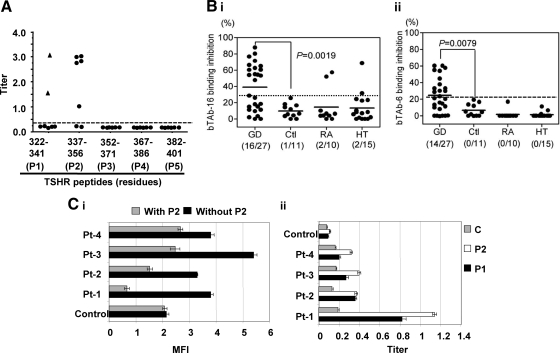
Figure 1.
Hamster mAbs recognized TSHR linear epitopes. A, Titers of mAbs indicated that the major epitopes were directed against the peptide sequence of 322–341 (P1) and 337–356 (P2) amino acid residues by a competitive inhibition ELISA with specific mAbs against the epitopes (Tab-16 and Tab-6, respectively). B, These two epitopes were also recognized by human IgGs from patients with GD. The frequency of these Abs was significantly higher in Grave’s patients compared with IgG from healthy individuals (P < 0.008). Ctl, Control; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; HT: Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. C, Flow cytometry recognized Abs against the human TSHR in CHO cells (i) and the indirect peptide ELISA (ii) also confirmed the presence of serum IgGs against peptides P1 and P2. A TSHR unrelated control peptide (C) failed to produce any significant binding (ii). Flow cytometry indicated that the binding of Abs was apparently inhibited by peptide (P2) as deduced by the reduction in binding of individual patient’s IgGs when incubated with the specific peptide (i). Inhibition ELISA and indirect ELISA were performed in duplicate and repeated twice. Similarly flow cytometry was repeated twice with different IgG preparations. MFI, Mean fluorescent intensity.