Abstract
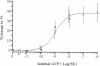
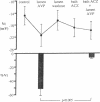
We explored the action of luminal AVP in rabbit CCD perfused in vitro at 37 degrees C. Nanomolar concentrations of luminal AVP induced a sustained hyperpolarization of transepithelial voltage (Vt) in contrast to a transient hyperpolarization caused by basolateral AVP. 10 microM basolateral ouabain abolished the latter but not the former change in Vt. Despite a sustained hyperpolarization (from -20.7 +/- 2.9 to -34.1 +/- 4.7 mV; P less than 0.01), 10 nM luminal AVP only slightly altered net Na+ and K+ fluxes (7.6% stimulation and no significant change, respectively). Instead, luminal AVP appeared to modulate an acetazolamide-sensitive electrogenic ion transport because 200 microM basolateral acetazolamide suppressed the luminal AVP-induced hyperpolarization (percentage of Vt from -50.4 +/- 10.8 to -5.1 +/- 1.4; P less than 0.005). In terms of water transport, 10 nM luminal AVP did not change hydraulic conductivity (Lp, x 10(-7) cm/atm per s) (from 3.9 +/- 0.8 to 5.0 +/- 1.2), but suppressed the increase in Lp induced by 20 pM basolateral AVP (134.9 +/- 19.2 vs. 204.3 +/- 21.1 in control; P less than 0.05). These findings demonstrate distinct luminal action of AVP, suggesting amphilateral regulation of epithelial transport by AVP in the CCD.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando Y., Breyer M. D., Jacobson H. R. Dose-dependent heterogenous actions of vasopressin in rabbit cortical collecting ducts. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 2):F556–F562. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.4.F556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando Y., Jacobson H. R., Breyer M. D. Phorbol ester and A23187 have additive but mechanistically separate effects on vasopressin action in rabbit collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1578–1584. doi: 10.1172/JCI113491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando Y., Jacobson H. R., Breyer M. D. Phorbol myristate acetate, dioctanoylglycerol, and phosphatidic acid inhibit the hydroosmotic effect of vasopressin on rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):590–593. doi: 10.1172/JCI113110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando Y., Tabei K., Furuya H., Asano Y. Glucagon stimulates chloride transport independently of cyclic AMP in the rat medullary TAL. Kidney Int. 1989 Nov;36(5):760–767. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brem A. S., Eich E., Pearl M., Taylor A. Anion transport inhibitors: effects on water and sodium transport in the toad urinary bladder. Am J Physiol. 1985 Apr;248(4 Pt 2):F594–F601. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.4.F594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnatowska-Hledin M. A., Spielman W. S. Vasopressin V1 receptors on the principal cells of the rabbit cortical collecting tubule. Stimulation of cytosolic free calcium and inositol phosphate production via coupling to a pertussis toxin substrate. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):84–89. doi: 10.1172/JCI113888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fejes-Tóth G., Náray-Fejes-Tóth A. Isolated principal and intercalated cells: hormone responsiveness and Na+-K+-ATPase activity. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 2):F742–F750. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.4.F742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felder C. C., McKelvey A. M., Gitler M. S., Eisner G. M., Jose P. A. Dopamine receptor subtypes in renal brush border and basolateral membranes. Kidney Int. 1989 Aug;36(2):183–193. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frindt G., Burg M. B. Effect of vasopressin on sodium transport in renal cortical collecting tubules. Kidney Int. 1972 Apr;1(4):224–231. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frindt G., Palmer L. G. Ca-activated K channels in apical membrane of mammalian CCT, and their role in K secretion. Am J Physiol. 1987 Mar;252(3 Pt 2):F458–F467. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.3.F458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Perez A., Smith W. L. Apical-basolateral membrane asymmetry in canine cortical collecting tubule cells. Bradykinin, arginine vasopressin, prostaglandin E2 interrelationships. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):63–74. doi: 10.1172/JCI111419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J., Burg M. B. Effect of vasopressin and cyclic AMP on permeability of isolated collecting tubules. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jul;211(1):255–259. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.1.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J., Kurg M. B., Obloff J. The nature of transtubular Na and K transport in isolated rabbit renal collecting tubules. J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1815–1826. doi: 10.1172/JCI106399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm L. L., Gillespie C., Klahr S. NH4Cl inhibition of transport in the rabbit cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 2):F631–F637. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.5.F631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays S. R., Baum M., Kokko J. P. Effects of protein kinase C activation on sodium, potassium, chloride, and total CO2 transport in the rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1561–1570. doi: 10.1172/JCI113242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt W. F., Lechene C. ADH-PGE2 interactions in cortical collecting tubule. I. Depression of sodium transport. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F452–F460. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt W. F., Lechene C. ADH-PGE2 interactions in cortical collecting tubule. II. inhibition of Ca and P reabsorption. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F461–F467. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino Y., Imai M. Effects of prostaglandins on Na transport in isolated collecting tubules. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Feb 22;373(2):125–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00584850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino Y., Troy J. L., Brenner B. M. Effects of catecholamines on electrolyte transport in cortical collecting tubule. J Membr Biol. 1981;61(2):67–73. doi: 10.1007/BF02007632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel P. L., Goldfarb S. Effects of isoproterenol on potassium secretion by the cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jun;246(6 Pt 2):F804–F810. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.6.F804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura T., Share L. Characterization of the renal handling of vasopressin in the dog by stop-flow analysis. Endocrinology. 1981 Dec;109(6):2089–2094. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-6-2089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk K. L. Origin of ADH-induced vacuoles in rabbit cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1988 May;254(5 Pt 2):F719–F733. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.5.F719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppen B. M., Helman S. I. Acidification of luminal fluid by the rabbit cortical collecting tubule perfused in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):F521–F531. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.5.F521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krothapalli R. K., Duffy W. B., Senekjian H. O., Suki W. N. Modulation of the hydro-osmotic effect of vasopressin on the rabbit cortical collecting tubule by adrenergic agents. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):287–294. doi: 10.1172/JCI110968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAF A., ANDERSON J., PAGE L. B. Active sodium transport by the isolated toad bladder. J Gen Physiol. 1958 Mar 20;41(4):657–668. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.4.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laski M. E. Total CO2 flux in isolated collecting tubules during carbonic anhydrase inhibition. Am J Physiol. 1987 Feb;252(2 Pt 2):F322–F330. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.2.F322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light D. B., Ausiello D. A., Stanton B. A. Guanine nucleotide-binding protein, alpha i-3, directly activates a cation channel in rat renal inner medullary collecting duct cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):352–356. doi: 10.1172/JCI114162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzen M., Taylor A., Windhager E. E. pH effect on osmotic response of collecting tubules to vasopressin and 8-CPT-cAMP. Am J Physiol. 1983 Aug;245(2):F188–F197. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.2.F188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. M., Steciak E. Urinary and metabolic clearances of arginine vasopressin in normal subjects. Am J Physiol. 1986 Aug;251(2 Pt 2):R365–R370. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1986.251.2.R365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLOFF J., HANDLER J. S. The similarity of effects of vasopressin, adenosine-3',5'-phosphate (cyclic AMP) and theophylline on the toad bladder. J Clin Invest. 1962 Apr;41:702–709. doi: 10.1172/JCI104528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi M., Chevalier J., Bourguet J. Influence of mucosal and serosal pH on antidiuretic action in frog urinary bladder. Am J Physiol. 1979 Dec;237(6):F483–F489. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.237.6.F483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabkin R., Share L., Payne P. A., Young J., Crofton J. The handling of immunoreactive vasopressin by the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jan;63(1):6–13. doi: 10.1172/JCI109279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki S., Imai M. Effects of vasopressin on water and NaCl transport across the in vitro perfused medullary thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of mouse, rat, and rabbit kidneys. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Feb;383(3):215–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00587521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster V. L., Kokko J. P., Jacobson H. R. Interactions of lysyl-bradykinin and antidiuretic hormone in the rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jun;73(6):1659–1667. doi: 10.1172/JCI111372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster V. L., Stokes J. B. Chloride transport by the cortical and outer medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 2):F203–F212. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.2.F203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz I. L., Shlatz L. J., Kinne-Saffran E., Kinne R. Target cell polarity and membrane phosphorylation in relation to the mechanism of action of antidiuretic hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2595–2599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shareghi G. R., Stoner L. C. Calcium transport across segments of the rabbit distal nephron in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1978 Oct;235(4):F367–F375. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.235.4.F367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B., 3rd Modulation of vasopressin-induced water permeability of the cortical collecting tubule by endogenous and exogenous prostaglandins. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1985;11(4):240–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B. Effect of prostaglandin E2 on chloride transport across the rabbit thick ascending limb of Henle. Selective inhibitions of the medullary portion. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):495–502. doi: 10.1172/JCI109487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B. Ion transport by the cortical and outer medullary collecting tubule. Kidney Int. 1982 Nov;22(5):473–484. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B., Kokko J. P. Inhibition of sodium transport by prostaglandin E2 across the isolated, perfused rabbit collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1099–1104. doi: 10.1172/JCI108733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B. Potassium secretion by cortical collecting tubule: relation to sodium absorption, luminal sodium concentration, and transepithelial voltage. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F395–F402. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner L. C., Burg M. B., Orloff J. Ion transport in cortical collecting tubule; effect of amiloride. Am J Physiol. 1974 Aug;227(2):453–459. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.2.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita K., Pisano J. J., Knepper M. A. Control of sodium and potassium transport in the cortical collecting duct of the rat. Effects of bradykinin, vasopressin, and deoxycorticosterone. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):132–136. doi: 10.1172/JCI111935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tribollet E., Barberis C., Dreifuss J. J., Jard S. Autoradiographic localization of vasopressin and oxytocin binding sites in rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1988 May;33(5):959–965. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter R., Bowman R. H. Mechanism of inactivation of vasopressin and oxytocin by the isolated perfused rat kidney. Endocrinology. 1973 Jan;92(1):189–193. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-1-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingo C. S. Active proton secretion and potassium absorption in the rabbit outer medullary collecting duct. Functional evidence for proton-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):361–365. doi: 10.1172/JCI114165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]