Abstract
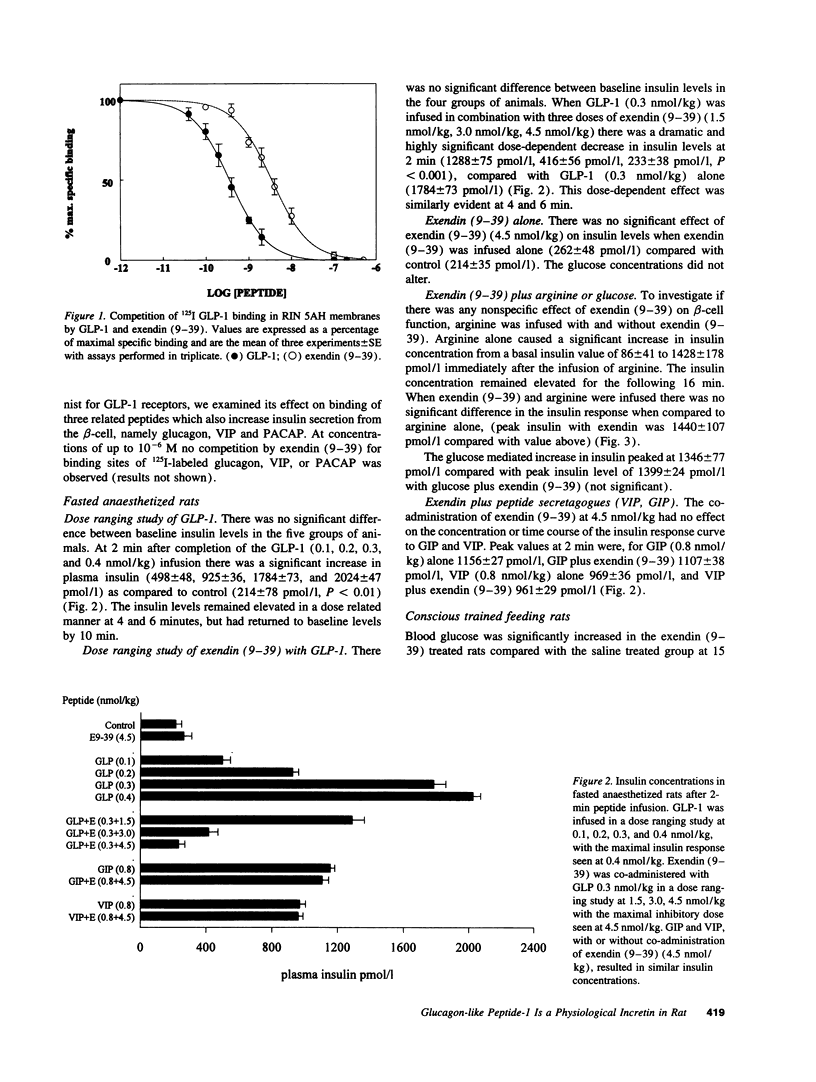
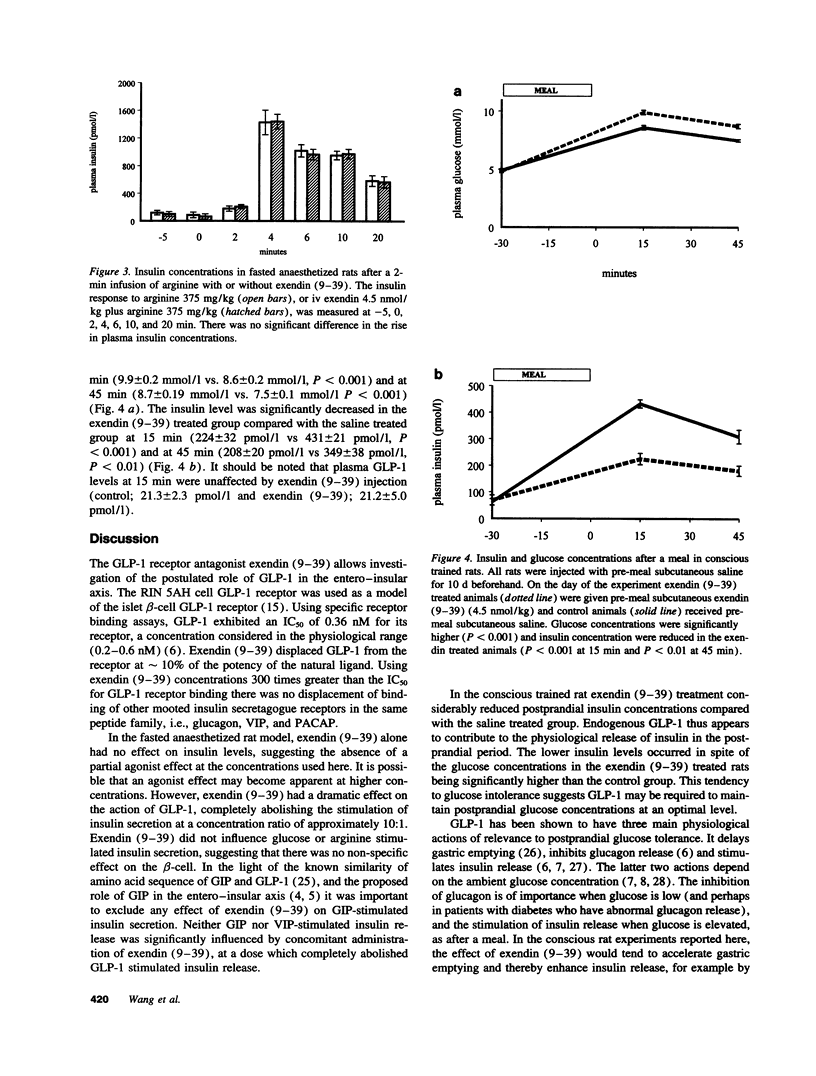
Glucagon-like peptide-1 7-36 amide (GLP-1) has been postulated to be the primary hormonal mediator of the entero-insular axis but evidence has been indirect. The discovery of exendin (9-39), a GLP-1 receptor antagonist, allowed this to be further investigated. The IC50 for GLP-1 receptor binding, using RIN 5AH beta-cell membranes, was found to be 0.36 nmol/l for GLP-1 and 3.44 nmol/l for exendin (9-39). There was no competition by exendin (9-39) at binding sites for glucagon or related peptides. In the anaesthetized fasted rat, insulin release after four doses of GLP-1 (0.1, 0.2, 0.3, and 0.4 nmol/kg) was tested by a 2-min intravenous infusion. Exendin (9-39) (1.5, 3.0, and 4.5 nmol/kg) was administered with GLP-1 0.3 nmol/kg, or saline, and only the highest dose fully inhibited insulin release. Exendin (9-39) at 4.5 nmol/kg had no effect on glucose, arginine, vasoactive intestinal peptide or glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide stimulated insulin secretion. Postprandial insulin release was studied in conditioned conscious rats after a standard meal. Exendin (9-39) (0.5 nmol/kg) considerably reduced postprandial insulin concentrations, for example by 48% at 15 min (431 +/- 21 pmol/l saline, 224 +/- 32 pmol/l exendin, P < 0.001). Thus, GLP-1 appears to play a major role in the entero-insular axis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albano J. D., Ekins R. P., Maritz G., Turner R. C. A sensitive, precise radioimmunoassay of serum insulin relying on charcoal separation of bound and free hormone moieties. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1972 Jul;70(3):487–509. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0700487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhogal R., Smith D. M., Purkiss P., Bloom S. R. Molecular identification of binding sites for calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) in mammalian lung: species variation and binding of truncated CGRP and IAPP. Endocrinology. 1993 Nov;133(5):2351–2361. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.5.8404688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupre J., Ross S. A., Watson D., Brown J. C. Stimulation of insulin secretion by gastric inhibitory polypeptide in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Nov;37(5):826–828. doi: 10.1210/jcem-37-5-826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert R., Creutzfeldt W. Gastrointestinal peptides and insulin secretion. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1987 Jan;3(1):1–26. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610030101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng J., Kleinman W. A., Singh L., Singh G., Raufman J. P. Isolation and characterization of exendin-4, an exendin-3 analogue, from Heloderma suspectum venom. Further evidence for an exendin receptor on dispersed acini from guinea pig pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7402–7405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehmann H. C., Habener J. F. Insulinotropic hormone glucagon-like peptide-I(7-37) stimulation of proinsulin gene expression and proinsulin biosynthesis in insulinoma beta TC-1 cells. Endocrinology. 1992 Jan;130(1):159–166. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.1.1309325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutniak M., Orskov C., Holst J. J., Ahrén B., Efendic S. Antidiabetogenic effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 (7-36)amide in normal subjects and patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1992 May 14;326(20):1316–1322. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199205143262003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göke R., Fehmann H. C., Linn T., Schmidt H., Krause M., Eng J., Göke B. Exendin-4 is a high potency agonist and truncated exendin-(9-39)-amide an antagonist at the glucagon-like peptide 1-(7-36)-amide receptor of insulin-secreting beta-cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19650–19655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst J. J., Orskov C., Nielsen O. V., Schwartz T. W. Truncated glucagon-like peptide I, an insulin-releasing hormone from the distal gut. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 26;211(2):169–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81430-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanse S. M., Kreymann B., Ghatei M. A., Bloom S. R. Identification and characterization of glucagon-like peptide-1 7-36 amide-binding sites in the rat brain and lung. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 5;241(1-2):209–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreymann B., Williams G., Ghatei M. A., Bloom S. R. Glucagon-like peptide-1 7-36: a physiological incretin in man. Lancet. 1987 Dec 5;2(8571):1300–1304. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91194-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra R., Singh L., Eng J., Raufman J. P. Exendin-4, a new peptide from Heloderma suspectum venom, potentiates cholecystokinin-induced amylase release from rat pancreatic acini. Regul Pept. 1992 Sep 22;41(2):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(92)90044-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mojsov S., Kopczynski M. G., Habener J. F. Both amidated and nonamidated forms of glucagon-like peptide I are synthesized in the rat intestine and the pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8001–8008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mojsov S., Weir G. C., Habener J. F. Insulinotropin: glucagon-like peptide I (7-37) co-encoded in the glucagon gene is a potent stimulator of insulin release in the perfused rat pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):616–619. doi: 10.1172/JCI112855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauck M. A., Kleine N., Orskov C., Holst J. J., Willms B., Creutzfeldt W. Normalization of fasting hyperglycaemia by exogenous glucagon-like peptide 1 (7-36 amide) in type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1993 Aug;36(8):741–744. doi: 10.1007/BF00401145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauck M., Schmidt W. E., Ebert R., Strietzel J., Cantor P., Hoffmann G., Creutzfeldt W. Insulinotropic properties of synthetic human gastric inhibitory polypeptide in man: interactions with glucose, phenylalanine, and cholecystokinin-8. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Sep;69(3):654–662. doi: 10.1210/jcem-69-3-654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov C., Bersani M., Johnsen A. H., Højrup P., Holst J. J. Complete sequences of glucagon-like peptide-1 from human and pig small intestine. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12826–12829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Krans H. M., Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. 3. Binding of glucagon: method of assay and specificity. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1861–1871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda K., Smith D. M., Ghatei M. A., Bloom S. R. Investigation of the interaction of VIP binding sites with VIP and PACAP in human brain. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Mar 16;137(1):19–23. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90288-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda K., Smith D. M., Ghatei M. A., Murphy J. K., Bloom S. R. Investigation and characterization of receptors for pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide in human brain by radioligand binding and chemical cross-linking. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 May;72(5):958–964. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-5-958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Porret A., Bühler L., Deng S. P., Morel P., Widmann C. Cloning and functional expression of the human islet GLP-1 receptor. Demonstration that exendin-4 is an agonist and exendin-(9-39) an antagonist of the receptor. Diabetes. 1993 Nov;42(11):1678–1682. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.11.1678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Eisentraut A. M. Entero-insular axis. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Mar;123(3):261–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varndell I. M., Bishop A. E., Sikri K. L., Uttenthal L. O., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Localization of glucagon-like peptide (GLP) immunoreactants in human gut and pancreas using light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Oct;33(10):1080–1086. doi: 10.1177/33.10.3900195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettergren A., Schjoldager B., Mortensen P. E., Myhre J., Christiansen J., Holst J. J. Truncated GLP-1 (proglucagon 78-107-amide) inhibits gastric and pancreatic functions in man. Dig Dis Sci. 1993 Apr;38(4):665–673. doi: 10.1007/BF01316798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


