Abstract
The liver is highly susceptible to a number of pathological insults, including ischemia/reperfusion injury. One of the striking consequences of liver injury is the associated pulmonary dysfunction that may be related to the release of hepatic-derived cytokines. We have previously employed an animal model of hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury, and demonstrated that this injury causes the production and release of hepatic-derived TNF, which mediates a neutrophil-dependent pulmonary microvascular injury. In this study, we have extended these previous observations to assess whether an interrelationship between TNF and the neutrophil chemoattractant/activating factor, epithelial neutrophil activating protein-78 (ENA-78), exists that may be accountable for the pathology of lung injury found in this model. In the context of hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury, we demonstrated the following alterations in lung pathophysiology: (a) an increase in pulmonary microvascular permeability, lung neutrophil sequestration, and production of pulmonary-derived ENA-78; (b) passive immunization with neutralizing TNF antiserum resulted in a significant suppression of pulmonary-derived ENA-78; and (c) passive immunization with neutralizing ENA-78 antiserum resulted in a significant attenuation of pulmonary neutrophil sequestration and microvascular permeability similar to our previous studies with anti-TNF. These findings support the notion that pulmonary ENA-78 produced in response to hepatic-derived TNF is an important mediator of lung injury.
Full text
PDF


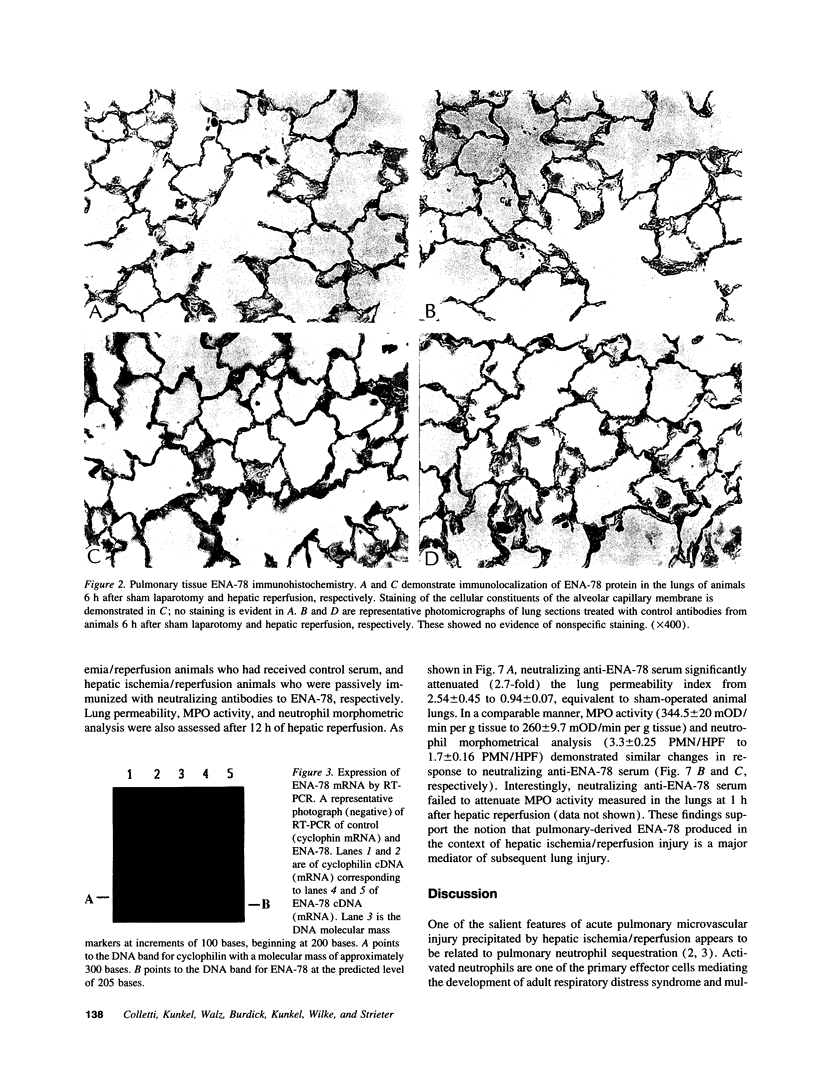
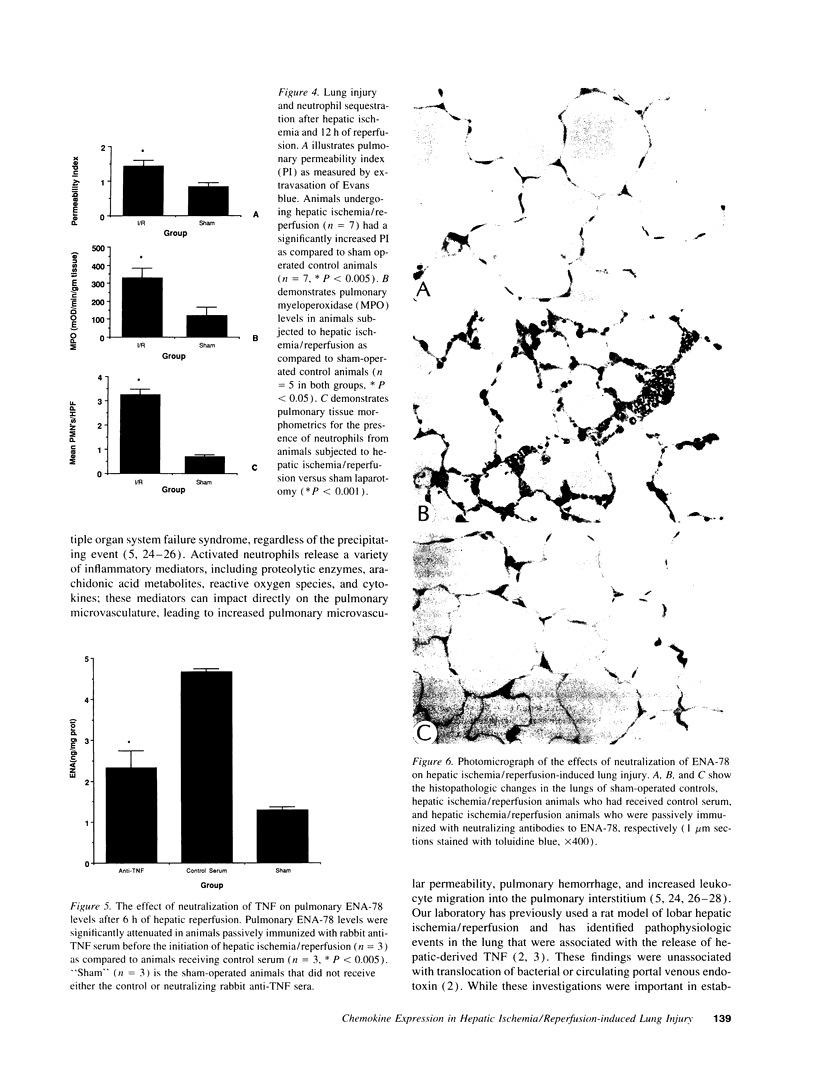
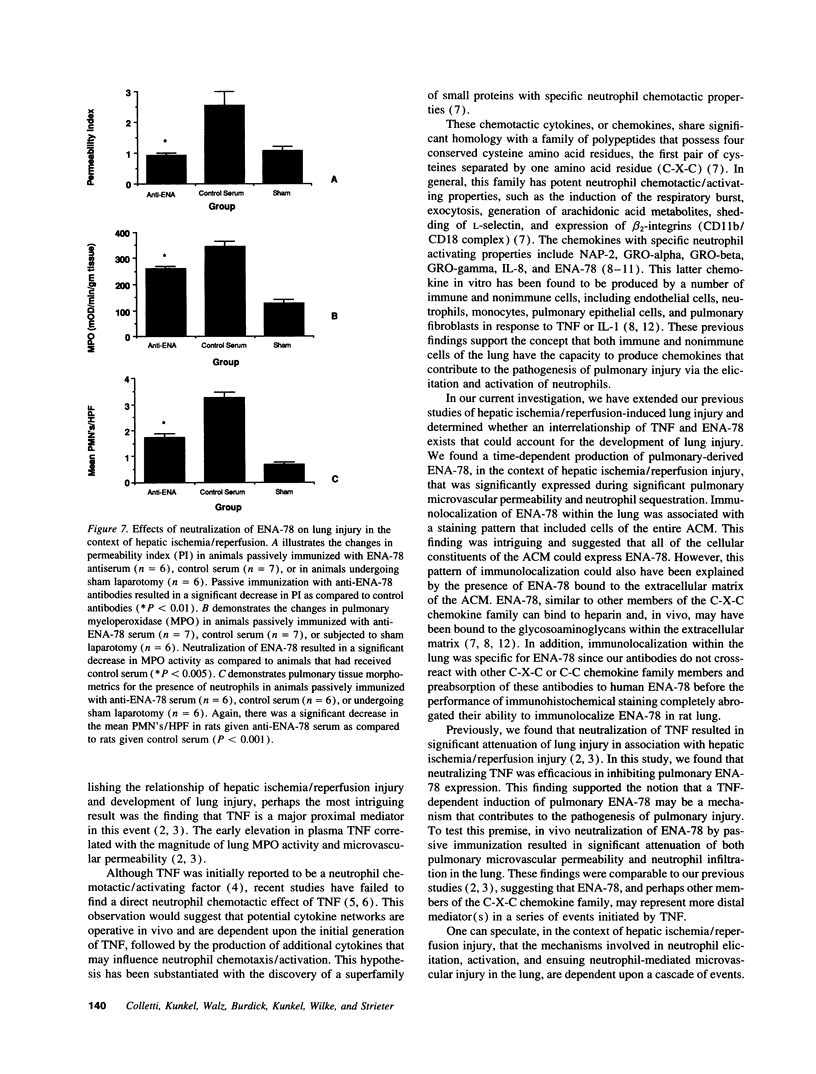

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnaout M. A. Structure and function of the leukocyte adhesion molecules CD11/CD18. Blood. 1990 Mar 1;75(5):1037–1050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Walz A., Kunkel S. L. Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin 8, a novel cytokine that activates neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1045–1049. doi: 10.1172/JCI114265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird B. R., Cheronis J. C., Sandhaus R. A., Berger E. M., White C. W., Repine J. E. O2 metabolites and neutrophil elastase synergistically cause edematous injury in isolated rat lungs. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Dec;61(6):2224–2229. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.6.2224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chensue S. W., Remick D. G., Shmyr-Forsch C., Beals T. F., Kunkel S. L. Immunohistochemical demonstration of cytoplasmic and membrane-associated tumor necrosis factor in murine macrophages. Am J Pathol. 1988 Dec;133(3):564–572. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colletti L. M., Burtch G. D., Remick D. G., Kunkel S. L., Strieter R. M., Guice K. S., Oldham K. T., Campbell D. A., Jr The production of tumor necrosis factor alpha and the development of a pulmonary capillary injury following hepatic ischemia/reperfusion. Transplantation. 1990 Feb;49(2):268–272. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199002000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colletti L. M., Remick D. G., Burtch G. D., Kunkel S. L., Strieter R. M., Campbell D. A., Jr Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the pathophysiologic alterations after hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1936–1943. doi: 10.1172/JCI114656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faist E., Baue A. E., Dittmer H., Heberer G. Multiple organ failure in polytrauma patients. J Trauma. 1983 Sep;23(9):775–787. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198309000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flick M. R., Perel A., Staub N. C. Leukocytes are required for increased lung microvascular permeability after microembolization in sheep. Circ Res. 1981 Mar;48(3):344–351. doi: 10.1161/01.res.48.3.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum S. E., Wu K. M., Jay M. Lung myeloperoxidase as a measure of pulmonary leukostasis in rabbits. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Dec;59(6):1978–1985. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.59.6.1978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green T. P., Johnson D. E., Marchessault R. P., Gatto C. W. Transvascular flux and tissue accrual of Evans blue: effects of endotoxin and histamine. J Lab Clin Med. 1988 Feb;111(2):173–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi H., Chaudry I. H., Clemens M. G., Baue A. E. Hepatic ischemia models for determining the effects of ATP-MgCl2 treatment. J Surg Res. 1986 Feb;40(2):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(86)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linderkamp O., Mader T., Butenandt O., Riegel K. P. Plasma volume estimation in severely ill infants and children using a simplified Evans blue method. Eur J Pediatr. 1977 Jun 1;125(2):135–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00489986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukacs N. W., Kunkel S. L., Strieter R. M., Warmington K., Chensue S. W. The role of macrophage inflammatory protein 1 alpha in Schistosoma mansoni egg-induced granulomatous inflammation. J Exp Med. 1993 Jun 1;177(6):1551–1559. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L. ARDS, neutrophils, and pentoxifylline. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Nov;138(5):1103–1105. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.5.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Oppenheim J. J. Interleukin 8 and MCAF: novel inflammatory cytokines inducible by IL 1 and TNF. Cytokine. 1989 Nov;1(1):2–13. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(89)91043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen D. T., Eskandai M. K., DeForge L. E., Raiford C. L., Strieter R. M., Kunkel S. L., Remick D. G. Cyclosporin a modulation of tumor necrosis factor gene expression and effects in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol. 1990 May 15;144(10):3822–3828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obayashi T. Addition of perchloric acid to blood samples for colorimetric limulus test using chromogenic substrate: comparison with conventional procedures and clinical applications. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Sep;104(3):321–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond A., Balentien E., Thomas H. G., Flaggs G., Barton D. E., Spiess J., Bordoni R., Francke U., Derynck R. Molecular characterization and chromosomal mapping of melanoma growth stimulatory activity, a growth factor structurally related to beta-thromboglobulin. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2025–2033. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03042.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saria A., Lundberg J. M. Evans blue fluorescence: quantitative and morphological evaluation of vascular permeability in animal tissues. J Neurosci Methods. 1983 May;8(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(83)90050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauder D. N., Mounessa N. L., Katz S. I., Dinarello C. A., Gallin J. I. Chemotactic cytokines: the role of leukocytic pyrogen and epidermal cell thymocyte-activating factor in neutrophil chemotaxis. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):828–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlag G., Redl H., Hallström S. The cell in shock: the origin of multiple organ failure. Resuscitation. 1991 Apr;21(2-3):137–180. doi: 10.1016/0300-9572(91)90044-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Chensue S. W., Basha M. A., Standiford T. J., Lynch J. P., Baggiolini M., Kunkel S. L. Human alveolar macrophage gene expression of interleukin-8 by tumor necrosis factor-alpha, lipopolysaccharide, and interleukin-1 beta. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Apr;2(4):321–326. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/2.4.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Kunkel S. L., Burdick M. D., Lincoln P. M., Walz A. The detection of a novel neutrophil-activating peptide (ENA-78) using a sensitive ELISA. Immunol Invest. 1992 Oct;21(6):589–596. doi: 10.3109/08820139209069393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Lukacs N. W., Standiford T. J., Kunkel S. L. Cytokines. 2. Cytokines and lung inflammation: mechanisms of neutrophil recruitment to the lung. Thorax. 1993 Jul;48(7):765–769. doi: 10.1136/thx.48.7.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Lynch J. P., 3rd, Basha M. A., Standiford T. J., Kasahara K., Kunkel S. L. Host responses in mediating sepsis and adult respiratory distress syndrome. Semin Respir Infect. 1990 Sep;5(3):233–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till G. O., Morganroth M. L., Kunkel R., Ward P. A. Activation of C5 by cobra venom factor is required in neutrophil-mediated lung injury in the rat. Am J Pathol. 1987 Oct;129(1):44–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz A., Burgener R., Car B., Baggiolini M., Kunkel S. L., Strieter R. M. Structure and neutrophil-activating properties of a novel inflammatory peptide (ENA-78) with homology to interleukin 8. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1355–1362. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Regiani S. Neutrophils degrade subendothelial matrices in the presence of alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor. Cooperative use of lysosomal proteinases and oxygen metabolites. J Clin Invest. 1984 May;73(5):1297–1303. doi: 10.1172/JCI111332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Matsushima K., Oppenheim J. J., Leonard E. J. Neutrophil chemotactic factor produced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated human blood mononuclear leukocytes: partial characterization and separation from interleukin 1 (IL 1). J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):788–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]