Abstract
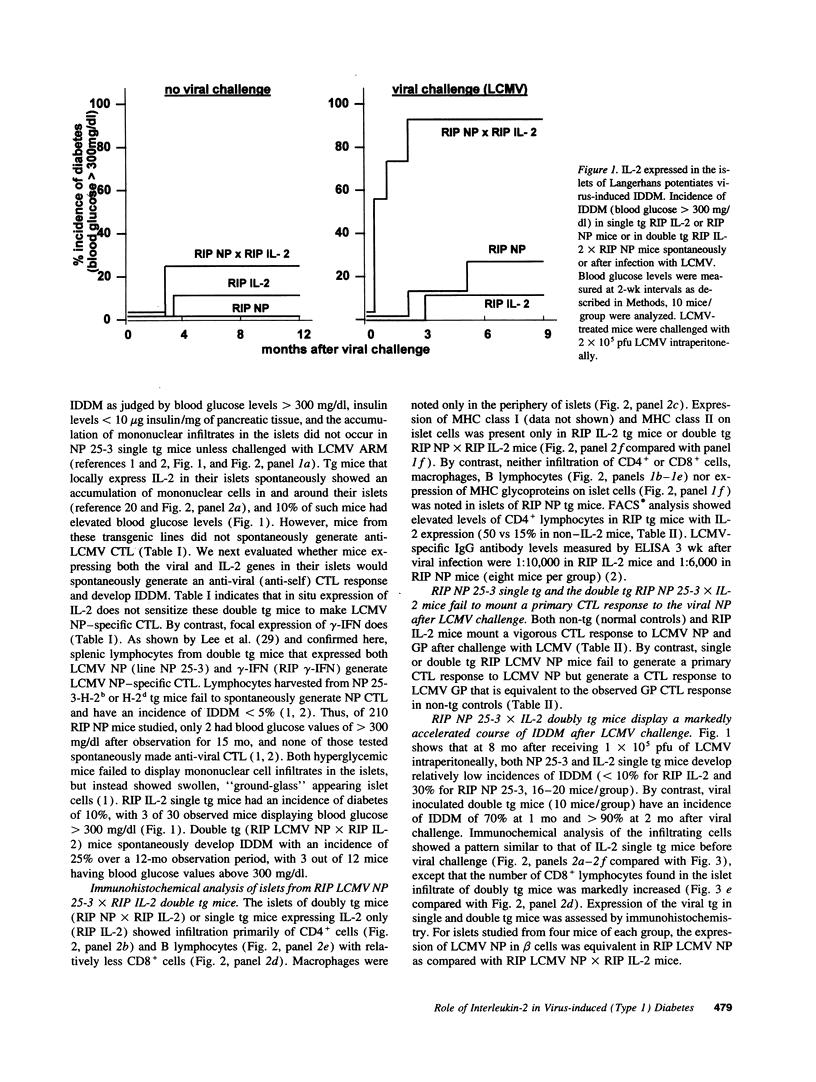
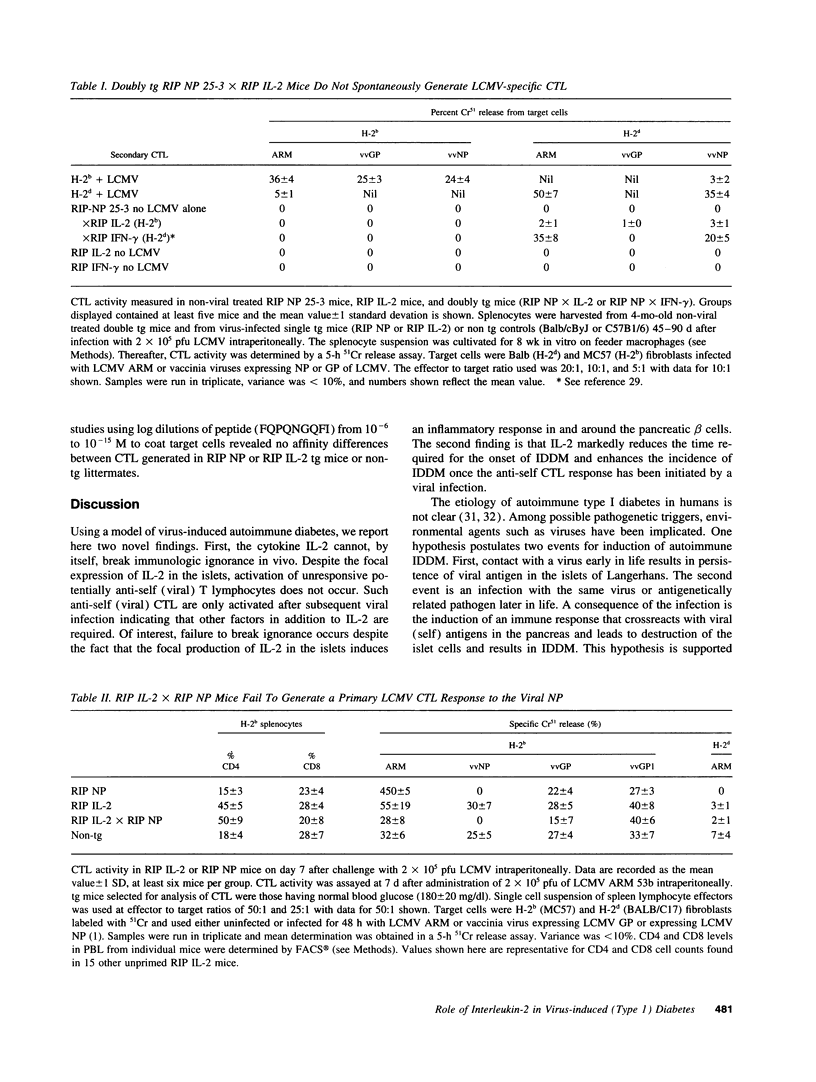
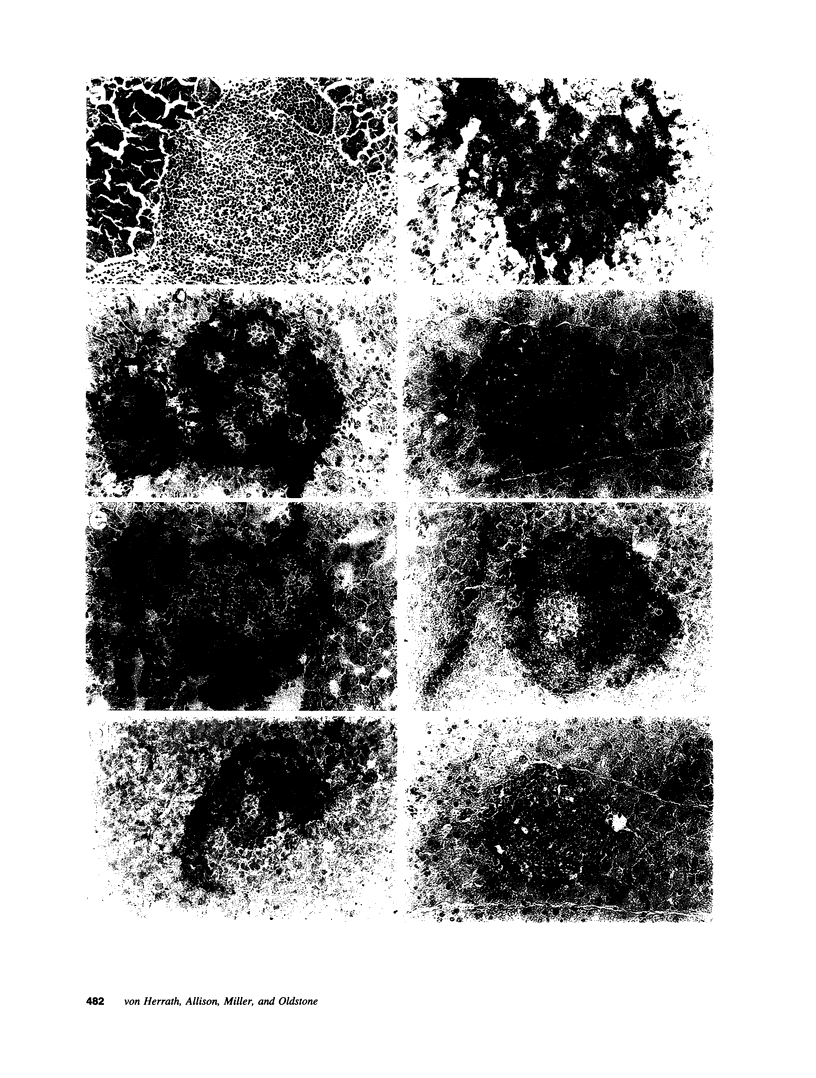
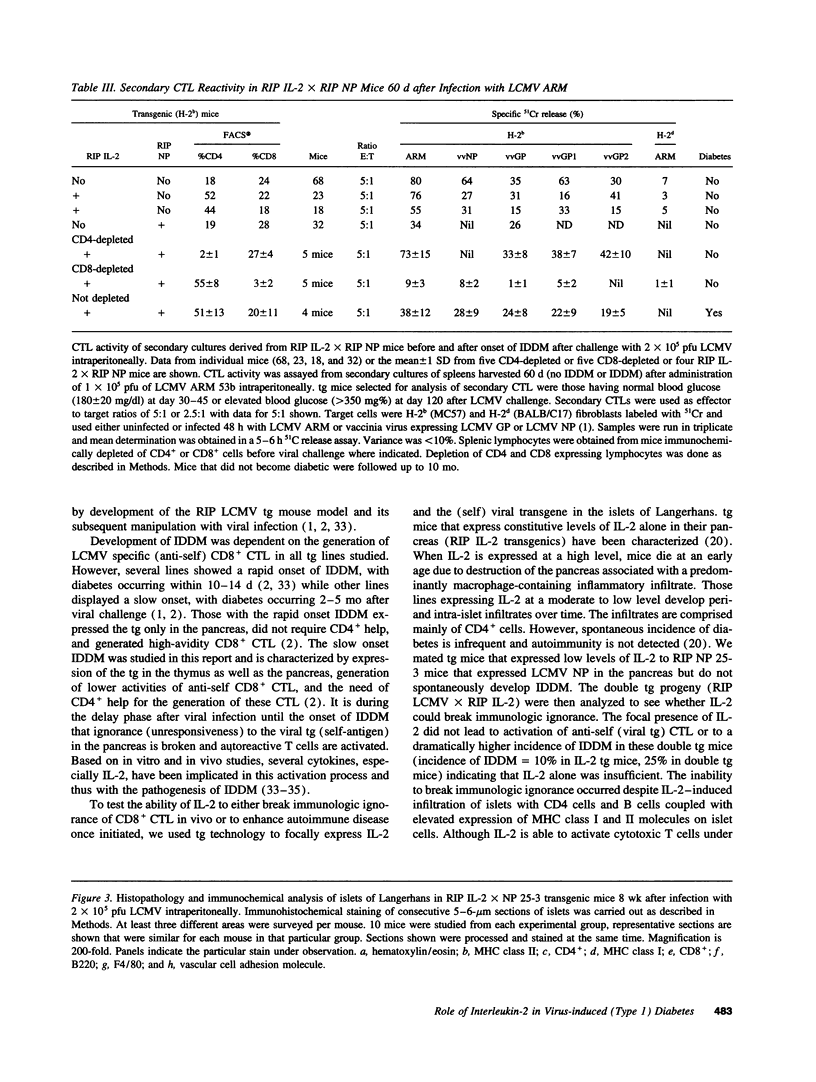
The participation of IL-2 in insulin-dependent (type 1) diabetes (IDDM) was analyzed in transgenic (tg) mice expressing the nucleoprotein (NP) of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus and IL-2 under control of the rat insulin promoter focally in beta cells of the islets of Langerhans. Insertion and expression of the viral (self) gene or of the IL-2 gene alone did not lead to IDDM. Infiltration primarily of CD4 and B lymphocytes and increased expression of MHC class I and II molecules occurred in islets where IL-2 was expressed. By contrast, neither cellular infiltrates nor expression of MHC class I or II glycoproteins above base levels was noted in tgs expressing the viral protein alone. Double tg mice expressing both the viral protein and IL-2 in their islets displayed a modest increase in incidence of spontaneous diabetes compared with that of single transgenic mice expressing IL-2 alone. Breaking of immunological unresponsiveness or sensitization to self antigens did not occur. Neither cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) nor antibodies directed against the viral tg (NP) were generated. However, after challenge with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus, double tg mice developed anti-self (viral) CTL and IDDM (incidence > 95%) within 2 mo. The generation of virus ("self")-specific MHC-restricted CTL was dependent on CD4+ help. In contrast, viral inoculum to single tg mice expressing either the viral protein or IL-2 failed to enhance the incidence of IDDM over 30% for viral protein or 10% for IL-2 after an 8-mo observation period. Hence, in this autoimmune model in situ expression of IL-2 did not break unresponsiveness but markedly enhanced ongoing disease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J., Malcolm L., Chosich N., Miller J. F. Inflammation but not autoimmunity occurs in transgenic mice expressing constitutive levels of interleukin-2 in islet beta cells. Eur J Immunol. 1992 May;22(5):1115–1121. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreu-Sánchez J. L., Moreno de Alborán I. M., Marcos M. A., Sánchez-Movilla A., Martínez-A C., Kroemer G. Interleukin 2 abrogates the nonresponsive state of T cells expressing a forbidden T cell receptor repertoire and induces autoimmune disease in neonatally thymectomized mice. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1323–1329. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass H. Z., Yamashita N., Clement L. T. Heterogeneous mechanisms of human cytotoxic T lymphocyte generation. I. Differential helper cell requirement for the generation of cytotoxic effector cells from CD8+ precursor subpopulations. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2489–2495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertagnolli M. M., Takai Y., Herrmann S. H. IL-4-supported induction of cytolytic T lymphocytes requires IL-2 and IL-6. Cell Immunol. 1991 Apr 1;133(2):327–341. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90108-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverly B., Kang S. M., Lenardo M. J., Schwartz R. H. Reversal of in vitro T cell clonal anergy by IL-2 stimulation. Int Immunol. 1992 Jun;4(6):661–671. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.6.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brissette-Storkus C. S., Kostyu D. D., Boyer C. M., Dawson J. R. Induction of HLA-specific CTL to nonimmunogenic, heat-inactivated lymphocytes by interleukin 2. Transplantation. 1990 Nov;50(5):862–869. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199011000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Harrison L. C. Molecular pathology of type 1 diabetes. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Aug;7(4):299–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Kay T. W., Oxbrow L., Harrison L. C. Essential role for interferon-gamma and interleukin-6 in autoimmune insulin-dependent diabetes in NOD/Wehi mice. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):739–742. doi: 10.1172/JCI115055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodetti L., Schwartz R. H. Induction of competence to respond to IL-4 by CD4+ T helper type 1 cells requires costimulation. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 1;149(3):901–910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutko F. J., Oldstone M. B. Genomic and biological variation among commonly used lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus strains. J Gen Virol. 1983 Aug;64(Pt 8):1689–1698. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-8-1689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbarth G. S. Type I diabetes mellitus. A chronic autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med. 1986 May 22;314(21):1360–1368. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198605223142106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast L. D. Generation and characterization of IL-2-activated veto cells. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 1;149(5):1510–1515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch F. W., McKisic M. D., Lancki D. W., Gajewski T. F. Differential regulation of murine T lymphocyte subsets. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:29–48. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gairin J. E., Oldstone M. B. Virus and cytotoxic T lymphocytes: crucial role of viral peptide secondary structure in major histocompatibility complex class I interactions. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2903–2907. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2903-2907.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E. A., Owen-Schaub L. The IL-2 mediated amplification of cellular cytotoxicity. J Cell Biochem. 1991 Apr;45(4):335–339. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240450405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Heritable formation of pancreatic beta-cell tumours in transgenic mice expressing recombinant insulin/simian virus 40 oncogenes. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):115–122. doi: 10.1038/315115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding F. A., Allison J. P. CD28-B7 interactions allow the induction of CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in the absence of exogenous help. J Exp Med. 1993 Jun 1;177(6):1791–1796. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath W. R., Allison J., Hoffmann M. W., Schönrich G., Hämmerling G., Arnold B., Miller J. F. Autoimmune diabetes as a consequence of locally produced interleukin-2. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):547–549. doi: 10.1038/359547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. A., Chin L. T., Merriam G. R., Nelson L. M., Kruisbeck A. M. Failure of clonal deletion in neonatally thymectomized mice: tolerance is preserved through clonal anergy. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1277–1285. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasaian M. T., Biron C. A. Effects of cyclosporin A on IL-2 production and lymphocyte proliferation during infection of mice with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):299–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasaian M. T., Leite-Morris K. A., Biron C. A. The role of CD4+ cells in sustaining lymphocyte proliferation during lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 15;146(6):1955–1963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klavinskis L. S., Whitton J. L., Oldstone M. B. Molecularly engineered vaccine which expresses an immunodominant T-cell epitope induces cytotoxic T lymphocytes that confer protection from lethal virus infection. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4311–4316. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4311-4316.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., von Herrath M., Reiser H., Oldstone M. B., Sarvetnick N. Sensitization to self (virus) antigen by in situ expression of murine interferon-gamma. J Clin Invest. 1995 Feb;95(2):486–492. doi: 10.1172/JCI117689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
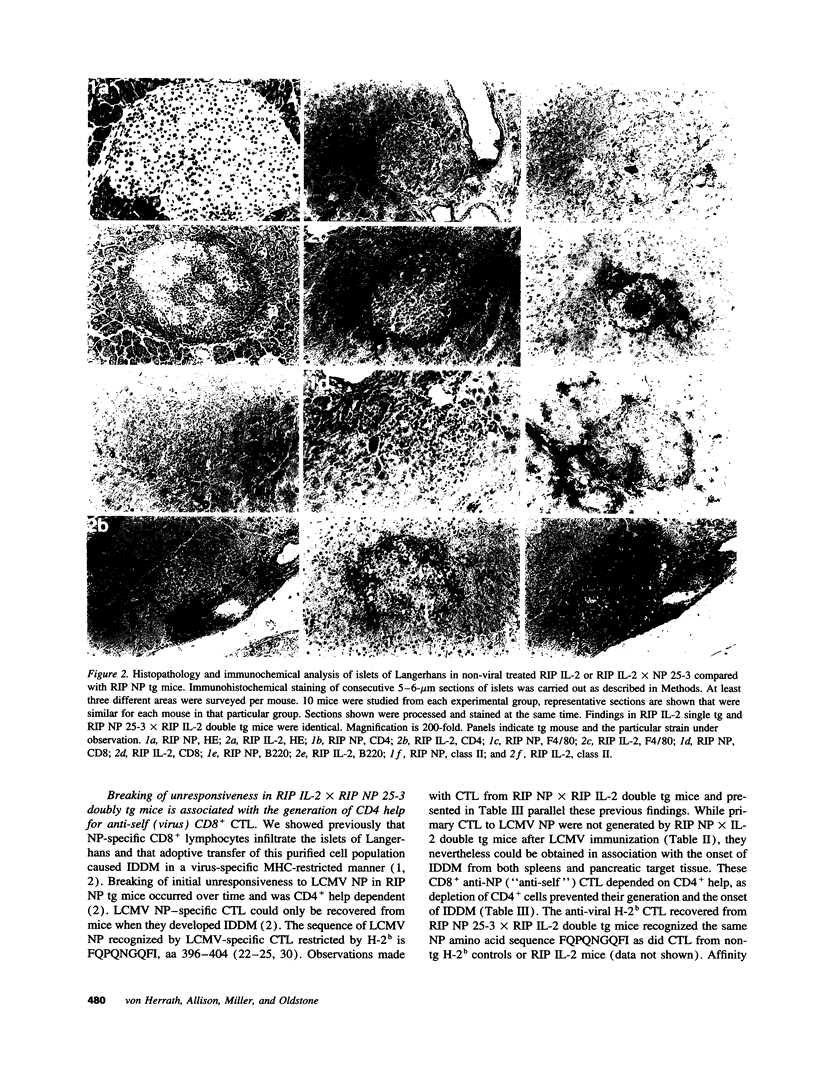
- Lewicki H., McKee T. A., Tishon A., Salvato M., Whitton J. L., Oldstone M. B. Novel LCMV-specific H-2k restricted CTL clones recognize internal viral gene products and cause CNS disease. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Nov;41(1):15–20. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90190-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley V., Langlade-Demoyen P., Kourilsky P., Larsson-Sciard E. L. Interleukin 2-dependent activation of tumor-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Mar;21(3):851–854. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Nutman T. B. Type 2 cytokines and negative immune regulation in human infections. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Aug;5(4):511–517. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90031-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovitch-Lopatin M., Petrillo R. J., Pankewycz O. G., Hadro E., Bleackley C. R., Strom T. B., Wieder K. J. Interleukin 2 counteracts the inhibition of cytotoxic T lymphocytes by cholera toxin in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jun;21(6):1439–1444. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi P. S., Oehen S., Aichele P., Pircher H., Odermatt B., Herrera P., Higuchi Y., Buerki K., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. M. Induction of diabetes is influenced by the infectious virus and local expression of MHC class I and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Immunol. 1993 Jun 1;150(11):5185–5194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Nerenberg M., Southern P., Price J., Lewicki H. Virus infection triggers insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in a transgenic model: role of anti-self (virus) immune response. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):319–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90165-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Seder R. A. Lymphocyte responses and cytokines. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):241–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90332-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagerström C. G., Kerr E. M., Allison J. P., Davis M. M. Activation and differentiation requirements of primary T cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8987–8991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarvetnick N., Shizuru J., Liggitt D., Martin L., McIntyre B., Gregory A., Parslow T., Stewart T. Loss of pancreatic islet tolerance induced by beta-cell expression of interferon-gamma. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):844–847. doi: 10.1038/346844a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schols D., Vandekerckhove B., Jones D., Roncarolo M. G. IL-2 reverses human T cell unresponsiveness induced by thymic epithelium in SCID-hu mice. J Immunol. 1994 Mar 1;152(5):2198–2206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Singh M. K., Riviere Y., Jacoby D. R., Buchmeier M. J., Oldstone M. B. Molecular characterization of the genomic S RNA segment from lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):145–155. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90323-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton J. L., Gebhard J. R., Lewicki H., Tishon A., Oldstone M. B. Molecular definition of a major cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitope in the glycoprotein of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):687–695. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.687-695.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagi Y., Tishon A., Lewicki H., Cubitt B. A., Oldstone M. B. Diversity of T-cell receptors in virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognizing three distinct viral epitopes restricted by a single major histocompatibility complex molecule. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2527–2531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2527-2531.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Herrath M. G., Dockter J., Nerenberg M., Gairin J. E., Oldstone M. B. Thymic selection and adaptability of cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses in transgenic mice expressing a viral protein in the thymus. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1901–1910. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Herrath M. G., Dockter J., Oldstone M. B. How virus induces a rapid or slow onset insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in a transgenic model. Immunity. 1994 Jun;1(3):231–242. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]