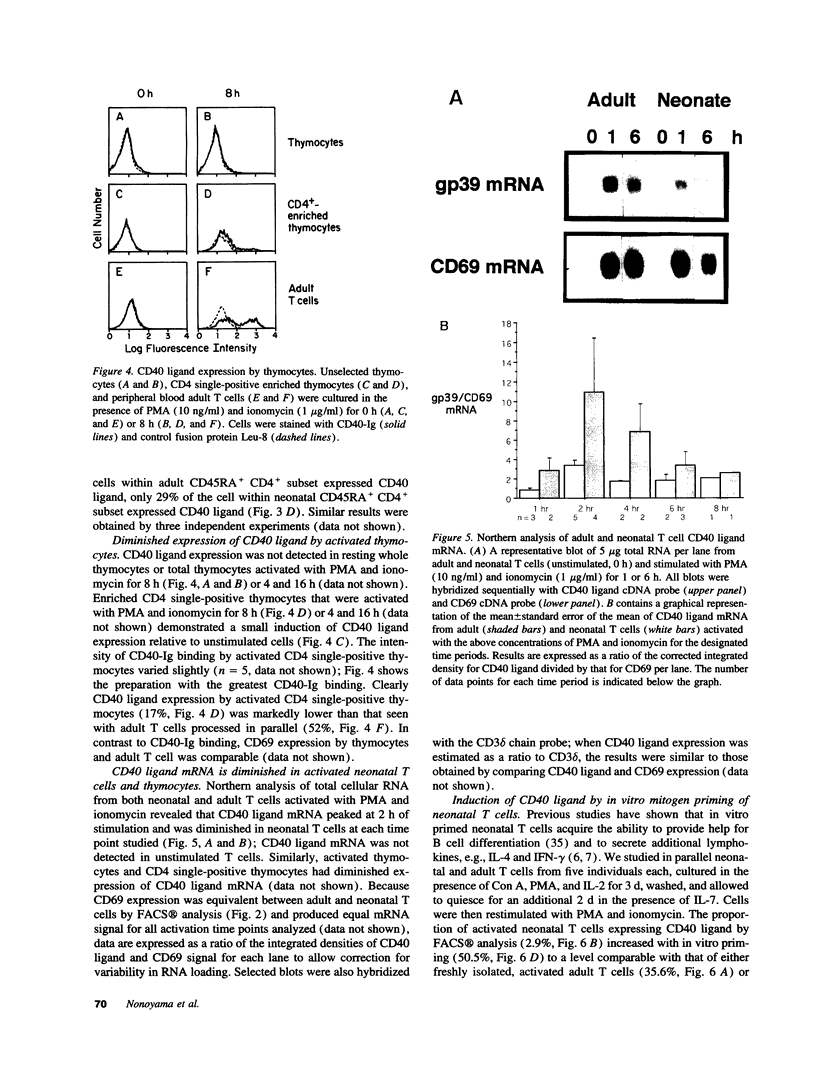
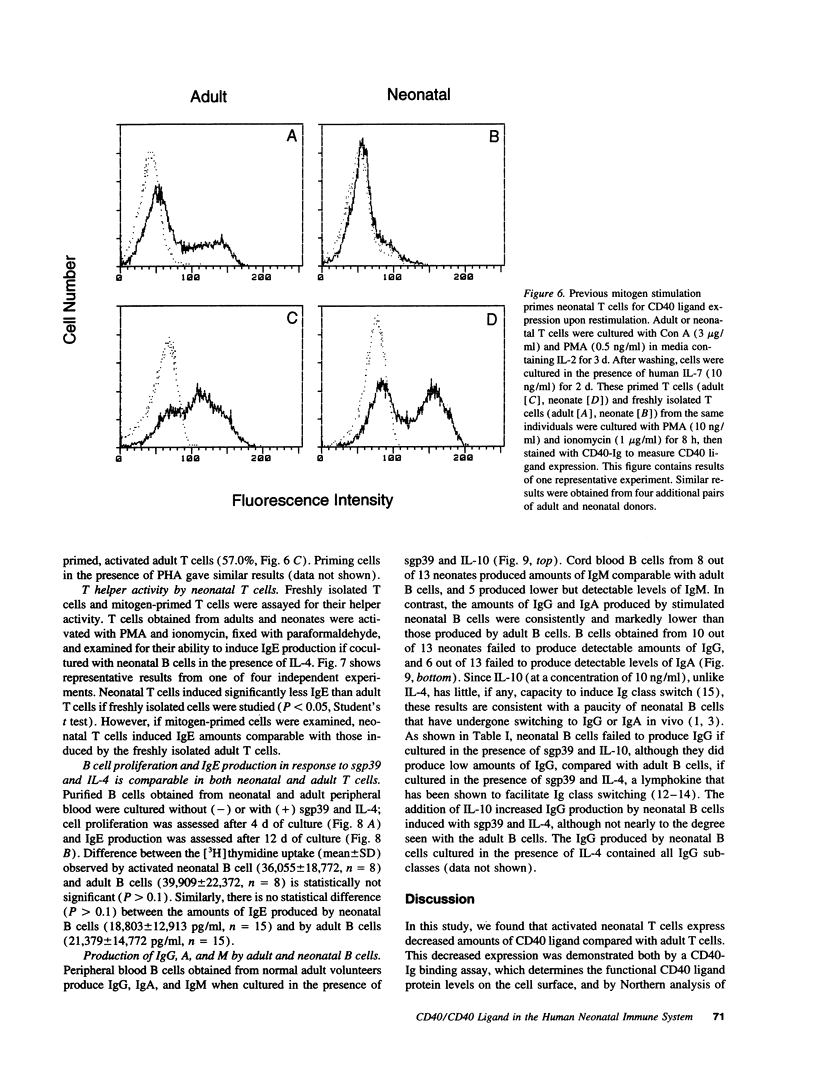
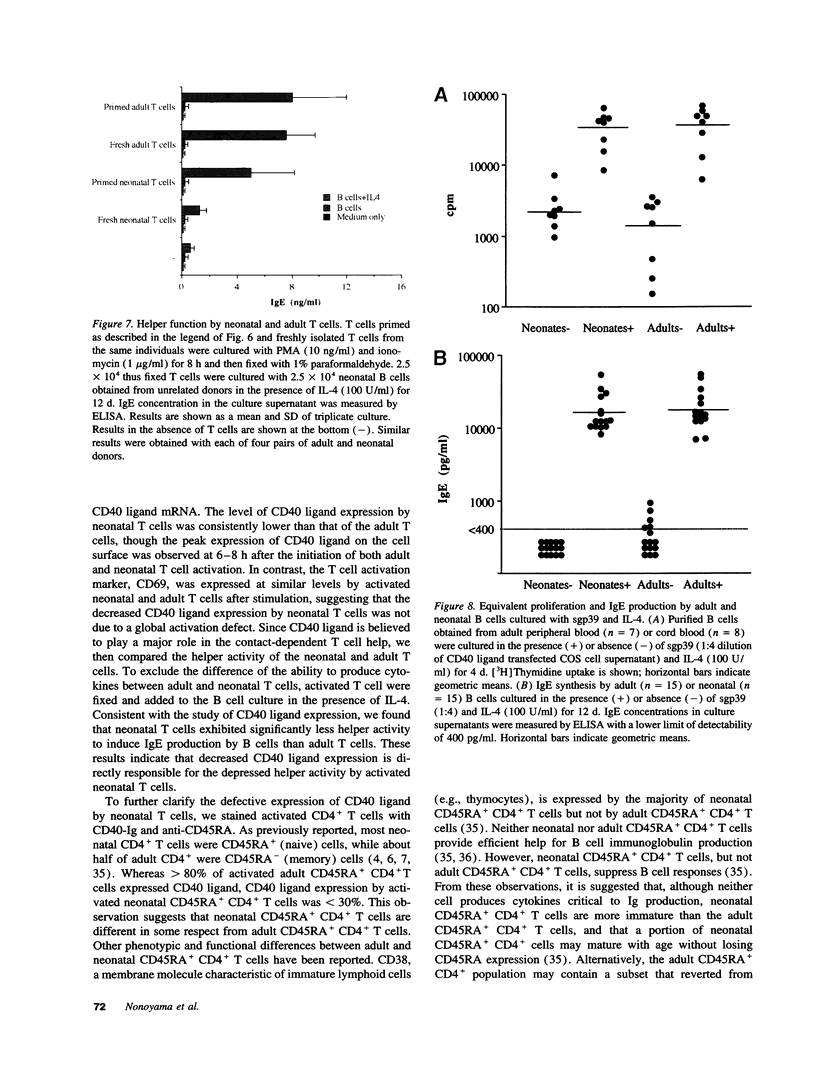
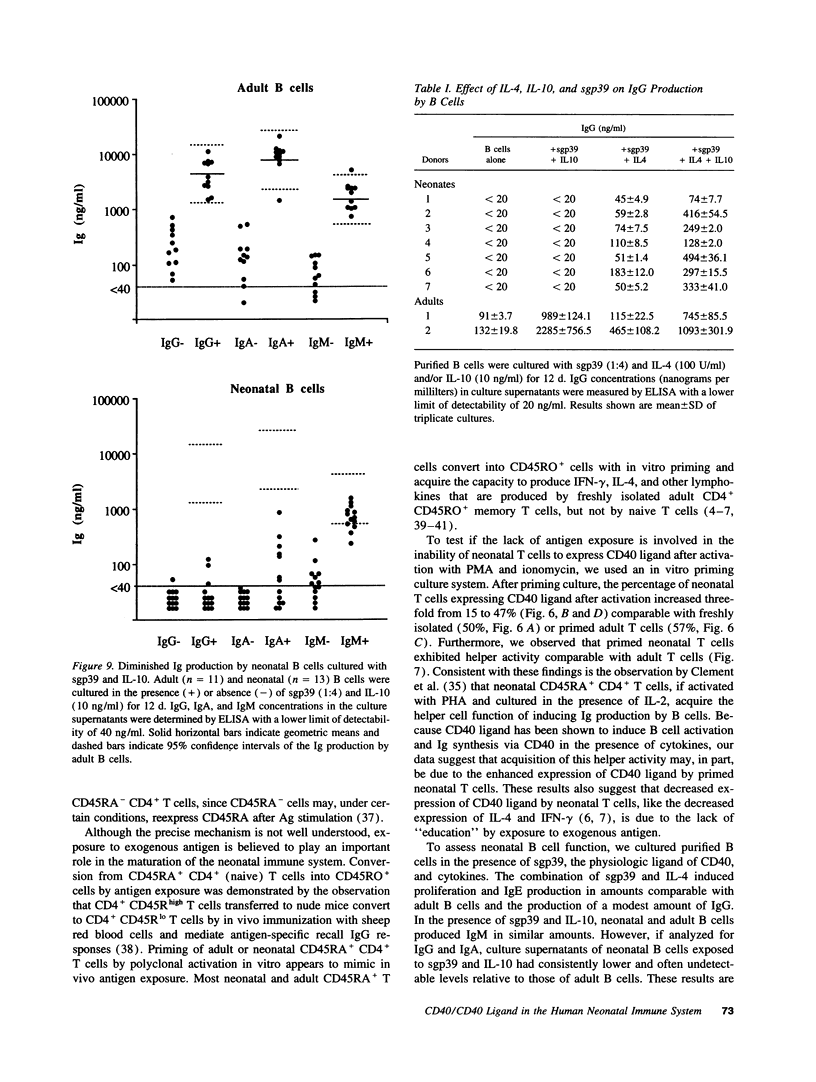
Abstract
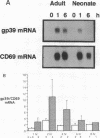
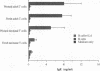
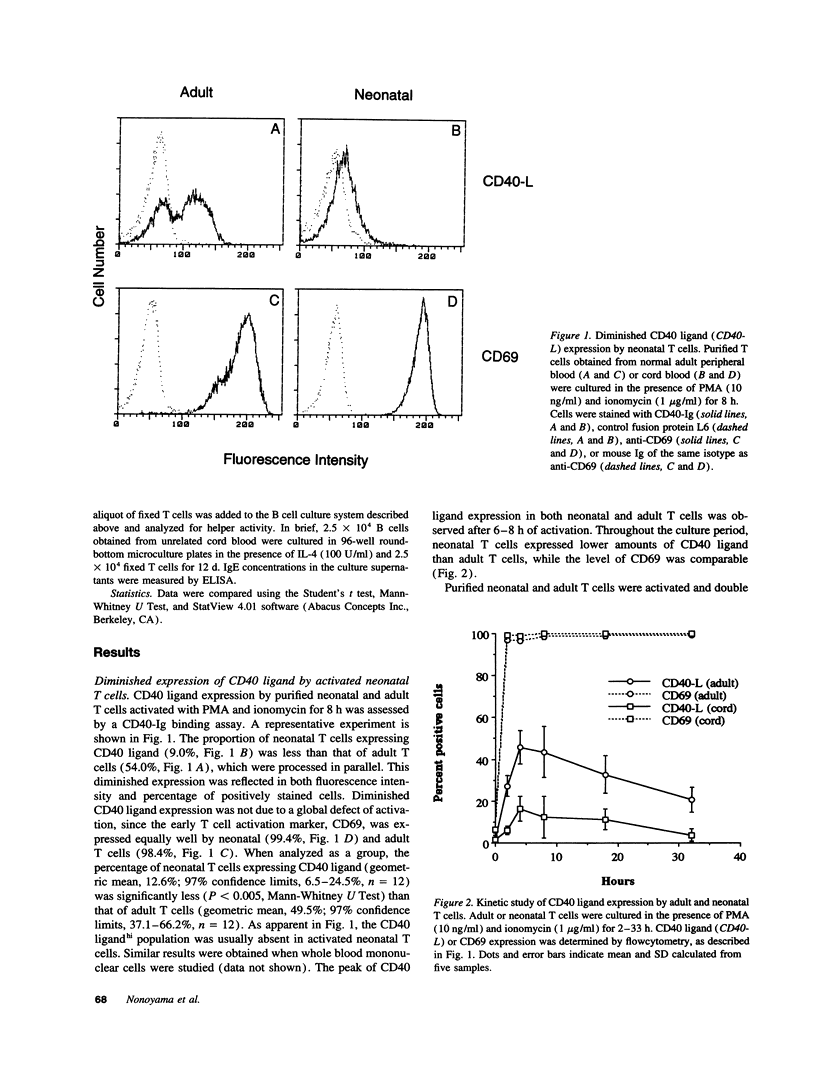
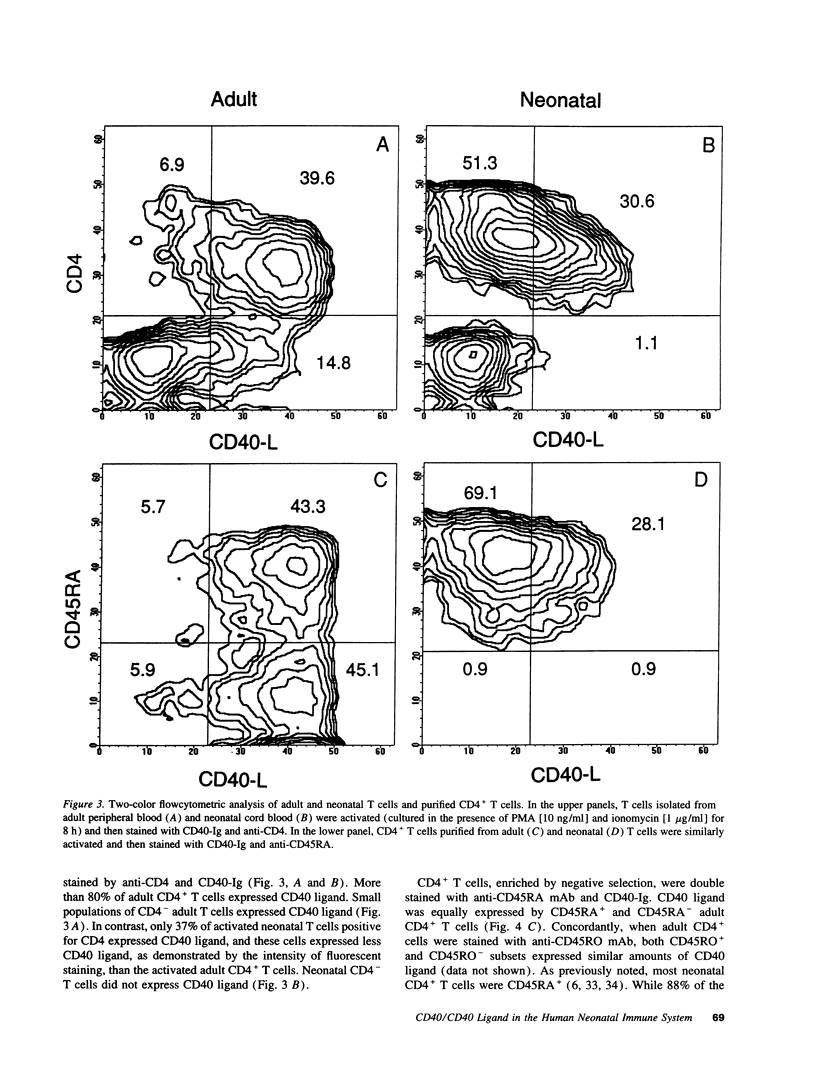
CD40 and CD40 ligand (gp39) mediate contact-dependent T-B cell interaction. We determined the expression of CD40 ligand by activated neonatal T cells and the response of neonatal B cells when activated through CD40. Although expression of CD40 ligand peaked simultaneously in both activated adult and neonatal cells, neonatal T cells expressed significantly less CD40 ligand surface protein and mRNA than adult T cells. Activated thymocytes also expressed far less CD40 ligand than adult T cells. Consistent with these results, activated neonatal T cells exhibited less helper function than activated adult T cells. Neonatal T cells primed and restimulated in vitro expressed CD40 ligand in amounts comparable with adult T cells and provided B cell help more effectively. This suggests that the poor expression of CD40 ligand reflects antigenic naiveté rather than an intrinsic defect of neonatal T cells. Neonatal B cells cultured with soluble CD40 ligand (sgp39) and IL-10 produced IgM in amounts comparable with adult cells, but much less IgG and IgA. Nevertheless, neonatal B cells were capable of proliferation and class switching, since sgp39 and IL-4 induced proliferation and IgE production comparable to adult B cells and production of modest amounts of IgG. Together, these results indicate that diminished CD40 ligand expression, along with decreased production of lymphokines, may be responsible, at least in part, for the transient immunodeficiency observed in human neonates.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. C., Armitage R. J., Conley M. E., Rosenblatt H., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Bedell M. A., Edelhoff S., Disteche C. M., Simoneaux D. K. CD40 ligand gene defects responsible for X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):990–993. doi: 10.1126/science.7679801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armitage R. J., Fanslow W. C., Strockbine L., Sato T. A., Clifford K. N., Macduff B. M., Anderson D. M., Gimpel S. D., Davis-Smith T., Maliszewski C. R. Molecular and biological characterization of a murine ligand for CD40. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):80–82. doi: 10.1038/357080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aruffo A., Farrington M., Hollenbaugh D., Li X., Milatovich A., Nonoyama S., Bajorath J., Grosmaire L. S., Stenkamp R., Neubauer M. The CD40 ligand, gp39, is defective in activated T cells from patients with X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90668-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brière F., Servet-Delprat C., Bridon J. M., Saint-Remy J. M., Banchereau J. Human interleukin 10 induces naive surface immunoglobulin D+ (sIgD+) B cells to secrete IgG1 and IgG3. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):757–762. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budd R. C., Cerottini J. C., MacDonald H. R. Selectively increased production of interferon-gamma by subsets of Lyt-2+ and L3T4+ T cells identified by expression of Pgp-1. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3583–3586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark E. A., Lane P. J. Regulation of human B-cell activation and adhesion. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:97–127. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.000525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark E. A., Ledbetter J. A. Activation of human B cells mediated through two distinct cell surface differentiation antigens, Bp35 and Bp50. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4494–4498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement L. T., Vink P. E., Bradley G. E. Novel immunoregulatory functions of phenotypically distinct subpopulations of CD4+ cells in the human neonate. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):102–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defrance T., Vanbervliet B., Brière F., Durand I., Rousset F., Banchereau J. Interleukin 10 and transforming growth factor beta cooperate to induce anti-CD40-activated naive human B cells to secrete immunoglobulin A. J Exp Med. 1992 Mar 1;175(3):671–682. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.3.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiSanto J. P., Bonnefoy J. Y., Gauchat J. F., Fischer A., de Saint Basile G. CD40 ligand mutations in x-linked immunodeficiency with hyper-IgM. Nature. 1993 Feb 11;361(6412):541–543. doi: 10.1038/361541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers S., Smith K. A. Differentiation of T cell lymphokine gene expression: the in vitro acquisition of T cell memory. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):25–36. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrington M., Grosmaire L. S., Nonoyama S., Fischer S. H., Hollenbaugh D., Ledbetter J. A., Noelle R. J., Aruffo A., Ochs H. D. CD40 ligand expression is defective in a subset of patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):1099–1103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuleihan R., Ramesh N., Loh R., Jabara H., Rosen R. S., Chatila T., Fu S. M., Stamenkovic I., Geha R. S. Defective expression of the CD40 ligand in X chromosome-linked immunoglobulin deficiency with normal or elevated IgM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2170–2173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gathings W. E., Kubagawa H., Cooper M. D. A distinctive pattern of B cell immaturity in perinatal humans. Immunol Rev. 1981;57:107–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward A. R., Lee J., Beverley P. C. Ontogeny of expression of UCHL1 antigen on TcR-1+ (CD4/8) and TcR delta+ T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Apr;19(4):771–773. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenbaugh D., Grosmaire L. S., Kullas C. D., Chalupny N. J., Braesch-Andersen S., Noelle R. J., Stamenkovic I., Ledbetter J. A., Aruffo A. The human T cell antigen gp39, a member of the TNF gene family, is a ligand for the CD40 receptor: expression of a soluble form of gp39 with B cell co-stimulatory activity. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4313–4321. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05530.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabara H. H., Fu S. M., Geha R. S., Vercelli D. CD40 and IgE: synergism between anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody and interleukin 4 in the induction of IgE synthesis by highly purified human B cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1861–1864. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korthäuer U., Graf D., Mages H. W., Brière F., Padayachee M., Malcolm S., Ugazio A. G., Notarangelo L. D., Levinsky R. J., Kroczek R. A. Defective expression of T-cell CD40 ligand causes X-linked immunodeficiency with hyper-IgM. Nature. 1993 Feb 11;361(6412):539–541. doi: 10.1038/361539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane P., Brocker T., Hubele S., Padovan E., Lanzavecchia A., McConnell F. Soluble CD40 ligand can replace the normal T cell-derived CD40 ligand signal to B cells in T cell-dependent activation. J Exp Med. 1993 Apr 1;177(4):1209–1213. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.4.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane P., Traunecker A., Hubele S., Inui S., Lanzavecchia A., Gray D. Activated human T cells express a ligand for the human B cell-associated antigen CD40 which participates in T cell-dependent activation of B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Oct;22(10):2573–2578. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. T., Vitetta E. S. Virgin T cells do not provide help for antigen-specific B cells in the absence of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-6. Int Immunol. 1991 Sep;3(9):907–916. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.9.907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. T., Yin X. M., Vitetta E. S. Functional and ontogenetic analysis of murine CD45Rhi and CD45Rlo CD4+ T cells. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3288–3295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. B., Larsen A., Wilson C. B. Reduced interferon-gamma mRNA levels in human neonates. Evidence for an intrinsic T cell deficiency independent of other genes involved in T cell activation. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):1018–1023. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. B., Prickett K. S., Larsen A., Grabstein K., Weaver M., Wilson C. B. Restricted production of interleukin 4 by activated human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9743–9747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. B., Yu C. C., Meyer J., English B. K., Kahn S. J., Wilson C. B. Cellular and molecular mechanisms for reduced interleukin 4 and interferon-gamma production by neonatal T cells. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):194–202. doi: 10.1172/JCI114970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maliszewski C. R., Grabstein K., Fanslow W. C., Armitage R., Spriggs M. K., Sato T. A. Recombinant CD40 ligand stimulation of murine B cell growth and differentiation: cooperative effects of cytokines. Eur J Immunol. 1993 May;23(5):1044–1049. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyawaki T., Kubagawa H., Butler J. L., Cooper M. D. Ig isotypes produced by EBV-transformed B cells as a function of age and tissue distribution. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3887–3892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noelle R. J., Roy M., Shepherd D. M., Stamenkovic I., Ledbetter J. A., Aruffo A. A 39-kDa protein on activated helper T cells binds CD40 and transduces the signal for cognate activation of B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6550–6554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S., Dierich M. P., Reisfeld R. A. Enhancement of sheep red blood cell human lymphocyte rosette formation by the sulfhydryl compound 2-amino ethylisothiouronium bromide. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Jan;3(3):324–333. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs J. E., Stowers R. S., Mosier D. E. Adoptive transfer of neonatal T lymphocytes rescues immunoglobulin production in mice with severe combined immune deficiency. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):265–268. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein D. M., Yamada A., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Cyclic regulation of CD45 isoform expression in a long term human CD4+CD45RA+ T cell line. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1175–1183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset F., Garcia E., Banchereau J. Cytokine-induced proliferation and immunoglobulin production of human B lymphocytes triggered through their CD40 antigen. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):705–710. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Makgoba M. W., Sharrow S. O., Stephany D., Springer T. A., Young H. A., Shaw S. Human memory T lymphocytes express increased levels of three cell adhesion molecules (LFA-3, CD2, and LFA-1) and three other molecules (UCHL1, CDw29, and Pgp-1) and have enhanced IFN-gamma production. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1401–1407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira S. K., Vercelli D., Jabara H. H., Fu S. M., Geha R. S. Molecular analysis of the induction of immunoglobulin E synthesis in human B cells by interleukin 4 and engagement of CD40 antigen. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):289–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Splawski J. B., Jelinek D. F., Lipsky P. E. Delineation of the functional capacity of human neonatal lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):545–553. doi: 10.1172/JCI115029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs M. K., Armitage R. J., Strockbine L., Clifford K. N., Macduff B. M., Sato T. A., Maliszewski C. R., Fanslow W. C. Recombinant human CD40 ligand stimulates B cell proliferation and immunoglobulin E secretion. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1543–1550. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Bradley L. M., Croft M., Tonkonogy S., Atkins G., Weinberg A. D., Duncan D. D., Hedrick S. M., Dutton R. W., Huston G. Helper T-cell subsets: phenotype, function and the role of lymphokines in regulating their development. Immunol Rev. 1991 Oct;123:115–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1991.tb00608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder T. F., Clement L. T., Cooper M. D. Human lymphocyte differentiation antigens HB-10 and HB-11. I. Ontogeny of antigen expression. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):2983–2988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele D. L., Lipsky P. E. Modulation of human natural killer cell function by L-leucine methyl ester: monocyte-dependent depletion from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):786–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Penix L., Melvin A., Lewis D. B. Lymphokine regulation and the role of abnormal regulation in immunodeficiency. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1993 Jun;67(3 Pt 2):S25–S32. doi: 10.1006/clin.1993.1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yssel H., De Waal Malefyt R., Roncarolo M. G., Abrams J. S., Lahesmaa R., Spits H., de Vries J. E. IL-10 is produced by subsets of human CD4+ T cell clones and peripheral blood T cells. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2378–2384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K., Clark E. A., Saxon A. CD40 stimulation provides an IFN-gamma-independent and IL-4-dependent differentiation signal directly to human B cells for IgE production. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 15;146(6):1836–1842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler S. F., Ramsdell F., Hjerrild K. A., Armitage R. J., Grabstein K. H., Hennen K. B., Farrah T., Fanslow W. C., Shevach E. M., Alderson M. R. Molecular characterization of the early activation antigen CD69: a type II membrane glycoprotein related to a family of natural killer cell activation antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jul;23(7):1643–1648. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]