Abstract
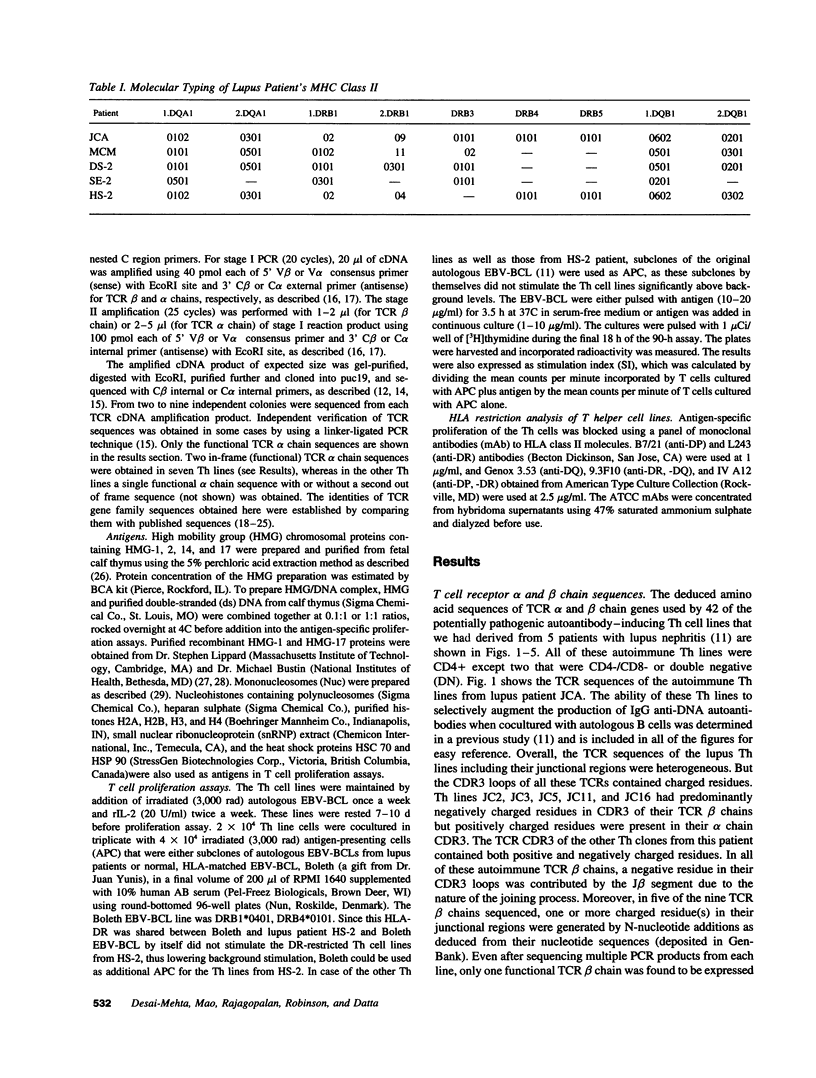
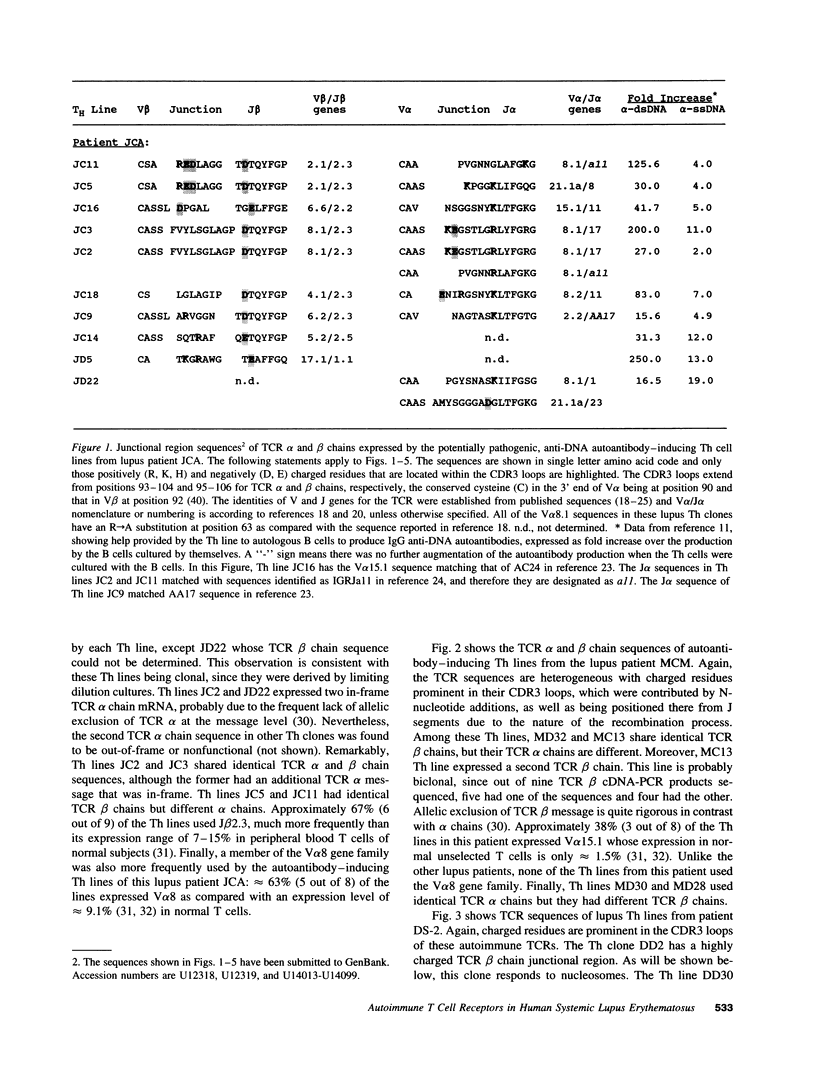
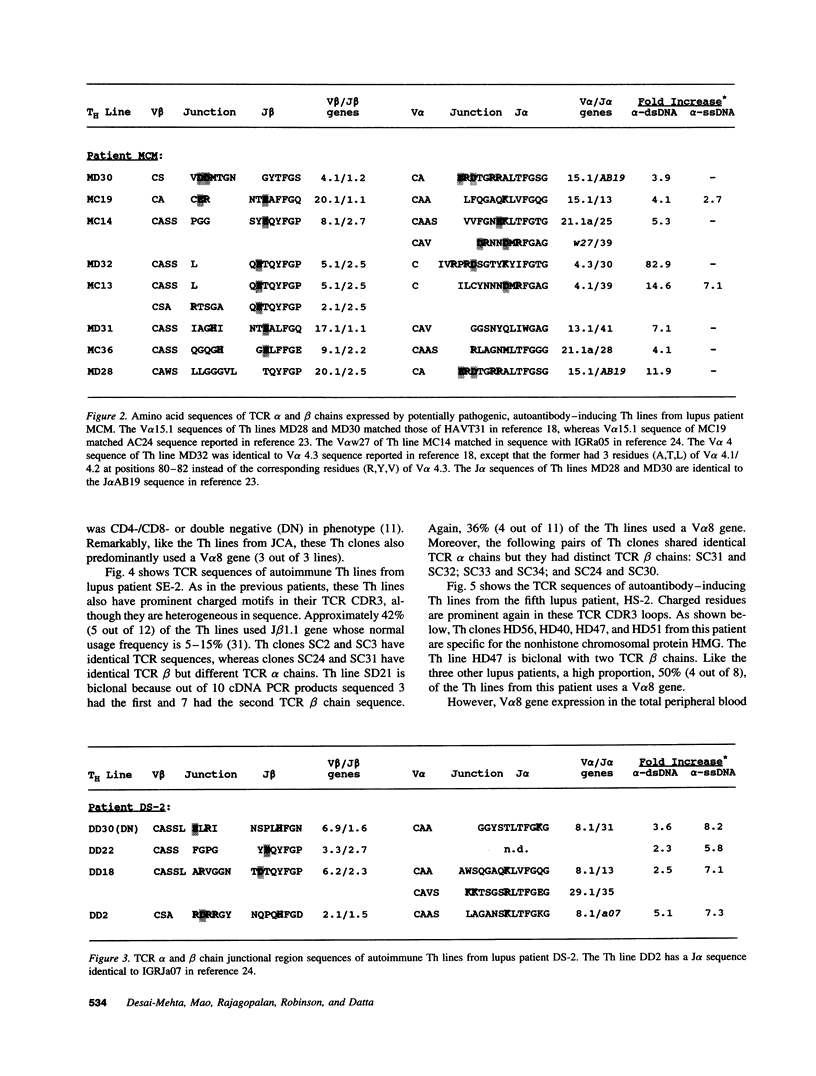
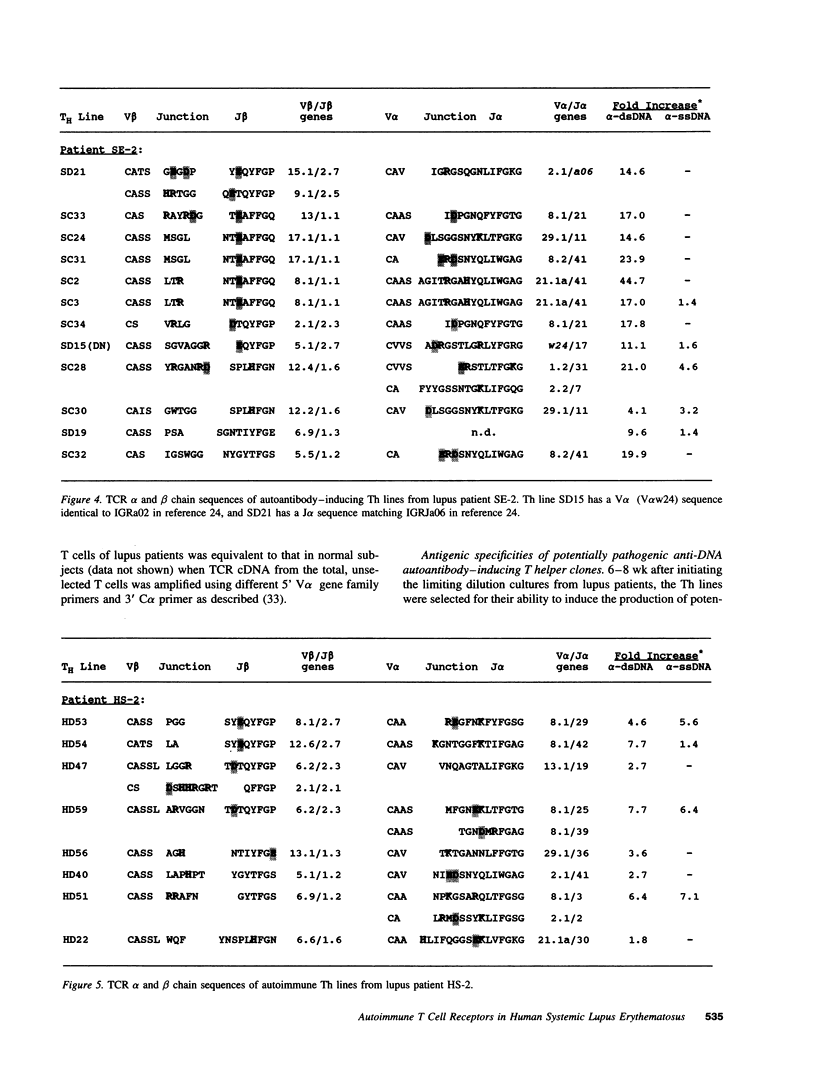
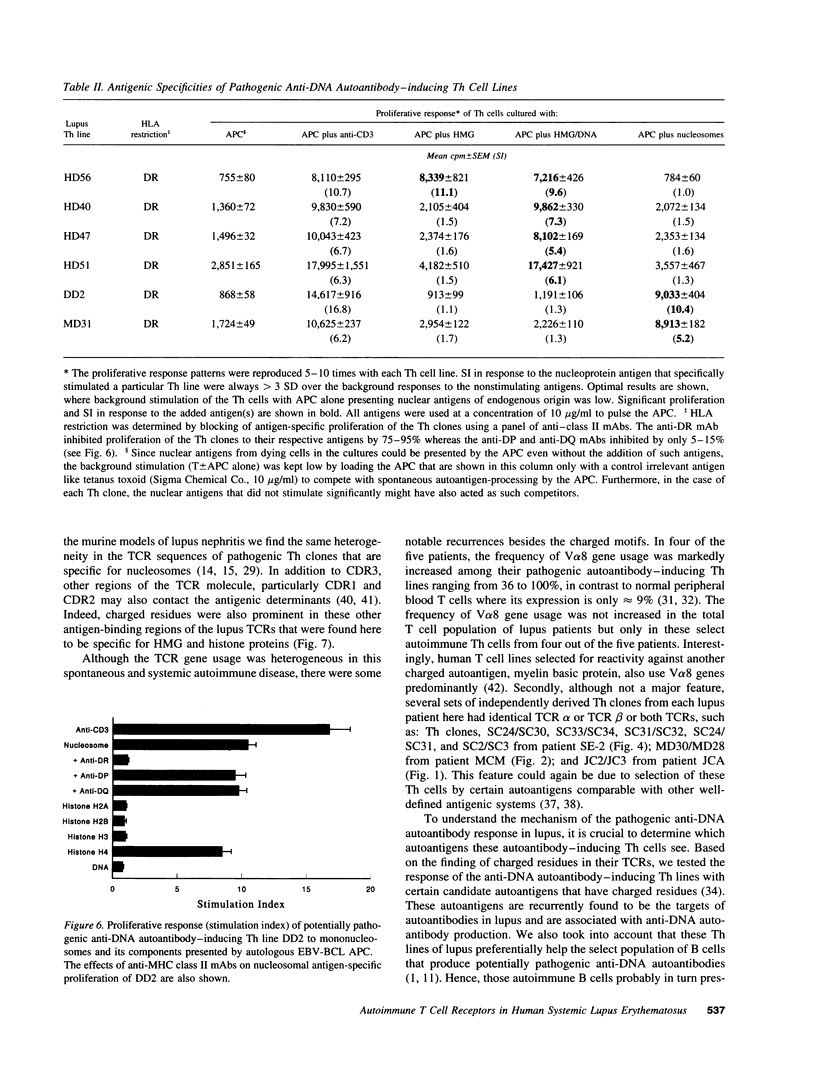
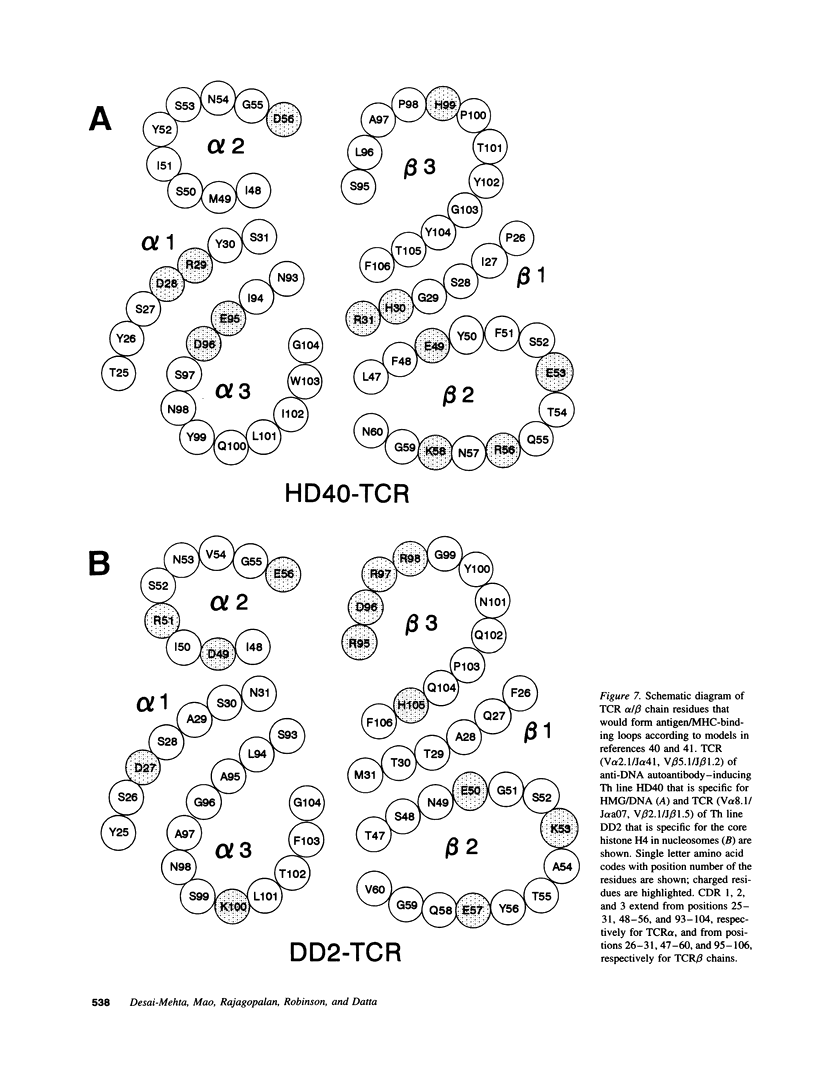
The production of potentially pathogenic anti-DNA autoantibodies in SLE is driven by special, autoimmune T helper (Th) cells. Herein, we sequenced the T cell receptor (TCR) alpha and beta chain genes expressed by 42 autoimmune Th lines from lupus patients that were mostly CD4+ and represented the strongest inducers of such autoantibodies. These autoimmune TCRs displayed a recurrent motif of highly charged residues in their CDR3 loops that were contributed by N-nucleotide additions and also positioned there by the recombination process. Furthermore, Th lines from four of the five patients showed a marked increase in the usage of the V alpha 8 gene family. Several independent Th lines expressed identical TCR alpha and/or beta chain sequences indicating again antigenic selection. 10 of these Th lines could be tested further for antigenic specificity. 4 of the 10 pathogenic anti-DNA autoantibody-inducing Th lines responded to the non-histone chromosomal protein HMG and two responded to nucleosomal histone proteins; all presented by HLA-DR molecules. Another Th line responded to purified DNA more than nucleosomes. Thus, these autoimmune Th cells of lupus patients respond to charged epitopes in various DNA-binding nucleoproteins that are probably processed and presented by the anti-DNA B cells they selectively help.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S., Leblanc P., Datta S. K. Junctional region sequences of T-cell receptor beta-chain genes expressed by pathogenic anti-DNA autoantibody-inducing helper T cells from lupus mice: possible selection by cationic autoantigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11271–11275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando D. G., Sercarz E. E., Hahn B. H. Mechanisms of T and B cell collaboration in the in vitro production of anti-DNA antibodies in the NZB/NZW F1 murine SLE model. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3185–3190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M. E. Production of functional rat HMG1 protein in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1991 Aug 15;104(2):271–275. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom D. D., St Clair E. W., Pisetsky D. S., Clarke S. H. The anti-La response of a single MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mouse: specificity for DNA and VH gene usage. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Jun;24(6):1332–1338. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendel V., Dohlman J., Blaisdell B. E., Karlin S. Very long charge runs in systemic lupus erythematosus-associated autoantigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1536–1540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broeren C. P., Verjans G. M., Van Eden W., Kusters J. G., Lenstra J. A., Logtenberg T. Conserved nucleotide sequences at the 5' end of T cell receptor variable genes facilitate polymerase chain reaction amplification. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Mar;21(3):569–575. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlingame R. W., Rubin R. L., Balderas R. S., Theofilopoulos A. N. Genesis and evolution of antichromatin autoantibodies in murine lupus implicates T-dependent immunization with self antigen. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1687–1696. doi: 10.1172/JCI116378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustin M., Reisch J., Einck L., Klippel J. H. Autoantibodies to nucleosomal proteins: antibodies to HMG-17 in autoimmune diseases. Science. 1982 Mar 5;215(4537):1245–1247. doi: 10.1126/science.6460317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A. The specificity of anti-DNA antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):1–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casciola-Rosen L. A., Anhalt G., Rosen A. Autoantigens targeted in systemic lupus erythematosus are clustered in two populations of surface structures on apoptotic keratinocytes. J Exp Med. 1994 Apr 1;179(4):1317–1330. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.4.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Boswell D. R., Lesk A. M. The outline structure of the T-cell alpha beta receptor. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3745–3755. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03258.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Concannon P., Pickering L. A., Kung P., Hood L. Diversity and structure of human T-cell receptor beta-chain variable region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6598–6602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constant P., Davodeau F., Peyrat M. A., Poquet Y., Puzo G., Bonneville M., Fournié J. J. Stimulation of human gamma delta T cells by nonpeptidic mycobacterial ligands. Science. 1994 Apr 8;264(5156):267–270. doi: 10.1126/science.8146660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow M. K., DelGiudice-Asch G., Zehetbauer J. B., Lawson J. L., Brot N., Weissbach H., Elkon K. B. Autoantigen-specific T cell proliferation induced by the ribosomal P2 protein in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jul;94(1):345–352. doi: 10.1172/JCI117328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danska J. S., Livingstone A. M., Paragas V., Ishihara T., Fathman C. G. The presumptive CDR3 regions of both T cell receptor alpha and beta chains determine T cell specificity for myoglobin peptides. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):27–33. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta S. K., Patel H., Berry D. Induction of a cationic shift in IgG anti-DNA autoantibodies. Role of T helper cells with classical and novel phenotypes in three murine models of lupus nephritis. J Exp Med. 1987 May 1;165(5):1252–1268. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.5.1252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai D. D., Krishnan M. R., Swindle J. T., Marion T. N. Antigen-specific induction of antibodies against native mammalian DNA in nonautoimmune mice. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 1;151(3):1614–1626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond B., Katz J. B., Paul E., Aranow C., Lustgarten D., Scharff M. D. The role of somatic mutation in the pathogenic anti-DNA response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:731–757. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.003503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebling F., Hahn B. H. Restricted subpopulations of DNA antibodies in kidneys of mice with systemic lupus. Comparison of antibodies in serum and renal eluates. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Apr;23(4):392–403. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferradini L., Roman-Roman S., Azocar J., Michalaki H., Triebel F., Hercend T. Studies on the human T cell receptor alpha/beta variable region genes. II. Identification of four additional V beta subfamilies. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Apr;21(4):935–942. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournié G. J., Lulé J., Dueymes J. M., Laval F., Delobbe I., Vernier I., Pourrat J. P. Plasma DNA in patients undergoing hemodialysis or hemofiltration: cytolysis in artificial kidney is responsible for the release of DNA in circulation. Am J Nephrol. 1989;9(5):384–391. doi: 10.1159/000168000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredriksen K., Osei A., Sundsfjord A., Traavik T., Rekvig O. P. On the biological origin of anti-double-stranded (ds) DNA antibodies: systemic lupus erythematosus-related anti-dsDNA antibodies are induced by polyomavirus BK in lupus-prone (NZBxNZW) F1 hybrids, but not in normal mice. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Jan;24(1):66–70. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganju R. K., Smiley S. T., Bajorath J., Novotny J., Reinherz E. L. Similarity between fluorescein-specific T-cell receptor and antibody in chemical details of antigen recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11552–11556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier V. J., Mannik M. A small proportion of cationic antibodies in immune complexes is sufficient to mediate their deposition in glomeruli. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3348–3352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavalchin J., Datta S. K. The NZB X SWR model of lupus nephritis. II. Autoantibodies deposited in renal lesions show a distinctive and restricted idiotypic diversity. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):138–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin G. H., Rabbani A., Nicolas P. H., Johns E. W. The isolation of the high mobility group non-histone chromosomal protein HMG 14. FEBS Lett. 1977 Aug 15;80(2):413–416. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80488-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley J. B., Sestak A. L., Willis L. G., Fu S. M., Hansen J. A., Reichlin M. A model for disease heterogeneity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Relationships between histocompatibility antigens, autoantibodies, and lymphopenia or renal disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Jul;32(7):826–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman R. W., Takeda Y., Sharp G. C., Lee D. R., Hill D. L., Kaneoka H., Caldwell C. W. Human T cell clones reactive against U-small nuclear ribonucleoprotein autoantigens from connective tissue disease patients and healthy individuals. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 1;151(11):6460–6469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob L., Viard J. P., Allenet B., Anin M. F., Slama F. B., Vandekerckhove J., Primo J., Markovits J., Jacob F., Bach J. F. A monoclonal anti-double-stranded DNA autoantibody binds to a 94-kDa cell-surface protein on various cell types via nucleosomes or a DNA-histone complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4669–4673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaulin C., Casanova J. L., Romero P., Luescher I., Cordey A. S., Maryanski J. L., Kourilsky P. Highly diverse T cell recognition of a single Plasmodium berghei peptide presented by a series of mutant H-2Kd molecules. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 15;149(12):3990–3994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. L., Esser U., Fazekas de St Groth B., Reay P. A., Davis M. M. Mapping T-cell receptor-peptide contacts by variant peptide immunization of single-chain transgenics. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):224–230. doi: 10.1038/355224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai Y., Takeda O., Kanai Y., Miura K., Kurosawa Y. Novel autoimmune phenomena induced in vivo by a new DNA binding protein Nuc: a study on MRL/n mice. Immunol Lett. 1993 Dec;39(1):83–89. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(93)90168-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasibhatla S., Nalefski E. A., Rao A. Simultaneous involvement of all six predicted antigen binding loops of the T cell receptor in recognition of the MHC/antigenic peptide complex. J Immunol. 1993 Sep 15;151(6):3140–3151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura N., Toyonaga B., Yoshikai Y., Du R. P., Mak T. W. Sequences and repertoire of the human T cell receptor alpha and beta chain variable region genes in thymocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Mar;17(3):375–383. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M. H., Concannon P., Everett M., Kim L. D., Hunkapiller T., Hood L. Diversity and structure of human T-cell receptor alpha-chain variable region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6884–6888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake P., Mitchison N. A. Regulatory mechanisms in the immune response to cell-surface antigens. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):589–595. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzavecchia A. Antigen-specific interaction between T and B cells. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):537–539. doi: 10.1038/314537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. DNA--protein interactions. HMG has DNA wrapped up. Nature. 1992 May 28;357(6376):282–283. doi: 10.1038/357282a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R. H., Mamula M. J., Hardin J. A., Janeway C. A., Jr Induction of autoreactive B cells allows priming of autoreactive T cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1433–1439. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linker-Israeli M., Quismorio F. P., Jr, Horwitz D. A. CD8+ lymphocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus sustain, rather than suppress, spontaneous polyclonal IgG production and synergize with CD4+ cells to support autoantibody synthesis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Aug;33(8):1216–1225. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen M., Trucy J., Jouvin-Marche E., Cazenave P. A., Scollay R., Malissen B. Regulation of TCR alpha and beta gene allelic exclusion during T-cell development. Immunol Today. 1992 Aug;13(8):315–322. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamula M. J., Fatenejad S., Craft J. B cells process and present lupus autoantigens that initiate autoimmune T cell responses. J Immunol. 1994 Feb 1;152(3):1453–1461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao C., Osman G. E., Adams S., Datta S. K. T cell receptor alpha-chain repertoire of pathogenic autoantibody-inducing T cells in lupus mice. J Immunol. 1994 Feb 1;152(3):1462–1470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., Howell M. D., Jaraquemada D., Flerlage M., Richert J., Brostoff S., Long E. O., McFarlin D. E., McFarland H. F. A myelin basic protein peptide is recognized by cytotoxic T cells in the context of four HLA-DR types associated with multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):19–24. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan C., Adams S., Stanik V., Datta S. K. Nucleosome: a major immunogen for pathogenic autoantibody-inducing T cells of lupus. J Exp Med. 1993 May 1;177(5):1367–1381. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.5.1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss P. A., Rosenberg W. M., Bell J. I. The human T cell receptor in health and disease. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:71–96. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naiki M., Chiang B. L., Cawley D., Ansari A., Rozzo S. J., Kotzin B. L., Zlotnik A., Gershwin M. E. Generation and characterization of cloned T helper cell lines for anti-DNA responses in NZB.H-2bm12 mice. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 15;149(12):4109–4115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obata F., Tsunoda M., Kaneko T., Ito K., Ito I., Masewicz S., Mickelson E. M., Ollier W. E., Pawelec G., Cella M. Human T-cell receptor TCRAV, TCRBV, and TCRAJ sequences newly found in T-cell clones reactive with allogeneic HLA class II antigens. Immunogenetics. 1993;38(1):67–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00216395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oksenberg J. R., Stuart S., Begovich A. B., Bell R. B., Erlich H. A., Steinman L., Bernard C. C. Limited heterogeneity of rearranged T-cell receptor V alpha transcripts in brains of multiple sclerosis patients. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):344–346. doi: 10.1038/345344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluschke G., Ricken G., Taube H., Kroninger S., Melchers I., Peter H. H., Eichmann K., Krawinkel U. Biased T cell receptor V alpha region repertoire in the synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Nov;21(11):2749–2754. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portanova J. P., Arndt R. E., Kotzin B. L. Selective production of autoantibodies in graft-vs-host-induced and spontaneous murine lupus. Predominant reactivity with histone regions accessible in chromatin. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):755–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radic M. Z., Weigert M. Genetic and structural evidence for antigen selection of anti-DNA antibodies. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:487–520. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopalan S., Mao C., Datta S. K. Pathogenic autoantibody-inducing gamma/delta T helper cells from patients with lupus nephritis express unusual T cell receptors. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1992 Mar;62(3):344–350. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(92)90113-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopalan S., Zordan T., Tsokos G. C., Datta S. K. Pathogenic anti-DNA autoantibody-inducing T helper cell lines from patients with active lupus nephritis: isolation of CD4-8- T helper cell lines that express the gamma delta T-cell antigen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7020–7024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin M., Martin A., Taylor-Albert E., Tsuzaka K., Zhang W., Reichlin M. W., Koren E., Ebling F. M., Tsao B., Hahn B. H. Lupus autoantibodies to native DNA cross-react with the A and D SnRNP polypeptides. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jan;93(1):443–449. doi: 10.1172/JCI116980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman-Roman S., Ferradini L., Azocar J., Genevée C., Hercend T., Triebel F. Studies on the human T cell receptor alpha/beta variable region genes. I. Identification of 7 additional V alpha subfamilies and 14 J alpha gene segments. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Apr;21(4):927–933. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumore P. M., Steinman C. R. Endogenous circulating DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Occurrence as multimeric complexes bound to histone. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):69–74. doi: 10.1172/JCI114716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sainis K., Datta S. K. CD4+ T cell lines with selective patterns of autoreactivity as well as CD4- CD8- T helper cell lines augment the production of idiotypes shared by pathogenic anti-DNA autoantibodies in the NZB x SWR model of lupus nephritis. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2215–2224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivakumar S., Tsokos G. C., Datta S. K. T cell receptor alpha/beta expressing double-negative (CD4-/CD8-) and CD4+ T helper cells in humans augment the production of pathogenic anti-DNA autoantibodies associated with lupus nephritis. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):103–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Rauch J., Massicotte H., Datta S. K., André-Schwartz J., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. Polyspecificity of monoclonal lupus autoantibodies produced by human-human hybridomas. N Engl J Med. 1983 Feb 24;308(8):414–420. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198302243080802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel E. S., Kakkanaiah V. N., Kakkanaiah M., Cheek R. L., Cohen P. L., Eisenberg R. A. T-B collaboration for autoantibody production in lpr mice is cognate and MHC-restricted. J Immunol. 1994 Jun 15;152(12):6011–6016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suenaga R., Abdou N. I. Cationic and high affinity serum IgG anti-dsDNA antibodies in active lupus nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Dec;94(3):418–422. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb08211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Harada T., Mizushima Y., Sakane T. Possible pathogenic role of cationic anti-DNA autoantibodies in the development of nephritis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 15;151(2):1128–1136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Termaat R. M., Brinkman K., Nossent J. C., Swaak A. J., Smeenk R. J., Berden J. H. Anti-heparan sulphate reactivity in sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with renal or non-renal manifestations. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Nov;82(2):268–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05438.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyonaga B., Yoshikai Y., Vadasz V., Chin B., Mak T. W. Organization and sequences of the diversity, joining, and constant region genes of the human T-cell receptor beta chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8624–8628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uematsu Y., Wege H., Straus A., Ott M., Bannwarth W., Lanchbury J., Panayi G., Steinmetz M. The T-cell-receptor repertoire in the synovial fluid of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis is polyclonal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8534–8538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utz U., Brooks J. A., McFarland H. F., Martin R., Biddison W. E. Heterogeneity of T-cell receptor alpha-chain complementarity-determining region 3 in myelin basic protein-specific T cells increases with severity of multiple sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5567–5571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wucherpfennig K. W., Ota K., Endo N., Seidman J. G., Rosenzweig A., Weiner H. L., Hafler D. A. Shared human T cell receptor V beta usage to immunodominant regions of myelin basic protein. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1016–1019. doi: 10.1126/science.1693015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



