers, nonsmokers, and recent exsmokers: relation to lung function, airway symptoms, and atopic predisposition. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992 Aug;90(2):224–229. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(92)90075-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. L., Poindexter R. W., Ragunathan J., Fleisher T. A., Ottesen E. A., Nutman T. B. Frequency analysis of IgE-secreting B lymphocytes in persons with normal or elevated serum IgE levels. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 1;146(5):1478–1483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. L., Thyphronitis G., Nutman T. B. Enumeration of IgE secreting B cells. A filter spot-ELISA. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Aug 28;132(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90395-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren H. S., Hatch G. E., Graham D. E. Nasal lavage as a tool in assessing acute inflammation in response to inhaled pollutants. Toxicology. 1990 Jan-Feb;60(1-2):15–25. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(90)90159-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer C. M., Johnson K. W., Dooley R. K., Holsapple M. P. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) enhances antibody production and protein kinase activity in murine B cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 May 29;145(1):25–33. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macy E., Kemeny M., Saxon A. Enhanced ELISA: how to measure less than 10 picograms of a specific protein (immunoglobulin) in less than 8 hours. FASEB J. 1988 Nov;2(14):3003–3009. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.14.3263291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura Y. The effects of ozone, nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide on the experimentally induced allergic respiratory disorder in guinea pigs. I. The effect on sensitization with albumin through the airway. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1970 Sep;102(3):430–437. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1970.102.3.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. L., Karras J. G., Holsapple M. P. Direct effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) on responses to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) by isolated murine B-cells. Immunopharmacology. 1993 Sep-Oct;26(2):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(93)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muranaka M., Suzuki S., Koizumi K., Takafuji S., Miyamoto T., Ikemori R., Tokiwa H. Adjuvant activity of diesel-exhaust particulates for the production of IgE antibody in mice. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 Apr;77(4):616–623. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagarkatti P. S., Sweeney G. D., Gauldie J., Clark D. A. Sensitivity to suppression of cytotoxic T cell generation by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) is dependent on the Ah genotype of the murine host. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;72(1):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(84)90261-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng C., Davis F. M., Sun L. K., Liou R. S., Kim Y. W., Chang T. W. A new isoform of human membrane-bound IgE. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):129–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel F., Krämer M., Scheibenbogen C., Rieger C. H. Effects of SO2 exposure on allergic sensitization in the guinea pig. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1988 Oct;82(4):527–534. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(88)90961-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staynov D. Z., Lee T. H. Expression of interleukin-5 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells after activation with phorbol myristate acetate. Immunology. 1992 Jan;75(1):196–201. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takafuji S., Suzuki S., Koizumi K., Tadokoro K., Miyamoto T., Ikemori R., Muranaka M. Diesel-exhaust particulates inoculated by the intranasal route have an adjuvant activity for IgE production in mice. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1987 Apr;79(4):639–645. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(87)80161-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takafuji S., Suzuki S., Koizumi K., Tadokoro K., Ohashi H., Muranaka M., Miyamoto T. Enhancing effect of suspended particulate matter on the IgE antibody production in mice. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1989;90(1):1–7. doi: 10.1159/000234990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takafuji S., Suzuki S., Muranaka M., Miyamoto T. Influence of environmental factors on IgE production. Ciba Found Symp. 1989;147:188–204. doi: 10.1002/9780470513866.ch12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thyphronitis G., Max E. E., Finkelman F. D. Generation and cloning of stable human IgE-secreting cells that have rearranged the C epsilon gene. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 1;146(5):1496–1502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner K. J. Epidemiology of the allergic response. Ciba Found Symp. 1989;147:205–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura M., Wang X. H., Ohmen J. D., Uyemura K., Rea T. H., Bloom B. R., Modlin R. L. Cytokine patterns of immunologically mediated tissue damage. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 15;149(4):1470–1475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetterström O., Nordvall S. L., Björkstén B., Ahlstedt S., Stelander M. Increased IgE antibody responses in rats exposed to tobacco smoke. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1985 May;75(5):594–598. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(85)90035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K., Clark E. A., Saxon A. CD40 stimulation provides an IFN-gamma-independent and IL-4-dependent differentiation signal directly to human B cells for IgE production. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 15;146(6):1836–1842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
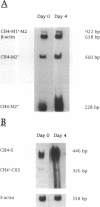
- Zhang K., Max E. E., Cheah H. K., Saxon A. Complex alternative RNA splicing of epsilon-immunoglobulin transcripts produces mRNAs encoding four potential secreted protein isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):456–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K., Saxon A., Max E. E. Two unusual forms of human immunoglobulin E encoded by alternative RNA splicing of epsilon heavy chain membrane exons. J Exp Med. 1992 Jul 1;176(1):233–243. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.1.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]