Abstract
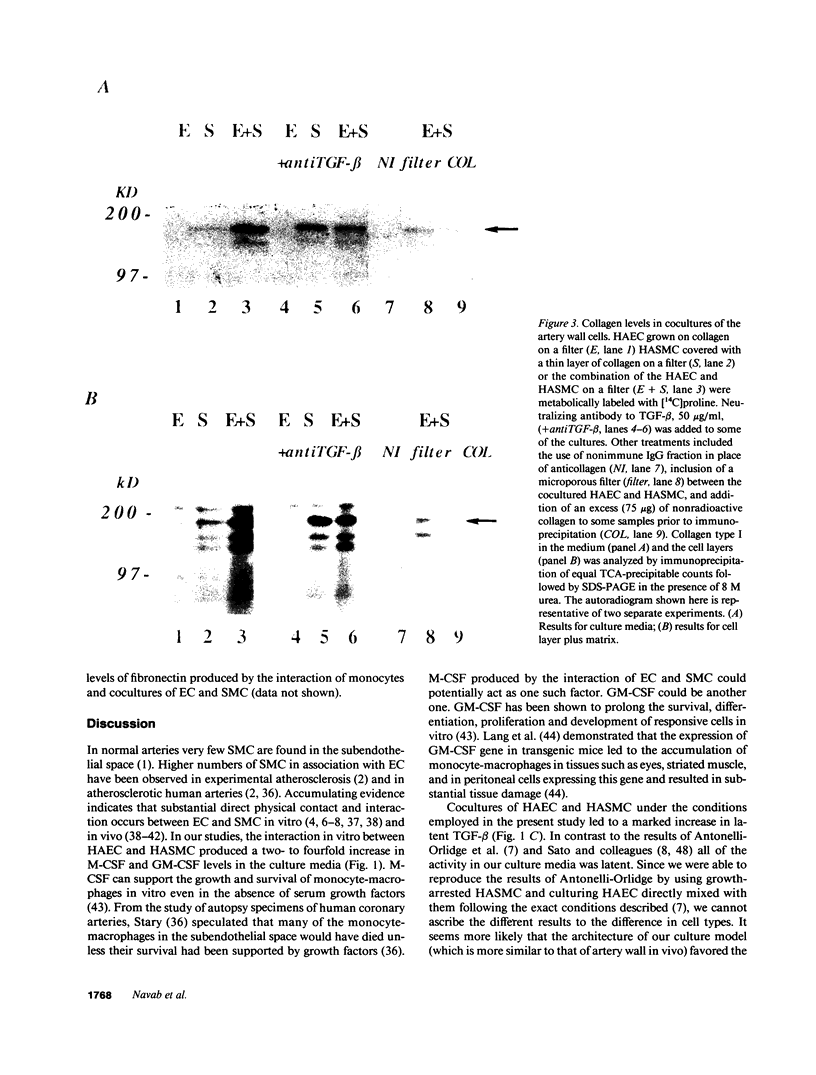
Medium from cocultures of human aortic endothelial cells (HAEC) and smooth muscle cells (HASMC) taken from the same donor contained approximately two- to fourfold more macrophage colony-stimulating factor, granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and up to 5.1-fold more transforming growth factor beta than could be accounted for by the sum of the activities of media from equivalent numbers of HAEC and HASMC cultured separately. After pulse labeling, immunoprecipitated [35S]fibronectin and [14C]collagen were also found to be substantially increased in the coculture compared to the sum of HAEC and HASMC cultured separately. The cocultivation of HAEC and HASMC resulted in a 2.7-fold increase in connexin43 messenger RNA. When direct physical contact between HAEC and HASMC was prevented by a membrane that was permeable to medium, the levels of [35S]fibronectin and [14C]collagen in the coculture were significantly reduced. Monocytes cultured alone contained low levels of [35S]fibronectin and [14C]collagen but when added to the coculture there was up to a 22-fold increase in [35S]fibronectin and a 1.9-fold increase in [14C]collagen compared to the coculture alone. The increase in fibronectin was prevented in the presence of neutralizing antibody to interleukin 1 and antibody to interleukin 6 by 45% and 67%, respectively. Addition of monocytes to cocultures also induced the levels of mRNA for connexin43 by 2.8-fold. We conclude that the interaction of HAEC, HASMC, and monocytes in coculture can result in marked increases in the levels of several biologically important molecules and that increased gap junction formation between the cells and interleukins 1 and 6 may be partially responsible for these changes.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O., Hamilton T. A. The cell biology of macrophage activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:283–318. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonelli-Orlidge A., Saunders K. B., Smith S. R., D'Amore P. A. An activated form of transforming growth factor beta is produced by cocultures of endothelial cells and pericytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4544–4548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARR L., DEWEY M. M., BERGER W. PROPAGATION OF ACTION POTENTIALS AND THE STRUCTURE OF THE NEXUS IN CARDIAC MUSCLE. J Gen Physiol. 1965 May;48:797–823. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.5.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey R. R., Peddie B. A., Davies P. R. Single dose fosfomycin trometamol (Monuril) for the treatment of women with bacterial cystitis. N Z Med J. 1988 Sep 14;101(853):582–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer E. C., Paul D. L., Goodenough D. A. Connexin43: a protein from rat heart homologous to a gap junction protein from liver. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2621–2629. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. R., Palade G. E. Studies on blood capillaries. I. General organization of blood capillaries in muscle. J Cell Biol. 1968 May;37(2):244–276. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.2.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corsaro C. M., Migeon B. R. Contact-mediated communication of ouabain resistance in mammalian cells in culture. Nature. 1977 Aug 25;268(5622):737–739. doi: 10.1038/268737a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. F., Truskey G. A., Warren H. B., O'Connor S. E., Eisenhaure B. H. Metabolic cooperation between vascular endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells in co-culture: changes in low density lipoprotein metabolism. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):871–879. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., de Rochemonteix B., Burrus B., Demczuk S., Dinarello C. A. Human recombinant interleukin 1 stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):645–648. doi: 10.1172/JCI112350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson E. S., Dennis P. A., Slakey L. L. Time course of release into the medium of newly synthesized proteins by cultured aortic endothelial cells. Role of serum in preventing proteolytic degradation. Arteriosclerosis. 1986 Nov-Dec;6(6):627–637. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.6.6.627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P. A., Lan S. F., Tanaka R. D., Fogelman A. M. Mevalonolactone inhibits the rate of synthesis and enhances the rate of degradation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7272–7275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eghbali B., Kessler J. A., Spray D. C. Expression of gap junction channels in communication-incompetent cells after stable transfection with cDNA encoding connexin 32. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1328–1331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias J. A., Lentz V. IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor synergistically stimulate fibroblast IL-6 production and stabilize IL-6 messenger RNA. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):161–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelman A. M., Elahi F., Sykes K., Van Lenten B. J., Territo M. C., Berliner J. A. Modification of the Recalde method for the isolation of human monocytes. J Lipid Res. 1988 Sep;29(9):1243–1247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golde D. W., Cline M. J. Identification of the colony-stimulating cell in human peripheral blood. J Clin Invest. 1972 Nov;51(11):2981–2983. doi: 10.1172/JCI107124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara T., Kono I., Nemoto K., Kashiwagi H., Onozaki K. Recombinant interleukin-1 triggers the increase of circulating fibronectin level in rats. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1989;89(4):376–380. doi: 10.1159/000234978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara T., Suzuki H., Kono I., Kashiwagi H., Akiyama Y., Onozaki K. Regulation of fibronectin synthesis by interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 in rat hepatocytes. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jan;136(1):39–47. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar D. P., Falcone D. J., Amberson J. B., Hefton J. M. Interaction of arterial cells. I. Endothelial cells alter cholesterol metabolism in co-cultured smooth muscle cells. J Lipid Res. 1985 Oct;26(10):1212–1223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar D. P., Marcus A. J., Hajjar K. A. Interactions of arterial cells. Studies on the mechanisms of endothelial cell modulation of cholesterol metabolism in co-cultured smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):6976–6981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hüttner I., Boutet M., More R. H. Gap junctions in arterial endothelium. J Cell Biol. 1973 Apr;57(1):247–252. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignotz R. A., Massagué J. Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates the expression of fibronectin and collagen and their incorporation into the extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4337–4345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A. Construction of an artificial blood vessel wall from cultured endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1882–1886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVENE C. I., POOLE J. C. The collagen content of the normal and atherosclerotic human aortic intima. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Oct;43:469–471. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanser M. E., Brown G. E. Stimulation of rat hepatocyte fibronectin production by monocyte-conditioned medium is due to interleukin 6. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1781–1786. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D. M., Haudenschild C. C., Beyer E. C. Gap junction messenger RNA expression by vascular wall cells. Circ Res. 1990 Apr;66(4):1074–1080. doi: 10.1161/01.res.66.4.1074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lash J. A., Critser E. S., Pressler M. L. Cloning of a gap junctional protein from vascular smooth muscle and expression in two-cell mouse embryos. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13113–13117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liau G., Chan L. M. Regulation of extracellular matrix RNA levels in cultured smooth muscle cells. Relationship to cellular quiescence. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):10315–10320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Permeability of membrane junctions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):441–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch S. E., Colvin R. B., Antoniades H. N. Growth factors in wound healing. Single and synergistic effects on partial thickness porcine skin wounds. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):640–646. doi: 10.1172/JCI114210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madri J. A., Pratt B. M., Tucker A. M. Phenotypic modulation of endothelial cells by transforming growth factor-beta depends upon the composition and organization of the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1375–1384. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majack R. A., Majesky M. W., Goodman L. V. Role of PDGF-A expression in the control of vascular smooth muscle cell growth by transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;111(1):239–247. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.1.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayne R. Collagenous proteins of blood vessels. Arteriosclerosis. 1986 Nov-Dec;6(6):585–593. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.6.6.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey T. A., Falcone D. J., Brayton C. F., Agarwal L. A., Welt F. G., Weksler B. B. Transforming growth factor-beta activity is potentiated by heparin via dissociation of the transforming growth factor-beta/alpha 2-macroglobulin inactive complex. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):441–448. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecham R. P., Whitehouse L. A., Wrenn D. S., Parks W. C., Griffin G. L., Senior R. M., Crouch E. C., Stenmark K. R., Voelkel N. F. Smooth muscle-mediated connective tissue remodeling in pulmonary hypertension. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):423–426. doi: 10.1126/science.3603030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrilees M. J., Scott L. Interaction of aortic endothelial and smooth muscle cells in culture. Effect on glycosaminoglycan levels. Atherosclerosis. 1981 May;39(2):147–161. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(81)90064-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Begley C. G., Johnson G. R., Nicola N. A., Vadas M. A., Lopez A. F., Williamson D. J., Wong G. G., Clark S. C., Wang E. A. Biologic properties in vitro of a recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Blood. 1986 Jan;67(1):37–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. The molecular control of cell division, differentiation commitment and maturation in haemopoietic cells. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):27–30. doi: 10.1038/339027a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Mossaz A., Ryser J. E., Orci L., Vassalli P. Leukocyte interleukins induce cultured endothelial cells to produce a highly organized, glycosaminoglycan-rich pericellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1706–1715. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navab M., Hough G. P., Berliner J. A., Frank J. A., Fogelman A. M., Haberland M. E., Edwards P. A. Rabbit beta-migrating very low density lipoprotein increases endothelial macromolecular transport without altering electrical resistance. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):389–397. doi: 10.1172/JCI112589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navab M., Hough G. P., Stevenson L. W., Drinkwater D. C., Laks H., Fogelman A. M. Monocyte migration into the subendothelial space of a coculture of adult human aortic endothelial and smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):1853–1863. doi: 10.1172/JCI113802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navab M., Hough G. P., Van Lenten B. J., Berliner J. A., Fogelman A. M. Low density lipoproteins transfer bacterial lipopolysaccharides across endothelial monolayers in a biologically active form. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):601–605. doi: 10.1172/JCI113359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul D. L. Molecular cloning of cDNA for rat liver gap junction protein. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):123–134. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajavashisth T. B., Andalibi A., Territo M. C., Berliner J. A., Navab M., Fogelman A. M., Lusis A. J. Induction of endothelial cell expression of granulocyte and macrophage colony-stimulating factors by modified low-density lipoproteins. Nature. 1990 Mar 15;344(6263):254–257. doi: 10.1038/344254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajavashisth T. B., Eng R., Shadduck R. K., Waheed A., Ben-Avram C. M., Shively J. E., Lusis A. J. Cloning and tissue-specific expression of mouse macrophage colony-stimulating factor mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1157–1161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen L. M., Heickendorff L. Quantification of fibronectin in extracts of human aortae by an ELISA. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1989 May;49(3):205–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Assoian R. K., Smith J. M., Roche N. S., Wakefield L. M., Heine U. I., Liotta L. A., Falanga V., Kehrl J. H. Transforming growth factor type beta: rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesis in vivo and stimulation of collagen formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4167–4171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts C. J., Birkenmeier T. M., McQuillan J. J., Akiyama S. K., Yamada S. S., Chen W. T., Yamada K. M., McDonald J. A. Transforming growth factor beta stimulates the expression of fibronectin and of both subunits of the human fibronectin receptor by cultured human lung fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4586–4592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F., Roberts A. B., Danielpour D., Dart L. L., Sporn M. B., Dawid I. B. Mesoderm induction in amphibians: the role of TGF-beta 2-like factors. Science. 1988 Feb 12;239(4841 Pt 1):783–785. doi: 10.1126/science.3422517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis--an update. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 20;314(8):488–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602203140806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH E. B. THE INFLUENCE OF AGE AND ATHEROSCLEROSIS ON THE CHEMISTRY OF AORTIC INTIMA.2. COLLAGEN AND MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDES. J Atheroscler Res. 1965 Mar-Apr;5(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1319(65)80065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Rifkin D. B. Inhibition of endothelial cell movement by pericytes and smooth muscle cells: activation of a latent transforming growth factor-beta 1-like molecule by plasmin during co-culture. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):309–315. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Tsuboi R., Lyons R., Moses H., Rifkin D. B. Characterization of the activation of latent TGF-beta by co-cultures of endothelial cells and pericytes or smooth muscle cells: a self-regulating system. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):757–763. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segarini P. R., Seyedin S. M. The high molecular weight receptor to transforming growth factor-beta contains glycosaminoglycan chains. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8366–8370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shekhonin B. V., Domogatsky S. P., Idelson G. L., Koteliansky V. E., Rukosuev V. S. Relative distribution of fibronectin and type I, III, IV, V collagens in normal and atherosclerotic intima of human arteries. Atherosclerosis. 1987 Sep;67(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(87)90259-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spagnoli L. G., Villaschi S., Neri L., Palmieri G. Gap junctions in myo-endothelial bridges of rabbit carotid arteries. Experientia. 1982 Jan 15;38(1):124–125. doi: 10.1007/BF01944566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Autocrine growth factors and cancer. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):745–747. doi: 10.1038/313745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Peptide growth factors are multifunctional. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):217–219. doi: 10.1038/332217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli C. H., Bissell M. J. Expression of extracellular matrix components is regulated by substratum. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):1405–1415. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subak-Sharpe H., Bürk R. R., Pitts J. D. Metabolic co-operation between biochemically marked mammalian cells in tissue culture. J Cell Sci. 1969 Mar;4(2):353–367. doi: 10.1242/jcs.4.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker R. F., Shipley G. D., Moses H. L., Holley R. W. Growth inhibitor from BSC-1 cells closely related to platelet type beta transforming growth factor. Science. 1984 Nov 9;226(4675):705–707. doi: 10.1126/science.6093254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield L. M., Smith D. M., Masui T., Harris C. C., Sporn M. B. Distribution and modulation of the cellular receptor for transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):965–975. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]