Abstract
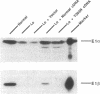
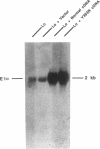
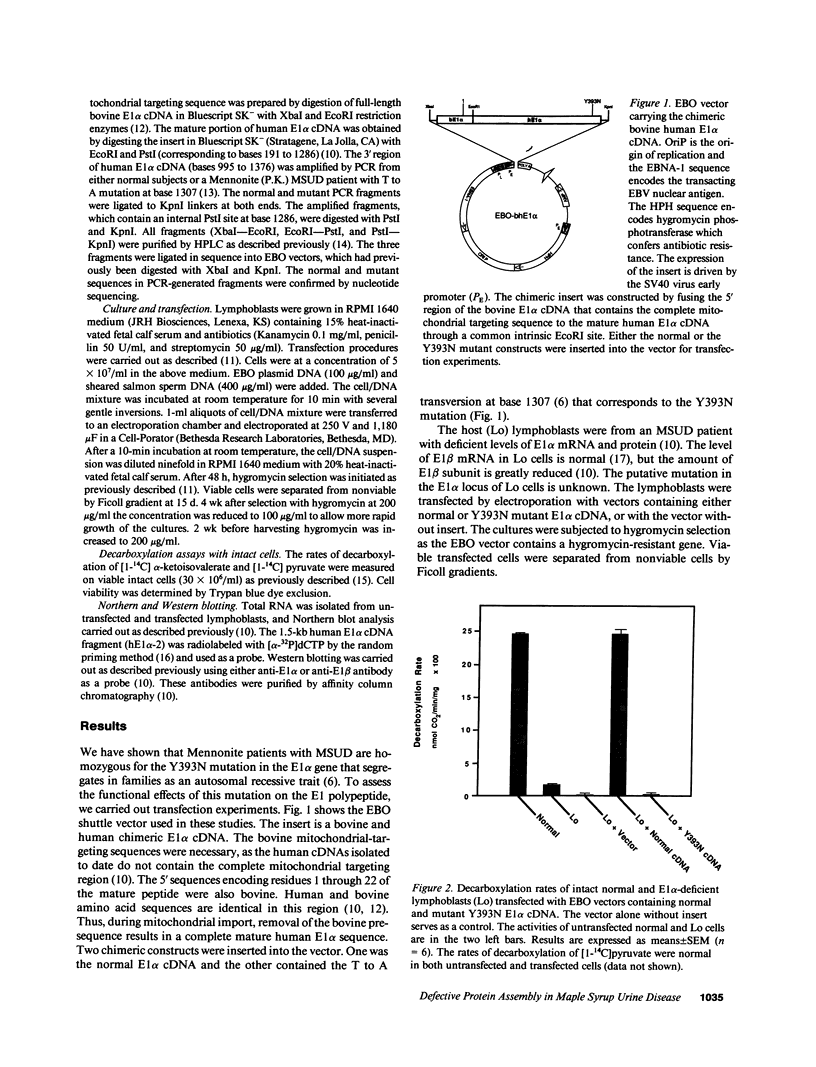
Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD) in Mennonites is associated with homozygosity for a T to A transversion in the E1 alpha gene of the branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex. This causes a tyrosine to asparagine substitution at position 393 (Y393N). To assess the functional significance of this missense mutation, we have carried out transfection studies using E1 alpha-deficient MSUD lymphoblasts (Lo) as a host. The level of E1 beta subunit is also greatly reduced in Lo cells. Efficient episomal expression in lymphoblasts was achieved using the EBO vector. The inserts employed were chimeric bovine-human cDNAs which encode mitochondrial import competent E1 alpha subunit precursors. Transfection with normal E1 alpha cDNA into Lo cells restored decarboxylation activity of intact cells. Western blotting showed that both E1 alpha and E1 beta subunits were markedly increased. Introduction of Y393N mutant E1 alpha cDNA failed to produce any measurable decarboxylation activity. Mutant E1 alpha subunit was expressed at a normal level, however, the E1 beta subunit was undetectable. These results provide the first evidence that Y393N mutation is the cause of MSUD. Moreover, this mutation impedes the assembly of E1 alpha with E1 beta into a stable alpha 2 beta 2 structure, resulting in the degradation of the free E1 beta subunit.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chuang D. T., Cox R. P. Enzyme assays with mutant cell lines of maple syrup urine disease. Methods Enzymol. 1988;166:135–146. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)66020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang J. L., Cox R. P., Chuang D. T. Molecular cloning of the mature E1b-beta subunit of human branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 26;262(2):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dariush N., Fisher C. W., Cox R. P., Chuang D. T. Structure of the gene encoding the entire mature E1 alpha subunit of human branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jun 17;284(1):34–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80755-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. R., Fisher C. W., Chuang D. T., Cox R. P. Occurrence of a Tyr393----Asn (Y393N) mutation in the E1 alpha gene of the branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex in maple syrup urine disease patients from a Mennonite population. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Aug;49(2):429–434. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu C. W., Lau K. S., Griffin T. A., Chuang J. L., Fisher C. W., Cox R. P., Chuang D. T. Isolation and sequencing of a cDNA encoding the decarboxylase (E1)alpha precursor of bovine branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex. Expression of E1 alpha mRNA and subunit in maple-syrup-urine-disease and 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):9007–9014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau K. S., Eddy R. L., Shows T. B., Fisher C. W., Chuang D. T., Cox R. P. Localization of the dihydrolipoamide branched-chain transacylase gene (DBT) of the human branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase complex to chromosome 1. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1991;56(1):33–35. doi: 10.1159/000133041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MENKES J. H., HURST P. L., CRAIG J. M. A new syndrome: progressive familial infantile cerebral dysfunction associated with an unusual urinary substance. Pediatrics. 1954 Nov;14(5):462–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolskee R. F., Kavathas P., Berg P. Epstein-Barr virus shuttle vector for stable episomal replication of cDNA expression libraries in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2837–2847. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Lipman M. Release of infectious Epstein-Barr virus by transformed marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):190–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler I. D., Kerr D. S., Ho L., Lusk M. M., Pepin R. A., Javed A. A., Mole J. E., Jesse B. W., Thekkumkara T. J., Pons G. Heterogeneous expression of protein and mRNA in pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7336–7340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeaman S. J. The 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase complexes: recent advances. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 1;257(3):625–632. doi: 10.1042/bj2570625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang B., Edenberg H. J., Crabb D. W., Harris R. A. Evidence for both a regulatory mutation and a structural mutation in a family with maple syrup urine disease. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1425–1429. doi: 10.1172/JCI114033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang B., Healy P. J., Zhao Y., Crabb D. W., Harris R. A. Premature translation termination of the pre-E1 alpha subunit of the branched chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase as a cause of maple syrup urine disease in Polled Hereford calves. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2425–2427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang B., Kuntz M. J., Goodwin G. W., Harris R. A., Crabb D. W. Molecular cloning of a cDNA for the E1 alpha subunit of rat liver branched chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15220–15224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]