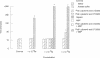Abstract
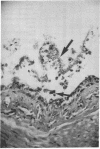
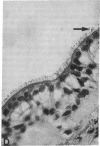
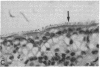
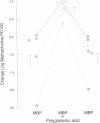
Eosinophil granule major basic protein (MBP), a potent toxin for helminths and mammalian cells in vitro, is a single polypeptide chain rich in arginine. MBP has been localized on damaged helminths and tissues in hypersensitivity diseases including bronchial asthma. The MBP cDNA indicates that MBP is translated as a slightly acidic preproprotein with an acidic propart. To test the hypothesis that the acidic pro-part of proMBP inhibits the toxicity of mature MBP, acidic polyamino acids (aa) were used as antagonists of MBP toxicity to K562 cells and guinea pig tracheal epithelium and used as antagonists of MBP airway hyperresponsiveness in primates. The acidic poly aa inhibited MBP toxicity and MBP airway hyperresposiveness. The acidic poly aa inhibited MBP toxicity in a charge-dependent manner similar to that proposed for proMBP, suggesting that the acidic pro-part of proMBP functions to mask mature MBP toxicity. This inhibition was not limited to MBP, but also applied to polyarginine and eosinophil cationic protein. These acidic poly aa may be useful to inhibit the actions of a number of cationic toxins released by the eosinophil in numerous hypersensitivity diseases.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman S. J., Loegering D. A., Venge P., Olsson I., Harley J. B., Fauci A. S., Gleich G. J. Distinctive cationic proteins of the human eosinophil granule: major basic protein, eosinophil cationic protein, and eosinophil-derived neurotoxin. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2977–2982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker R. L., Gleich G. J., Pease L. R. Acidic precursor revealed in human eosinophil granule major basic protein cDNA. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1493–1498. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker R. L., Loegering D. A., Ten R. M., Hamann K. J., Pease L. R., Gleich G. J. Eosinophil cationic protein cDNA. Comparison with other toxic cationic proteins and ribonucleases. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 1;143(3):952–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., Wassom D. L., Gleich G. J., Loegering D. A., David J. R. Damage to schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni induced directly by eosinophil major basic protein. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):221–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Adolphson C. R. The eosinophilic leukocyte: structure and function. Adv Immunol. 1986;39:177–253. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60351-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Loegering D. A., Mann K. G., Maldonado J. E. Comparative properties of the Charcot-Leyden crystal protein and the major basic protein from human eosinophils. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):633–640. doi: 10.1172/JCI108319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundel R. H., Gerritsen M. E., Gleich G. J., Wegner C. D. Repeated antigen inhalation results in a prolonged airway eosinophilia and airway hyperresponsiveness in primates. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 Feb;68(2):779–786. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.68.2.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundel R. H., Letts L. G., Gleich G. J. Human eosinophil major basic protein induces airway constriction and airway hyperresponsiveness in primates. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1470–1473. doi: 10.1172/JCI115155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierszenbaum F., Ackerman S. J., Gleich G. J. Destruction of bloodstream forms of Trypanosoma cruzi by eosinophil granule major basic protein. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1981 Jul;30(4):775–779. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1981.30.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierszenbaum F., Ackerman S. J., Gleich G. J. Inhibition of antibody-dependent eosinophil-mediated cytotoxicity by heparin. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):515–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreil G., Haiml L., Suchanek G. Stepwise cleavage of the pro part of promelittin by dipeptidylpeptidase IV. Evidence for a new type of precursor--product conversion. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(1):49–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroegel C., Costabel U., Matthys H. Mechanism of membrane damage mediated by eosinophil major basic protein. Lancet. 1987 Jun 13;1(8546):1380–1381. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90686-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane B. P., Miller S. L., Drummond E. J. Use of tracheal organ cultures in toxicity testing. Environ Health Perspect. 1976 Aug;16:89–98. doi: 10.1289/ehp.761689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motojima S., Frigas E., Loegering D. A., Gleich G. J. Toxicity of eosinophil cationic proteins for guinea pig tracheal epithelium in vitro. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Mar;139(3):801–805. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.3.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pineda A. A., Brzica S. M., Jr, Taswell H. F. Continuous- and semicontinuous-flow blood centrifugation systems: therapeutic applications, with plasma-, platelet, lympha-, and eosinapheresis. Transfusion. 1977 Sep-Oct;17(5):407–416. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1977.17578014576.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponz F., Paz-Ares J., Hernández-Lucas C., García-Olmedo F., Carbonero P. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the precursor of the barley toxin alpha-hordothionin. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 1;156(1):131–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09557.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasmoen T. L., Bell M. P., Loegering D. A., Gleich G. J., Prendergast F. G., McKean D. J. Biochemical and amino acid sequence analysis of human eosinophil granule major basic protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12559–12563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner C. D., Jackson A. C., Berry J. D., Gillespie J. R. Dynamic respiratory mechanics in monkeys measured by forced oscillations. Respir Physiol. 1984 Jan;55(1):47–61. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(84)90116-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Peterson C. G., Venge P., Cohn Z. A. Mechanism of membrane damage mediated by human eosinophil cationic protein. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):613–616. doi: 10.1038/321613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]