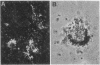
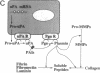
Full text
PDF

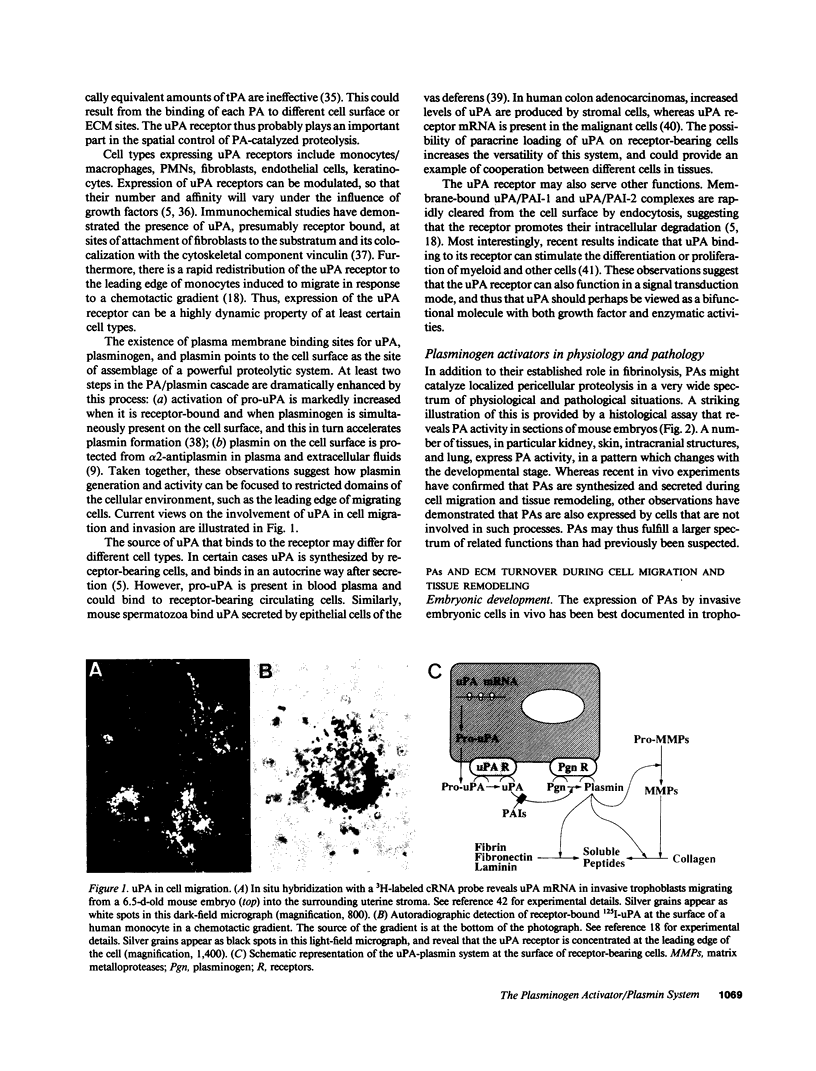



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrade-Gordon P., Strickland S. Interaction of heparin with plasminogen activators and plasminogen: effects on the activation of plasminogen. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 15;25(14):4033–4040. doi: 10.1021/bi00362a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreasen P. A., Georg B., Lund L. R., Riccio A., Stacey S. N. Plasminogen activator inhibitors: hormonally regulated serpins. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Jan 2;68(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belin D., Wohlwend A., Schleuning W. D., Kruithof E. K., Vassalli J. D. Facultative polypeptide translocation allows a single mRNA to encode the secreted and cytosolic forms of plasminogen activators inhibitor 2. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3287–3294. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasi F., Behrendt N., Cubellis M. V., Ellis V., Lund L. R., Masucci M. T., Møller L. B., Olson D. P., Pedersen N., Ploug M. The urokinase receptor and regulation of cell surface plasminogen activation. Cell Differ Dev. 1990 Dec 2;32(3):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(90)90037-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart M. A., Belin D., Vassalli J. D., Vassalli P. Modulations of functional activity in differentiated macrophages are accompanied by early and transient increase or decrease in c-fos gene transcription. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):949–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich H. J., Keijer J., Preissner K. T., Gebbink R. K., Pannekoek H. Functional interaction of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1) and heparin. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 29;30(4):1021–1028. doi: 10.1021/bi00218a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis V., Scully M. F., Kakkar V. V. Plasminogen activation initiated by single-chain urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Potentiation by U937 monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2185–2188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis V., Wun T. C., Behrendt N., Rønne E., Danø K. Inhibition of receptor-bound urokinase by plasminogen-activator inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9904–9908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estreicher A., Mühlhauser J., Carpentier J. L., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. The receptor for urokinase type plasminogen activator polarizes expression of the protease to the leading edge of migrating monocytes and promotes degradation of enzyme inhibitor complexes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):783–792. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estreicher A., Wohlwend A., Belin D., Schleuning W. D., Vassalli J. D. Characterization of the cellular binding site for the urokinase-type plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1180–1189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Adler B., Boose J. A., Gerard R. D., Madison E. L., McGookey D., Meidell R. S., Roman L. M., Sambrook J. Variants of human tissue-type plasminogen activator that lack specific structural domains of the heavy chain. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2731–2740. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03127.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J. L., Krupp M. N., Rifkin D. B., Lane M. D. Down-regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor correlates with plasminogen activator activity in human A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2276–2280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HE C. S., Wilhelm S. M., Pentland A. P., Marmer B. L., Grant G. A., Eisen A. Z., Goldberg G. I. Tissue cooperation in a proteolytic cascade activating human interstitial collagenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2632–2636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar K. A., Hamel N. M. Identification and characterization of human endothelial cell membrane binding sites for tissue plasminogen activator and urokinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2908–2916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiple J. M., Ossowski L. Human neutrophil plasminogen activator is localized in specific granules and is translocated to the cell surface by exocytosis. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):826–840. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huarte J., Belin D., Bosco D., Sappino A. P., Vassalli J. D. Plasminogen activator and mouse spermatozoa: urokinase synthesis in the male genital tract and binding of the enzyme to the sperm cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1281–1289. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huarte J., Belin D., Vassalli A., Strickland S., Vassalli J. D. Meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes triggers the translation and polyadenylation of dormant tissue-type plasminogen activator mRNA. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1201–1211. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huarte J., Belin D., Vassalli J. D. Plasminogen activator in mouse and rat oocytes: induction during meiotic maturation. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):551–558. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90184-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Schmitt M., Goretzki L., Chucholowski N., Calvete J., Kramer M., Günzler W. A., Jänicke F., Graeff H. Cathepsin B efficiently activates the soluble and the tumor cell receptor-bound form of the proenzyme urokinase-type plasminogen activator (Pro-uPA). J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5147–5152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Skriver L., Nielsen L. S., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Danø K. Distribution of urokinase-type plasminogen activator immunoreactivity in the mouse. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):894–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longstaff C., Gaffney P. J. Serpin-serine protease binding kinetics: alpha 2-antiplasmin as a model inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 29;30(4):979–986. doi: 10.1021/bi00218a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medcalf R. L., Rüegg M., Schleuning W. D. A DNA motif related to the cAMP-responsive element and an exon-located activator protein-2 binding site in the human tissue-type plasminogen activator gene promoter cooperate in basal expression and convey activation by phorbol ester and cAMP. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14618–14626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles L. A., Dahlberg C. M., Plescia J., Felez J., Kato K., Plow E. F. Role of cell-surface lysines in plasminogen binding to cells: identification of alpha-enolase as a candidate plasminogen receptor. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 12;30(6):1682–1691. doi: 10.1021/bi00220a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusrat A. R., Chapman H. A., Jr An autocrine role for urokinase in phorbol ester-mediated differentiation of myeloid cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):1091–1097. doi: 10.1172/JCI115070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L. In vivo invasion of modified chorioallantoic membrane by tumor cells: the role of cell surface-bound urokinase. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2437–2445. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper M. S., Belin D., Montesano R., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 modulates basic fibroblast growth factor-induced proteolytic and angiogenic properties of endothelial cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):743–755. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper M. S., Montesano R., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 is induced in microvascular endothelial cells by a chondrocyte-derived transforming growth factor-beta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 30;176(2):633–638. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80231-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper M. S., Montesano R. Proteolytic balance and capillary morphogenesis. Cell Differ Dev. 1990 Dec 2;32(3):319–327. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(90)90046-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper M. S., Montesano R., Vassalli J. D., Orci L. Chondrocytes inhibit endothelial sprout formation in vitro: evidence for involvement of a transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Jan;146(1):170–179. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041460122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen L. C., Lund L. R., Nielsen L. S., Danø K., Skriver L. One-chain urokinase-type plasminogen activator from human sarcoma cells is a proenzyme with little or no intrinsic activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11189–11195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploug M., Rønne E., Behrendt N., Jensen A. L., Blasi F., Danø K. Cellular receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator. Carboxyl-terminal processing and membrane anchoring by glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1926–1933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Miles L. A. Plasminogen receptors in the mediation of pericellular proteolysis. Cell Differ Dev. 1990 Dec 2;32(3):293–298. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(90)90042-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke C., Kristensen P., Ralfkiaer E., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Eriksen J., Blasi F., Danø K. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator is expressed in stromal cells and its receptor in cancer cells at invasive foci in human colon adenocarcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1991 May;138(5):1059–1067. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley J. P., Berkenpas M. B., Aimes R. T., Chen J. M. Serine protease and metallo protease cascade systems involved in pericellular proteolysis. Cell Differ Dev. 1990 Dec 2;32(3):263–275. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(90)90039-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin D. B., Moscatelli D., Bizik J., Quarto N., Blei F., Dennis P., Flaumenhaft R., Mignatti P. Growth factor control of extracellular proteolysis. Cell Differ Dev. 1990 Dec 2;32(3):313–318. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(90)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Otter M., Kuiper J., van Berkel T. J. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) by liver cells. Thromb Res Suppl. 1990;10:63–71. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(90)90379-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rørth P., Nerlov C., Blasi F., Johnsen M. Transcription factor PEA3 participates in the induction of urokinase plasminogen activator transcription in murine keratinocytes stimulated with epidermal growth factor or phorbol-ester. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5009–5017. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Huarte J., Belin D., Vassalli J. D. Plasminogen activators in tissue remodeling and invasion: mRNA localization in mouse ovaries and implanting embryos. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2471–2479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Huarte J., Vassalli J. D., Belin D. Sites of synthesis of urokinase and tissue-type plasminogen activators in the murine kidney. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):962–970. doi: 10.1172/JCI115104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiffert D., Mimuro J., Schleef R. R., Loskutoff D. J. Interactions between type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor, extracellular matrix and vitronectin. Cell Differ Dev. 1990 Dec 2;32(3):287–292. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(90)90041-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsafriri A., Bicsak T. A., Cajander S. B., Ny T., Hsueh A. J. Suppression of ovulation rate by antibodies to tissue-type plasminogen activator and alpha 2-antiplasmin. Endocrinology. 1989 Jan;124(1):415–421. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-1-415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri A., Stephens R. W., Salonen E. M., Pöllänen J., Tapiovaara H. Plasminogen activation at the cell surface-matrix interface. Cell Differ Dev. 1990 Dec 2;32(3):255–262. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(90)90038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valinsky J. E., Reich E., Le Douarin N. M. Plasminogen activator in the bursa of Fabricius: correlations with morphogenetic remodeling and cell migrations. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):471–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Baccino D., Belin D. A cellular binding site for the Mr 55,000 form of the human plasminogen activator, urokinase. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):86–92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrall S., Seeds N. W. Characterization of 125I-tissue plasminogen activator binding to cerebellar granule neurons. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):265–271. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hinsbergh V. W., van den Berg E. A., Fiers W., Dooijewaard G. Tumor necrosis factor induces the production of urokinase-type plasminogen activator by human endothelial cells. Blood. 1990 May 15;75(10):1991–1998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Ahe D., Pearson D., Nagamine Y. Macromolecular interaction on a cAMP responsive region in the urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene: a role of protein phosphorylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):1991–1999. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]