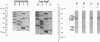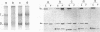Abstract
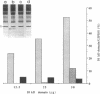
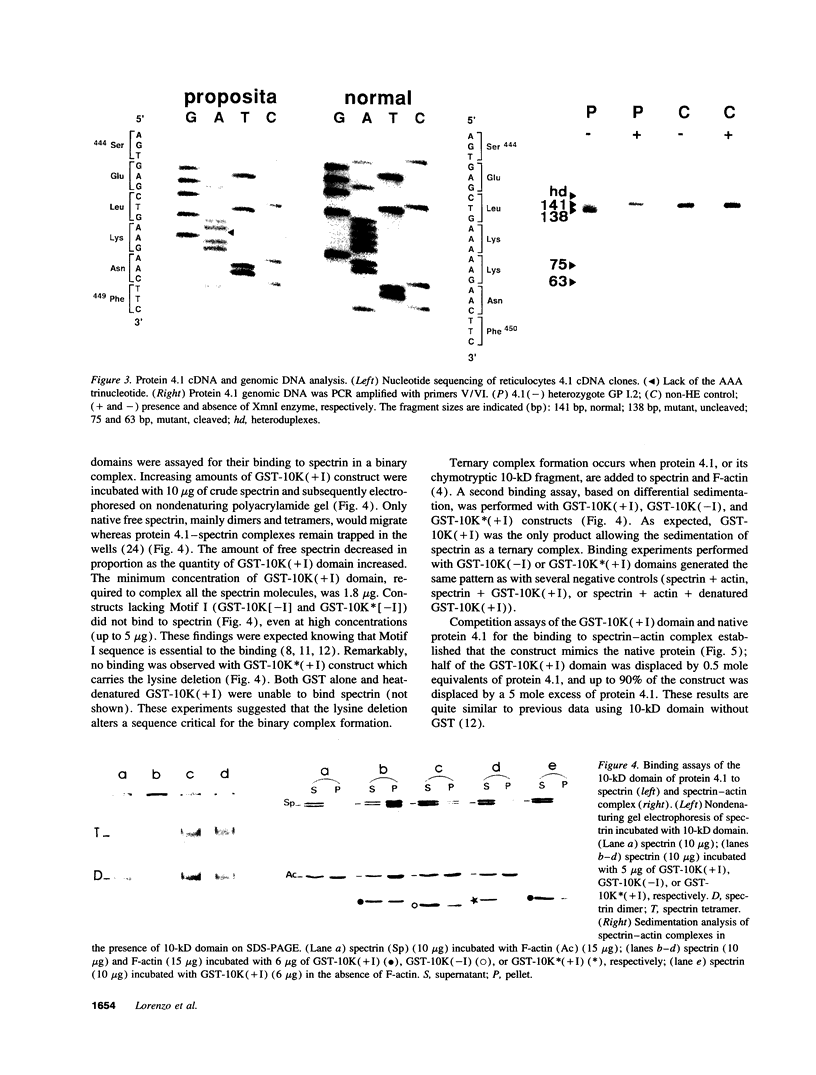
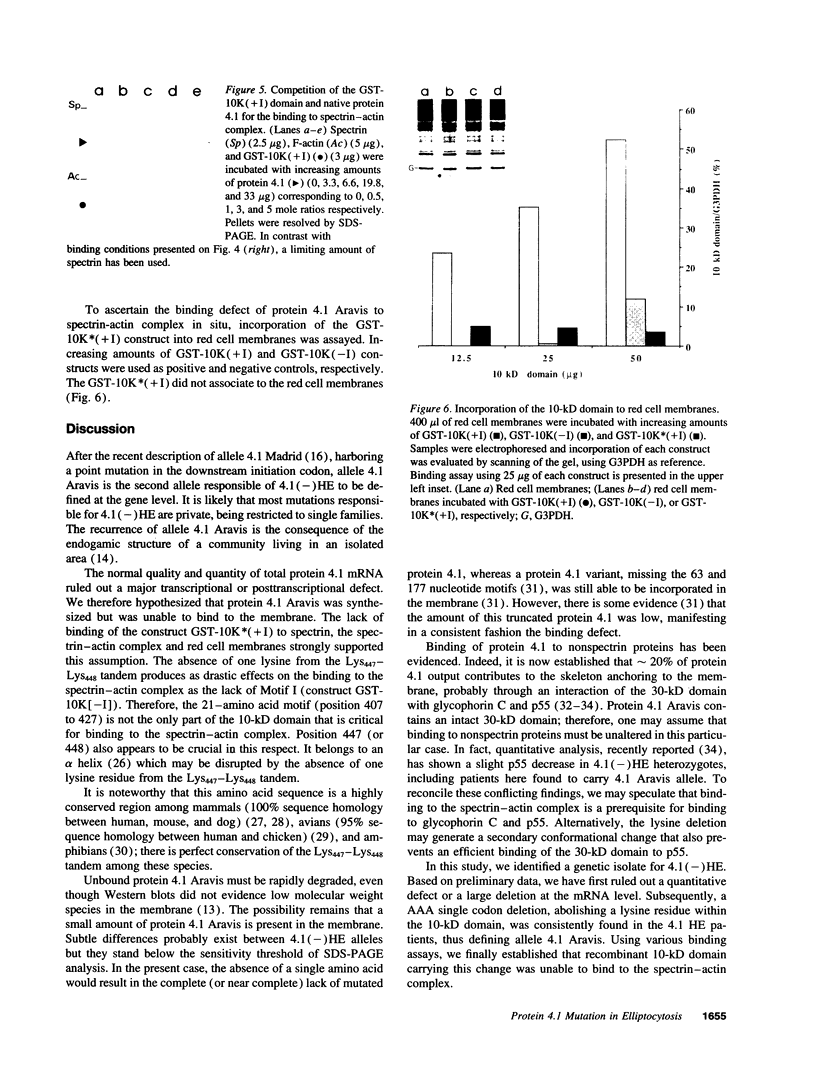
Protein 4.1 has been defined as a major component of the subcortical skeleton of erythrocytes. It binds the spectrin--actin scaffold through a 10-kD internal domain. This binding requires an essential 21-amino acid sequence motif, Motif I, which is retained by alternative splicing at the late stage of erythroid differentiation. We here analyze the molecular basis of heterozygous 4.1(-) hereditary elliptocytosis, associated with protein 4.1 partial deficiency, in nine related French families. cDNA sequencing revealed a single codon deletion (AAA) resulting in a lysine residue deletion within the 10-kD binding domain, 3' of Motif I. The mutated allele was designated allele 4.1 Aravis. In order to assess the functional effect of the codon deletion, recombinant 10-kD constructs were made and various binding assays were performed using spectrin, purified spectrin-actin complex, or red cell membranes. These experiments demonstrated that the deletion of the Lys residue clearly prevents the binding capacity. Similar results were obtained with a construct containing the Lys residue but lacking Motif I. These data strongly suggest that the binding site to the spectrin-actin complex must contain the Lys 447 (or 448), and therefore resides not only on Motif I but extends 3' of this essential motif.
Full text
PDF

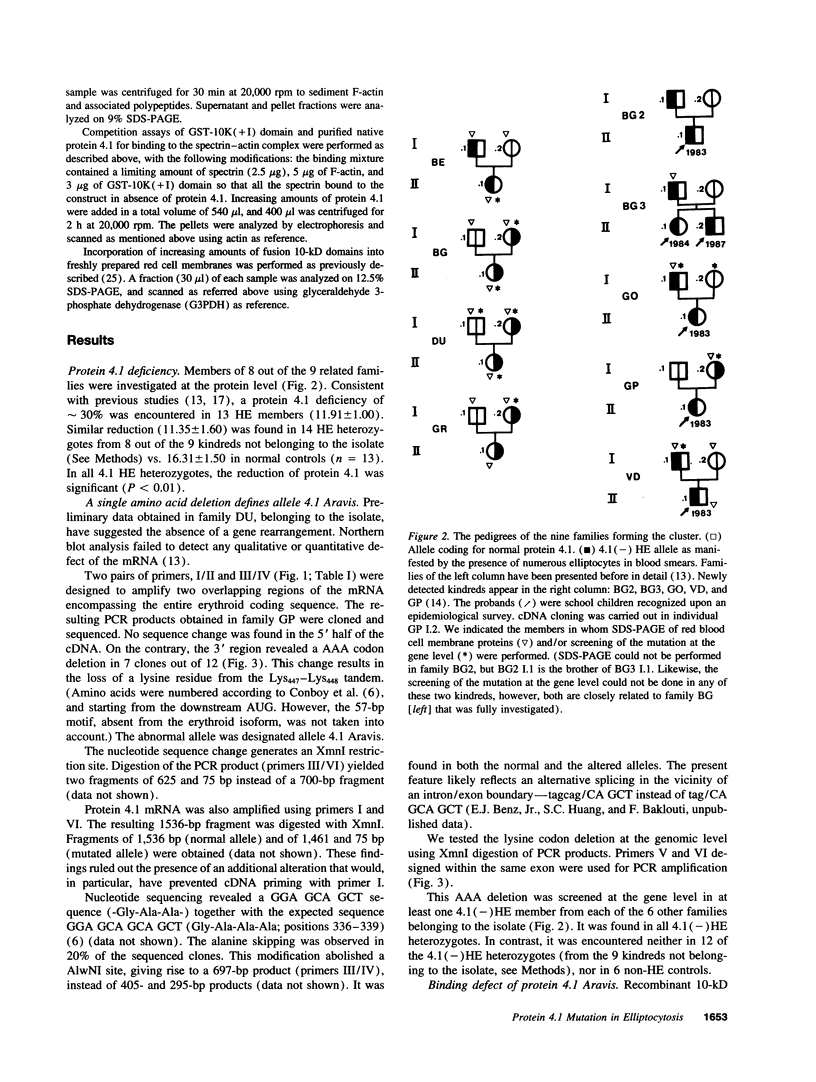

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alloisio N., Dalla Venezia N., Rana A., Andrabi K., Texier P., Gilsanz F., Cartron J. P., Delaunay J., Chishti A. H. Evidence that red blood cell protein p55 may participate in the skeleton-membrane linkage that involves protein 4.1 and glycophorin C. Blood. 1993 Aug 15;82(4):1323–1327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alloisio N., Dorléac E., Girot R., Delaunay J. Analysis of the red cell membrane in a family with hereditary elliptocytosis--total or partial of protein 4.1. Hum Genet. 1981;59(1):68–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00278857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alloisio N., Morlé L., Dorléac E., Gentilhomme O., Bachir D., Guetarni D., Colonna P., Bost M., Zouaoui Z., Roda L. The heterozygous form of 4.1(-) hereditary elliptocytosis [the 4.1(-) trait]. Blood. 1985 Jan;65(1):46–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baklouti F., Maréchal J., Wilmotte R., Alloisio N., Morlé L., Ducluzeau M. T., Denoroy L., Mrad A., Ben Aribia M. H., Kastally R. Elliptocytogenic alpha I/36 spectrin Sfax lacks nine amino acids in helix 3 of repeat 4. Evidence for the activation of a cryptic 5'-splice site in exon 8 of spectrin alpha-gene. Blood. 1992 May 1;79(9):2464–2470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunet G., Ducluzeau M. T., Roda L., Lefrancois P., Baklouti F., Delaunay J., Robert J. M. Diffusion of a particular 4.1(-) hereditary elliptocytosis allele in the French Northern Alps. J Biosoc Sci. 1993 Apr;25(2):239–247. doi: 10.1017/s0021932000020526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasis J. A., Coulombel L., Conboy J., McGee S., Andrews K., Kan Y. W., Mohandas N. Differentiation-associated switches in protein 4.1 expression. Synthesis of multiple structural isoforms during normal human erythropoiesis. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):329–338. doi: 10.1172/JCI116189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conboy J. G., Chan J. Y., Chasis J. A., Kan Y. W., Mohandas N. Tissue- and development-specific alternative RNA splicing regulates expression of multiple isoforms of erythroid membrane protein 4.1. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8273–8280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conboy J. G., Shitamoto R., Parra M., Winardi R., Kabra A., Smith J., Mohandas N. Hereditary elliptocytosis due to both qualitative and quantitative defects in membrane skeletal protein 4.1. Blood. 1991 Nov 1;78(9):2438–2443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conboy J. G. Structure, function, and molecular genetics of erythroid membrane skeletal protein 4.1 in normal and abnormal red blood cells. Semin Hematol. 1993 Jan;30(1):58–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conboy J., Kan Y. W., Shohet S. B., Mohandas N. Molecular cloning of protein 4.1, a major structural element of the human erythrocyte membrane skeleton. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9512–9516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correas I., Leto T. L., Speicher D. W., Marchesi V. T. Identification of the functional site of erythrocyte protein 4.1 involved in spectrin-actin associations. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3310–3315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla Venezia N., Gilsanz F., Alloisio N., Ducluzeau M. T., Benz E. J., Jr, Delaunay J. Homozygous 4.1(-) hereditary elliptocytosis associated with a point mutation in the downstream initiation codon of protein 4.1 gene. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):1713–1717. doi: 10.1172/JCI116044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Discher D., Parra M., Conboy J. G., Mohandas N. Mechanochemistry of the alternatively spliced spectrin-actin binding domain in membrane skeletal protein 4.1. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):7186–7195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feddal S., Brunet G., Roda L., Chabanis S., Alloisio N., Morlé L., Ducluzeau M. T., Maréchal J., Robert J. M., Benz E. J., Jr Molecular analysis of hereditary elliptocytosis with reduced protein 4.1 in the French Northern Alps. Blood. 1991 Oct 15;78(8):2113–2119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbarz M., Dhermy D., Lecomte M. C., Féo C., Chaveroche I., Galand C., Bournier O., Bertrand O., Boivin P. A variant of erythrocyte membrane skeletal protein band 4.1 associated with hereditary elliptocytosis. Blood. 1984 Nov;64(5):1006–1015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebelhaus D. H., Eib D. W., Moon R. T. Antisense RNA inhibits expression of membrane skeleton protein 4.1 during embryonic development of Xenopus. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):601–615. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90576-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemming N. J., Anstee D. J., Mawby W. J., Reid M. E., Tanner M. J. Localization of the protein 4.1-binding site on human erythrocyte glycophorins C and D. Biochem J. 1994 Apr 1;299(Pt 1):191–196. doi: 10.1042/bj2990191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne W. C., Huang S. C., Becker P. S., Tang T. K., Benz E. J., Jr Tissue-specific alternative splicing of protein 4.1 inserts an exon necessary for formation of the ternary complex with erythrocyte spectrin and F-actin. Blood. 1993 Oct 15;82(8):2558–2563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. P., Tang C. J., Kou G. H., Marchesi V. T., Benz E. J., Jr, Tang T. K. Genomic structure of the locus encoding protein 4.1. Structural basis for complex combinational patterns of tissue-specific alternative RNA splicing. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3758–3766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecomte M. C., Galand C., Boivin P. Protéines hydrosolubles des membranes erythrocytaires humaines. Différences de composition et de phosphorylation selon les conditions d'extraction. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1982;24(6):349–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leto T. L., Marchesi V. T. A structural model of human erythrocyte protein 4.1. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4603–4608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi S. L., Conboy J., Agre P., Letsinger J. T., Marchesi V. T., Speicher D. W., Mohandas N. Molecular analysis of insertion/deletion mutations in protein 4.1 in elliptocytosis. I. Biochemical identification of rearrangements in the spectrin/actin binding domain and functional characterizations. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):516–523. doi: 10.1172/JCI114738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takakuwa Y., Tchernia G., Rossi M., Benabadji M., Mohandas N. Restoration of normal membrane stability to unstable protein 4.1-deficient erythrocyte membranes by incorporation of purified protein 4.1. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):80–85. doi: 10.1172/JCI112577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang T. K., Leto T. L., Correas I., Alonso M. A., Marchesi V. T., Benz E. J., Jr Selective expression of an erythroid-specific isoform of protein 4.1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3713–3717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang T. K., Qin Z., Leto T., Marchesi V. T., Benz E. J., Jr Heterogeneity of mRNA and protein products arising from the protein 4.1 gene in erythroid and nonerythroid tissues. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):617–624. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. M., Hargreaves W. R., Branton D. Purification of two spectrin-binding proteins: biochemical and electron microscopic evidence for site-specific reassociation between spectrin and bands 2.1 and 4.1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5192–5196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yew N. S., Choi H. R., Gallarda J. L., Engel J. D. Expression of cytoskeletal protein 4.1 during avian erythroid cellular maturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1035–1039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Ouggouti S., Bournier O., Boivin P., Bertrand O., Dhermy D. Purification of erythrocyte protein 4.1 by selective interaction with inositol hexaphosphate. Protein Expr Purif. 1992 Dec;3(6):488–496. doi: 10.1016/1046-5928(92)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]