Abstract
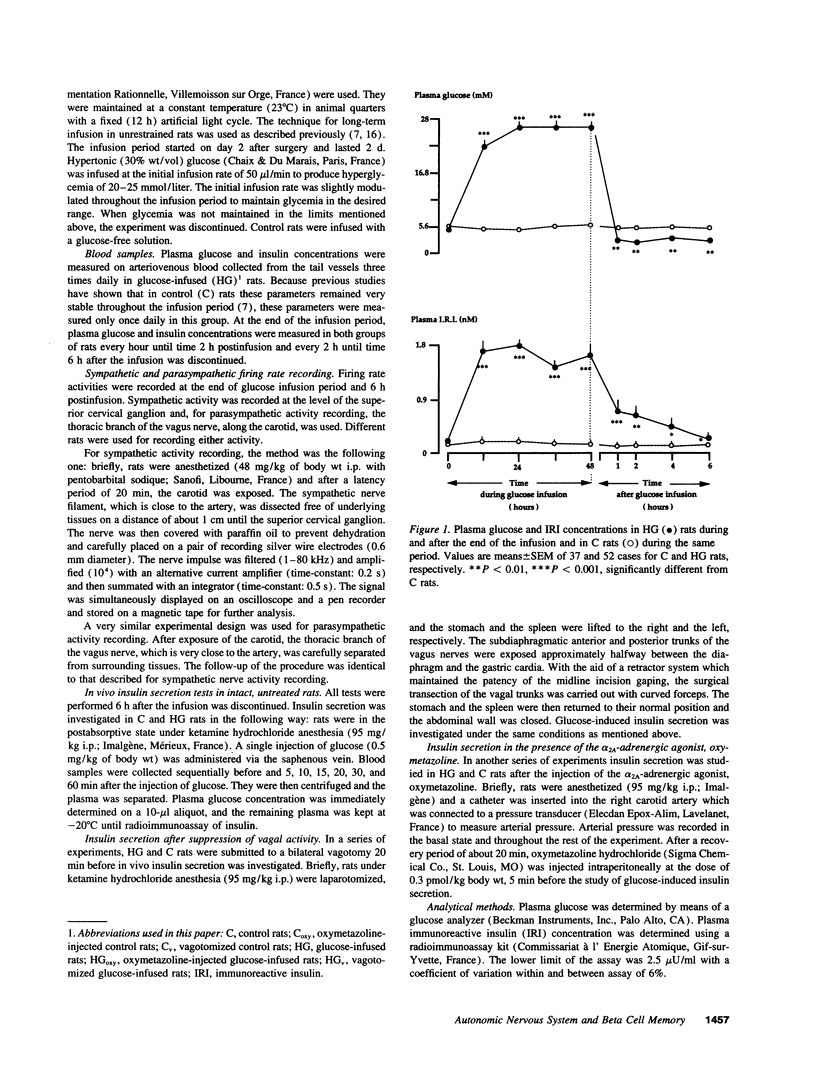
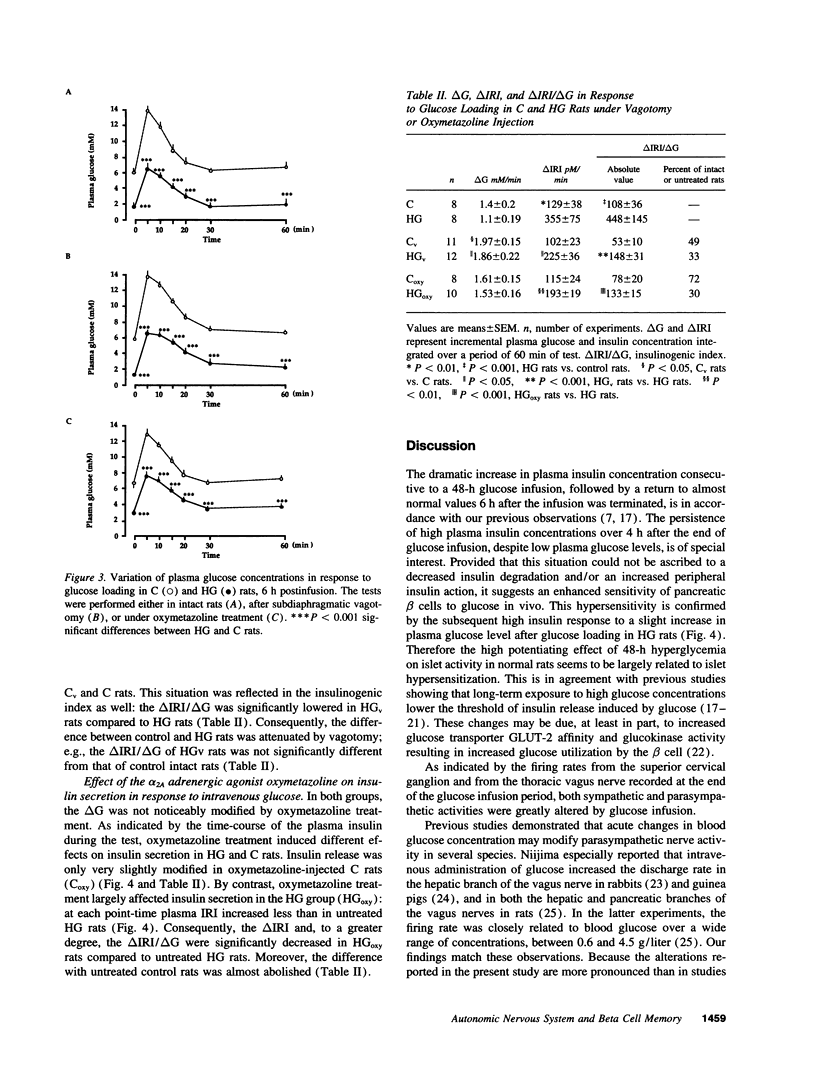
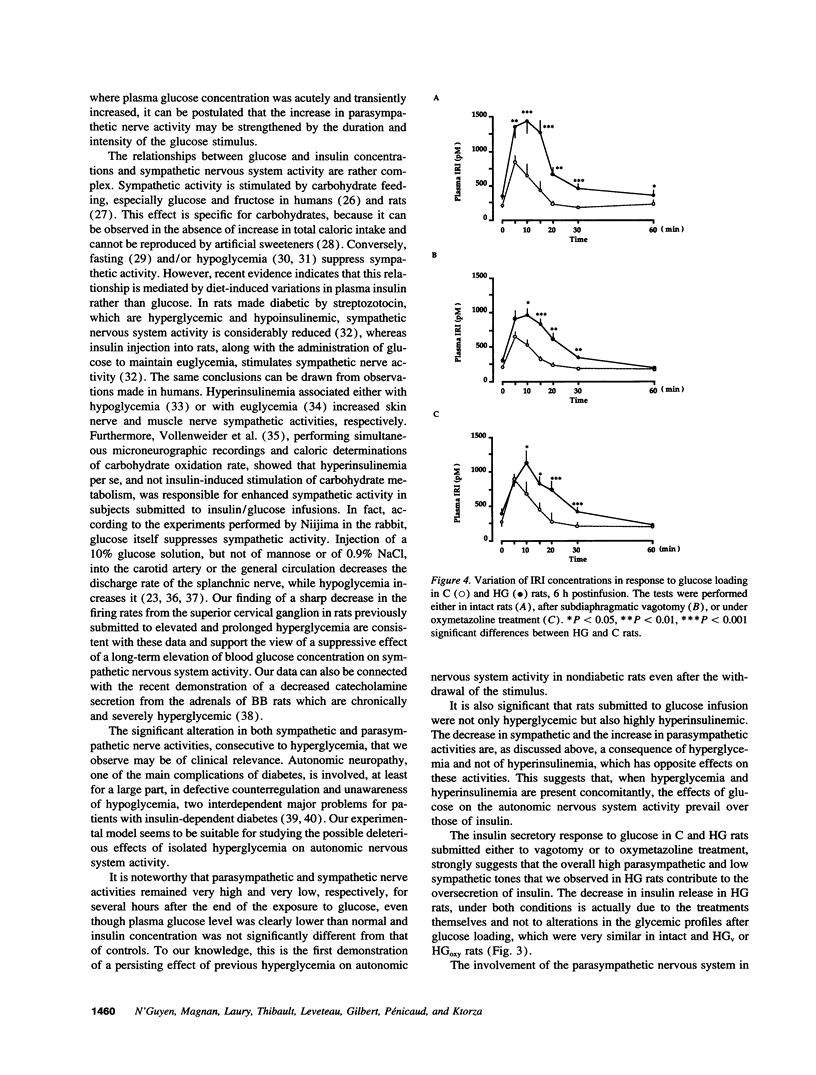
The fact that the potentiating effect of prolonged hyperglycemia on the subsequent insulin secretion is observed in vivo but not in vitro suggests the involvement of extrapancreatic factors in the in vivo memory of pancreatic beta cells to glucose. We have investigated the possible role of the autonomic nervous system. Rats were made hyperglycemic by a 48-h infusion with glucose (HG rats). At the end of glucose infusion as well as 6 h postinfusion, both parasympathetic and sympathetic nerve activities were profoundly altered: parasympathetic and sympathetic activities, assessed by the firing rate either of the thoracic vagus nerve or the superior cervical ganglion, were dramatically increased and decreased, respectively. Moreover, 6 h after the end of glucose infusion, insulin secretion in response to a glucose load was dramatically increased in HG rats compared to controls. To determine whether these changes could be responsible for the increased sensitivity of the beta cell to glucose, insulin release in response to glucose was measured in HG and control rats, either under subdiaphragmatic vagotomy or after administration of the alpha 2A-adrenergic agonist oxymetazoline. Both treatments partially abolished the hyperresponsiveness of the beta cell to glucose in HG rats. Therefore chronic hyperglycemia brings about changes in the activity of the autonomic nervous system, which in turn are responsible, at least in part, for the generation of enhanced beta cell responsiveness to glucose in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Latif A. A. Calcium-mobilizing receptors, polyphosphoinositides, and the generation of second messengers. Pharmacol Rev. 1986 Sep;38(3):227–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahrén B., Taborsky G. J., Jr, Porte D., Jr Neuropeptidergic versus cholinergic and adrenergic regulation of islet hormone secretion. Diabetologia. 1986 Dec;29(12):827–836. doi: 10.1007/BF00870137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson A. Long-term effects of glucose on insulin release and glucose oxidation by mouse pancreatic islets maintained in tissue culture. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;140(3):377–382. doi: 10.1042/bj1400377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel I., Niddam R., Langer S. Z. Involvement of alpha-2 adrenergic receptor subtypes in hyperglycemia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Sep;254(3):877–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atef N., Ktorza A., Picon L., Pénicaud L. Increased islet blood flow in obese rats: role of the autonomic nervous system. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 1):E736–E740. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1992.262.5.E736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berne C., Fagius J., Pollare T., Hjemdahl P. The sympathetic response to euglycaemic hyperinsulinaemia. Evidence from microelectrode nerve recordings in healthy subjects. Diabetologia. 1992 Sep;35(9):873–879. doi: 10.1007/BF00399935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berne C., Fagius J. Skin nerve sympathetic activity during insulin-induced hypoglycaemia. Diabetologia. 1986 Dec;29(12):855–860. doi: 10.1007/BF00870140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brelje T. C., Sorenson R. L. Nutrient and hormonal regulation of the threshold of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in isolated rat pancreases. Endocrinology. 1988 Sep;123(3):1582–1590. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-3-1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E. Potentiation of insulin release by glucose in man. I. Quantitative analysis of the enhancement of glucose-induced insulin secretion by pretreatment with glucose in normal subjects. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1975 Jul;79(3):483–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E., Gerich J. E. Glucose counterregulation, hypoglycemia, and intensive insulin therapy in diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jul 25;313(4):232–241. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198507253130405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efendić S., Cerasi E., Luft R., Gladnikoff G. Potentiation of glucose-induced insulin release by glucose in the isolated pancreas of fed and fasted rats. Diabetes. 1976 Oct;25(10):949–954. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.10.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grill V., Adamson U., Cerasi E. Immediate and time-dependent effects of glucose on insulin release from rat pancreatic tissue. Evidence for different mechanisms of action. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1034–1043. doi: 10.1172/JCI109002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M. A threshold distribution hypothesis for packet storage of insulin and its mathematical modeling. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):2047–2059. doi: 10.1172/JCI107011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeanrenaud B., Halimi S., van de Werve G. Neuro-endocrine disorders seen as triggers of the triad: obesity--insulin resistance--abnormal glucose tolerance. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1985;1(3):261–291. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610010303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn S. E., Bergman R. N., Schwartz M. W., Taborsky G. J., Jr, Porte D., Jr Short-term hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia improve insulin action but do not alter glucose action in normal humans. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):E518–E523. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1992.262.4.E518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ktorza A., Girard J. R., Kinebanyan M. F., Picon L. Hyperglycaemia induced by glucose infusion in the unrestrained pregnant rat during the last three days of gestation: metabolic and hormonal changes in the mother and the fetuses. Diabetologia. 1981 Dec;21(6):569–574. doi: 10.1007/BF00281551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landsberg L., Greff L., Gunn S., Young J. B. Adrenergic mechanisms in the metabolic adaptation to fasting and feeding: effects of phlorizin on diet-induced changes in sympathoadrenal activity in the rat. Metabolism. 1980 Nov;29(11 Suppl 1):1128–1137. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laury M. C., Takao F., Bailbe D., Penicaud L., Portha B., Picon L., Ktorza A. Differential effects of prolonged hyperglycemia on in vivo and in vitro insulin secretion in rats. Endocrinology. 1991 May;128(5):2526–2533. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-5-2526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahy J. L., Bonner-Weir S., Weir G. C. Minimal chronic hyperglycemia is a critical determinant of impaired insulin secretion after an incomplete pancreatectomy. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1407–1414. doi: 10.1172/JCI113470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahy J. L., Cooper H. E., Deal D. A., Weir G. C. Chronic hyperglycemia is associated with impaired glucose influence on insulin secretion. A study in normal rats using chronic in vivo glucose infusions. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):908–915. doi: 10.1172/JCI112389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marynissen G., Leclercq-Meyer V., Sener A., Malaisse W. J. Perturbation of pancreatic islet function in glucose-infused rats. Metabolism. 1990 Jan;39(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(90)90153-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niddam R., Angel I., Bidet S., Langer S. Z. Pharmacological characterization of alpha-2 adrenergic receptor subtype involved in the release of insulin from isolated rat pancreatic islets. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Sep;254(3):883–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niijima A. An electrophysiological study on the regulatory mechanism of blood sugar level in the rabbit. Brain Res. 1975 Apr 11;87(2-3):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90416-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niijima A. Blood glucose levels modulate efferent activity in the vagal supply to the rat liver. J Physiol. 1985 Jul;364:105–112. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niijima A. Glucose-sensitive afferent nerve fibres in the hepatic branch of the vagus nerve in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:315–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niki I., Tamagawa T., Niki H., Niki A., Koide T., Sakamoto N. Possible involvement of diacylglycerol-activated, Ca2+-dependent protein kinase in glucose memory of the rat pancreatic B-cell. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1988 Jun;118(2):204–208. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1180204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purrello F., Buscema M., Rabuazzo A. M., Caltabiano V., Forte F., Vinci C., Vetri M., Vigneri R. Glucose modulates glucose transporter affinity, glucokinase activity, and secretory response in rat pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes. 1993 Jan;42(1):199–205. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.1.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purrello F., Vetri M., Gatta C., Gullo D., Vigneri R. Effects of high glucose on insulin secretion by isolated rat islets and purified beta-cells and possible role of glycosylation. Diabetes. 1989 Nov;38(11):1417–1422. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.11.1417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibault C., Guettet C., Laury M. C., N'Guyen J. M., Tormo M. A., Bailbé D., Portha B., Pénicaud L., Ktorza A. In vivo and in vitro increased pancreatic beta-cell sensitivity to glucose in normal rats submitted to a 48-h hyperglycaemic period. Diabetologia. 1993 Jul;36(7):589–595. doi: 10.1007/BF00404066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmers K. I., Powell A. M., Voyles N. R., Solomon D., Wilkins S. D., Bhathena S., Recant L. Multiple alterations in insulin responses to glucose in islets from 48-h glucose-infused nondiabetic rats. Diabetes. 1990 Nov;39(11):1436–1444. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.11.1436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler D. A., Havlin C. E., Craft S., Cryer P. Mechanism of awareness of hypoglycemia. Perception of neurogenic (predominantly cholinergic) rather than neuroglycopenic symptoms. Diabetes. 1993 Dec;42(12):1791–1798. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.12.1791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollenweider P., Tappy L., Randin D., Schneiter P., Jéquier E., Nicod P., Scherrer U. Differential effects of hyperinsulinemia and carbohydrate metabolism on sympathetic nerve activity and muscle blood flow in humans. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jul;92(1):147–154. doi: 10.1172/JCI116542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walgren M. C., Young J. B., Kaufman L. N., Landsberg L. The effects of various carbohydrates on sympathetic activity in heart and interscapular brown adipose tissue of the rat. Metabolism. 1987 Jun;36(6):585–594. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(87)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward W. K., Halter J. B., Beard J. C., Porte D., Jr Adaptation of B and A cell function during prolonged glucose infusion in human subjects. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 1):E405–E411. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.246.5.E405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilke R. A., Riley D. A., Lelkes P. I., Hillard C. J. Decreased catecholamine secretion from the adrenal medullae of chronically diabetic BB-Wistar rats. Diabetes. 1993 Jun;42(6):862–868. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.6.862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. B., Landsberg L. Stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system during sucrose feeding. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):615–617. doi: 10.1038/269615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. B., Landsberg L. Suppression of sympathetic nervous system during fasting. Science. 1977 Jun 24;196(4297):1473–1475. doi: 10.1126/science.867049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. B., Landsberg L. Sympathoadrenal activity in fasting pregnant rats. Dissociation of adrenal medullary and sympathetic nervous system responses. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):109–116. doi: 10.1172/JCI109429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. B., Rowe J. W., Pallotta J. A., Sparrow D., Landsberg L. Enhanced plasma norepinephrine response to upright posture and oral glucose administration in elderly human subjects. Metabolism. 1980 Jun;29(6):532–539. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawalich W. S., Diaz V. A., Zawalich K. C. Role of phosphoinositide metabolism in induction of memory in isolated perifused rat islets. Am J Physiol. 1988 May;254(5 Pt 1):E609–E616. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.5.E609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawalich W. S., Zawalich K. C., Rasmussen H. Cholinergic agonists prime the beta-cell to glucose stimulation. Endocrinology. 1989 Nov;125(5):2400–2406. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-5-2400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



