Abstract
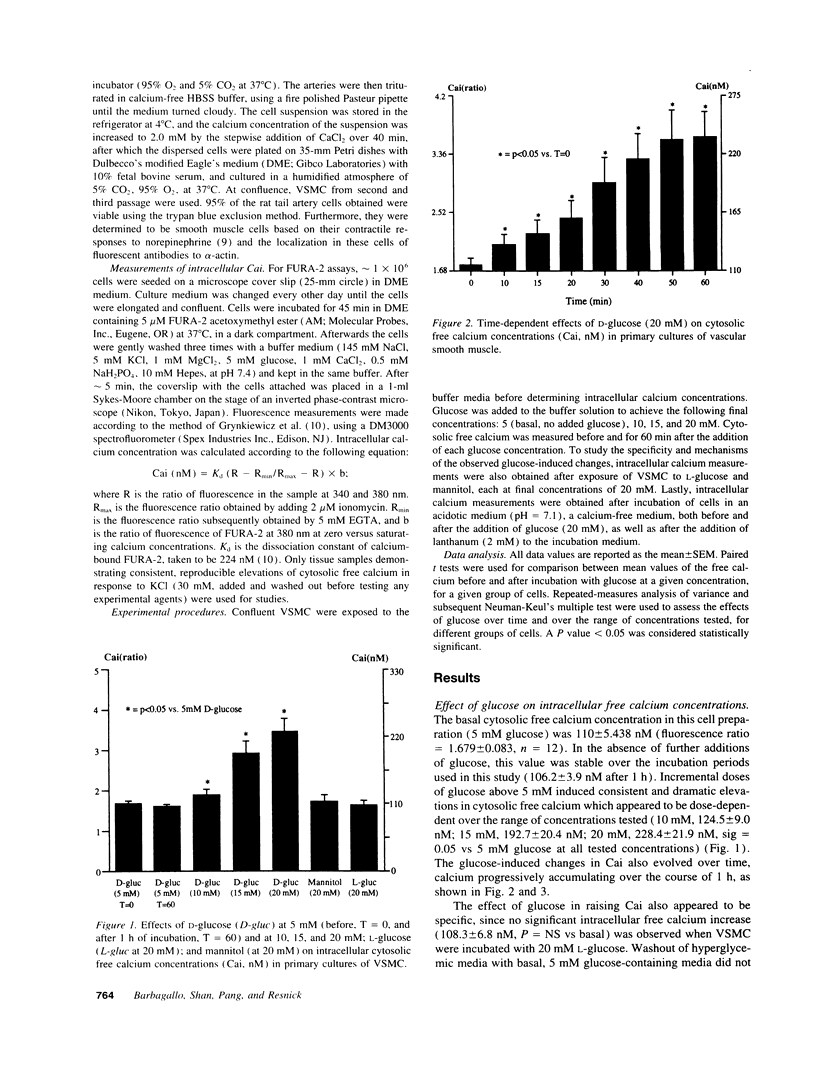
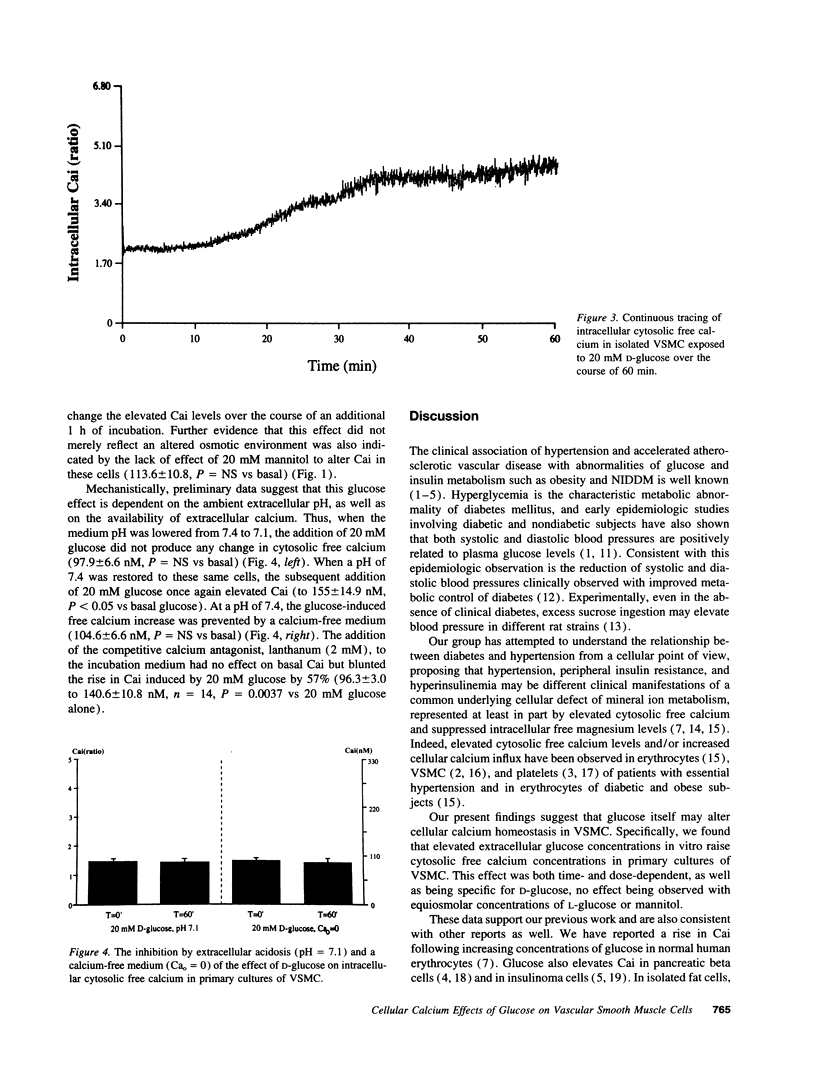
We have previously suggested that hyperglycemia per se may contribute to diabetic hypertensive and vascular disease by altering cellular ion content. To more directly investigate the potential role of glucose in this process, we measured cytosolic free calcium in primary cultures of vascular smooth muscle cells isolated from Sprague-Dawley rat tail artery before and after incubation with 5 (basal), 10, 15, and 20 mM glucose. Glucose significantly elevated cytosolic free calcium in a dose- and time-dependent manner, from 110.0 +/- 5.4 to 124.5 +/- 9.0, 192.7 +/- 20.4, and 228.4 +/- 21.9 nM at 5, 10, 15, and 20 mM glucose concentrations, respectively. This glucose-induced cytosolic free calcium elevation was also specific, no change being observed after incubation with equivalent concentrations of L-glucose or mannitol. This glucose effect was also dependent on extracellular calcium and pH, since these calcium changes were inhibited in an acidotic or a calcium-free medium, or by the competitive calcium antagonist lanthanum. We conclude that ambient glucose concentrations within clinically observed limits may alter cellular calcium ion homeostasis in vascular smooth muscle cells. We suggest that these cellular ionic effects of hyperglycemia may underlie the predisposition to hypertension and vascular diseases among diabetic subjects and/or those with impaired glucose tolerance.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davis F. B., Davis P. J., Nat G., Blas S. D., MacGillivray M., Gutman S., Feldman M. J. The effect of in vivo glucose administration on human erythrocyte Ca2+-ATPase activity and on enzyme responsiveness in vitro to thyroid hormone and calmodulin. Diabetes. 1985 Jul;34(7):639–646. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.7.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deziel M. R., Safeer R. S., Blas S. D., Davis F. B., Davis P. J. Hexose-specific inhibition in vitro of human red cell Ca(2+)-ATPase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Sep 21;1110(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90302-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draznin B., Kao M., Sussman K. E. Insulin and glyburide increase cytosolic free-Ca2+ concentration in isolated rat adipocytes. Diabetes. 1987 Feb;36(2):174–178. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.2.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draznin B., Leitner J. W., Sussman K. E., Sherman N. A. Insulin and glucose modulate protein kinase C activity in rat adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):570–575. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80880-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilam Y., Othman M., Halachmi D. Transient increase in Ca2+ influx in Saccharomyces cerevisiae in response to glucose: effects of intracellular acidification and cAMP levels. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Dec;136(12):2537–2543. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-12-2537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erne P., Bolli P., Bürgisser E., Bühler F. R. Correlation of platelet calcium with blood pressure. Effect of antihypertensive therapy. N Engl J Med. 1984 Apr 26;310(17):1084–1088. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198404263101705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrannini E., Buzzigoli G., Bonadonna R., Giorico M. A., Oleggini M., Graziadei L., Pedrinelli R., Brandi L., Bevilacqua S. Insulin resistance in essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1987 Aug 6;317(6):350–357. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198708063170605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genuth S. M. Plasma insulin and glucose profiles in normal, obese, and diabetic persons. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Dec;79(6):812–822. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-6-812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoenig M., Sharp G. W. Glucose induces insulin release and a rise in cytosolic calcium concentration in a transplantable rat insulinoma. Endocrinology. 1986 Dec;119(6):2502–2507. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-6-2502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. M., Ishizuka T., Farese R. V. Interrelated effects of insulin and glucose on diacylglycerol-protein kinase-C signalling in rat adipocytes and solei muscle in vitro and in vivo in diabetic rats. Endocrinology. 1991 Jun;128(6):2937–2948. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-6-2937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett R. J., Keen H., McCartney M., Fuller J. H., Hamilton P. J., Reid D. D., Rose G. Glucose tolerance and blood pressure in two population samples: their relation to diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Int J Epidemiol. 1978 Mar;7(1):15–24. doi: 10.1093/ije/7.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juntti-Berggren L., Arkhammar P., Nilsson T., Rorsman P., Berggren P. O. Glucose-induced increase in cytoplasmic pH in pancreatic beta-cells is mediated by Na+/H+ exchange, an effect not dependent on protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23537–23541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser N., Sasson S., Feener E. P., Boukobza-Vardi N., Higashi S., Moller D. E., Davidheiser S., Przybylski R. J., King G. L. Differential regulation of glucose transport and transporters by glucose in vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Diabetes. 1993 Jan;42(1):80–89. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.1.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim D., Smith T. W. Cellular mechanisms underlying calcium-proton interactions in cultured chick ventricular cells. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:391–410. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama H., Ito Y., Suzuki H., Kitamura K., Itoh T. Factors modifying contraction-relaxation cycle in vascular smooth muscles. Am J Physiol. 1982 Nov;243(5):H641–H662. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1982.243.5.H641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda M., Honnor R. C., Cushman S. W., Londos C., Simpson I. A. Regulation of insulin-stimulated glucose transport in the isolated rat adipocyte. cAMP-independent effects of lipolytic and antilipolytic agents. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):245–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modan M., Halkin H., Almog S., Lusky A., Eshkol A., Shefi M., Shitrit A., Fuchs Z. Hyperinsulinemia. A link between hypertension obesity and glucose intolerance. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):809–817. doi: 10.1172/JCI111776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. Effects of fasting on insulin binding, glucose transport, and glucose oxidation in isolated rat adipocytes: relationships between insulin receptors and insulin action. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1450–1460. doi: 10.1172/JCI108601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preuss H. G., el Zein M., Knapka J., MacArthy P., Yousufi A. K., Gleim G. W., Glace B., Zukowska-Grojec Z. Blood pressure responses to sucrose ingestion in four rat strains. Am J Hypertens. 1992 Apr;5(4 Pt 1):244–250. doi: 10.1093/ajh/5.4.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Hoffman B. B. A role for insulin in the aetiology and course of hypertension? Lancet. 1987 Aug 22;2(8556):435–437. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90968-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick L. M., Gupta R. K., Bhargava K. K., Gruenspan H., Alderman M. H., Laragh J. H. Cellular ions in hypertension, diabetes, and obesity. A nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic study. Hypertension. 1991 Jun;17(6 Pt 2):951–957. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.17.6.951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick L. M. Hypertension and abnormal glucose homeostasis. Possible role of divalent ion metabolism. Am J Med. 1989 Dec 8;87(6A):17S–22S. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(89)90490-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick L. M. Ionic basis of hypertension, insulin resistance, vascular disease, and related disorders. The mechanism of "syndrome X". Am J Hypertens. 1993 Apr;6(4):123S–134S. doi: 10.1093/ajh/6.4s.123s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamler J., Stamler R., Rhomberg P., Dyer A., Berkson D. M., Reedus W., Wannamaker J. Multivariate analysis of the relationship of six variables to blood pressure: findings from Chicago community surveys, 1965--1971. J Chronic Dis. 1975 Nov;28(10):499–525. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(75)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Yoshizumi M., Takaku F., Urabe H., Tsukakoshi M., Kasuya T., Yazaki Y. The elevation of the cytoplasmic calcium ions in vascular smooth muscle cells in SHR--measurement of the free calcium ions in single living cells by lasermicrofluorospectrometry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 26;141(1):340–345. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80374-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swislocki A. L., Hoffman B. B., Reaven G. M. Insulin resistance, glucose intolerance and hyperinsulinemia in patients with hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 1989 Jun;2(6 Pt 1):419–423. doi: 10.1093/ajh/2.6.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan-Jones R. D., Lederer W. J., Eisner D. A. Ca2+ ions can affect intracellular pH in mammalian cardiac muscle. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):522–524. doi: 10.1038/301522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R., Karpinski E., Pang P. K. Two types of calcium channels in isolated smooth muscle cells from rat tail artery. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 2):H1361–H1368. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.5.H1361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B., Schrier R. W. Effect of elevated extracellular glucose concentrations on calcium ion uptake by cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1992;18(2-5):145–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B., Tsai P., Schrier R. W. Glucose-induced downregulation of angiotensin II and arginine vasopressin receptors in cultured rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cells. Role of protein kinase C. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):1992–1999. doi: 10.1172/JCI116079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa-Miwa A., Ito H., Sugimoto T. Effects of insulin on vasoconstriction induced by thromboxane A2 in porcine coronary artery. Circulation. 1990 May;81(5):1654–1659. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.5.1654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



