Abstract
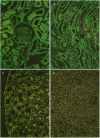
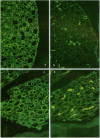
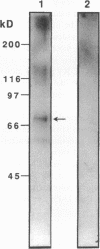
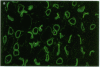
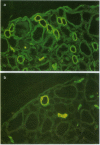
To investigate the physiological role of a kidney-specific chloride channel (ClC-K1), we sought to determine its exact localization by immunohistochemistry and its functional regulation using Xenopus oocyte expression system. The antiserum specifically recognized a 70-kD protein in SDS-PAGE of membrane protein from rat inner medulla and an in vitro translated ClC-K1 protein. Immunohistochemistry revealed that ClC-K1 was exclusively localized to the thin limb of Henle's loop in rat inner medulla. In comparison with the immunostaining with anti-aquaporin-CHIP antibody that only stains the descending thin limb of Henle's loop (tDL), ClC-K1 was found to be localized only in the ascending limb (tAL) which has the highest chloride permeability among nephron segments. Immunoelectron microscopy confirmed that the staining of ClC-K1 in tAL was observed in the region of both apical and basolateral plasma membranes. Expressed chloride current in Xenopus oocytes by ClC-K1 cRNA was regulated by extracellular pH and extracellular calcium. Furosemide inhibited the expressed current (Ki = 100 microM), whereas N-ethyl-maleimide stimulated the current. These functional characteristics were consistent with the in vitro perfusion studies of chloride transport in tAL. The localization and the functional characteristics described here indicate that ClC-K1 is responsible for the transepithelial chloride transport in tAL.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biemesderfer D., Pizzonia J., Abu-Alfa A., Exner M., Reilly R., Igarashi P., Aronson P. S. NHE3: a Na+/H+ exchanger isoform of renal brush border. Am J Physiol. 1993 Nov;265(5 Pt 2):F736–F742. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.265.5.F736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. L., Nielsen S., Knepper M. A. Structural-functional correlation in chinchilla long loop of Henle thin limbs: a novel papillary subsegment. Am J Physiol. 1993 Dec;265(6 Pt 2):F863–F874. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.265.6.F863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greger R. Ion transport mechanisms in thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of mammalian nephron. Physiol Rev. 1985 Jul;65(3):760–797. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1985.65.3.760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halm D. R., Rechkemmer G. R., Schoumacher R. A., Frizzell R. A. Apical membrane chloride channels in a colonic cell line activated by secretory agonists. Am J Physiol. 1988 Apr;254(4 Pt 1):C505–C511. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.4.C505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Kokko J. P. Sodium chloride, urea, and water transport in the thin ascending limb of Henle. Generation of osmotic gradients by passive diffusion of solutes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):393–402. doi: 10.1172/JCI107572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Kondo Y., Koseki C., Yoshitomi K. Dual effect of N-ethylmaleimide on Cl- transport across the thin ascending limb of Henle's loop. Pflugers Arch. 1988 May;411(5):520–528. doi: 10.1007/BF00582373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Taniguchi J., Tabei K. Function of thin loops of Henle. Kidney Int. 1987 Feb;31(2):565–579. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Taniguchi J., Yoshitomi K. Transition of permeability properties along the descending limb of long-loop nephron. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 2):F323–F328. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.3.F323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi K., Sasaki S., Uchida S., Imai T., Marumo F. Tissue expression of mRNA of chloride channel from MDCK cells and its regulation by protein kinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Apr 30;192(2):561–567. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isozaki T., Yoshitomi K., Imai M. Selectivity of ion permeability across ascending thin limb of Henle's loop: interaction of Cl- and other halogens with anion transport system. Kidney Int Suppl. 1991 Jul;33:S113–S118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch T. J., Steinmeyer K., Schwarz G. Primary structure of Torpedo marmorata chloride channel isolated by expression cloning in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):510–514. doi: 10.1038/348510a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokko J. P., Rector F. C., Jr Countercurrent multiplication system without active transport in inner medulla. Kidney Int. 1972 Oct;2(4):214–223. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo Y., Yoshitomi K., Imai M. Effect of Ca2+ on Cl- transport in thin ascending limb of Henle's loop. Am J Physiol. 1988 Feb;254(2 Pt 2):F232–F239. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.2.F232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo Y., Yoshitomi K., Imai M. Effect of pH on Cl- transport in TAL of Henle's loop. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 2):F1216–F1222. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.6.F1216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo Y., Yoshitomi K., Imai M. Effects of anion transport inhibitors and ion substitution on Cl- transport in TAL of Henle's loop. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 2):F1206–F1215. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.6.F1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapivinsky G. B., Ackerman M. J., Gordon E. A., Krapivinsky L. D., Clapham D. E. Molecular characterization of a swelling-induced chloride conductance regulatory protein, pICln. Cell. 1994 Feb 11;76(3):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landry D., Sullivan S., Nicolaides M., Redhead C., Edelman A., Field M., al-Awqati Q., Edwards J. Molecular cloning and characterization of p64, a chloride channel protein from kidney microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14948–14955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann J. D., Welsh M. J. Regulation of Cl- and K+ channels in airway epithelium. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:115–135. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.000555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulmichl M., Li Y., Wickman K., Ackerman M., Peralta E., Clapham D. New mammalian chloride channel identified by expression cloning. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):238–241. doi: 10.1038/356238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. B., Andreoli T. E. Renal epithelial chloride channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:29–50. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki S., Fushimi K., Saito H., Saito F., Uchida S., Ishibashi K., Kuwahara M., Ikeuchi T., Inui K., Nakajima K. Cloning, characterization, and chromosomal mapping of human aquaporin of collecting duct. J Clin Invest. 1994 Mar;93(3):1250–1256. doi: 10.1172/JCI117079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmeyer K., Ortland C., Jentsch T. J. Primary structure and functional expression of a developmentally regulated skeletal muscle chloride channel. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):301–304. doi: 10.1038/354301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. L. Concentration of urine in a central core model of the renal counterflow system. Kidney Int. 1972 Aug;2(2):85–94. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemann A., Gründer S., Pusch M., Jentsch T. J. A chloride channel widely expressed in epithelial and non-epithelial cells. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):57–60. doi: 10.1038/356057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornhill W. B., Levinson S. R. Biosynthesis of electroplax sodium channels in Electrophorus electrocytes and Xenopus oocytes. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4381–4388. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida S., Kwon H. M., Preston A. S., Handler J. S. Expression of Madin-Darby canine kidney cell Na(+)-and Cl(-)-dependent taurine transporter in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9605–9609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida S., Sasaki S., Furukawa T., Hiraoka M., Imai T., Hirata Y., Marumo F. Molecular cloning of a chloride channel that is regulated by dehydration and expressed predominantly in kidney medulla. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):3821–3824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshitomi K., Kondo Y., Imai M. Evidence for conductive Cl- pathways across the cell membranes of the thin ascending limb of Henle's loop. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):866–871. doi: 10.1172/JCI113691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]