Abstract
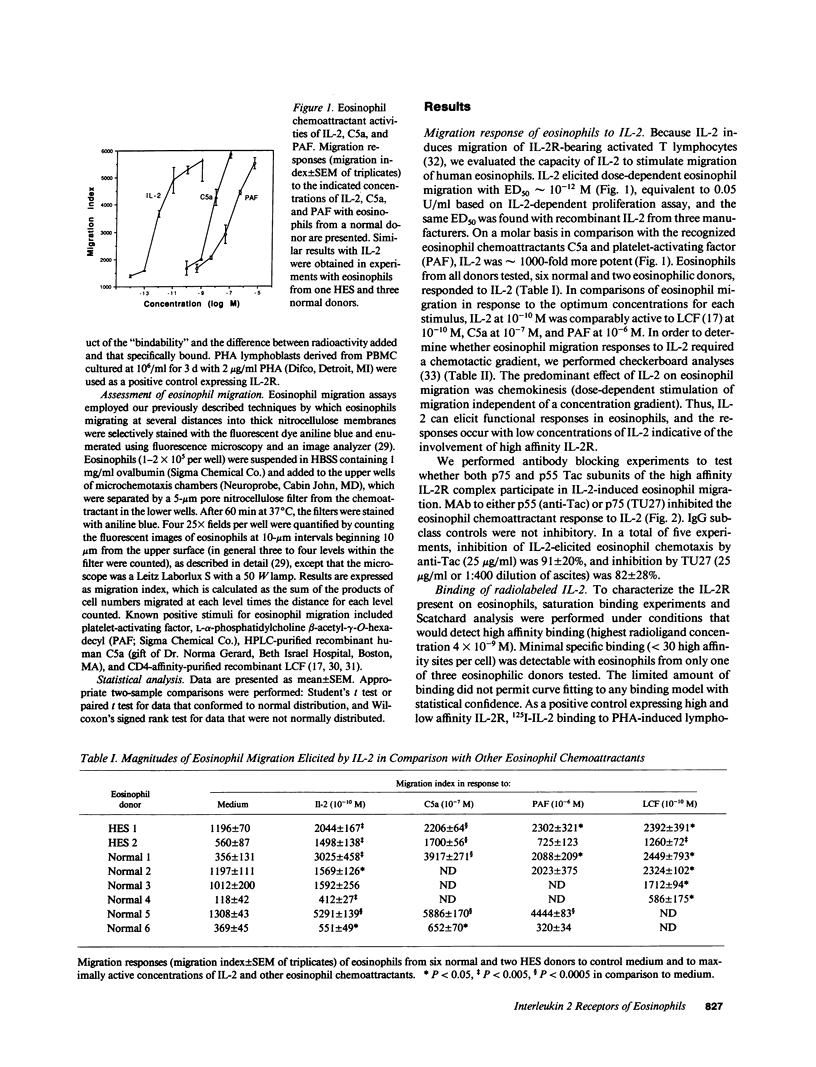
Because T cell-derived cytokines may affect the functioning of eosinophils, we have investigated the capacity of human eosinophils to respond to IL-2. IL-2 was a potent chemoattractant with ED50 of 10(-12) M with eosinophils from all normal and eosinophilic donors tested. The monoclonal antibodies anti-Tac and TU27 against p55 (Tac/CD25) and p75 receptor subunits, respectively, each inhibited IL-2-dependent eosinophil migration. The molar potency of IL-2 and the inhibitory activity of each of the above antibodies suggest that high affinity heterodimeric IL-2 receptor complexes mediated the migration responses of eosinophils to IL-2. Binding of monoclonal antibody against p75 was not detectable by flow cytometry, and high affinity binding sites for 125I-IL-2 were below the limits of quantitation on eosinophils from individuals with eosinophilia. Expression of p55 (Tac/CD25) by eosinophils, without requirement for in vitro activation, was demonstrable by flow cytometry, radioimmunoprecipitation, and Northern blotting for mRNA. Surface expression of p55 on eosinophils from normal or eosinophilic individuals increased during culture for 24-48 h with a biologic activity purified from stimulated U937 cells and to a lesser extent with granulocyte-macrophage CSF or lymphocyte chemoattractant factor but not with nine other cytokines. These studies indicate that blood eosinophils respond to IL-2 and identify one mechanism whereby activation of T lymphocytes may influence the function of eosinophils.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armitage R. J., Lai A. P., Roberts P. J., Cawley J. C. Certain myeloid cells possess receptors for interleukin-2. Br J Haematol. 1986 Dec;64(4):799–807. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1986.tb02242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azzawi M., Bradley B., Jeffery P. K., Frew A. J., Wardlaw A. J., Knowles G., Assoufi B., Collins J. V., Durham S., Kay A. B. Identification of activated T lymphocytes and eosinophils in bronchial biopsies in stable atopic asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Dec;142(6 Pt 1):1407–1413. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.6_Pt_1.1407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben Aribia M. H., Moiré N., Métivier D., Vaquero C., Lantz O., Olive D., Charpentier B., Senik A. IL-2 receptors on circulating natural killer cells and T lymphocytes. Similarity in number and affinity but difference in transmission of the proliferation signal. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):490–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchenall-Sparks M. C., Farrar W. L., Rennick D., Kilian P. L., Ruscetti F. W. Regulation of expression of the interleukin-2 receptor on hematopoietic cells by interleukin-3. Science. 1986 Jul 25;233(4762):455–458. doi: 10.1126/science.3088729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruikshank W. W., Berman J. S., Theodore A. C., Bernardo J., Center D. M. Lymphokine activation of T4+ T lymphocytes and monocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3817–3823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depper J. M., Leonard W. J., Krönke M., Noguchi P. D., Cunningham R. E., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Regulation of interleukin 2 receptor expression: effects of phorbol diester, phospholipase C, and reexposure to lectin or antigen. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3054–3061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enokihara H., Furusawa S., Nakakubo H., Kajitani H., Nagashima S., Saito K., Shishido H., Hitoshi Y., Takatsu K., Noma T. T cells from eosinophilic patients produce interleukin-5 with interleukin-2 stimulation. Blood. 1989 May 15;73(7):1809–1813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza-Delgado I., Ortaldo J. R., Winkler-Pickett R., Sugamura K., Varesio L., Longo D. L. Expression and role of p75 interleukin 2 receptor on human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1821–1826. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Harley J. B., Roberts W. C., Ferrans V. J., Gralnick H. R., Bjornson B. H. NIH conference. The idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Clinical, pathophysiologic, and therapeutic considerations. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jul;97(1):78–92. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-1-78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleit H. B., Wright S. D., Unkeless J. C. Human neutrophil Fc gamma receptor distribution and structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3275–3279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa T., Abu-Ghazaleh R., Kita H., Sanderson C. J., Gleich G. J. Regulatory effect of cytokines on eosinophil degranulation. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):642–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard N. P., Hodges M. K., Drazen J. M., Weller P. F., Gerard C. Characterization of a receptor for C5a anaphylatoxin on human eosinophils. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1760–1766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansel T. T., Pound J. D., Pilling D., Kitas G. D., Salmon M., Gentle T. A., Lee S. S., Thompson R. A. Purification of human blood eosinophils by negative selection using immunomagnetic beads. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Aug 15;122(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90339-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann F., Cannistra S. A., Levine H., Griffin J. D. Expression of interleukin 2 receptors and binding of interleukin 2 by gamma interferon-induced human leukemic and normal monocytic cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):1111–1116. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holter W., Goldman C. K., Casabo L., Nelson D. L., Greene W. C., Waldmann T. A. Expression of functional IL 2 receptors by lipopolysaccharide and interferon-gamma stimulated human monocytes. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2917–2922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huland E., Huland H. Local continuous high dose interleukin 2: a new therapeutic model for the treatment of advanced bladder carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1989 Oct 1;49(19):5469–5474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld H., Berman J. S., Beer D. J., Center D. M. Induction of human T lymphocyte motility by interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3887–3890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Crabtree G. R., Rudikoff S., Pumphrey J., Robb R. J., Krönke M., Svetlik P. B., Peffer N. J., Waldmann T. A. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNAs for the human interleukin-2 receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):626–631. doi: 10.1038/311626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotze M. T., Custer M. C., Rosenberg S. A. Intraperitoneal administration of interleukin-2 in patients with cancer. Arch Surg. 1986 Dec;121(12):1373–1379. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1986.01400120019002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucey D. R., Nicholson-Weller A., Weller P. F. Mature human eosinophils have the capacity to express HLA-DR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1348–1351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggiano N., Colotta F., Castellino F., Ricci R., Valitutti S., Larocca L. M., Musiani P. Interleukin-2 receptor expression in human mast cells and basophils. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1990;91(1):8–14. doi: 10.1159/000235082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrone E. L., Lucey D. R., Weller P. F. Fluorescent staining for leukocyte chemotaxis. Eosinophil-specific fluorescence with aniline blue. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Nov 10;114(1-2):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton D. K., Gere R. J., Feldman H. A., Greaves I. A. Endotoxin measurement: aerosol sampling and application of a new Limulus method. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1990 Jun;51(6):331–337. doi: 10.1080/15298669091369754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Fong T. A. Specific assays for cytokine production by T cells. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Jan 17;116(2):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagler A., Lanier L. L., Phillips J. H. Constitutive expression of high affinity interleukin 2 receptors on human CD16-natural killer cells in vivo. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1527–1533. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Ozaki T., Yanagawa H., Yasuoka S., Ogura T. Eosinophil colony-stimulating factor induced by administration of interleukin-2 into the pleural cavity of patients with malignant pleurisy. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Oct;3(4):291–300. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/3.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narumiya S., Hirata M., Nanba T., Nikaido T., Taniguchi Y., Tagaya Y., Okada M., Mitsuya H., Yodoi J. Activation of interleukin-2 receptor gene by forskolin and cyclic AMP analogues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 13;143(2):753–760. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91418-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prin L., Ameisen J. C., Plumas J., Gruart V., Loiseau S., Bletry O., Fenaux P., Capron M., Capron A. High levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptor in the serum of 30 patients with idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Br J Haematol. 1990 Feb;74(2):233–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb02572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand T. H., Cruikshank W. W., Center D. M., Weller P. F. CD4-mediated stimulation of human eosinophils: lymphocyte chemoattractant factor and other CD4-binding ligands elicit eosinophil migration. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1521–1528. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Greene W. C., Rusk C. M. Low and high affinity cellular receptors for interleukin 2. Implications for the level of Tac antigen. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1126–1146. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secor W. E., Stewart S. J., Colley D. G. Eosinophils and immune mechanisms. VI. The synergistic combination of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and IL-5 accounts for eosinophil-stimulation promoter activity in Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1484–1489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberstein D. S., Ali M. H., Baker S. L., David J. R. Human eosinophil cytotoxicity-enhancing factor. Purification, physical characteristics, and partial amino acid sequence of an active polypeptide. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 1;143(3):979–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberstein D. S., Schoof D. D., Rodrick M. L., Tai P. C., Spry C. J., David J. R., Eberlein T. J. Activation of eosinophils in cancer patients treated with IL-2 and IL-2-generated lymphokine-activated killer cells. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):2162–2167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Cantrell D. A. Interleukin 2 regulates its own receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):864–868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockinger H., Valent P., Majdic O., Bettelheim P., Knapp W. Human blood basophils synthesize interleukin-2 binding sites. Blood. 1990 May 1;75(9):1820–1826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagaya Y., Maeda Y., Mitsui A., Kondo N., Matsui H., Hamuro J., Brown N., Arai K., Yokota T., Wakasugi H. ATL-derived factor (ADF), an IL-2 receptor/Tac inducer homologous to thioredoxin; possible involvement of dithiol-reduction in the IL-2 receptor induction. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):757–764. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03436.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita T., Goto Y., Tada K., Nagata K., Asao H., Sugamura K. Monoclonal antibody defining a molecule possibly identical to the p75 subunit of interleukin 2 receptor. J Exp Med. 1989 Apr 1;169(4):1323–1332. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.4.1323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne K. J., Richardson B. A., Taverne J., Williamson D. J., Vadas M. A., Butterworth A. E. A comparison of eosinophil-activating factor (EAF) with other monokines and lymphokines. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Sep;16(9):1143–1149. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toossi Z., Sedor J. R., Lapurga J. P., Ondash R. J., Ellner J. J. Expression of functional interleukin 2 receptors by peripheral blood monocytes from patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1777–1784. doi: 10.1172/JCI114635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsudo M., Kozak R. W., Goldman C. K., Waldmann T. A. Demonstration of a non-Tac peptide that binds interleukin 2: a potential participant in a multichain interleukin 2 receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9694–9698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Broder S., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. I. Production of anti-Tac monoclonal antibody and distribution of Tac (+) cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valerius T., Repp R., Kalden J. R., Platzer E. Effects of IFN on human eosinophils in comparison with other cytokines. A novel class of eosinophil activators with delayed onset of action. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):2950–2958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visani G., Delwel R., Touw I., Bot F., Löwenberg B. Membrane receptors for interleukin 2 on hematopoietic precursors in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 1987 Apr;69(4):1182–1187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A. The multi-subunit interleukin-2 receptor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:875–911. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. M., Smith K. A. The interleukin 2 receptor. Functional consequences of its bimolecular structure. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):1055–1069. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw A. J., Moqbel R., Cromwell O., Kay A. B. Platelet-activating factor. A potent chemotactic and chemokinetic factor for human eosinophils. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1701–1706. doi: 10.1172/JCI112765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagita H., Nakata M., Azuma A., Nitta T., Takeshita T., Sugamura K., Okumura K. Activation of peripheral blood T cells via the p75 interleukin 2 receptor. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1445–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Hattori T., Matsuoka M., Ishii T., Asou N., Okada M., Tagaya Y., Yodoi J., Takatsuki K. Induction of Tac antigen and proliferation of myeloid leukemic cells by ATL-derived factor: comparison with other agents that promote differentiation of human myeloid or monocytic leukemic cells. Blood. 1986 Jun;67(6):1714–1720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto T., Nakanishi K., Matsui K., Hirose S., Hiroishi K., Tanaka T., Hada T., Hamaoka T., Higashino K. IL-5 up-regulates but IL-4 down-regulates IL-2R expression on a cloned B lymphoma line. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):183–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





