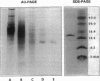
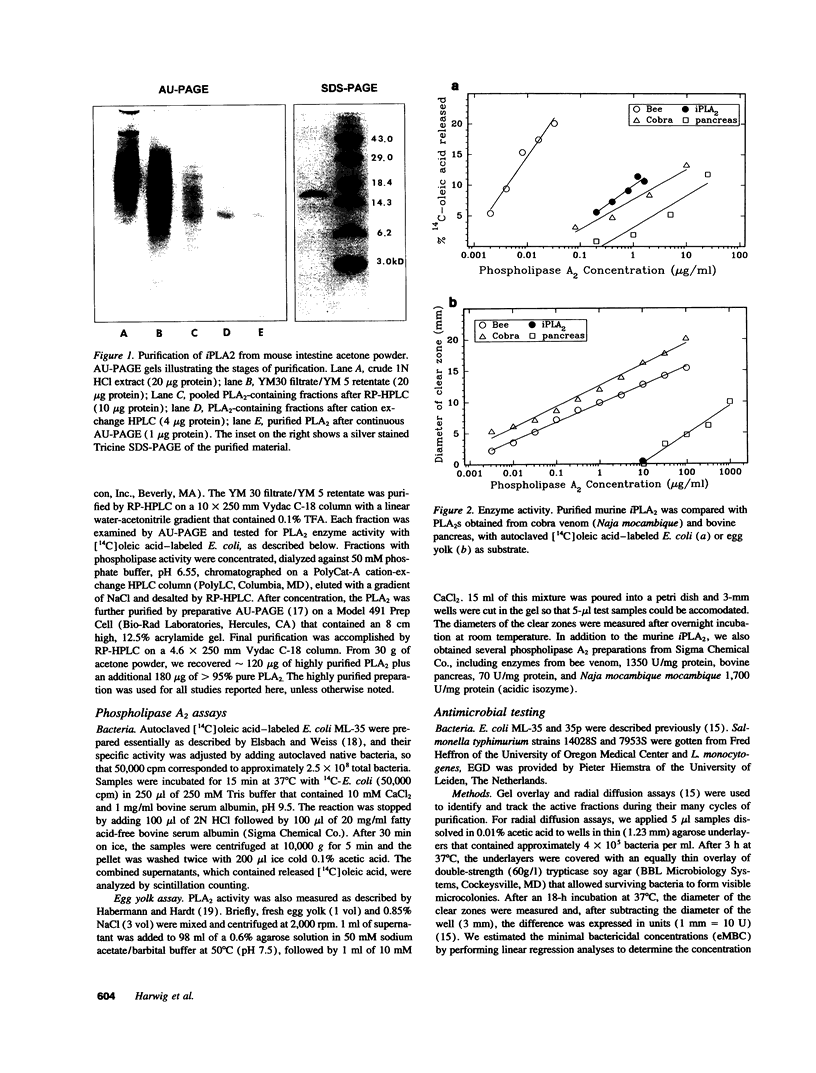
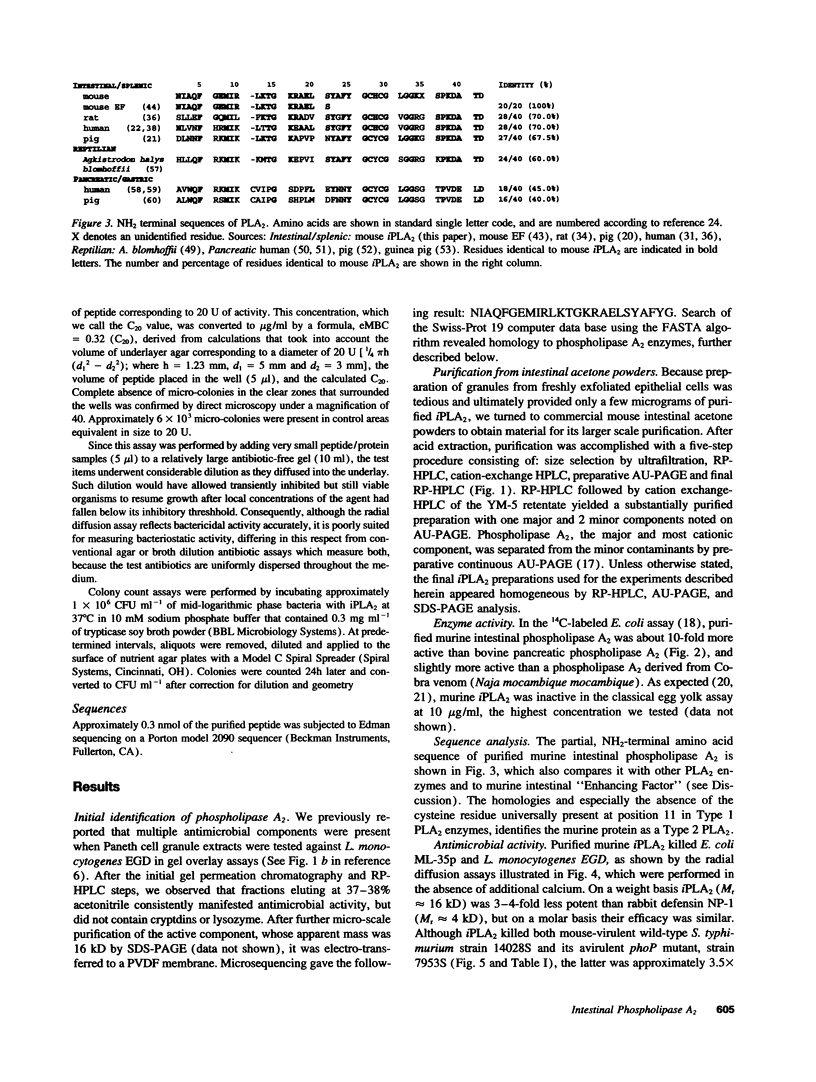
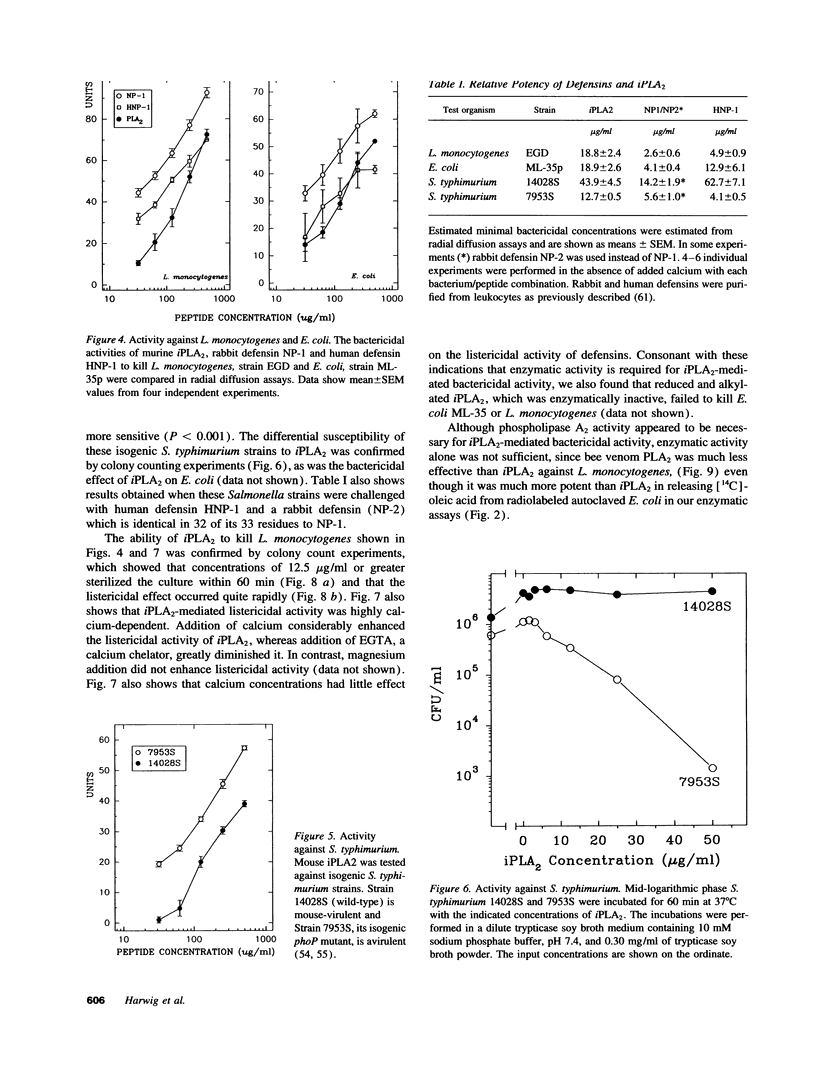
Abstract
We purified a molecule from the murine small intestine that killed both Escherichia coli and Listeria monocytogenes, and identified it as intestinal phospholipase A2 (iPLA2) by NH2-terminal sequencing and enzymatic measurements. The ability of iPLA2 to kill. L. monocytogenes was greatly enhanced by 5 mM calcium, inhibited by EGTA and abolished after reduction and alkylation, suggesting that enzymatic activity was required for iPLA2-mediated bactericidal activity. A mouse-avirulent phoP mutant, S. typhimurium 7953S, was 3.5-fold more susceptible to iPLA2 than its isogenic virulent parent, S. typhimurium 14028S (estimated minimal bactericidal concentrations 12.7 +/- 0.5 micrograms/ml vs. 43.9 +/- 4.5 micrograms/ml P < 0.001). Overall, these findings identify iPLA2 as part of the antimicrobial arsenal that equips Paneth cells to protect the small intestinal crypts from microbial invasion. Because iPLA2 is identical to Type 2 phospholipase A2 molecules found in other sites, including spleen, platelets and inflammatory exudate cells, this enzyme may also contribute to antibacterial defenses elsewhere in the body.
Full text
PDF
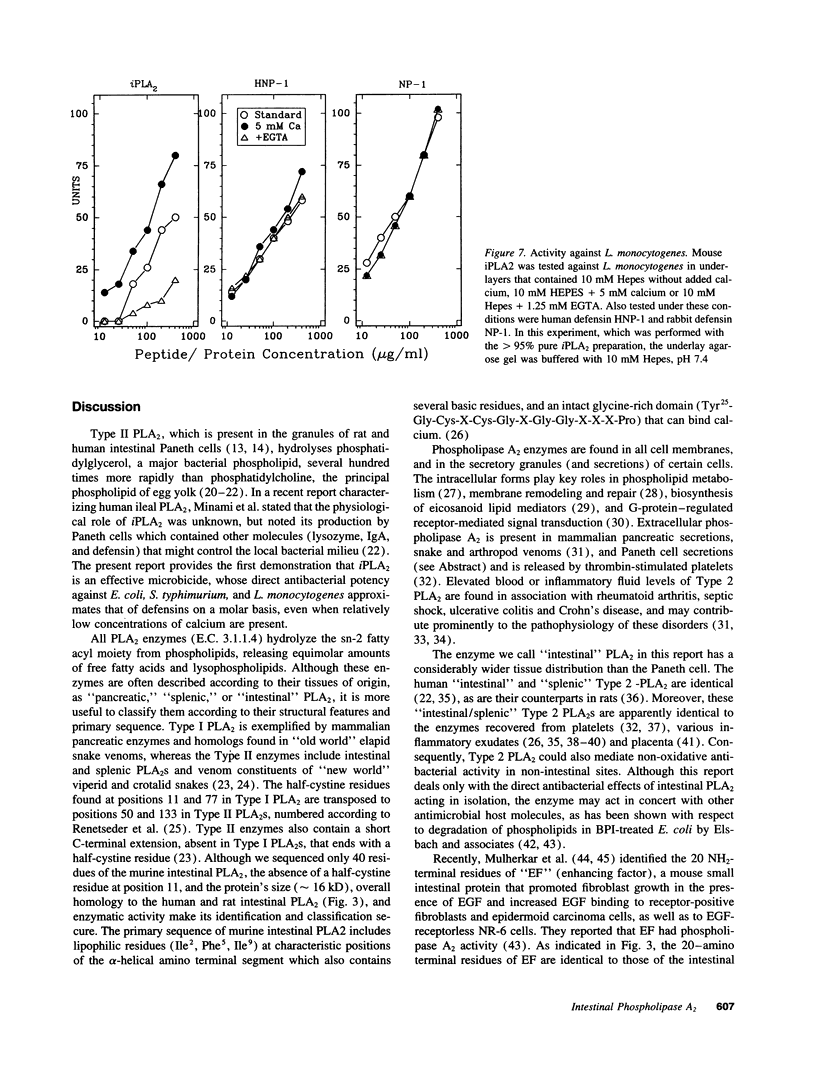
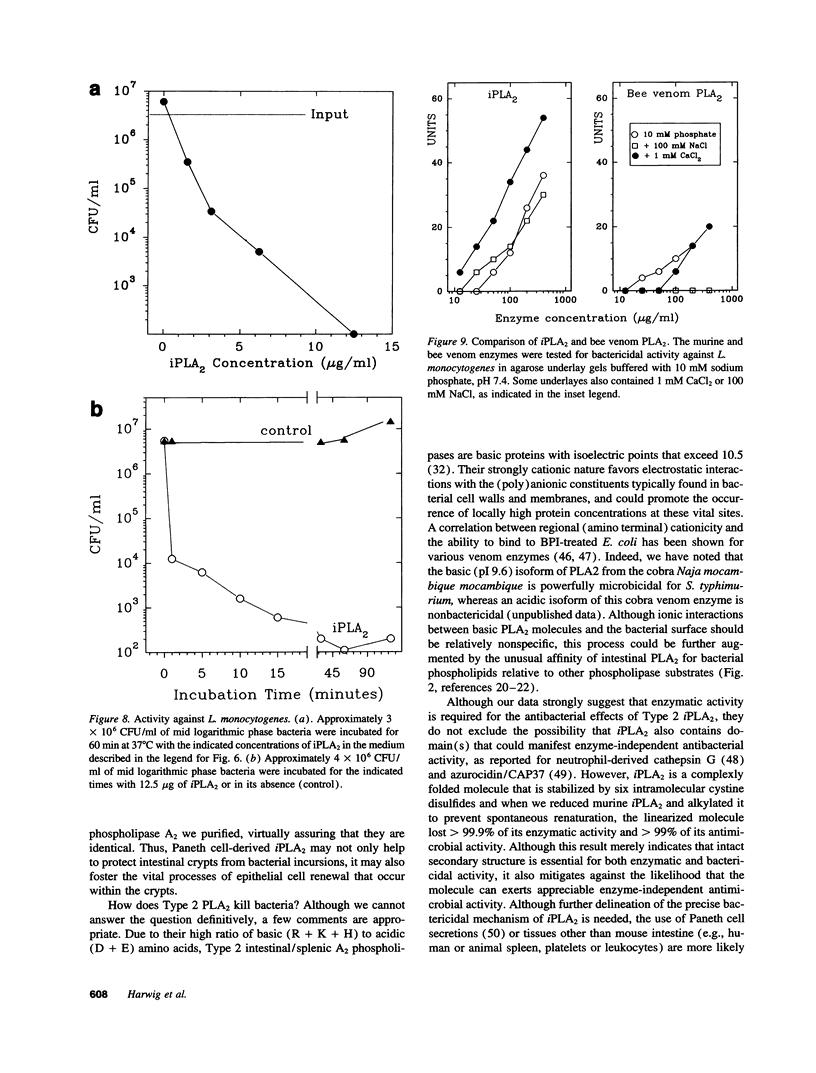


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod J., Burch R. M., Jelsema C. L. Receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase A2 via GTP-binding proteins: arachidonic acid and its metabolites as second messengers. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Mar;11(3):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. W., Kudo I., Tomita M., Inoue K. Purification and characterization of extracellular phospholipase A2 from peritoneal cavity of caseinate-treated rat. J Biochem. 1987 Jul;102(1):147–154. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J., Musser J. H., McGregor H. Phospholipase A2: function and pharmacological regulation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Aug 1;36(15):2429–2436. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90512-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhauer P. B., Harwig S. S., Lehrer R. I. Cryptdins: antimicrobial defensins of the murine small intestine. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3556–3565. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3556-3565.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P., Weiss J. Utilization of labeled Escherichia coli as phospholipase substrate. Methods Enzymol. 1991;197:24–31. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)97130-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandsen S. L., Chase D. G. Paneth cell function: phagocytosis and intracellular digestion of intestinal microorganisms. I. Hexamita muris. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Nov;41(3):296–318. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandsen S. L., Chase D. G. Paneth cell function: phagocytosis and intracellular digestion of intestinal microorganisms. II. Spiral microorganism. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Nov;41(3):319–333. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields P. I., Swanson R. V., Haidaris C. G., Heffron F. Mutants of Salmonella typhimurium that cannot survive within the macrophage are avirulent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5189–5193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forst S., Weiss J., Blackburn P., Frangione B., Goni F., Elsbach P. Amino acid sequence of a basic Agkistrodon halys blomhoffii phospholipase A2. Possible role of NH2-terminal lysines in action on phospholipids of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 29;25(15):4309–4314. doi: 10.1021/bi00363a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forst S., Weiss J., Elsbach P., Maraganore J. M., Reardon I., Heinrikson R. L. Structural and functional properties of a phospholipase A2 purified from an inflammatory exudate. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 30;25(26):8381–8385. doi: 10.1021/bi00374a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forst S., Weiss J., Maraganore J. M., Heinrikson R. L., Elsbach P. Relation between binding and the action of phospholipases A2 on Escherichia coli exposed to the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein of neutrophils. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Aug 15;920(3):221–225. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. W., Hall H. K. Adaptive acidification tolerance response of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):771–778. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.771-778.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser K. B., Mobilio D., Chang J. Y., Senko N. Phospholipase A2 enzymes: regulation and inhibition. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Mar;14(3):92–98. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90071-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L. Intestinal microflora. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jun;60(6):1110–1129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groisman E. A., Parra-Lopez C., Salcedo M., Lipps C. J., Heffron F. Resistance to host antimicrobial peptides is necessary for Salmonella virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11939–11943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E., Hardt K. L. A sensitive and specific plate test for the quantitation of phospholipases. Anal Biochem. 1972 Nov;50(1):163–173. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90495-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara S., Kudo I., Matsuta K., Miyamoto T., Inoue K. Amino acid composition and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of human phospholipase A2 purified from rheumatoid synovial fluid. J Biochem. 1988 Sep;104(3):326–328. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwig S. S., Chen N. P., Park A. S., Lehrer R. I. Purification of cysteine-rich bioactive peptides from leukocytes by continuous acid-urea-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1993 Feb 1;208(2):382–386. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwig S. S., Ganz T., Lehrer R. I. Neutrophil defensins: purification, characterization, and antimicrobial testing. Methods Enzymol. 1994;236:160–172. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)36015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa M., Horigome K., Kudo I., Tomita M., Nojima S., Inoue K. Amino acid composition and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of rat platelet secretory phospholipase A2. J Biochem. 1987 May;101(5):1311–1314. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrikson R. L., Krueger E. T., Keim P. S. Amino acid sequence of phospholipase A2-alpha from the venom of Crotalus adamanteus. A new classification of phospholipases A2 based upon structural determinants. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4913–4921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. K., Frank S., Vades P., Pruzanski W., Lusis A. J., Seilhamer J. J. Localization and evolution of two human phospholipase A2 genes and two related genetic elements. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1990;275:17–34. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5805-3_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. E., Bevins C. L. Defensin-6 mRNA in human Paneth cells: implications for antimicrobial peptides in host defense of the human bowel. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jan 4;315(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. E., Bevins C. L. Paneth cells of the human small intestine express an antimicrobial peptide gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23216–23225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda A., Ono T., Yoshida N., Tojo H., Okamoto M. The primary structure of a membrane-associated phospholipase A2 from human spleen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 30;163(1):42–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyohara H., Egami H., Shibata Y., Murata K., Ohshima S., Ogawa M. Light microscopic immunohistochemical analysis of the distribution of group II phospholipase A2 in human digestive organs. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Nov;40(11):1659–1664. doi: 10.1177/40.11.1431054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Hession C., Johansen B., Hayes G., McGray P., Chow E. P., Tizard R., Pepinsky R. B. Structure and properties of a human non-pancreatic phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5768–5775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Hession C., Johansen B., Hayes G., McGray P., Chow E. P., Tizard R., Pepinsky R. B. Structure and properties of a human non-pancreatic phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5768–5775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. Y., Wada K. Phospholipase A2 from human synovial fluid: purification and structural homology to the placental enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):488–493. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80275-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Rosenman M., Harwig S. S., Jackson R., Eisenhauer P. Ultrasensitive assays for endogenous antimicrobial polypeptides. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Mar 21;137(2):167–173. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansbach C. M., 2nd, Pieroni G., Verger R. Intestinal phospholipase, a novel enzyme. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):368–376. doi: 10.1172/JCI110460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. I., Kukral A. M., Mekalanos J. J. A two-component regulatory system (phoP phoQ) controls Salmonella typhimurium virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5054–5058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. I., Pulkkinen W. S., Selsted M. E., Mekalanos J. J. Characterization of defensin resistance phenotypes associated with mutations in the phoP virulence regulon of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3706–3710. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3706-3710.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami T., Tojo H., Shinomura Y., Komatsubara T., Matsuzawa Y., Okamoto M. Elevation of phospholipase A2 protein in sera of patients with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1993 Jul;88(7):1076–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami T., Tojo H., Shinomura Y., Matsuzawa Y., Okamoto M. Purification and characterization of a phospholipase A2 from human ileal mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Oct 13;1170(2):125–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulherkar R., Deo M. G. Further studies on the enhancing factor and its possible mechanism of action. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Apr;127(1):183–188. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041270122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulherkar R., Rao R., Rao L., Patki V., Chauhan V. S., Deo M. G. Enhancing factor protein from mouse small intestines belongs to the phospholipase A2 family. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 15;317(3):263–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81289-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono T., Tojo H., Kuramitsu S., Kagamiyama H., Okamoto M. Purification and characterization of a membrane-associated phospholipase A2 from rat spleen. Its comparison with a cytosolic phospholipase A2 S-1. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5732–5738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette A. J., Lualdi J. C. A novel mouse gene family coding for cationic, cysteine-rich peptides. Regulation in small intestine and cells of myeloid origin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9831–9837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette A. J., Miller S. I., Henschen A. H., Selsted M. E. Purification and primary structure of murine cryptdin-1, a Paneth cell defensin. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jun 15;304(2-3):146–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80606-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira H. A., Erdem I., Pohl J., Spitznagel J. K. Synthetic bactericidal peptide based on CAP37: a 37-kDa human neutrophil granule-associated cationic antimicrobial protein chemotactic for monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4733–4737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzanski W., Vadas P. Secretory synovial fluid phospholipase A2 and its role in the pathogenesis of inflammation in arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1988 Nov;15(11):1601–1603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puijk W. C., Verheij H. M., De Haas G. H. The primary structure of phospholipase A2 from porcine pancreas. A reinvestigation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 24;492(2):254–259. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renetseder R., Brunie S., Dijkstra B. W., Drenth J., Sigler P. B. A comparison of the crystal structures of phospholipase A2 from bovine pancreas and Crotalus atrox venom. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11627–11634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh Y. Atropine inhibits the degranulation of Paneth cells in ex-germ-free mice. Cell Tissue Res. 1988 Aug;253(2):397–402. doi: 10.1007/BF00222296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh Y. Effect of live and heat-killed bacteria on the secretory activity of Paneth cells in germ-free mice. Cell Tissue Res. 1988 Jan;251(1):87–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00215451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seilhamer J. J., Pruzanski W., Vadas P., Plant S., Miller J. A., Kloss J., Johnson L. K. Cloning and recombinant expression of phospholipase A2 present in rheumatoid arthritic synovial fluid. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5335–5338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seilhamer J. J., Randall T. L., Yamanaka M., Johnson L. K. Pancreatic phospholipase A2: isolation of the human gene and cDNAs from porcine pancreas and human lung. DNA. 1986 Dec;5(6):519–527. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1986.5.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Miller S. I., Henschen A. H., Ouellette A. J. Enteric defensins: antibiotic peptide components of intestinal host defense. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(4):929–936. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.4.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senegas-Balas F., Balas D., Verger R., de Caro A., Figarella C., Ferrato F., Lechene P., Bertrand C., Ribet A. Immunohistochemical localization of intestinal phospholipase A2 in rat paneth cells. Histochemistry. 1984;81(6):581–584. doi: 10.1007/BF00489538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Pruzanski W. Role of secretory phospholipases A2 in the pathobiology of disease. Lab Invest. 1986 Oct;55(4):391–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verger R., Ferrato F., Mansbach C. M., Pieroni G. Novel intestinal phospholipase A2: purification and some molecular characteristics. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6883–6889. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheij H. M., Westerman J., Sternby B., De Haas G. H. The complete primary structure of phospholipase A2 from human pancreas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 14;747(1-2):93–99. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Wright G., Bekkers A. C., van den Bergh C. J., Verheij H. M. Conversion of pig pancreas phospholipase A2 by protein engineering into enzyme active against Escherichia coli treated with the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4162–4167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright G. W., Ooi C. E., Weiss J., Elsbach P. Purification of a cellular (granulocyte) and an extracellular (serum) phospholipase A2 that participate in the destruction of Escherichia coli in a rabbit inflammatory exudate. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6675–6681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch H. Intracellular phospholipases A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 30;604(2):191–246. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90574-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]