Abstract
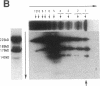
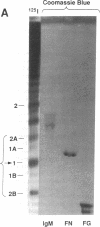
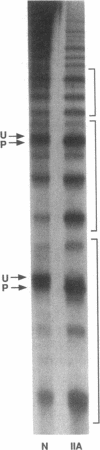
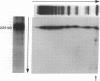
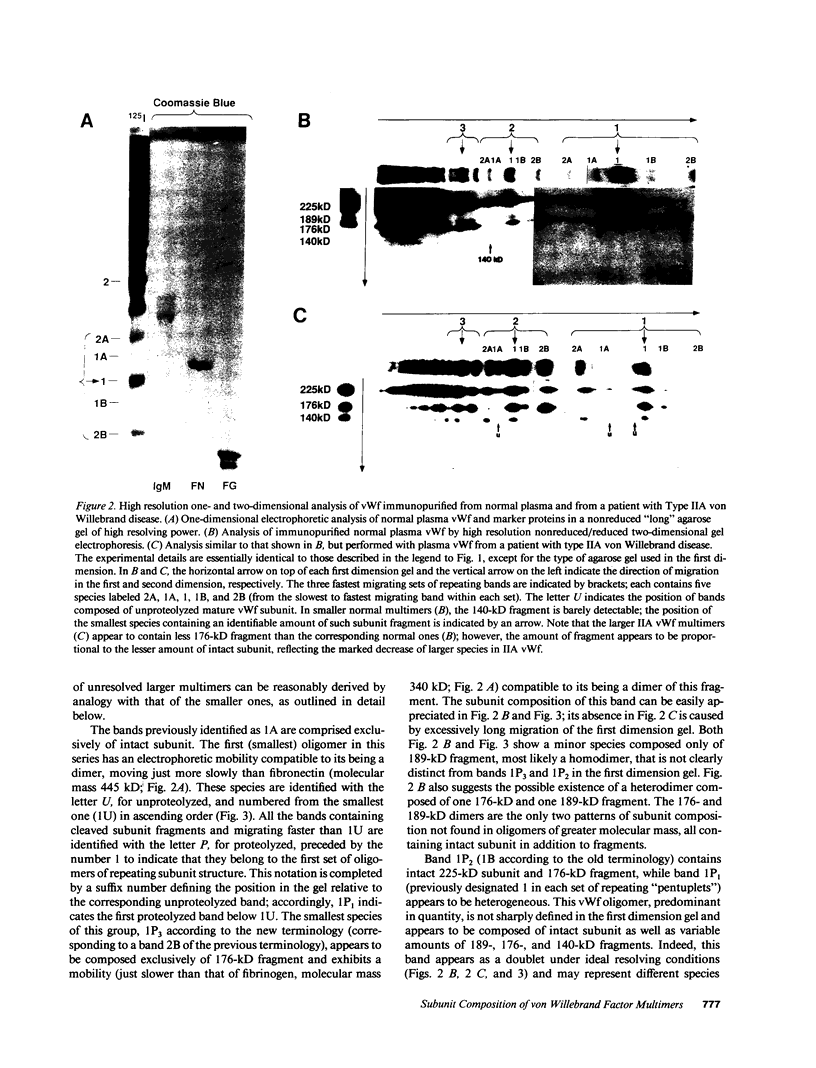
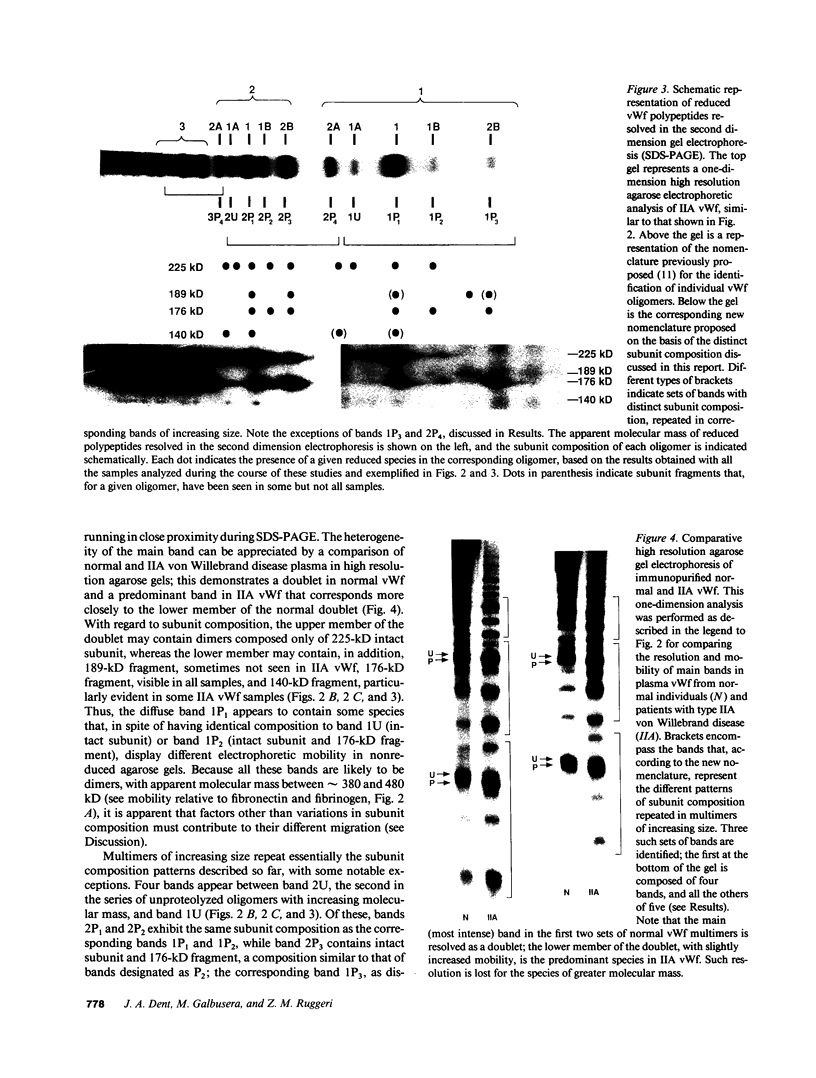
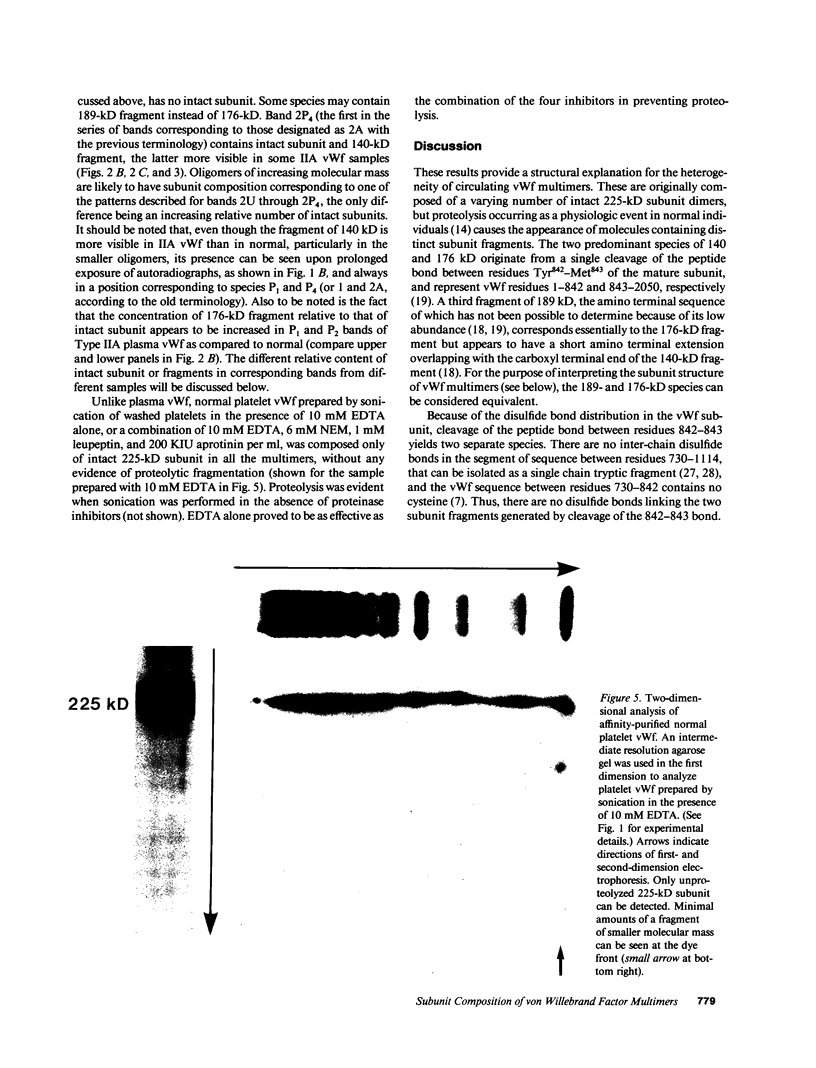
In this report we demonstrate that proteolytic cleavage of the constituent subunit is one of the causes determining the heterogeneous size distribution of plasma von Willebrand factor (vWf) multimers. As shown by two-dimensional nonreduced/reduced agarose/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, the structure of circulating vWf molecules may deviate from that represented by assemblage of a variable number of identical subunits. Indeed, even though the largest multimers in normal plasma appear to be composed predominantly of intact 225-kD subunits, those of intermediate and smaller size contain also 189-, 176-, and 140-kD proteolytic fragments. Different subunit composition patterns are repeated regularly in multimers of increasing molecular mass, yielding series of bands with similar structure. One of these series consists of molecules without evidence of proteolytic fragmentation, and its smallest member appears to be a dimer of 225-kD subunits. Type IIA von Willebrand disease, characterized by absence of the largest multimers, displays a pattern wherein the fragments of 176 and 140 kD are relatively increased, that of 189 kD is markedly decreased or absent, but the composition of individual multimers is otherwise similar to that of species seen also in normal plasma. In contrast to those in the circulation, all normal platelet vWf multimers contain only intact subunit. These results suggest that proteolytic cleavage of plasma vWf subunits occurs after release from cellular sites, whereas platelet vWf stored in alpha-granules is protected from proteolysis. These findings provide information that may be relevant for understanding the normal processing of vWf multimers and for elucidating the pathogenesis of some of the congenital and acquired structural abnormalities of this molecule.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batlle J., Lopez Fernandez M. F., Campos M., Justica B., Berges C., Navarro J. L., Diaz Cremades J. M., Kasper C. K., Dent J. A., Ruggeri Z. M. The heterogeneity of type IIA von Willebrand's disease: studies with protease inhibitors. Blood. 1986 Dec;68(6):1207–1212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batlle J., Lopez Fernandez M. F., Lasierra J., Fernandez Villamor A., Lopez Berges C., Lopez Borrasca A., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. von Willebrand disease type IIC with different abnormalities of von Willebrand factor in the same sibship. Am J Hematol. 1986 Feb;21(2):177–188. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830210207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz S. D., Dent J., Roberts J., Fujimura Y., Plow E. F., Titani K., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Epitope mapping of the von Willebrand factor subunit distinguishes fragments present in normal and type IIA von Willebrand disease from those generated by plasmin. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):524–531. doi: 10.1172/JCI112843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonthron D., Orr E. C., Mitsock L. M., Ginsburg D., Handin R. I., Orkin S. H. Nucleotide sequence of pre-pro-von Willebrand factor cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7125–7127. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopek M. W., Girma J. P., Fujikawa K., Davie E. W., Titani K. Human von Willebrand factor: a multivalent protein composed of identical subunits. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3146–3155. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciavarella G., Ciavarella N., Antoncecchi S., De Mattia D., Ranieri P., Dent J., Zimmerman T. S., Ruggeri Z. M. High-resolution analysis of von Willebrand factor multimeric composition defines a new variant of type I von Willebrand disease with aberrant structure but presence of all size multimers (type IC). Blood. 1985 Dec;66(6):1423–1429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco L., Mazzucato M., De Roia D., Casonato A., Federici A. B., Girolami A., Ruggeri Z. M. Distinct abnormalities in the interaction of purified types IIA and IIB von Willebrand factor with the two platelet binding sites, glycoprotein complexes Ib-IX and IIb-IIIa. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):785–792. doi: 10.1172/JCI114775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J. A., Berkowitz S. D., Ware J., Kasper C. K., Ruggeri Z. M. Identification of a cleavage site directing the immunochemical detection of molecular abnormalities in type IIA von Willebrand factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6306–6310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Binding of soluble form of fibroblast surface protein, fibronectin, to collagen. Int J Cancer. 1977 Jul 15;20(1):1–5. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay P. J., Kawai Y., Wagner D. D., Ginsburg D., Bonthron D., Ohlsson-Wilhelm B. M., Chavin S. I., Abraham G. N., Handin R. I., Orkin S. H. Propolypeptide of von Willebrand factor circulates in blood and is identical to von Willebrand antigen II. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):995–998. doi: 10.1126/science.3486471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federici A. B., Bader R., Pagani S., Colibretti M. L., De Marco L., Mannucci P. M. Binding of von Willebrand factor to glycoproteins Ib and IIb/IIIa complex: affinity is related to multimeric size. Br J Haematol. 1989 Sep;73(1):93–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb00226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler W. E., Fretto L. J., Hamilton K. K., Erickson H. P., McKee P. A. Substructure of human von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1491–1500. doi: 10.1172/JCI112129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Titani K., Holland L. Z., Russell S. R., Roberts J. R., Elder J. H., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. von Willebrand factor. A reduced and alkylated 52/48-kDa fragment beginning at amino acid residue 449 contains the domain interacting with platelet glycoprotein Ib. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):381–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Zimmerman T. S. Characterization of the human factor VIII procoagulant protein with a heterologous precipitating antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg D., Konkle B. A., Gill J. C., Montgomery R. R., Bockenstedt P. L., Johnson T. A., Yang A. Y. Molecular basis of human von Willebrand disease: analysis of platelet von Willebrand factor mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3723–3727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralnick H. R., Williams S. B., McKeown L. P., Maisonneuve P., Jenneau C., Sultan Y. A variant of type II von Willebrand disease with an abnormal triplet structure and discordant effects of protease inhibitors on plasma and platelet von Willebrand factor structure. Am J Hematol. 1987 Mar;24(3):259–266. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830240305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralnick H. R., Williams S. B., McKeown L. P., Maisonneuve P., Jenneau C., Sultan Y., Rick M. E. In vitro correction of the abnormal multimeric structure of von Willebrand factor in type IIa von Willebrand's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5968–5972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAZAL L. A., AMSEL S., MILLER O. P., TOCANTINS L. M. THE PREPARATION AND SOME PROPERTIES OF FIBRINOGEN PRECIPITATED FROM HUMAN PLASMA BY GLYCINE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Aug-Sep;113:989–994. doi: 10.3181/00379727-113-28553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita S., Harrison J., Lazerson J., Abildgaard C. F. A new variant of dominant type II von Willebrand's disease with aberrant multimeric pattern of factor VIII-related antigen (type IID). Blood. 1984 Jun;63(6):1369–1371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Bohn J. W., Ferry E. L., Yamamoto H., Molinaro C. A., Sherman L. A., Klinman N. R., Katz D. H. Monoclonal dinitrophenyl-specific murine IgE antibody: preparation, isolation, and characterization. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2728–2737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch D. C., Williams R., Zimmerman T. S., Kirby E. P., Livingston D. M. Biosynthesis of the subunits of factor VIIIR by bovine aortic endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2738–2742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch D. C., Zimmerman T. S., Ling E. H., Browning P. J. An explanation for minor multimer species in endothelial cell-synthesized von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):2048–2051. doi: 10.1172/JCI112535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannucci P. M., Lombardi R., Federici A. B., Dent J. A., Zimmerman T. S., Ruggeri Z. M. A new variant of type II von Willebrand disease with aberrant multimeric structure of plasma but not platelet von Willebrand factor (type IIF). Blood. 1986 Jul;68(1):269–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moake J. L., Rudy C. K., Troll J. H., Weinstein M. J., Colannino N. M., Azocar J., Seder R. H., Hong S. L., Deykin D. Unusually large plasma factor VIII:von Willebrand factor multimers in chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 1982 Dec 2;307(23):1432–1435. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198212023072306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery R. R., Zimmerman T. S. von Willebrand's disease antigen II. A new plasma and platelet antigen deficient in severe von Willebrand's disease. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1498–1507. doi: 10.1172/JCI109070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pareti F. I., Niiya K., McPherson J. M., Ruggeri Z. M. Isolation and characterization of two domains of human von Willebrand factor that interact with fibrillar collagen types I and III. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13835–13841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Androlewicz M. J., Brodsky F. M., Holmes N. J., Ways J. P. Monoclonal antibodies: purification, fragmentation and application to structural and functional studies of class I MHC antigens. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Sep 17;53(2):133–173. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Nilsson I. M., Lombardi R., Holmberg L., Zimmerman T. S. Aberrant multimeric structure of von Willebrand factor in a new variant of von Willebrand's disease (type IIC). J Clin Invest. 1982 Nov;70(5):1124–1127. doi: 10.1172/JCI110700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. The complex multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1981 Jun;57(6):1140–1143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. von Willebrand factor and von Willebrand disease. Blood. 1987 Oct;70(4):895–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Kumar S., Takio K., Ericsson L. H., Wade R. D., Ashida K., Walsh K. A., Chopek M. W., Sadler J. E., Fujikawa K. Amino acid sequence of human von Willebrand factor. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3171–3184. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D., Lawrence S. O., Ohlsson-Wilhelm B. M., Fay P. J., Marder V. J. Topology and order of formation of interchain disulfide bonds in von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1987 Jan;69(1):27–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D., Marder V. J. Biosynthesis of von Willebrand protein by human endothelial cells. Identification of a large precursor polypeptide chain. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2065–2067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Dent J. A., Ruggeri Z. M., Nannini L. H. Subunit composition of plasma von Willebrand factor. Cleavage is present in normal individuals, increased in IIA and IIB von Willebrand disease, but minimal in variants with aberrant structure of individual oligomers (types IIC, IID, and IIE). J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):947–951. doi: 10.1172/JCI112394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]