Abstract
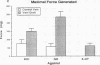
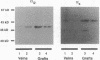
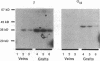
G-proteins are membrane-bound signal transduction proteins which couple extracellular receptor signals to various effectors. This study examines the expression and the function of G-proteins (alpha i, alpha s, alpha q, and alpha o) in experimental intimal hyperplasia. Vein bypass grafts were placed in 30 New Zealand White rabbits and were harvested after 28 d. The contralateral jugular veins served as controls. Isometric tension studies were performed on rings from veins and vein grafts (n = 10), and Western blot and mRNA analyses were performed in another 20 vessels. There was a fivefold increase in alpha q, a 2.7-fold increase in the alpha i2, and a 3.3-fold increase in alpha s expressions in vein grafts compared with veins. Detectable expression of alpha i3 was observed in vein grafts but not in jugular veins. In addition, there was a 3.8-fold increase in beta subunits in the vein grafts compared with the veins. mRNA for alpha s, alpha i3, and alpha i2 were all elevated in the vein grafts. No detectable levels of the alpha i1 protein or its mRNA were present in either veins or vein grafts. Contractile responses in the veins were not inhibited by pertussis toxin. The contractile responses to norepinephrine were enhanced by twofold, and the responses to serotonin developed de novo in vein grafts compared with veins. The contractile responses to both norepinephrine and serotonin were only partially inhibited by pertussis toxin in the vein grafts even though there was 100% ADP ribosylation with pertussis toxin in both veins and vein grafts. These data suggest that intimal hyperplasia is associated with increased or novel expression of G-proteins in vivo which occur simultaneously with the development of pertussis toxin-sensitive contractile responses. Changes in G-proteins at a transcriptional level or at the level of RNA stability may be involved in the response of smooth muscle cells to injury and to intimal hyperplasia formation.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blank J. L., Brattain K. A., Exton J. H. Activation of cytosolic phosphoinositide phospholipase C by G-protein beta gamma subunits. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23069–23075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B. Subtypes of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. FASEB J. 1992 Feb 1;6(3):832–839. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.3.1346768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camps M., Hou C., Sidiropoulos D., Stock J. B., Jakobs K. H., Gierschik P. Stimulation of phospholipase C by guanine-nucleotide-binding protein beta gamma subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 15;206(3):821–831. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chervu A., Moore W. S. An overview of intimal hyperplasia. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1990 Nov;171(5):433–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. L., Chiasson D. A., Gotlieb A. I. Stranger in a strange land: the pathogenesis of saphenous vein graft stenosis with emphasis on structural and functional differences between veins and arteries. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1991 Jul-Aug;34(1):45–68. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(91)90019-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross K. S., el-Sanadiki M. N., Murray J. J., Mikat E. M., McCann R. L., Hagen P. O. Functional abnormalities of experimental autogenous vein graft neoendothelium. Ann Surg. 1988 Nov;208(5):631–638. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198811000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P., Rossiter K., Carter A., Simonds W., Unson C. G., Vinitsky R., Spiegel A. M. Identification of the GTP-binding protein encoded by Gi3 complementary DNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6476–6479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaziro Y., Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nakafuku M., Satoh T. Structure and function of signal-transducing GTP-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:349–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazawa T., Masuo M., Somlyo A. P. G protein-mediated inhibition of myosin light-chain phosphatase in vascular smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9307–9310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ku D. D., Caulfield J. B., Kirklin J. K. Endothelium-dependent responses in long-term human coronary artery bypass grafts. Circulation. 1991 Feb;83(2):402–411. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.2.402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makhoul R. G., Davis W. S., Mikat E. M., McCann R. L., Hagen P. O. Responsiveness of vein bypass grafts to stimulation with norepinephrine and 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Vasc Surg. 1987 Jul;6(1):32–38. doi: 10.1067/mva.1987.avs0060032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. Roles of G protein subunits in transmembrane signalling. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):129–134. doi: 10.1038/333129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens J. R., Frame L. T., Ui M., Cooper D. M. Cholera toxin ADP-ribosylates the islet-activating protein substrate in adipocyte membranes and alters its function. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15946–15952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park D., Jhon D. Y., Lee C. W., Lee K. H., Rhee S. G. Activation of phospholipase C isozymes by G protein beta gamma subunits. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):4573–4576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radic Z. S., O'Donohoe M. K., Schwartz L. B., Stein A. D., Mikat E. M., McCann R. L., Hagen P. O. Alterations in serotonergic receptor expression in experimental vein grafts. J Vasc Surg. 1991 Jul;14(1):40–47. doi: 10.1067/mva.1991.27700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramkumar V., Stiles G. L. In vivo pertussis toxin administration: effects on the function and levels of Gi alpha proteins and their messenger ribonucleic acids. Endocrinology. 1990 Feb;126(2):1295–1304. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-2-1295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond J. R., Olsen C. L., Gettys T. W. Cell-specific physical and functional coupling of human 5-HT1A receptors to inhibitory G protein alpha-subunits and lack of coupling to Gs alpha. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 19;32(41):11064–11073. doi: 10.1021/bi00092a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robishaw J. D., Foster K. A. Role of G proteins in the regulation of the cardiovascular system. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:229–244. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis--an update. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 20;314(8):488–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602203140806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweinsberg P. D., Loo T. L. Simultaneous analysis of ATP, ADP, AMP, and other purines in human erythrocytes by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1980 Jan 11;181(1):103–107. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seuwen K., Magnaldo I., Pouysségur J. Serotonin stimulates DNA synthesis in fibroblasts acting through 5-HT1B receptors coupled to a Gi-protein. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):254–256. doi: 10.1038/335254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa H., Flavahan N. A., Vanhoutte P. M. Natural course of the impairment of endothelium-dependent relaxations after balloon endothelium removal in porcine coronary arteries. Possible dysfunction of a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein. Circ Res. 1989 Sep;65(3):740–753. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.3.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel A. M. Signal transduction by guanine nucleotide binding proteins. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Jan;49(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steen S., Willén R., Sjöberg T., Carlén B. Contractile and morphologic properties of a saphenous vein after 12 years as an aortocoronary bypass graft. Blood Vessels. 1991;28(5):349–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig R., Iñiguez-Lluhi J. A., Gilman A. G. Inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by Gi alpha. Science. 1993 Jul 9;261(5118):218–221. doi: 10.1126/science.8327893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]