Abstract
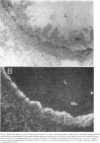
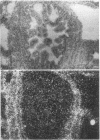
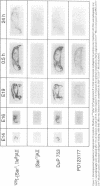
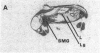
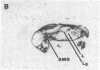
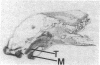
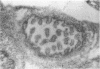
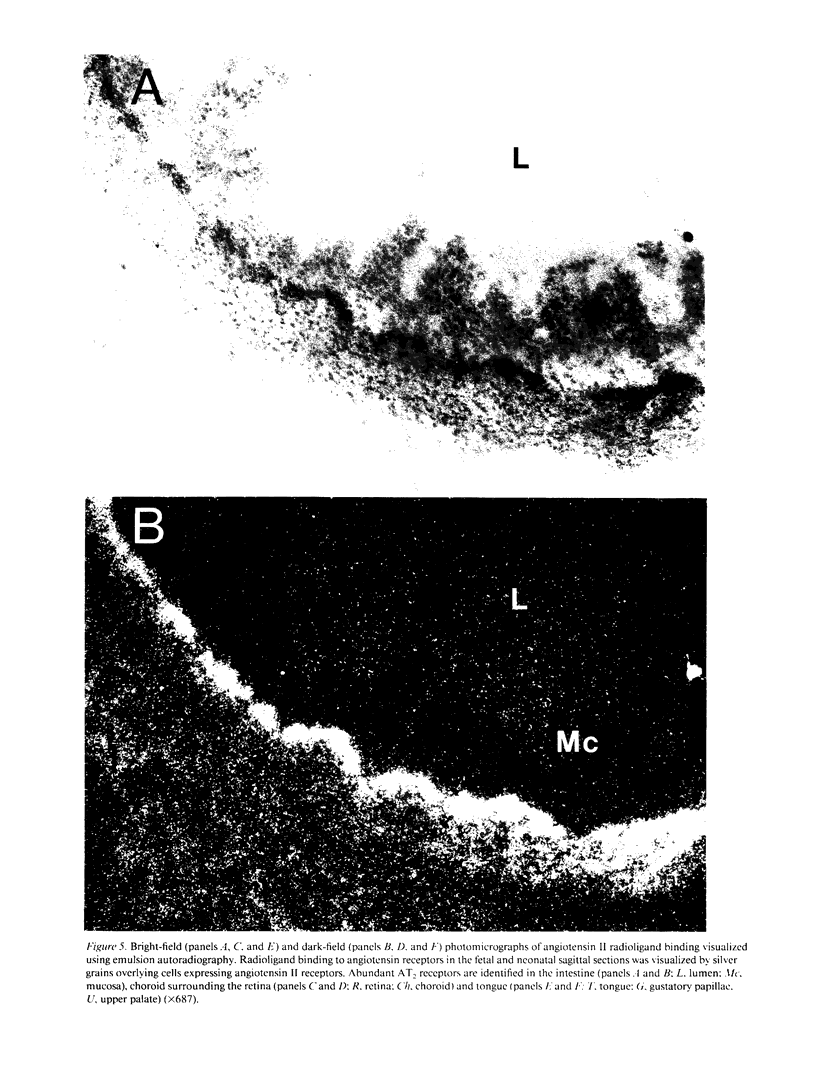
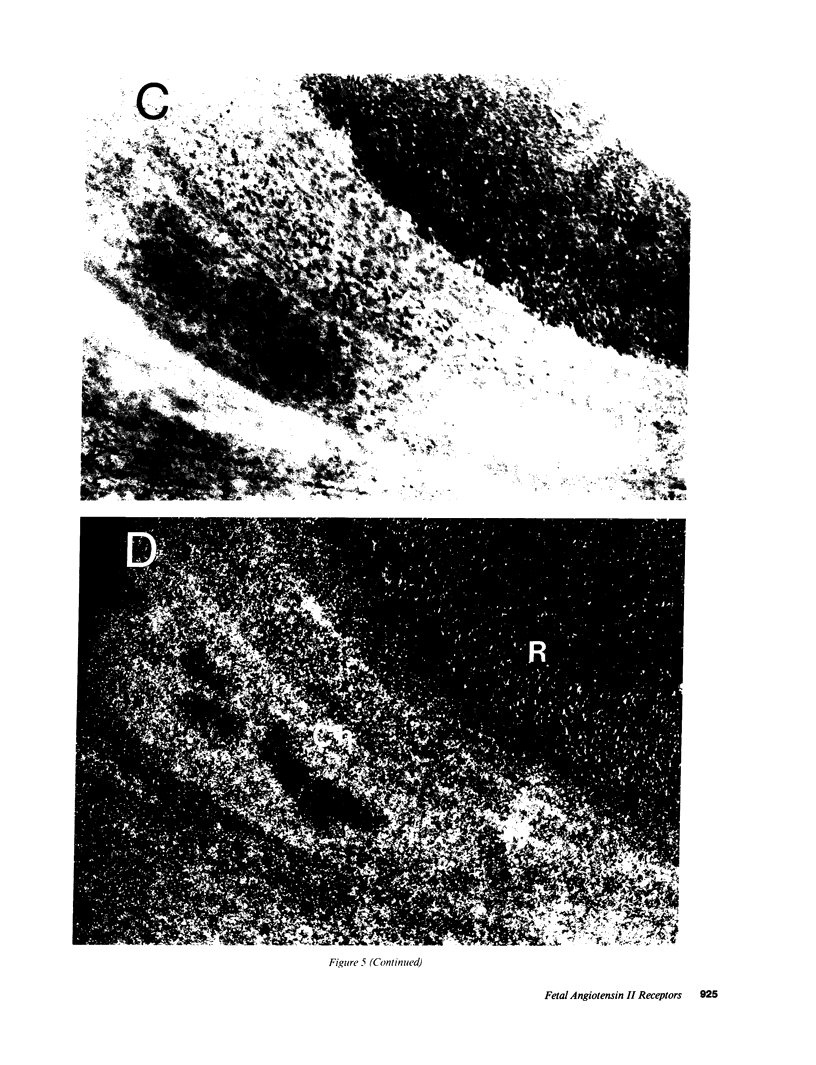
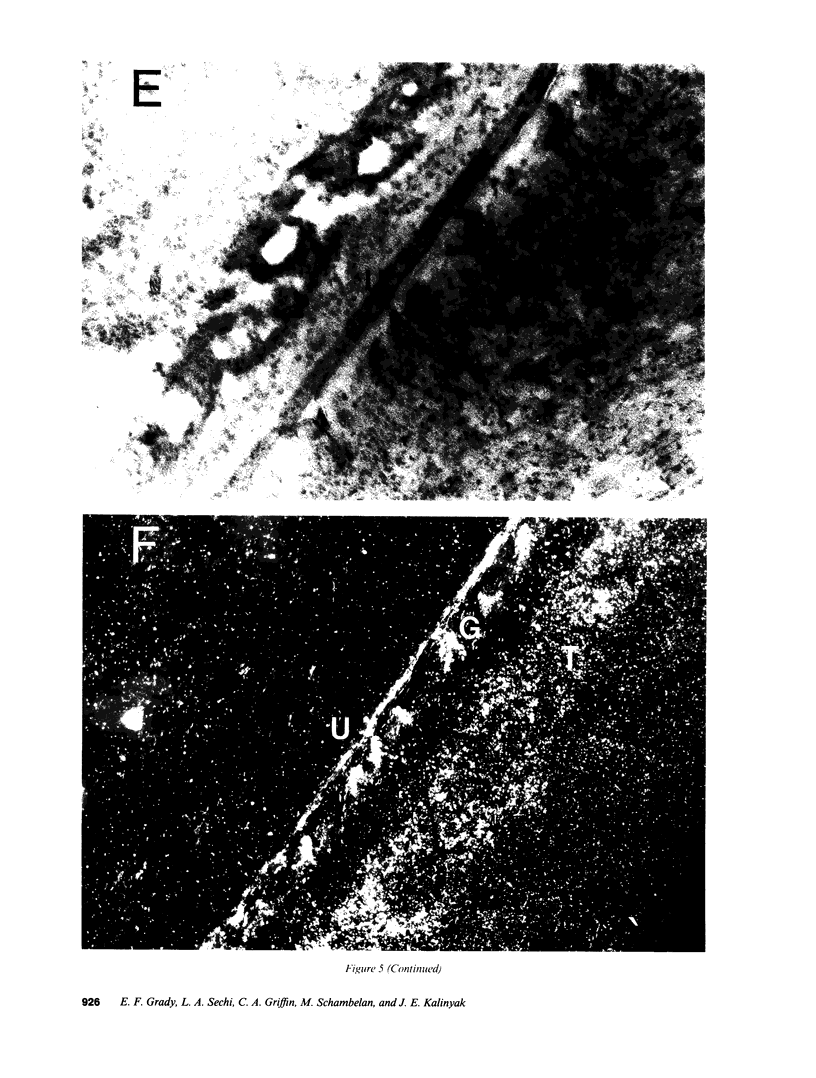
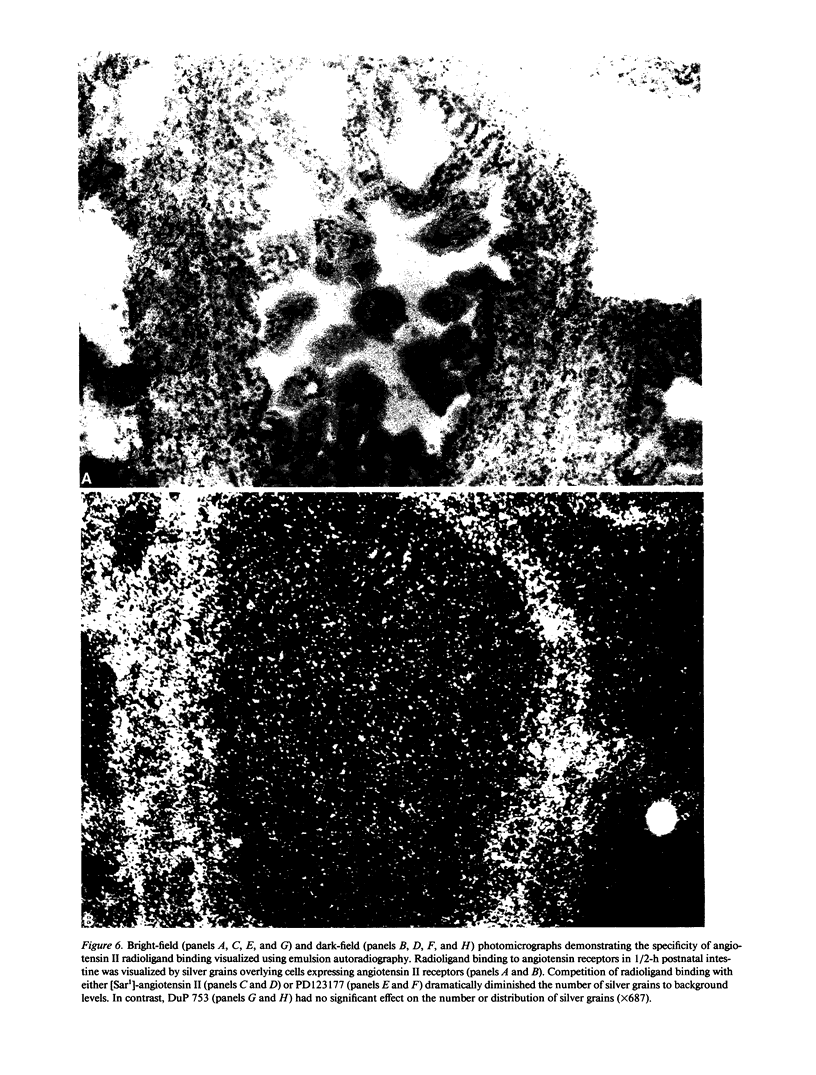
Angiotensin II is known primarily for its effects on blood pressure and electrolyte homeostasis, but recent studies suggest that angiotensin II may play a role in the regulation of cellular growth. This study was undertaken to identify the angiotensin II receptor subtypes expressed during fetal and neonatal development and to characterize their cellular localization. Using an in situ receptor binding assay on sagittal frozen sections of fetal and neonatal rats, bound 125I-[Sar1,Ile8]-angiotensin II was visualized by film and emulsion autoradiography. Bound radioligand was detected by E11 (embryonic day 11) and maximal binding occurred by E19-21. Radioligand binding remained unaltered 30 min after birth, whereas a noticeable and stable decrease was observed 12 h postparturition. The highly abundant angiotensin II receptors were shown to be AT2 by the marked reduction in radioligand binding achieved with PD123177 (10(-7)M), a specific AT2 receptor antagonist, whereas DuP 753 (10(-5)M), an AT1 receptor antagonist, had little effect. Emulsion autoradiography showed radioligand binding in the undifferentiated mesenchyme of the submucosal layers of the intestine and stomach, connective tissue and choroid surrounding the retina, subdermal mesenchyme adjacent to developing cartilage, diaphragm, and tongue. Residual AT2 receptors were found on the dorsal subdermal region of the tongue 72 h after birth. AT1 receptors were detected in the placenta at E13 and in the aorta, kidney, lung, liver, and adrenal gland at E19-21, consistent with an adult distribution. The transient expression of AT2 receptors in the mesenchyme of the fetus suggests a role of angiotensin II in fetal development.
Full text
PDF

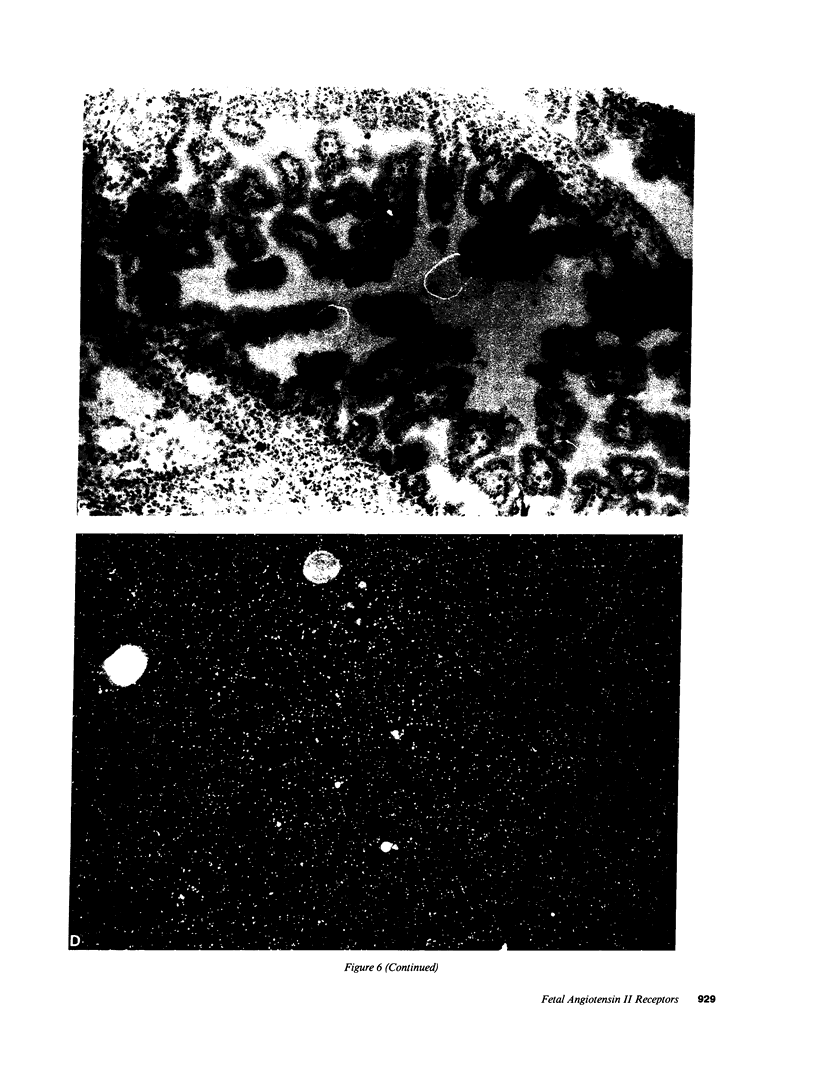
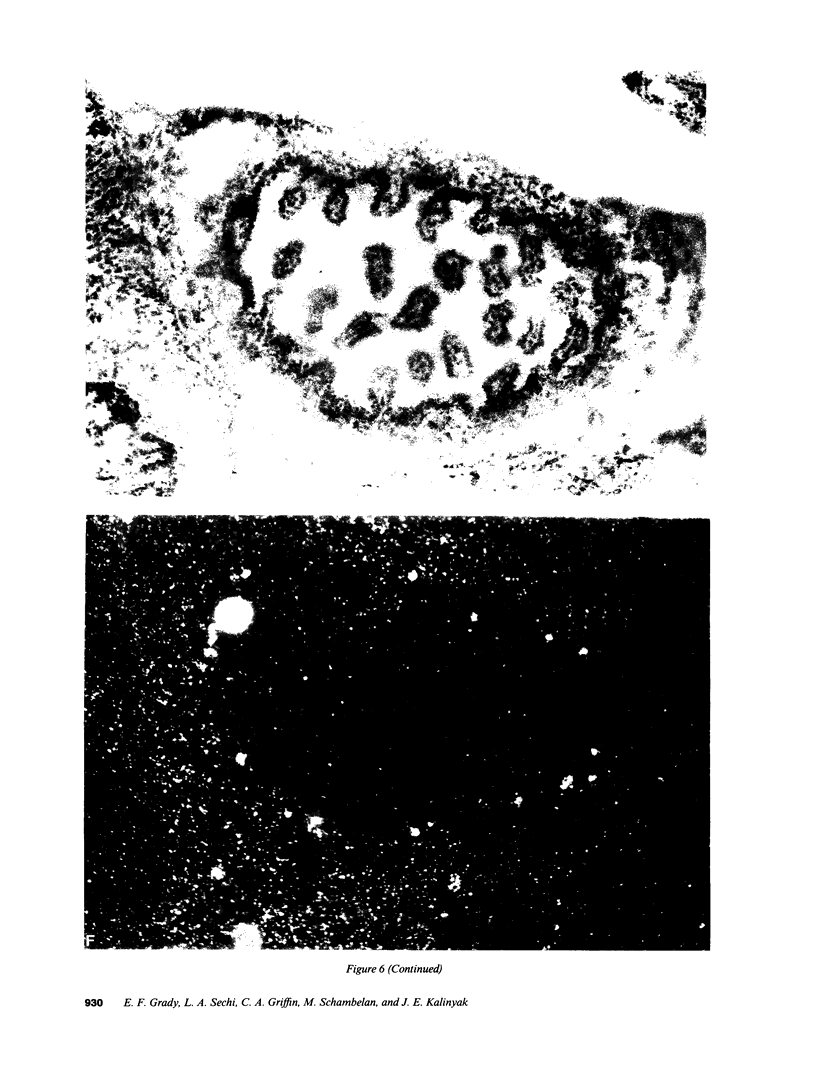
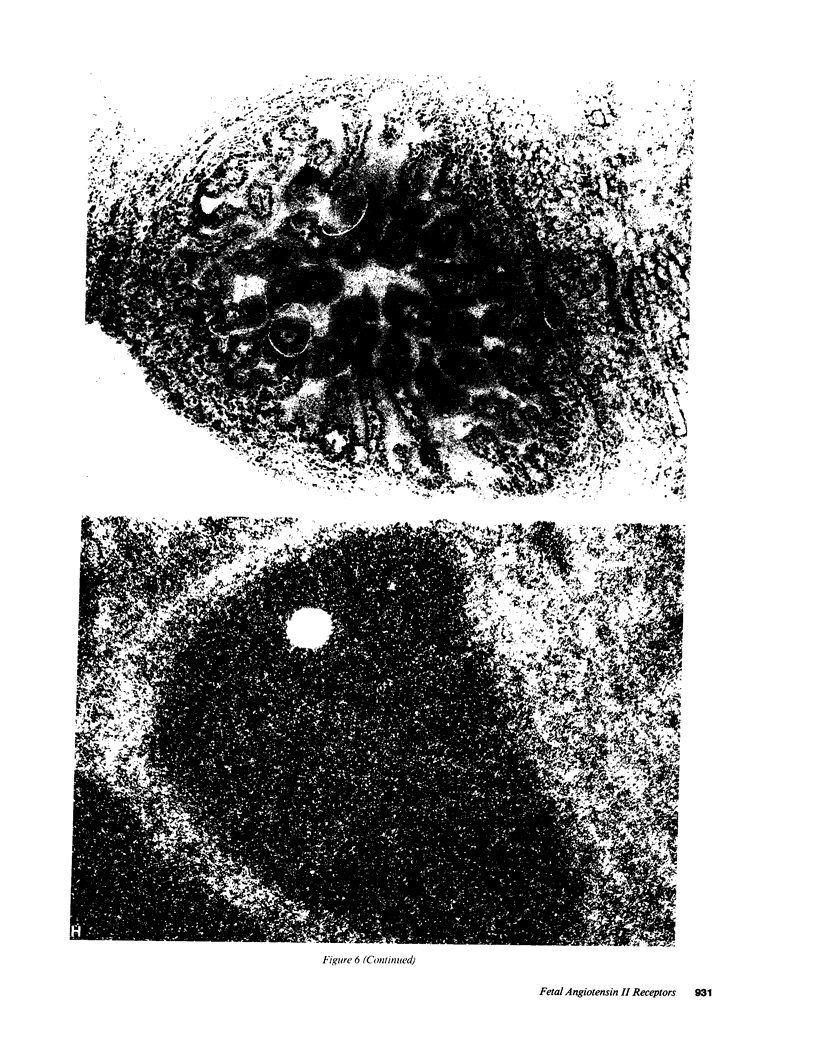


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES R. P., BORKOWSKI A. J., SICINSKI A. M., LARAGH J. H. PROLONGED INFUSIONS OF ANGIOTENSIN II AND NOREPINEPHRINE AND BLOOD PRESSURE, ELECTROLYTE BALANCE, AND ALDOSTERONE AND CORTISOL SECRETION IN NORMAL MAN AND IN CIRRHOSIS WITH ASCITES. J Clin Invest. 1965 Jul;44:1171–1186. doi: 10.1172/JCI105224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguilera G., Millan M. A., Harwood J. P. Angiotensin II receptors in the gonads. Am J Hypertens. 1989 May;2(5 Pt 1):395–402. doi: 10.1093/ajh/2.5.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen A. M., Yamada H., Mendelsohn F. A. In vitro autoradiographic localization of binding to angiotensin receptors in the rat heart. Int J Cardiol. 1990 Jul;28(1):25–33. doi: 10.1016/0167-5273(90)90005-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy C. A., Werner H., Roberts C. T., Jr, LeRoith D. Cellular pattern of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and type I IGF receptor gene expression in early organogenesis: comparison with IGF-II gene expression. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1386–1398. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-9-1386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. J., Habener J. F. Angiotensinogen gene is expressed and differentially regulated in multiple tissues of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):31–39. doi: 10.1172/JCI112566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. S., Lotti V. J., Chen T. B., Faust K. A. Two angiotensin II binding sites in rat brain revealed using [125I]Sar1, Ile8-angiotensin II and selective nonpeptide antagonists. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 14;171(2):813–817. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91218-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu A. T., Herblin W. F., McCall D. E., Ardecky R. J., Carini D. J., Duncia J. V., Pease L. J., Wong P. C., Wexler R. R., Johnson A. L. Identification of angiotensin II receptor subtypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 30;165(1):196–203. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu A. T., McCall D. E., Nguyen T. T., Carini D. J., Duncia J. V., Herblin W. F., Uyeda R. T., Wong P. C., Wexler R. R., Johnson A. L. Discrimination of angiotensin II receptor subtypes by dithiothreitol. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Oct 24;170(1-2):117–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha G. R., Young P., Brody J. R. Role of uterine epithelium in the development of myometrial smooth muscle cells. Biol Reprod. 1989 Apr;40(4):861–871. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod40.4.861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J. G. Angiotensin receptor subtypes of the kidney cortex. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 2):F1–F7. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.1.F1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson W. J. Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions during vertebrate palatogenesis. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1984;19:137–164. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60398-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisterfer A. A., Peach M. J., Owens G. K. Angiotensin II induces hypertrophy, not hyperplasia, of cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1988 Apr;62(4):749–756. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.4.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiani P., Uva B. M., Mandich A., Masini M. A. Angiotensin II vascular receptors in fetal and neonatal rats. Cell Biochem Funct. 1988 Oct;6(4):283–287. doi: 10.1002/cbf.290060411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glossmann H., Baukal A., Aguilera G., Catt K. J. Radioligand assay for angiotensin II receptors. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:110–126. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09080-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez R. A., Cassis L., Lynch K. R., Chevalier R. L., Wilfong N., Carey R. M., Peach M. J. Fetal expression of the angiotensinogen gene. Endocrinology. 1988 Nov;123(5):2298–2302. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-5-2298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine U., Munoz E. F., Flanders K. C., Ellingsworth L. R., Lam H. Y., Thompson N. L., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Role of transforming growth factor-beta in the development of the mouse embryo. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 2):2861–2876. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Pert C. B. Light microscopic localization of brain opiate receptors: a general autoradiographic method which preserves tissue quality. J Neurosci. 1982 Aug;2(8):1129–1149. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-08-01129.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C., Millan M. A., Naftolin F., Aguilera G. Characterization of angiotensin II receptors in the rat fetus. Peptides. 1989 Mar-Apr;10(2):459–463. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalinyak J. E., Perlman A. J. Tissue-specific regulation of angiotensinogen mRNA accumulation by dexamethasone. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):460–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara Y., Sunako M., Tsuda T., Fukuzaki H., Fukumoto Y., Takai Y. Angiotensin II induces expression of the c-fos gene through protein kinase C activation and calcium ion mobilization in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 15;150(1):52–59. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90485-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. U., Campbell D. J., Habener J. F. Developmental expression of the angiotensinogen gene in rat embryos. Endocrinology. 1987 Oct;121(4):1335–1342. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-4-1335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightman A., Jones C. L., MacLusky N. J., Palumbo A., DeCherney A. H., Naftolin F. Immunocytochemical localization of angiotensin II immunoreactivity and demonstration of angiotensin II binding in the rat ovary. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Aug;159(2):526–530. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(88)80122-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn F. A., Aguilera G., Saavedra J. M., Quirion R., Catt K. J. Characteristics and regulation of angiotensin II receptors in pituitary, circumventricular organs and kidney. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1983;5(7-8):1081–1097. doi: 10.3109/10641968309048843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn F. A., Millan M., Quirion R., Aguilera G., Chou S. T., Catt K. J. Localization of angiotensin II receptors in rat and monkey kidney by in vitro autoradiography. Kidney Int Suppl. 1987 May;20:S40–S44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn F. A., Quirion R., Saavedra J. M., Aguilera G., Catt K. J. Autoradiographic localization of angiotensin II receptors in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1575–1579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millan M. A., Carvallo P., Izumi S., Zemel S., Catt K. J., Aguilera G. Novel sites of expression of functional angiotensin II receptors in the late gestation fetus. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1340–1342. doi: 10.1126/science.2734613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naftilan A. J., Gilliland G. K., Eldridge C. S., Kraft A. S. Induction of the proto-oncogene c-jun by angiotensin II. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5536–5540. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naftilan A. J., Pratt R. E., Dzau V. J. Induction of platelet-derived growth factor A-chain and c-myc gene expressions by angiotensin II in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1419–1424. doi: 10.1172/JCI114032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman J., Badie-Dezfooly B., Nord E. P., Kurtz I., Schlosser J., Chaudhari A., Fine L. G. EGF-induced mitogenesis in proximal tubular cells: potentiation by angiotensin II. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 2):F299–F309. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.2.F299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo H., Nakayama K., Tanaka T., Nakanishi S. Tissue distribution of rat angiotensinogen mRNA and structural analysis of its heterogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):319–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oparil S., Haber E. The renin-angiotensin system (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1974 Aug 22;291(8):389–401. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197408222910805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellicer A., Palumbo A., DeCherney A. H., Naftolin F. Blockage of ovulation by an angiotensin antagonist. Science. 1988 Jun 17;240(4859):1660–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.3381087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. I. Functions of angiotensin in the central nervous system. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:413–435. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.002213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J. S., Clozel J. P., Müller R. K., Kuhn H., Hefti F., Hosang M., Baumgartner H. R. Inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme prevent myointimal proliferation after vascular injury. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):186–188. doi: 10.1126/science.2526370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pucell A. G., Hodges J. C., Sen I., Bumpus F. M., Husain A. Biochemical properties of the ovarian granulosa cell type 2-angiotensin II receptor. Endocrinology. 1991 Apr;128(4):1947–1959. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-4-1947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay D. J., Keil L. C., Sharpe M. C., Shinsako J. Angiotensin II infusion increases vasopressin, ACTH, and 11-hydroxycorticosteroid secretion. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jan;234(1):R66–R71. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1978.234.1.R66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richoux J. P., Amsaguine S., Grignon G., Bouhnik J., Menard J., Corvol P. Earliest renin containing cell differentiation during ontogenesis in the rat. An immunocytochemical study. Histochemistry. 1987;88(1):41–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00490165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier C., Vale W. Effect of angiotensin II on ACTH release in vivo: role of corticotropin-releasing factor. Regul Pept. 1983 Nov;7(3):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(83)90018-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogg H., Schmid A., de Gasparo M. Identification and characterization of angiotensin II receptor subtypes in rabbit ventricular myocardium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 30;173(1):416–422. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe B. P., Grove K. L., Saylor D. L., Speth R. C. Angiotensin II receptor subtypes in the rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep 21;186(2-3):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90457-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schelling P., Fischer H., Ganten D. Angiotensin and cell growth: a link to cardiovascular hypertrophy? J Hypertens. 1991 Jan;9(1):3–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shughrue P. J., Stumpf W. E., Sar M. The distribution of progesterone receptor in the 20-day-old fetal mouse: an autoradiographic study with [125I]progestin. Endocrinology. 1988 Nov;123(5):2382–2389. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-5-2382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speth R. C., Kim K. H. Discrimination of two angiotensin II receptor subtypes with a selective agonist analogue of angiotensin II, p-aminophenylalanine6 angiotensin II. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 29;169(3):997–1006. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91993-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele M. K., Negro-Vilar A., McCann S. M. Effect of angiotensin II on in vivo and in vitro release of anterior pituitary hormones in the female rat. Endocrinology. 1981 Sep;109(3):893–899. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-3-893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taubman M. B., Berk B. C., Izumo S., Tsuda T., Alexander R. W., Nadal-Ginard B. Angiotensin II induces c-fos mRNA in aortic smooth muscle. Role of Ca2+ mobilization and protein kinase C activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):526–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G. M., Peart W. S., Porter K. A., Zondek L. H., Zondek T. Concentration and molecular forms of active and inactive renin in human fetal kidney, amniotic fluid and adrenal gland: evidence for renin-angiotensin system hyperactivity in 2nd trimester of pregnancy. J Hypertens. 1986 Feb;4(1):121–129. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198602000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace K. B., Bailie M. D., Hook J. B. Development of angiotensin-converting enzyme in fetal rat lungs. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jan;236(1):R57–R60. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1979.236.1.R57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitebread S., Mele M., Kamber B., de Gasparo M. Preliminary biochemical characterization of two angiotensin II receptor subtypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 30;163(1):284–291. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92133-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigger H. J., Stalcup S. A. Distribution and development of angiotensin converting enzyme in the fetal and newborn rabbit. An immunofluorescence study. Lab Invest. 1978 May;38(5):581–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkes B. M., Krim E., Mento P. F. Evidence for a functional renin-angiotensin system in full-term fetoplacental unit. Am J Physiol. 1985 Oct;249(4 Pt 1):E366–E373. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.249.4.E366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkes B. M., Pion I., Sollott S., Michaels S., Kiesel G. Intrarenal renin-angiotensin system modulates glomerular angiotensin receptors in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 2):F345–F350. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.3.F345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf G., Neilson E. G. Angiotensin II induces cellular hypertrophy in cultured murine proximal tubular cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Nov;259(5 Pt 2):F768–F777. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.5.F768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. C., Hart S. D., Zaspel A. M., Chiu A. T., Ardecky R. J., Smith R. D., Timmermans P. B. Functional studies of nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor subtype-specific ligands: DuP 753 (AII-1) and PD123177 (AII-2). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Nov;255(2):584–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. C., Price W. A., Chiu A. T., Duncia J. V., Carini D. J., Wexler R. R., Johnson A. L., Timmermans P. B. Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. IX. Antihypertensive activity in rats of DuP 753, an orally active antihypertensive agent. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Feb;252(2):726–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. C., Price W. A., Chiu A. T., Duncia J. V., Carini D. J., Wexler R. R., Johnson A. L., Timmermans P. B. Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. VIII. Characterization of functional antagonism displayed by DuP 753, an orally active antihypertensive agent. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Feb;252(2):719–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright F. S., Briggs J. P. Feedback control of glomerular blood flow, pressure, and filtration rate. Physiol Rev. 1979 Oct;59(4):958–1006. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.4.958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemel S., Millan M. A., Aguilera G. Distribution of angiotensin II receptors and renin in the mouse fetus. Endocrinology. 1989 Apr;124(4):1774–1780. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-4-1774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemel S., Millan M. A., Feuillan P., Aguilera G. Characterization and distribution of angiotensin-II receptors in the primate fetus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Oct;71(4):1003–1007. doi: 10.1210/jcem-71-4-1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]