Abstract
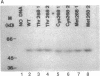
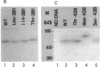
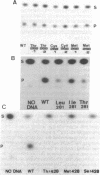
Steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency is the major cause of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH), a common genetic disease. To define the relationship between gene mutations and enzyme deficiency, we generated missense mutations of the 21-hydroxylase cDNA at three different sites and characterized the mutant proteins after expressing them in cultured mammalian and yeast cells. Among them, Ser268 and Val281 have been found to be mutated in CAH patients, whereas Cys428 has been implicated as the heme ligand. Our results show mutations at these sites result in complete, partial, or no loss of the enzymatic activity. All the Cys428 mutants had neither enzymatic activity nor P450 absorption, thus supporting the notion that Cys428 is the heme ligand. All the 268-mutants exhibited the same activity as normal 21-hydroxylase, demonstrating that the clinically observed Ser268----Thr change represents a polymorphism rather than the cause of the enzyme deficiency. The 281-mutants had normal Km but greatly reduced Vmax values that also paralleled the reduction in the heme content, in the order Val281 (normal, 100%) greater than Ile281 (50%) greater than Leu281 (20%) greater than Thr281 (10%). Our findings suggest that the methyl group at the beta-carbon of Val281 is required for heme incorporation and consequently enzymatic activity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amor M., Parker K. L., Globerman H., New M. I., White P. C. Mutation in the CYP21B gene (Ile-172----Asn) causes steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1600–1604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitter G. A., Egan K. M. Expression of heterologous genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae from vectors utilizing the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene promoter. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Palsdottir A., Belt K. T., Porter R. R. Deletion of complement C4 and steroid 21-hydroxylase genes in the HLA class III region. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2547–2552. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03969.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou S. H., Hu M. C., Chung B. C. A missense mutation at Ile172----Asn or Arg356----Trp causes steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3549–3552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohoue P. A., Sandrini Neto R., Collins M. M., Migeon C. J. Exon 7 Ncol restriction site within CYP21B (steroid 21-hydroxylase) is a normal polymorphism. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1354–1362. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-9-1354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. J., Murray B. P., Boobis A. R., Davies D. S. Identification and location of alpha-helices in mammalian cytochromes P450. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3762–3770. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Globerman H., Amor M., Parker K. L., New M. I., White P. C. Nonsense mutation causing steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jul;82(1):139–144. doi: 10.1172/JCI113562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Tanae A., Inoue H., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Evidence for frequent gene conversion in the steroid 21-hydroxylase P-450(C21) gene: implications for steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;42(1):17–25. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Tanae A., Inoue H., Hiromasa T., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Aberrant splicing and missense mutations cause steroid 21-hydroxylase [P-450(C21)] deficiency in humans: possible gene conversion products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7486–7490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Yoshioka H., Yamane M., Gotoh O., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of two steroid 21-hydroxylase genes tandemly arranged in human chromosome: a pseudogene and a genuine gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2841–2845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M. C., Chung B. C. Expression of human 21-hydroxylase (P450c21) in bacterial and mammalian cells: a system to characterize normal and mutant enzymes. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Jun;4(6):893–898. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-6-893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. W. Proteinase mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1977 Jan;85(1):23–33. doi: 10.1093/genetics/85.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L., Levine L. S. Molecular and clinical advances in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Pediatr. 1987 Jul;111(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80334-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L., Morel Y. The molecular genetics of 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:371–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel Y., André J., Uring-Lambert B., Hauptmann G., Bétuel H., Tossi M., Forest M. G., David M., Bertrand J., Miller W. L. Rearrangements and point mutations of P450c21 genes are distinguished by five restriction endonuclease haplotypes identified by a new probing strategy in 57 families with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):527–536. doi: 10.1172/JCI113914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Nelson D. R., Adesnik M., Coon M. J., Estabrook R. W., Gonzalez F. J., Guengerich F. P., Gunsalus I. C., Johnson E. F., Kemper B. The P450 superfamily: updated listing of all genes and recommended nomenclature for the chromosomal loci. DNA. 1989 Jan-Feb;8(1):1–13. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Strobel H. W. On the membrane topology of vertebrate cytochrome P-450 proteins. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6038–6050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T., SATO R. THE CARBON MONOXIDE-BINDING PIGMENT OF LIVER MICROSOMES. I. EVIDENCE FOR ITS HEMOPROTEIN NATURE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2370–2378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos T. L., Finzel B. C., Howard A. J. High-resolution crystal structure of cytochrome P450cam. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):687–700. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYAN K. J., ENGEL L. L. Hydroxylation of steroids at carbon 21. J Biol Chem. 1957 Mar;225(1):103–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues N. R., Dunham I., Yu C. Y., Carroll M. C., Porter R. R., Campbell R. D. Molecular characterization of the HLA-linked steroid 21-hydroxylase B gene from an individual with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1653–1661. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02414.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen A. L., Porter T. D., Wilson T. E., Kasper C. B. Structural analysis of the FMN binding domain of NADPH-cytochrome P-450 oxidoreductase by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7584–7589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Hirano K., Takahashi M., Hatano M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Site-directed mutageneses of rat liver cytochrome P-450d: axial ligand and heme incorporation. Biochemistry. 1988 May 31;27(11):4138–4141. doi: 10.1021/bi00411a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speiser P. W., New M. I., White P. C. Molecular genetic analysis of nonclassic steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency associated with HLA-B14,DR1. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jul 7;319(1):19–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198807073190104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tusie-Luna M. T., Traktman P., White P. C. Determination of functional effects of mutations in the steroid 21-hydroxylase gene (CYP21) using recombinant vaccinia virus. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20916–20922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. HLA-linked congenital adrenal hyperplasia results from a defective gene encoding a cytochrome P-450 specific for steroid 21-hydroxylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7505–7509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. Structure of human steroid 21-hydroxylase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5111–5115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Vitek A., Dupont B., New M. I. Characterization of frequent deletions causing steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4436–4440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D. A., Hu M. C., Chung B. C. Expression and functional study of wild-type and mutant human cytochrome P450c21 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;10(3):201–209. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]