Abstract
The Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome is a recessive inherited disorder characterized by neurologic developmental defects and dysmorphic features in many organs. Recently, abnormal cholesterol biosynthesis with impaired conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol to cholesterol has been discovered in homozygotes. To reproduce the biochemical abnormality, BM 15.766, a competitive inhibitor of 7-dehydrocholesterol-delta 7-reductase, the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol into cholesterol was fed by gavage to rats. After 14 d, plasma cholesterol concentrations declined from 48 mg/dl to 16 mg/dl and 7-dehydro-cholesterol levels rose from trace to 17 mg/dl. Hepatocytes surrounding the central vein developed balloon necrosis. Stimulating cholesterol synthesis with cholestyramine followed by BM 15.766 produced an additional 40% decline (P < 0.05) in plasma cholesterol and 34% increase in 7-dehydrocholesterol levels compared to the inhibitor alone. Adding 2% cholesterol to the diet during the second week of BM 15.766 treatment increased plasma cholesterol threefold and decreased 7-dehydrocholesterol concentrations 55%. Hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl co-enzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase activity increased 73% with a 3.9-fold rise in mRNA levels but cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase activity decreased slightly though mRNA levels increased 1.4 times with BM 15.766 treatment. These results demonstrate that BM 15.766 is a potent inhibitor of 7-dehydrocholesterol-delta 7-reductase. The model reproduces abnormal cholesterol biosynthesis as seen in the Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome and is useful to test different treatment strategies. Stimulating early steps of cholesterol synthesis worsens the biochemical abnormalities while feeding cholesterol inhibits abnormal synthesis, improves the biochemical abnormalities and prevents liver damage.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aufenanger J., Pill J., Schmidt F. H., Stegmeier K. The effects of BM 15.766, an inhibitor of 7-dehydrocholesterol delta 7-reductase, on cholesterol biosynthesis in primary rat hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Mar 15;35(6):911–916. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasalow F. I., Blethen S. L., Taysi K. Possible abnormalities of steroid secretion in children with Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome and their parents. Steroids. 1985 Oct-Nov;46(4-5):827–843. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(85)90032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George R., Davis P. J., Luong L., Poznansky M. J. Cholesterol-mediated regulation of HMG-CoA reductase in microsomes from human skin fibroblasts and rat liver. Biochem Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;68(3):674–679. doi: 10.1139/o90-097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen L. B., Shefer S., Salen G., Horak I., Tint G. S., McNamara D. J. The effect of abnormal plasma and cellular sterol content and composition on low density lipoprotein uptake and degradation by monocytes and lymphocytes in sitosterolemia with xanthomatosis. Metabolism. 1988 Apr;37(4):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(88)90134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen L. B., Shefer S., Salen G., Ness G. C., Tint G. S., Zaki F. G., Rani I. A molecular defect in hepatic cholesterol biosynthesis in sitosterolemia with xanthomatosis. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):923–931. doi: 10.1172/JCI114794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opitz J. M., Penchaszadeh V. B., Holt M. C., Spano L. M. Smith-Lemli-Opitz (RSH) syndrome bibliography. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Nov;28(3):745–750. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pill J., Schmidt F. H., Stegmeier K., Witte E. C. Effects of BM 15.766 on serum lipids in rats. Horm Metab Res. 1985 Oct;17(10):543–544. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1013600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROUX C. ACTION TERATOGENE DU TRIPARANOL CHEZ L'ANIMAL. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1964 Apr;21:451–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux C., Aubry M. Action tératogène chez le rat d'un inhibiteur de la synthèse du cholestérol, le AY 9944. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1966;160(7):1353–1357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux C., Dupuis R., Horvath C., Talbot J. N. Teratogenic effect of an inhibitor of cholesterol synthesis (AY 9944) in rats: correlation with maternal cholesterolemia. J Nutr. 1980 Nov;110(11):2310–2312. doi: 10.1093/jn/110.11.2310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH D. W., LEMLI L., OPITZ J. M. A NEWLY RECOGNIZED SYNDROME OF MULTIPLE CONGENITAL ANOMALIES. J Pediatr. 1964 Feb;64:210–217. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(64)80264-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
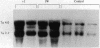
- Shefer S., Nguyen L. B., Salen G., Ness G. C., Chowdhary I. R., Lerner S., Batta A. K., Tint G. S. Differing effects of cholesterol and taurocholate on steady state hepatic HMG-CoA reductase and cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase activities and mRNA levels in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1992 Aug;33(8):1193–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tint G. S., Irons M., Elias E. R., Batta A. K., Frieden R., Chen T. S., Salen G. Defective cholesterol biosynthesis associated with the Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jan 13;330(2):107–113. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199401133300205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G., Salen G., Shefer S., Batta A. K., Ness G. C., Nguyen L. B., Zhao Z., Chen T. S., Niemann W., Tint G. S. Different feedback regulation of hepatic cholesterol and bile acid synthesis by glycodeoxycholic acid in rabbits. Gastroenterology. 1993 Oct;105(4):1192–1199. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90967-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]