Abstract
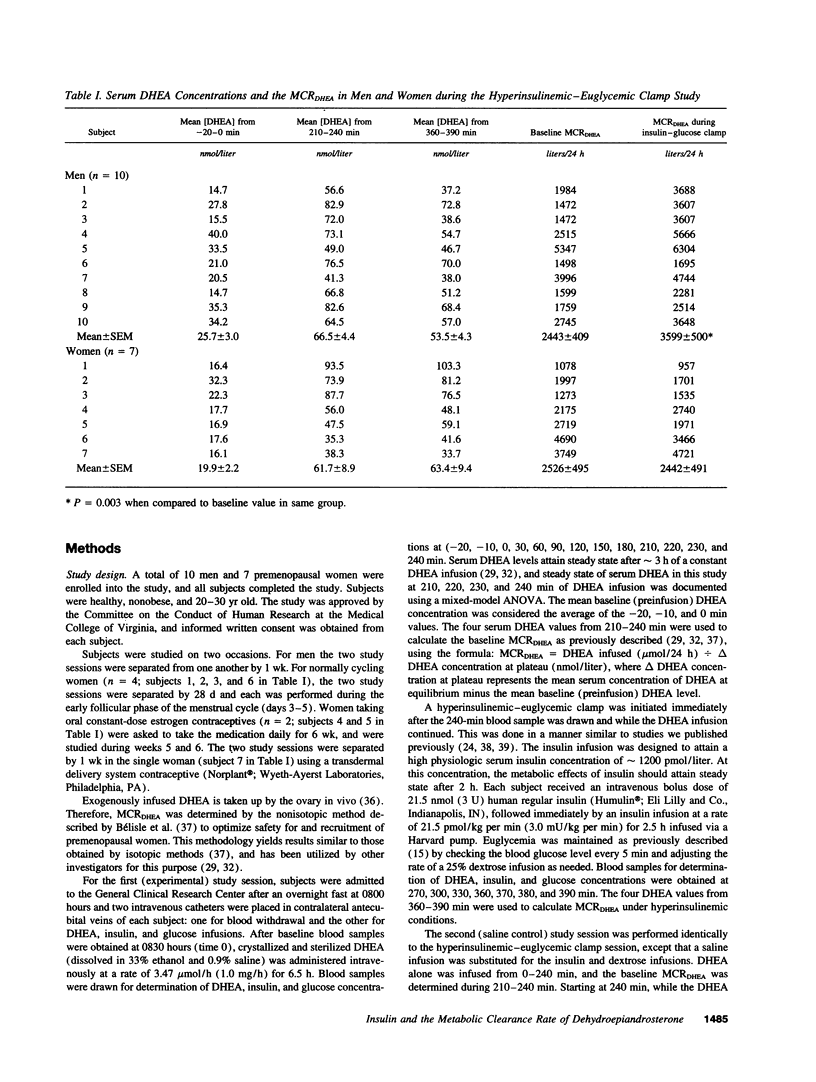
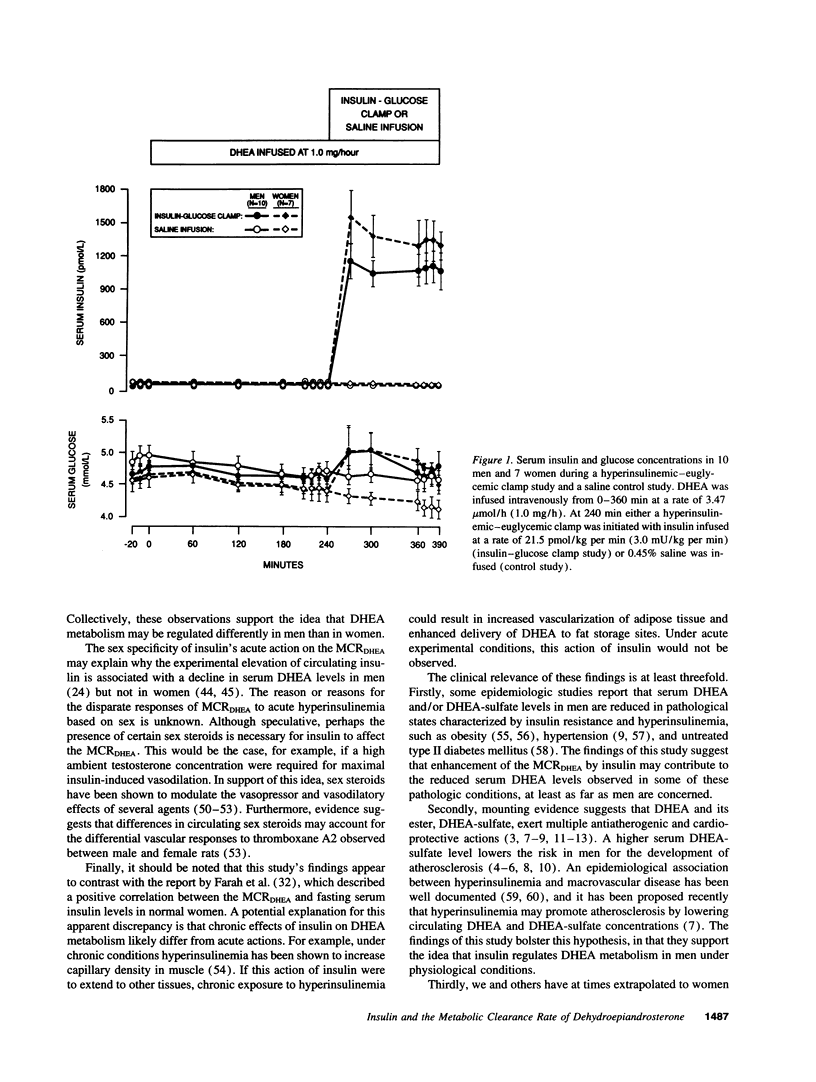
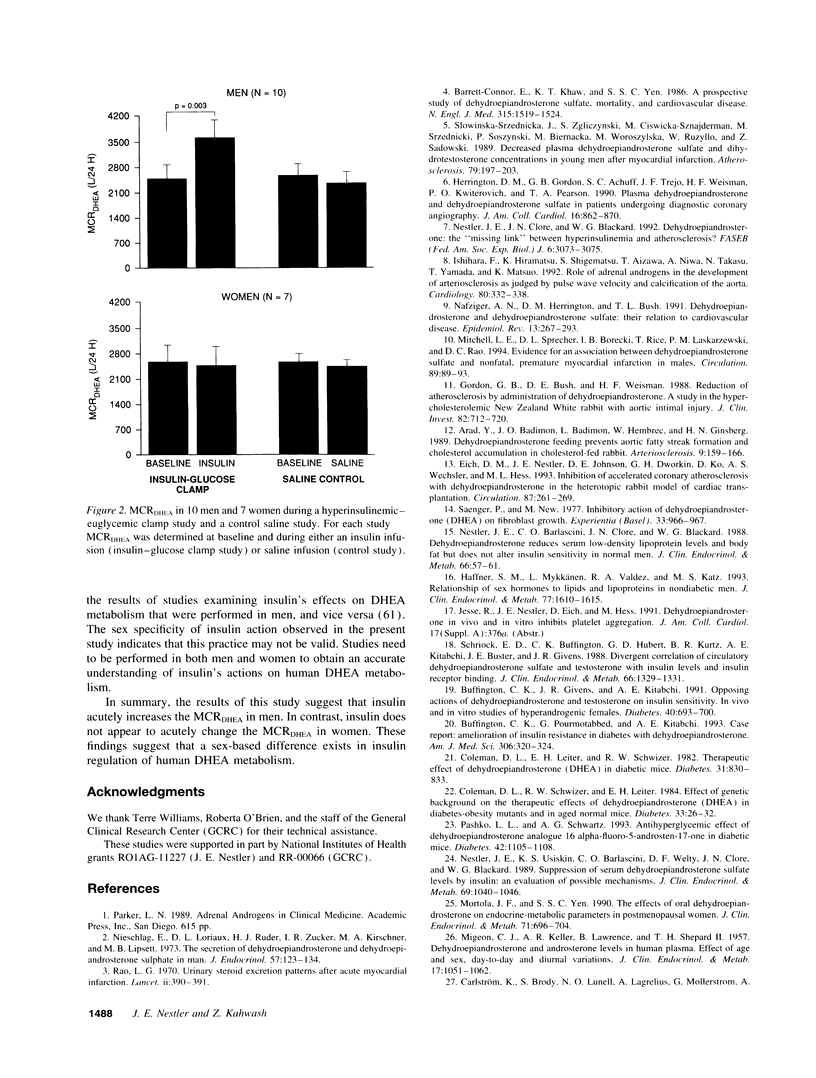
To test the hypothesis that insulin acutely enhances the metabolic clearance rate (MCR) of dehydroepiandrosterone in humans, the effect of a short-term insulin infusion on the MCR of dehydroepiandrosterone was assessed in 10 men and 7 women. After an overnight fast, dehydroepiandrosterone was infused at 3.47 mumol/h for 6.5 h. At 240 min, a hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp was begun by infusing insulin at 21.5 pmol/kg per min for 2.5 h. MCR of dehydroepiandrosterone was calculated at baseline (210-240 min) and during the insulin infusion (360-390 min). A control study was conducted at least 1 wk later, in which 0.45% saline was substituted for the hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp. During the insulin clamp study, serum insulin rose from 34 +/- 2 to 1084 +/- 136 pmol/liter (P = 0.0001) in men and from 40 +/- 5 to 1357 +/- 175 pmol/liter (P = 0.0003) in women, while serum glucose remained constant in both groups. MCR of dehydroepiandrosterone rose in men during the insulin infusion from 2443 +/- 409 to 3599 +/- 500 liters/24 h (P = 0.003), but did not change during the control saline infusion. In contrast, MCR of dehydroepiandrosterone in women did not change in the insulin clamp study during insulin infusion (2526 +/- 495 liters/24 h at baseline vs. 2442 +/- 491 liters/24 h during insulin infusion; P = 0.78). These findings suggest that insulin acutely increases the MCR of dehydroepiandrosterone in men but not in women.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arad Y., Badimon J. J., Badimon L., Hembree W. C., Ginsberg H. N. Dehydroepiandrosterone feeding prevents aortic fatty streak formation and cholesterol accumulation in cholesterol-fed rabbit. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Mar-Apr;9(2):159–166. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.2.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett-Connor E., Khaw K. T., Yen S. S. A prospective study of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, mortality, and cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 1986 Dec 11;315(24):1519–1524. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198612113152405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett-Connor E. Lower endogenous androgen levels and dyslipidemia in men with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Nov 15;117(10):807–811. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-10-807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buffington C. K., Givens J. R., Kitabchi A. E. Opposing actions of dehydroepiandrosterone and testosterone on insulin sensitivity. In vivo and in vitro studies of hyperandrogenic females. Diabetes. 1991 Jun;40(6):693–700. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.6.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buffington C. K., Pourmotabbed G., Kitabchi A. E. Case report: amelioration of insulin resistance in diabetes with dehydroepiandrosterone. Am J Med Sci. 1993 Nov;306(5):320–324. doi: 10.1097/00000441-199311000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bélisle S., Schiff I., Tulchinsky D. The use of constant infusion of unlabeled dehydroepiandrosterone for the assessment of its metabolic clearance rate, its half-life, and its conversion into estrogens. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Jan;50(1):117–121. doi: 10.1210/jcem-50-1-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlström K., Brody S., Lunell N. O., Lagrelius A., Möllerström G., Pousette A., Rannevik G., Stege R., von Schoultz B. Dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate and dehydroepiandrosterone in serum: differences related to age and sex. Maturitas. 1988 Dec;10(4):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0378-5122(88)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L., Leiter E. H., Schwizer R. W. Therapeutic effects of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) in diabetic mice. Diabetes. 1982 Sep;31(9):830–833. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.9.830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L., Schwizer R. W., Leiter E. H. Effect of genetic background on the therapeutic effects of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) in diabetes-obesity mutants and in aged normal mice. Diabetes. 1984 Jan;33(1):26–32. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.1.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Ferrannini E. Insulin resistance. A multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care. 1991 Mar;14(3):173–194. doi: 10.2337/diacare.14.3.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. P., Grainger D. A., Laudano A. J., Starick-Zych K., DeFronzo R. A. Effect of acute physiological elevations of insulin on circulating androgen levels in nonobese women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Apr;72(4):883–887. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-4-883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eich D. M., Nestler J. E., Johnson D. E., Dworkin G. H., Ko D., Wechsler A. S., Hess M. L. Inhibition of accelerated coronary atherosclerosis with dehydroepiandrosterone in the heterotopic rabbit model of cardiac transplantation. Circulation. 1993 Jan;87(1):261–269. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.87.1.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison P. T. Correlations of basal oestrogens with adrenal androgens and relative weight in normal women. Ann Hum Biol. 1984 Jul-Aug;11(4):327–336. doi: 10.1080/03014468400007231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Hoffmann R. G., Kalkhoff R. K., Kissebah A. H. Relationship of androgenic activity to body fat topography, fat cell morphology, and metabolic aberrations in premenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Aug;57(2):304–310. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-2-304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farah M. J., Givens J. R., Kitabchi A. E. Bimodal correlation between the circulating insulin level and the production rate of dehydroepiandrosterone: positive correlation in controls and negative correlation in the polycystic ovary syndrome with acanthosis nigricans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Apr;70(4):1075–1081. doi: 10.1210/jcem-70-4-1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farhat M. Y., Ramwell P. W. Estradiol potentiates the vasopressor response of the isolated perfused rat lung to the thromboxane mimic U-46619. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 May;261(2):686–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehér T., Halmy L. Dehydroepiandrosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate dynamics in obesity. Can J Biochem. 1975 Feb;53(2):215–222. doi: 10.1139/o75-030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. D., Bierbrier G. S. Insulin-mediated vasodilation: impairment with increased blood pressure and body mass. Lancet. 1993 Sep 18;342(8873):707–709. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91708-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon G. B., Bush D. E., Weisman H. F. Reduction of atherosclerosis by administration of dehydroepiandrosterone. A study in the hypercholesterolemic New Zealand white rabbit with aortic intimal injury. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):712–720. doi: 10.1172/JCI113652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffner S. M., Mykkänen L., Valdez R. A., Katz M. S. Relationship of sex hormones to lipids and lipoproteins in nondiabetic men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Dec;77(6):1610–1615. doi: 10.1210/jcem.77.6.8263149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haning R. V., Jr, Hackett R. J., Flood C. A., Loughlin J. S., Zhao Q. Y., Longcope C. Plasma dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate serves as a prehormone for 48% of follicular fluid testosterone during treatment with menotropins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 May;76(5):1301–1307. doi: 10.1210/jcem.76.5.8496321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrikx A., Heyns W., De Moor P. Influence of a low-calorie diet and fasting on the metabolism of dehydroepiandosterone sulfate in adult obese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Nov;28(11):1525–1533. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-11-1525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington D. M., Gordon G. B., Achuff S. C., Trejo J. F., Weisman H. F., Kwiterovich P. O., Jr, Pearson T. A. Plasma dehydroepiandrosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate in patients undergoing diagnostic coronary angiography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990 Nov;16(6):862–870. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(10)80334-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmäng A., Brzezinska Z., Björntorp P. Effects of hyperinsulinemia on muscle fiber composition and capitalization in rats. Diabetes. 1993 Jul;42(7):1073–1081. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.7.1073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara F., Hiramatsu K., Shigematsu S., Aizawa T., Niwa A., Takasu N., Yamada T., Matsuo K. Role of adrenal androgens in the development of arteriosclerosis as judged by pulse wave velocity and calcification of the aorta. Cardiology. 1992;80(5-6):332–338. doi: 10.1159/000175022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juncos L. A., Ito S. Disparate effects of insulin on isolated rabbit afferent and efferent arterioles. J Clin Invest. 1993 Oct;92(4):1981–1985. doi: 10.1172/JCI116792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A. M., Seidel C. L., Allen J. C., O'Neil R. G., Shelat H., Song T. Insulin reduces contraction and intracellular calcium concentration in vascular smooth muscle. Hypertension. 1993 Nov;22(5):735–742. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.22.5.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner M. A., Samojlik E., Silber D. A comparison of androgen production and clearance in hirsute and obese women. J Steroid Biochem. 1983 Jul;19(1B):607–614. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(83)90225-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz B. R., Givens J. R., Komindr S., Stevens M. D., Karas J. G., Bittle J. B., Judge D., Kitabchi A. E. Maintenance of normal circulating levels of delta 4-androstenedione and dehydroepiandrosterone in simple obesity despite increased metabolic clearance rates: evidence for a servo-control mechanism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Jun;64(6):1261–1267. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-6-1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A., Krehl W. A. A possible interrelation between glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and dehydroepiandrosterone in obesity. Lancet. 1967 Sep 2;2(7514):485–487. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91654-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIGEON C. J., KELLER A. R., LAWRENCE B., SHEPARD T. H., 2nd Dehydroepiandrosterone and androsterone levels in human plasma: effect of age and sex; day-to-day and diurnal variations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1957 Sep;17(9):1051–1062. doi: 10.1210/jcem-17-9-1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda A., Mathur R., Halushka P. V. Testosterone increases thromboxane A2 receptors in cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1991 Sep;69(3):638–643. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.3.638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills T. M., Wiedmeier V. T., Stopper V. S. Androgen maintenance of erectile function in the rat penis. Biol Reprod. 1992 Mar;46(3):342–348. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod46.3.342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell L. E., Sprecher D. L., Borecki I. B., Rice T., Laskarzewski P. M., Rao D. C. Evidence for an association between dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate and nonfatal, premature myocardial infarction in males. Circulation. 1994 Jan;89(1):89–93. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.89.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortola J. F., Yen S. S. The effects of oral dehydroepiandrosterone on endocrine-metabolic parameters in postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Sep;71(3):696–704. doi: 10.1210/jcem-71-3-696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nafziger A. N., Herrington D. M., Bush T. L. Dehydroepiandrosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate: their relation to cardiovascular disease. Epidemiol Rev. 1991;13:267–293. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler J. E., Barlascini C. O., Clore J. N., Blackard W. G. Dehydroepiandrosterone reduces serum low density lipoprotein levels and body fat but does not alter insulin sensitivity in normal men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Jan;66(1):57–61. doi: 10.1210/jcem-66-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler J. E., Beer N. A., Jakubowicz D. J., Beer R. M. Effects of a reduction in circulating insulin by metformin on serum dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate in nondiabetic men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994 Mar;78(3):549–554. doi: 10.1210/jcem.78.3.8126125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler J. E., Clore J. N., Blackard W. G. Dehydroepiandrosterone: the "missing link" between hyperinsulinemia and atherosclerosis? FASEB J. 1992 Sep;6(12):3073–3075. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.12.1387859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler J. E., Clore J. N., Blackard W. G. Metabolism and actions of dehydroepiandrosterone in humans. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;40(4-6):599–605. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(91)90282-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler J. E., Clore J. N., Strauss J. F., 3rd, Blackard W. G. The effects of hyperinsulinemia on serum testosterone, progesterone, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, and cortisol levels in normal women and in a woman with hyperandrogenism, insulin resistance, and acanthosis nigricans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Jan;64(1):180–184. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-1-180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler J. E., McClanahan M. A., Clore J. N., Blackard W. G. Insulin inhibits adrenal 17,20-lyase activity in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Feb;74(2):362–367. doi: 10.1210/jcem.74.2.1730815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler J. E., Usiskin K. S., Barlascini C. O., Welty D. F., Clore J. N., Blackard W. G. Suppression of serum dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate levels by insulin: an evaluation of possible mechanisms. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Nov;69(5):1040–1046. doi: 10.1210/jcem-69-5-1040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieschlag E., Loriaux D. L., Ruder H. J., Zucker I. R., Kirschner M. A., Lipsett M. B. The secretion of dehydroepiandrosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate in man. J Endocrinol. 1973 Apr;57(1):123–134. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0570123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowaczynski W., Fragachan F., Silah J., Millette B., Genest J. Further evidence of altered adrenocortical function in hypertension. Dehydroepiandrosterone excretion rate. Can J Biochem. 1968 Sep;46(9):1031–1038. doi: 10.1139/o68-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orentreich N., Brind J. L., Rizer R. L., Vogelman J. H. Age changes and sex differences in serum dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate concentrations throughout adulthood. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Sep;59(3):551–555. doi: 10.1210/jcem-59-3-551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pashko L. L., Schwartz A. G. Antihyperglycemic effect of dehydroepiandrosterone analogue 16 alpha-fluoro-5-androsten-17-one in diabetic mice. Diabetes. 1993 Aug;42(8):1105–1108. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.8.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao L. G. Urinary steroid-excretion patterns after acute myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1970 Aug 22;2(7669):390–391. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. 1988 Dec;37(12):1595–1607. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.12.1595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice T., Sprecher D. L., Borecki I. B., Mitchell L. E., Laskarzewski P. M., Rao D. C. The Cincinnati Myocardial Infarction and Hormone Family Study: family resemblance for dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate in control and myocardial infarction families. Metabolism. 1993 Oct;42(10):1284–1290. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(93)90126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saenger P., New M. Inhibitory action of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) on fibroblast growth. Experientia. 1977 Jul 15;33(7):966–967. doi: 10.1007/BF01951309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schriock E. D., Buffington C. K., Hubert G. D., Kurtz B. R., Kitabchi A. E., Buster J. E., Givens J. R. Divergent correlations of circulating dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate and testosterone with insulin levels and insulin receptor binding. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Jun;66(6):1329–1331. doi: 10.1210/jcem-66-6-1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonka J. Dehydroepiandrosterone. Metabolic effects. Acta Univ Carol Med Monogr. 1976;71:1-137, 146-71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart C. A., Nagamani M. Insulin infusion acutely augments ovarian androgen production in normal women. Fertil Steril. 1990 Nov;54(5):788–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Słowínska-Srzednicka J., Zgliczyński S., Ciświcka-Sznajderman M., Srzednicki M., Soszyński P., Biernacka M., Woroszyłska M., Ruzyło W., Sadowski Z. Decreased plasma dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate and dihydrotestosterone concentrations in young men after myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis. 1989 Oct;79(2-3):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(89)90124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollenweider P., Tappy L., Randin D., Schneiter P., Jéquier E., Nicod P., Scherrer U. Differential effects of hyperinsulinemia and carbohydrate metabolism on sympathetic nerve activity and muscle blood flow in humans. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jul;92(1):147–154. doi: 10.1172/JCI116542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang A., Altura B. T., Altura B. M. Sexual dimorphism of vascular smooth muscle responsiveness is dependent on anions and estrogen. Steroids. 1991 Oct;56(10):524–526. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(91)90118-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumoff B. V., Bradlow H. L. Sex difference in the metabolism of dehydroisoandrosterone sulfate. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Aug;51(2):334–336. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-2-334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumoff B., Rosenfeld R. S., Strain G. W., Levin J., Fukushima D. K. Sex differences in the twenty-four-hour mean plasma concentrations of dehydroisoandrosterone (DHA) and dehydroisoandrosterone sulfate (DHAS) and the DHA to DHAS ratio in normal adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Aug;51(2):330–333. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-2-330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


