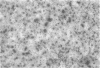
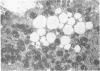
Abstract
Long-Evans Cinnamon (LEC) rats, an inbred strain of a mutant rat isolated from Long-Evans rats, develop hereditary hepatitis. To elucidate the role of copper metabolism in the development of the hepatitis in LEC rats, we examined the copper concentration in the tissues and serum levels of copper and ceruloplasmin. Copper concentration in the liver of LEC rats was over 40 times that of normal Long-Evans Agouti (LEA) rats, while the serum ceruloplasmin and copper concentrations in LEC rats decreased significantly. The hepatocytes of LEC rats show steatosis in cytoplasm and pleomorphism of mitochondria, resembling the histologic features of the liver in Wilson's disease. These findings suggest that the hereditary hepatitis in LEC rats is closely associated with copper toxicity, and may be dealing with a rat form of Wilson's disease. Thus the LEC rats will provide a unique and useful animal model for clarifying the mechanism and for developing treatment strategies for Wilson's disease and other abnormal copper metabolism in humans.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEARN A. G. Genetic and biochemical aspects of Wilson's disease. Am J Med. 1953 Oct;15(4):442–449. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(53)90134-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biempica L., Rauch H., Quintana N., Sternlieb I. Morphologic and chemical studies on a murine mutation (toxic milk mice) resulting in hepatic copper toxicosis. Lab Invest. 1988 Oct;59(4):500–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frommer D. J. Defective biliary excretion of copper in Wilson's disease. Gut. 1974 Feb;15(2):125–129. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.2.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydman M., Bonné-Tamir B., Farrer L. A., Conneally P. M., Magazanik A., Ashbel S., Goldwitch Z. Assignment of the gene for Wilson disease to chromosome 13: linkage to the esterase D locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1819–1821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda R., Yoshida M. C., Sasaki M., Dempo K., Mori M. High susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinoma development in LEC rats with hereditary hepatitis. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1988 Jul;79(7):828–835. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1988.tb00044.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nartey N. O., Frei J. V., Cherian M. G. Hepatic copper and metallothionein distribution in Wilson's disease (hepatolenticular degeneration). Lab Invest. 1987 Oct;57(4):397–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polio J., Enriquez R. E., Chow A., Wood W. M., Atterbury C. E. Hepatocellular carcinoma in Wilson's disease. Case report and review of the literature. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1989 Apr;11(2):220–224. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198904000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch H. Toxic milk, a new mutation affecting cooper metabolism in the mouse. J Hered. 1983 May-Jun;74(3):141–144. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a109751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche-Sicot J., Benhamou J. P. Acute intravascular hemolysis and acute liver failure associated as a first manifestation of Wilson's disease. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Mar;86(3):301–303. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-3-301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilsky M. L., Blank R. R., Czaja M. J., Zern M. A., Scheinberg I. H., Stockert R. J., Sternlieb I. Hepatocellular copper toxicity and its attenuation by zinc. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1562–1568. doi: 10.1172/JCI114333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schosinsky K. H., Lehmann H. P., Beeler M. F. Measurement of ceruloplasmin from its oxidase activity in serum by use of o-dianisidine dihydrochloride. Clin Chem. 1974 Dec;20(12):1556–1563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternlieb I., Scheinberg I. H. The role of radiocopper in the diagnosis of Wilson's disease. Gastroenterology. 1979 Jul;77(1):138–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su L. C., Ravanshad S., Owen C. A., Jr, McCall J. T., Zollman P. E., Hardy R. M. A comparison of copper-loading disease in Bedlington terriers and Wilson's disease in humans. Am J Physiol. 1982 Sep;243(3):G226–G230. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1982.243.3.G226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeichi N., Kobayashi H., Yoshida M. C., Sasaki M., Dempo K., Mori M. Spontaneous hepatitis in Long-Evans rats. A potential animal model for fulminant hepatitis in man. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1988 Nov;38(11):1369–1375. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1988.tb01080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALSHE J. M. Penicillamine, a new oral therapy for Wilson's disease. Am J Med. 1956 Oct;21(4):487–495. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(56)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walshe J. M. Treatment of Wilson's disease with trientine (triethylene tetramine) dihydrochloride. Lancet. 1982 Mar 20;1(8273):643–647. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92201-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M. C., Masuda R., Sasaki M., Takeichi N., Kobayashi H., Dempo K., Mori M. New mutation causing hereditary hepatitis in the laboratory rat. J Hered. 1987 Nov-Dec;78(6):361–365. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a110416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]