Abstract
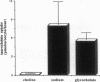
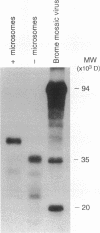
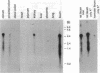
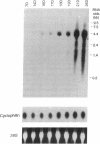
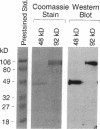
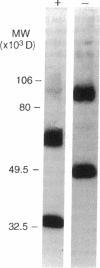
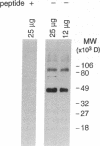
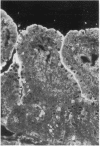
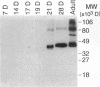
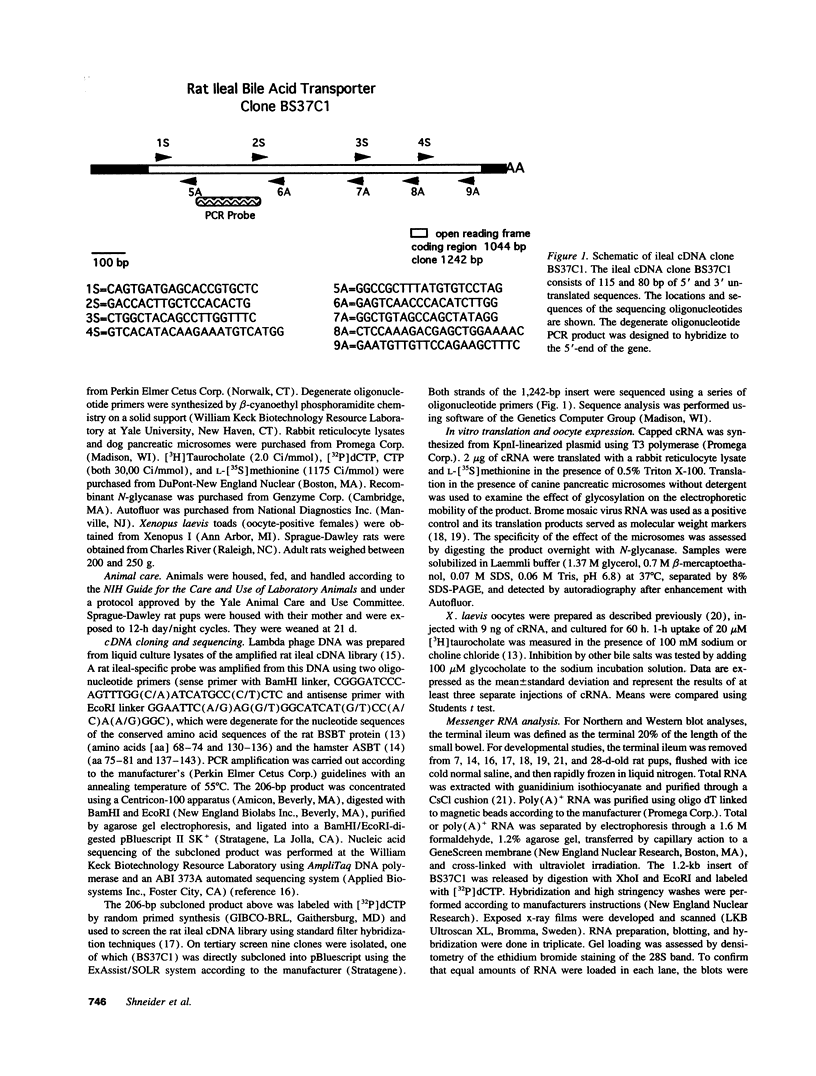
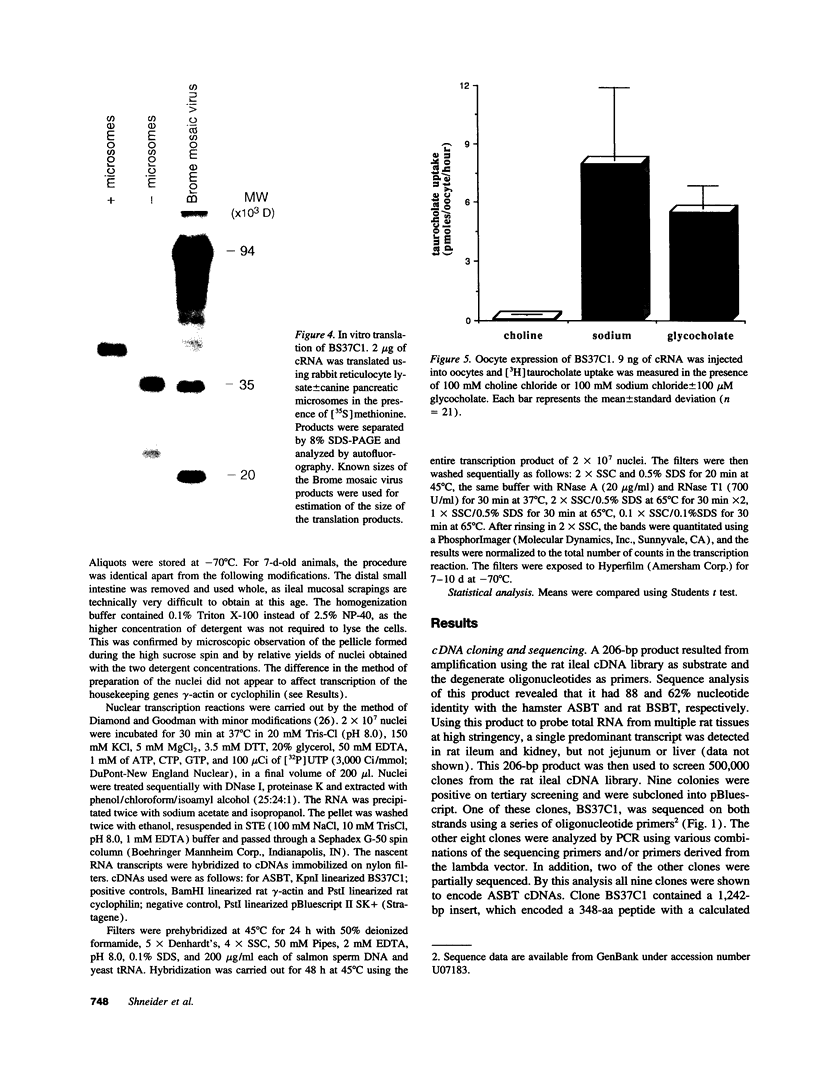
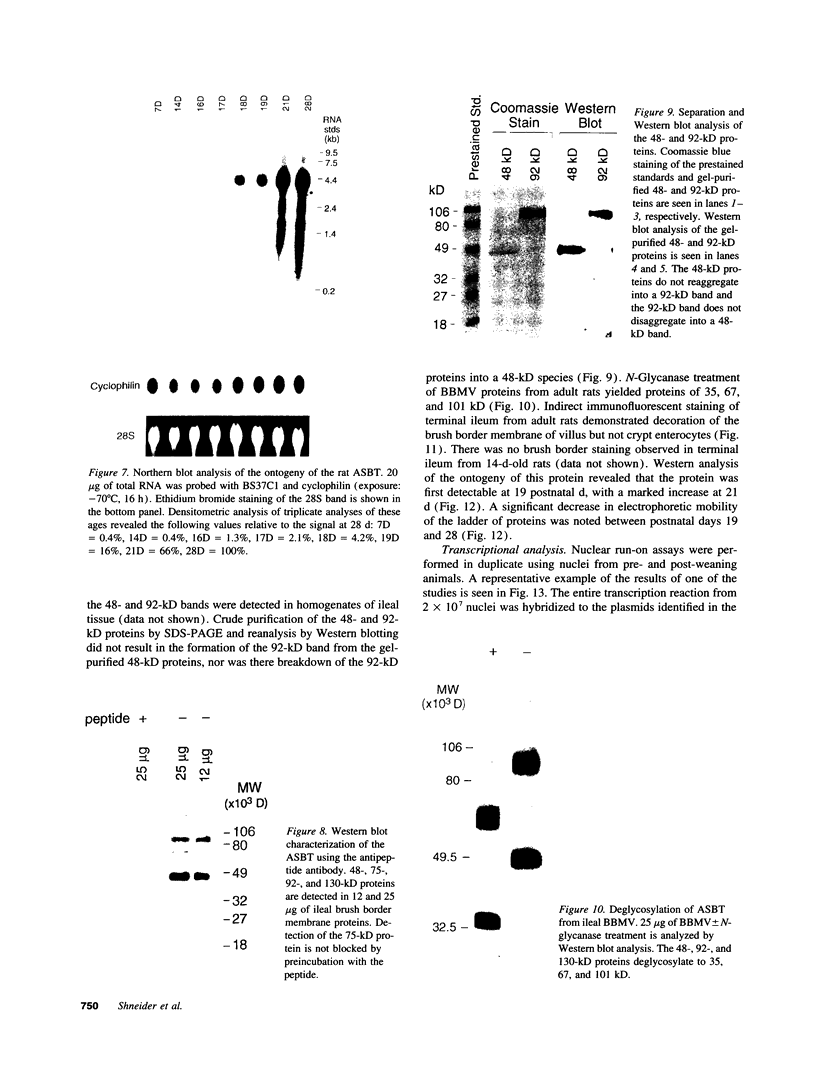
Sodium-dependent bile acid transport in the rat ileum is abruptly expressed at weaning. Degenerate oligonucleotides, based on amino acid sequence identities between the rat liver and hamster ileal transporters, were used to amplify a rat ileal probe. A 1.2-kb cDNA clone, which contains the full coding region (348 amino acids, 38 kD), was isolated by hybridization screening. In vitro translation yielded a 38-kD protein which glycosylated to 48 kD. Sodium-dependent uptake of taurocholate was observed in oocytes injected with cRNA. Northern blot analysis revealed a 5.0-kb mRNA in ileum, kidney, and cecum. A 48-kD protein was detected in ileal brush border membranes and localized to the apical border of villus ileal enterocytes. mRNA and protein expression, which were negligible before weaning, increased dramatically at weaning. Nuclear transcription rates for the transporter increased 15-fold between postnatal days 7 and 28. The apparent molecular weight of the transporter also increased between days 19 and 28. In summary, the developmental regulation of the rat ileal sodium-dependent bile acid cotransporter is characterized by transcriptionally regulated increases in mRNA and protein levels at the time of weaning with changes in apparent molecular weight of the protein after weaning.
Full text
PDF


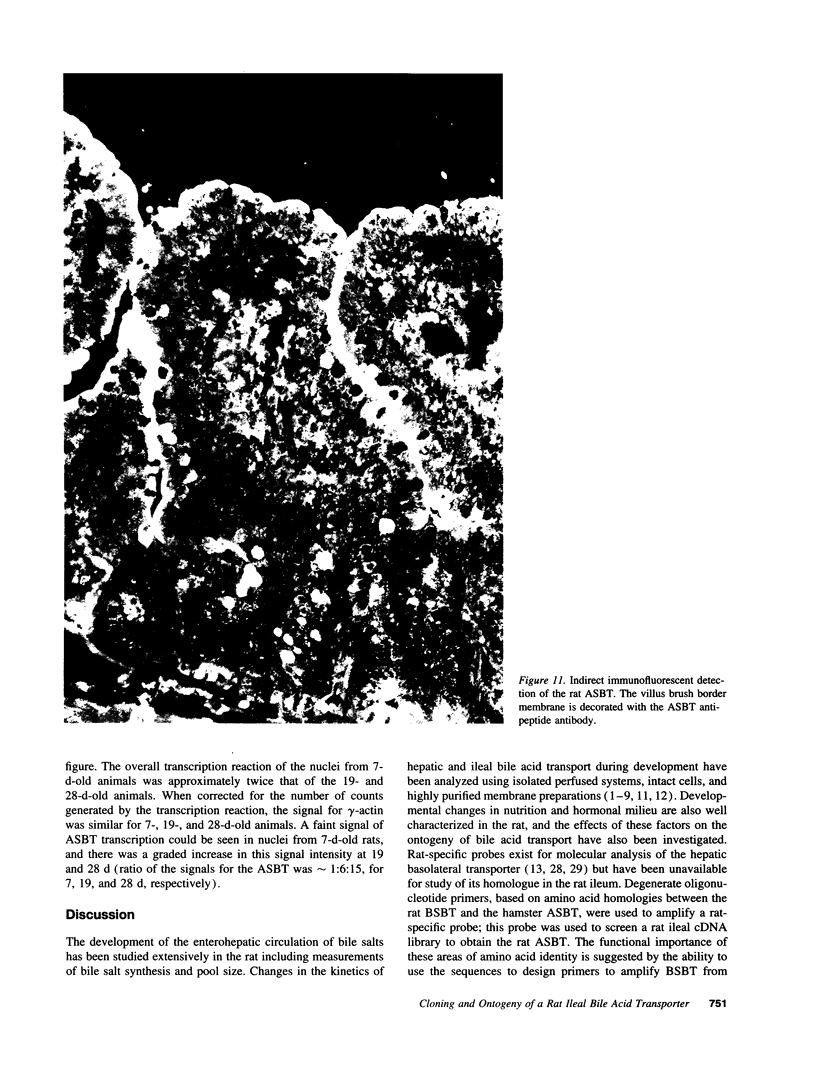



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlquist P., Dasgupta R., Kaesberg P. Nucleotide sequence of the brome mosaic virus genome and its implications for viral replication. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 5;172(4):369–383. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahlquist P., Luckow V., Kaesberg P. Complete nucleotide sequence of brome mosaic virus RNA3. J Mol Biol. 1981 Nov 25;153(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90524-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ananthanarayanan M., Ng O. C., Boyer J. L., Suchy F. J. Characterization of cloned rat liver Na(+)-bile acid cotransporter using peptide and fusion protein antibodies. Am J Physiol. 1994 Oct;267(4 Pt 1):G637–G643. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1994.267.4.G637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard J. A., Ghishan F. K. Methylprednisolone accelerates the ontogeny of sodium-taurocholate cotransport in rat ileal brush border membranes. J Lab Clin Med. 1986 Dec;108(6):549–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard J. A., Ghishan F. K., Wilson F. A. Ontogenesis of taurocholate transport by rat ileal brush border membrane vesicles. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):869–873. doi: 10.1172/JCI111785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumrich M., Petzinger E. Two distinct types of SH-groups are necessary for bumetanide and bile acid uptake into isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jul 4;1149(2):278–284. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90211-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büller H. A., Rings E. H., Pajkrt D., Montgomery R. K., Grand R. J. Glycosylation of lactase-phlorizin hydrolase in rat small intestine during development. Gastroenterology. 1990 Mar;98(3):667–675. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90287-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danbolt N. C., Pines G., Kanner B. I. Purification and reconstitution of the sodium- and potassium-coupled glutamate transport glycoprotein from rat brain. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 17;29(28):6734–6740. doi: 10.1021/bi00480a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielson P. E., Forss-Petter S., Brow M. A., Calavetta L., Douglass J., Milner R. J., Sutcliffe J. G. p1B15: a cDNA clone of the rat mRNA encoding cyclophilin. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):261–267. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond D. J., Goodman H. M. Regulation of growth hormone messenger RNA synthesis by dexamethasone and triiodothyronine. Transcriptional rate and mRNA stability changes in pituitary tumor cells. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):41–62. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90323-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliesler S. J., Basinger S. F. Tunicamycin blocks the incorporation of opsin into retinal rod outer segment membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1116–1120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong Y. Z., Zwarych P. P., Jr, Lin M. C., Wilson F. A. Effect of antiserum to a 99 kDa polypeptide on the uptake of taurocholic acid by rat ileal brush border membrane vesicles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):204–209. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91355-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbuch B., Stieger B., Foguet M., Lübbert H., Meier P. J. Functional expression cloning and characterization of the hepatocyte Na+/bile acid cotransport system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10629–10633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heubi J. E., Fellows J. L. Absence of relationship between the postnatal development of ileal active taurocholate transport and microvillus membrane fluidity. J Dev Physiol. 1990 Mar;13(3):135–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heubi J. E. Role of thyroxine on postnatal development of ileal active bile salt transport. Am J Physiol. 1986 Aug;251(2 Pt 1):G237–G242. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.2.G237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylemon P. B., Gurley E. C., Stravitz R. T., Litz J. S., Pandak W. M., Chiang J. Y., Vlahcevic Z. R. Hormonal regulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase mRNA levels and transcriptional activity in primary rat hepatocyte cultures. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16866–16871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapadia C. R., Essandoh L. K. Active absorption of vitamin B12 and conjugated bile salts by guinea pig ileum occurs in villous and not crypt cells. Dig Dis Sci. 1988 Nov;33(11):1377–1382. doi: 10.1007/BF01536991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaslow D. C. A rapid biochemical method for purifying lambda DNA from phage lysates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6767–6767. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Burckhardt G., Wilson F. A., Kurz G. Bile salt-binding polypeptides in brush-border membrane vesicles from rat small intestine revealed by photoaffinity labeling. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3623–3627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Nicol S. B., Girbig F., Gutjahr U., Kowalewski S., Fasold H. Characterization and chemical modification of the Na(+)-dependent bile-acid transport system in brush-border membrane vesicles from rabbit ileum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Oct 19;1111(1):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90278-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasinski S. D., Estrada G., Yeh K. Y., Yeh M., Traber P. G., Rings E. H., Büller H. A., Verhave M., Montgomery R. K., Grand R. J. Transcriptional regulation of intestinal hydrolase biosynthesis during postnatal development in rats. Am J Physiol. 1994 Oct;267(4 Pt 1):G584–G594. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1994.267.4.G584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R., Smallwood R. A., Little J. M., Brown A. S., Piasecki G. J., Jackson B. T. Fetal bile salt metabolism. The intestinal absorption of bile salt. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1009–1016. doi: 10.1172/JCI108723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. M., Lester R. Ontogenesis of intestinal bile salt absorption in the neonatal rat. Am J Physiol. 1980 Oct;239(4):G319–G323. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1980.239.4.G319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer M. S., Heubi J. E., Goodrich A. L., Balistreri W. F., Suchy F. J. Ontogeny of bile acid transport in brush border membrane vesicles from rat ileum. Gastroenterology. 1986 May;90(5 Pt 1):1188–1196. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90384-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahin-Tóth M., Lawrence M. C., Kaback H. R. Properties of permease dimer, a fusion protein containing two lactose permease molecules from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5421–5425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz S. M., Watkins J. B., Ling S. C. Taurocholate transport by brush-border membrane vesicles from the developing rabbit ileum: structure/function relationships. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1990 May;10(4):482–489. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199005000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shneider B. L., Michaud G. A., West A. B., Suchy F. J. The effects of bile acid feeding on the development of ileal bile acid transport. Pediatr Res. 1993 Mar;33(3):221–224. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199303000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shneider B. L., Moyer M. S. Characterization of endogenous carrier-mediated taurocholate efflux from Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):6985–6988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Hirayama B. A., Wright E. M. Baculovirus-mediated expression of the Na+/glucose cotransporter in Sf9 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Feb 17;1104(1):151–159. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90144-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson F. A., Burckhardt G., Murer H., Rumrich G., Ullrich K. J. Sodium-coupled taurocholate transport in the proximal convolution of the rat kidney in vivo and in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):1141–1150. doi: 10.1172/JCI110128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. H., Oelkers P., Craddock A. L., Dawson P. A. Expression cloning and characterization of the hamster ileal sodium-dependent bile acid transporter. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1340–1347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh K. Y., Holt P. R. Ontogenic timing mechanism initiates the expression of rat intestinal sucrase activity. Gastroenterology. 1986 Mar;90(3):520–526. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)91103-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Belle R. C., Vaupshas V., Vitullo B. B., Haber L. R., Shaffer E., Mackie G. G., Owen H., Little J. M., Lester R. Intestinal absorption of bile salts: immature development in the neonate. J Pediatr. 1979 Mar;94(3):472–476. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80604-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]