Abstract
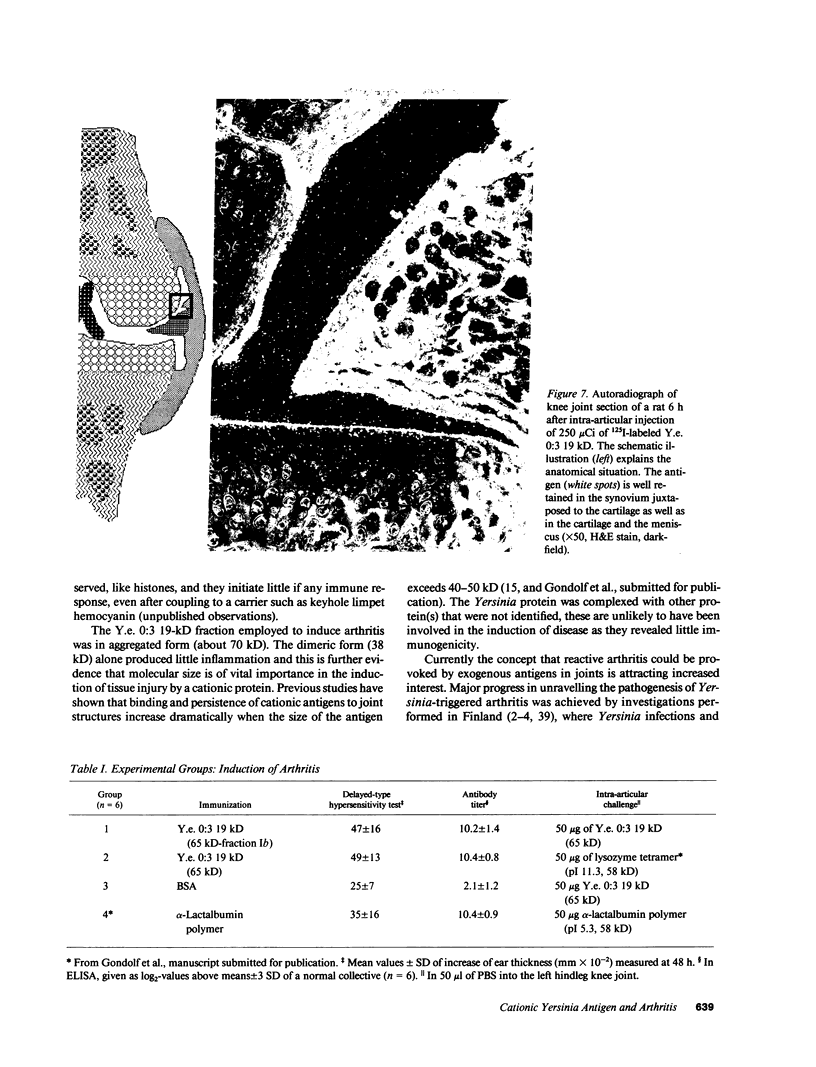
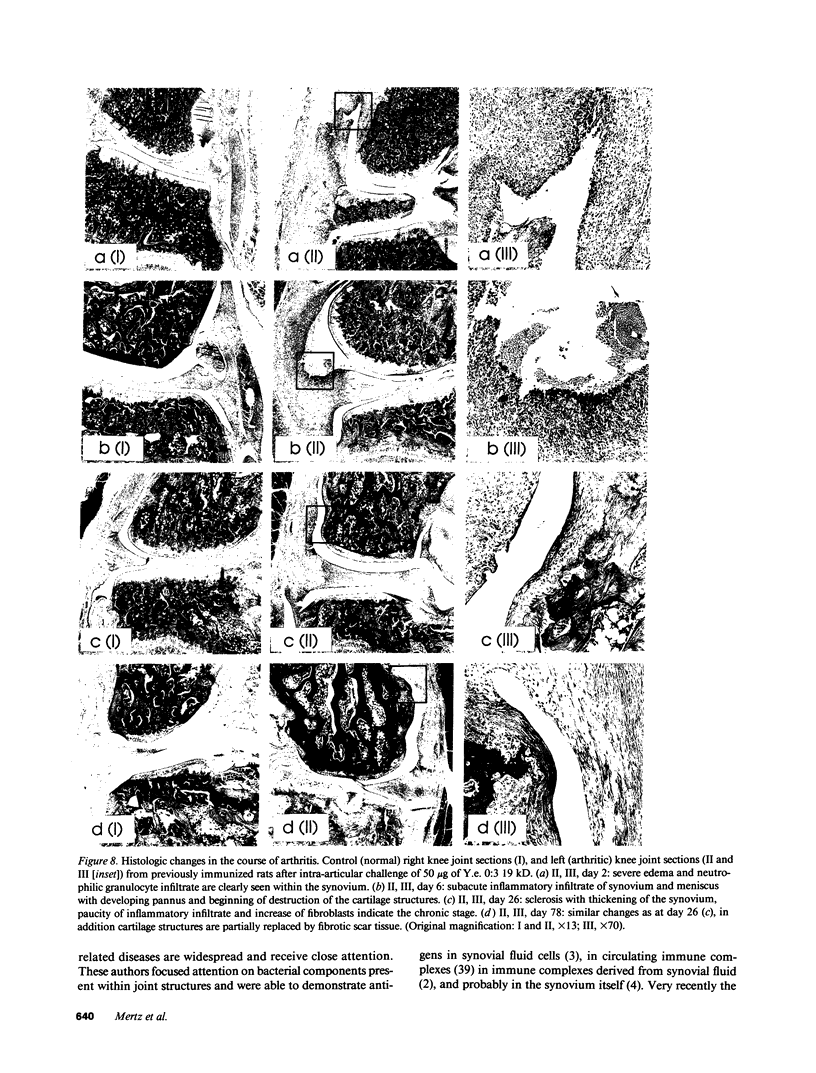
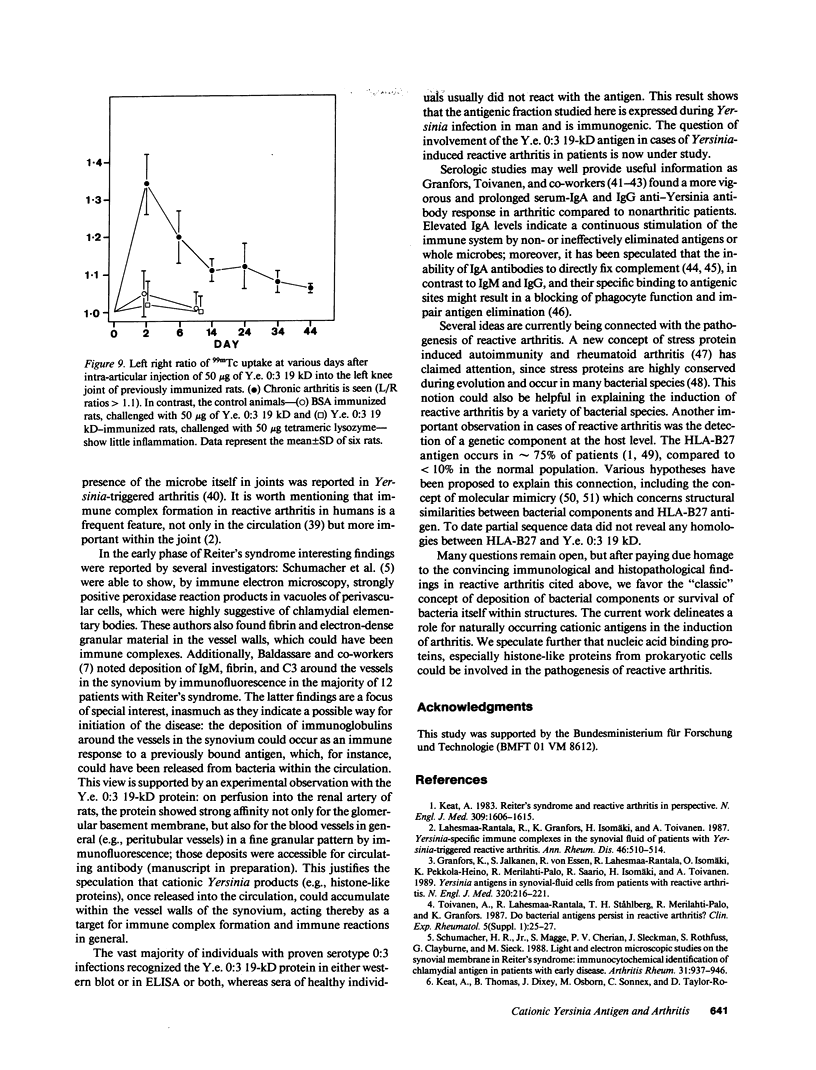
Cationic antigens are known to have considerable arthritogenic potential in experimental systems. During a systematic search for suitable, naturally occurring candidates an intracellular protein was isolated from the ribosomal pellet of Yersinia enterocolitica 0:3, a bacterial strain associated with reactive arthritis in humans. The protein is highly cationic, contains two 19-kD polypeptide chains linked by a disulfide bond, and reveals a strong tendency for spontaneous aggregation. It is suggested to be a nucleic acid binding protein. We tested this antigen for its ability to induce arthritis after intra-articular challenge in preimmunized rats. An acute inflammatory phase followed by transition to chronicity was observed both by technetium-99m scintigraphy and from histology. Massive polymorphonuclear leucocyte infiltration of the synovium was seen early on and fibrosis and thickening of the joint capsule occurred in later stages. Control groups showed no evidence of inflammation. Western blot and ELISA analysis of unselected sera from Yersinia enterocolitica 0:3-infected patients revealed antibodies to the antigen in the majority of cases, whereas healthy individuals rarely reacted. This is the first report of a naturally occurring cationic antigen capable of inducing immunologic tissue injury; it justifies the speculation that cationic antigens from prokaryotic cells could trigger reactive arthritis in humans.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldassare A. R., Weiss T. D., Tsai C. C., Arthur R. E., Moore T. L., Zuckner J. Immunoprotein deposition in synovial tissue in Reiter's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981 Jun;40(3):281–285. doi: 10.1136/ard.40.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batsford S. R., Takamiya M., Vogt A. A model of in situ immune complex glomerulonephritis in the rat employing cationized ferritin. Clin Nephrol. 1980 Nov;14(5):211–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackertz D., Mitchell G. F., Mackay I. R. Antigen-induced arthritis in mice. I. Induction of arthritis in various strains of mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Apr;20(3):841–850. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. H., Kono D. H., Yong Z., Park M. S., Oldstone M. M., Yu D. T. A Yersinia pseudotuberculosis protein which cross-reacts with HLA-B27. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):3003–3011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke T. D., Hurd E. R., Ziff M., Jasin H. E. The pathogenesis of chronic inflammation in experimental antigen-induced arthritis. II. Preferential localization of antigen-antibody complexes to collagenous tissues. J Exp Med. 1972 Feb 1;135(2):323–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke T. D., Jasin H. E. The pathogenesis of chronic inflammation in experimental antigen-induced arthritis. I. The role of antigen on the local immune response. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Jul-Aug;15(4):327–337. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUMONDE D. C., GLYNN L. E. The production of arthritis in rabbits by an immunological reaction to fibrin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Aug;43:373–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dequeker J., Jamar R., Walravens M. HLA-B27, arthritis and Yersinia enterocolitica infection. J Rheumatol. 1980 Sep-Oct;7(5):706–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K., Rouviere-Yaniv J. Histonelike proteins of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):301–319. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.301-319.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddie D. S., Schulkind M. L., Robbins J. B. The isolation and biologic activities of purified secretory IgA and IgG anti-Salmonella typhimurium "O" antibodies from rabbit intestinal fluid and colostrum. J Immunol. 1971 Jan;106(1):181–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geider K. Interaction of DNA with DNA-binding proteins: protein exchange and complex stability. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jul 3;87(3):617–622. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Jalkanen S., von Essen R., Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Isomäki O., Pekkola-Heino K., Merilahti-Palo R., Saario R., Isomäki H., Toivanen A. Yersinia antigens in synovial-fluid cells from patients with reactive arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jan 26;320(4):216–221. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198901263200404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Toivanen A. IgA-anti-yersinia antibodies in yersinia triggered reactive arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Jul;45(7):561–565. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.7.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiss J. M. Bactericidal activity of meningococcal antisera. Blocking by IgA of lytic antibody in human convalescent sera. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1779–1784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer M., Zeidler H., Klimsa S., Heesemann J. Yersinia enterocolitica in the synovial membrane of patients with Yersinia-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Dec;33(12):1795–1800. doi: 10.1002/art.1780331206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holck A., Kleppe K. Affinity of protein HU for different nucleic acids. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 3;185(1):121–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80753-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollister J. R., Mannik M. Antigen retention in joint tissues in antigen-induced synovitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Apr;16(4):615–627. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keat A. Reiter's syndrome and reactive arthritis in perspective. N Engl J Med. 1983 Dec 29;309(26):1606–1615. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198312293092604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijsen M. W., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B., van den Broek W. J. Detection and quantification of experimental joint inflammation in mice by measurement of 99mTc-pertechnetate uptake. Agents Actions. 1981 Dec;11(6-7):640–642. doi: 10.1007/BF01978775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Granfors K., Isomäki H., Toivanen A. Yersinia specific immune complexes in the synovial fluid of patients with yersinia triggered reactive arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Jul;46(7):510–514. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.7.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Granfors K., Kekomäki R., Toivanen A. Circulating yersinia specific immune complexes after acute yersiniosis: a follow up study of patients with and without reactive arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Feb;46(2):121–126. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. H., Hartzen S. H., Parm M. The determination of specific IgA-antibodies to Yersinia enterocolitica and their role in enteric infections and their complications. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1985 Oct;93(5):331–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02897.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R., Buc H., Lecocq J. P., Bautz E. K. Prokaryotic histone-like protein interacting with RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3548–3552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lens J. W., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B. Quantitation of arthritis by 99mTc-uptake measurements in the mouse knee-joint: correlation with histological joint inflammation scores. Agents Actions. 1984 Jun;14(5-6):723–728. doi: 10.1007/BF01978915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oite T., Batsford S. R., Mihatsch M. J., Takamiya H., Vogt A. Quantitative studies of in situ immune complex glomerulonephritis in the rat induced by planted, cationized antigen. J Exp Med. 1982 Feb 1;155(2):460–474. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.2.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettijohn D. E. Histone-like proteins and bacterial chromosome structure. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):12793–12796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvière-Yaniv J., Yaniv M., Germond J. E. E. coli DNA binding protein HU forms nucleosomelike structure with circular double-stranded DNA. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):265–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmiedeke T. M., Stöckl F. W., Weber R., Sugisaki Y., Batsford S. R., Vogt A. Histones have high affinity for the glomerular basement membrane. Relevance for immune complex formation in lupus nephritis. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):1879–1894. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.1879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher H. R., Jr, Magge S., Cherian P. V., Sleckman J., Rothfuss S., Clayburne G., Sieck M. Light and electron microscopic studies on the synovial membrane in Reiter's syndrome. Immunocytochemical identification of chlamydial antigen in patients with early disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Aug;31(8):937–946. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling R., Wachtel E. J. The histones. Adv Protein Chem. 1981;34:1–60. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60517-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanescu R., Leibovich S. J. The negative charge of articular cartilage surfaces. An electron microscopic study using cationized ferritin. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982 Mar;64(3):388–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toivanen A., Granfors K., Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Leino R., Ståhlberg T., Vuento R. Pathogenesis of Yersinia-triggered reactive arthritis: immunological, microbiological and clinical aspects. Immunol Rev. 1985 Aug;86:47–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Nedospasov S. A., Bakayev V. V., Bakayeva T. G., Georgiev G. P. Histone-like proteins in the purified Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleoprotein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2725–2745. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt A., Bockhorn H., Kozima K., Sasaki M. Electron microscopic localization of the nephrotoxic antibody in the glomeruli of the rat after intravenous application of purified nephritogenic antibody-ferritin conjugates. J Exp Med. 1968 May 1;127(5):867–878. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.5.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B. Stress proteins, arthritis, and autoimmunity. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Dec;32(12):1497–1504. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780321202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu D. T., Choo S. Y., Schaack T. Molecular mimicry in HLA-B27-related arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 1989 Oct 1;111(7):581–591. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-111-7-581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lent P. L., Dekker C., Mosterd J., van den Bersselaar L., van den Berg W. B. Allergic arthritis induced by cationic proteins: role of molecular weight. Immunology. 1989 Aug;67(4):447–452. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lent P. L., van den Bersselaar L., Grutters G. J., van den Berg W. B. Fate of antigen after intravenous and intraarticular injection into mice. Role of molecular weight and charge. J Rheumatol. 1989 Oct;16(10):1295–1303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., van Beusekom H. J., van de Putte L. B., Zwarts W. A., van der Sluis M. Antigen handling in antigen-induced arthritis in mice: an autoradiographic and immunofluorescence study using whole joint sections. Am J Pathol. 1982 Jul;108(1):9–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B., Zwarts W. A., Joosten L. A. Electrical charge of the antigen determines intraarticular antigen handling and chronicity of arthritis in mice. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1850–1859. doi: 10.1172/JCI111604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]