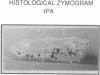
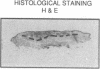
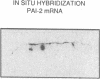
Abstract
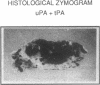
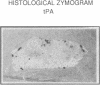
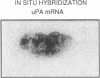
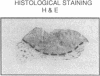
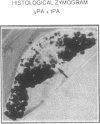
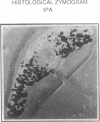
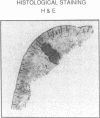
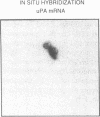
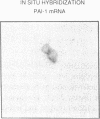
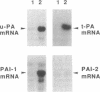
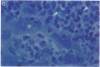
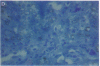
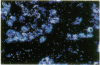
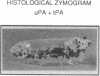
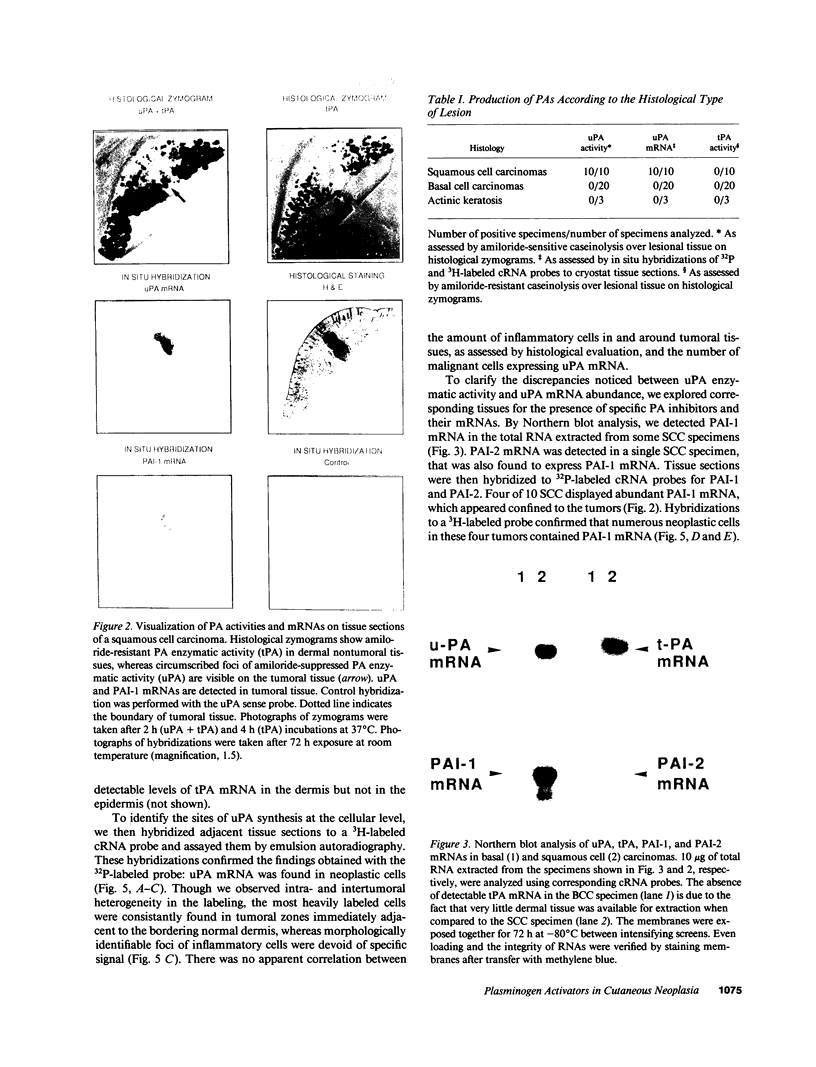
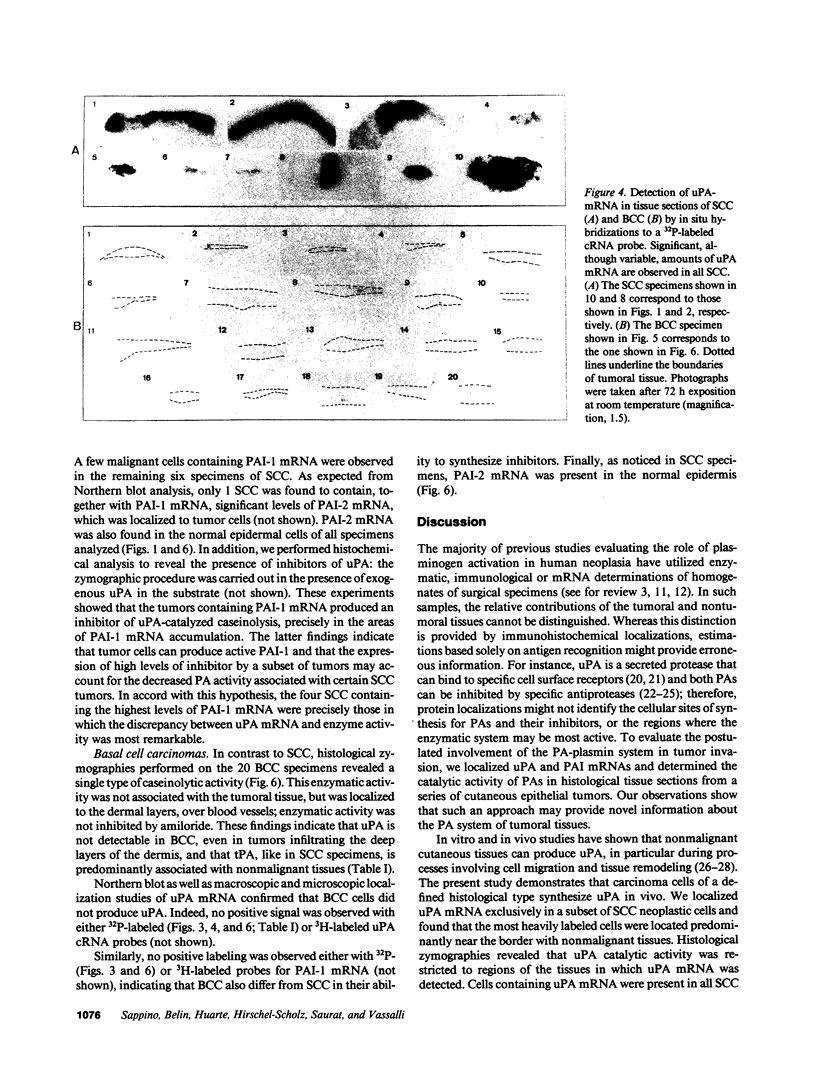
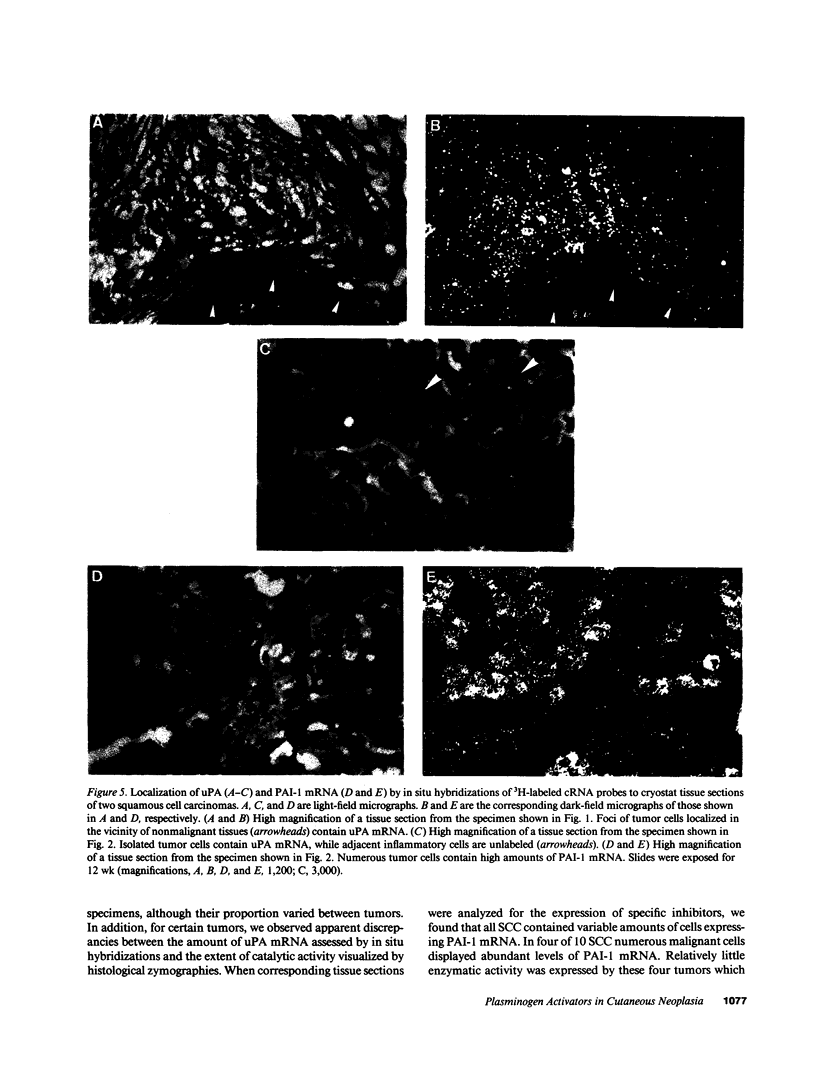
To assess the postulated role of plasminogen activation in tumor invasion, we have investigated the cellular sites of synthesis for urokinase-type (uPA) and tissue-type (tPA) plasminogen activators and their inhibitors (PAI-1 and PAI-2) in two human cutaneous neoplasia that differ in their metastatic potential. The combined use of zymography on tissue sections and in situ hybridization demonstrates that uPA is produced by malignant cells of squamous cell carcinomas (SCC) but not by basal cell carcinomas (BCC), whereas tPA is detected exclusively in nonmalignant dermal tissue. In addition, we show that SCC neoplastic cells simultaneously produce variable amounts of PAI-1, and that PAI-1 production correlates inversely with uPA enzymatic activity. These observations establish that invasive human malignant cells in vivo can activate plasminogen through uPA production during the early phases of tumor growth; they also demonstrate that the proteolytic activity of tumor cells can be modulated by the concomitant production of PAI-1. Because SCC have a higher invasive and metastatic potential than BCC, our findings lend further support to the involvement of plasminogen activation in malignant behavior.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander C. M., Werb Z. Proteinases and extracellular matrix remodeling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;1(5):974–982. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreasen P. A., Georg B., Lund L. R., Riccio A., Stacey S. N. Plasminogen activator inhibitors: hormonally regulated serpins. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Jan 2;68(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreasen P. A., Riccio A., Welinder K. G., Douglas R., Sartorio R., Nielsen L. S., Oppenheimer C., Blasi F., Danø K. Plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1: reactive center and amino-terminal heterogeneity determined by protein and cDNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. B., Low D. A., Simmer R. L., Cunningham D. D. Protease-nexin: a cellular component that links thrombin and plasminogen activator and mediates their binding to cells. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker M. S., Bleakley P., Woodrow G. C., Doe W. F. Inhibition of cancer cell urokinase plasminogen activator by its specific inhibitor PAI-2 and subsequent effects on extracellular matrix degradation. Cancer Res. 1990 Aug 1;50(15):4676–4684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belin D., Wohlwend A., Schleuning W. D., Kruithof E. K., Vassalli J. D. Facultative polypeptide translocation allows a single mRNA to encode the secreted and cytosolic forms of plasminogen activators inhibitor 2. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3287–3294. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cajot J. F., Kruithof E. K., Schleuning W. D., Sordat B., Bachmann F. Plasminogen activators, plasminogen activator inhibitors and procoagulant analyzed in twenty human tumor cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1986 Nov 15;38(5):719–727. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910380516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy M. J., Reilly D., O'Sullivan C., O'Higgins N., Fennelly J. J., Andreasen P. Urokinase-plasminogen activator, a new and independent prognostic marker in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1990 Nov 1;50(21):6827–6829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R., Waller E. K., Grossi G., Thompson D., Tizard R., Schleuning W. D. Isolation and characterization of the human tissue-type plasminogen activator structural gene including its 5' flanking region. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11223–11230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb R. H., Liotta L. A. Proteolytic enzymes in cancer invasion and metastasis. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1986 Oct;12(4):294–307. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb A. B., Chang C. K., Posnett D. N., Fanelli B., Tam J. P. Detection of transforming growth factor alpha in normal, malignant, and hyperproliferative human keratinocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):670–675. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Di Fiore P., Locatelli E. K., Falco J., Blasi F. Modulation of urokinase plasminogen activator gene expression during the transition from quiescent to proliferative state in normal mouse cells. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):855–861. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04295.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grøndahl-Hansen J., Lund L. R., Ralfkiaer E., Ottevanger V., Danø K. Urokinase- and tissue-type plasminogen activators in keratinocytes during wound reepithelialization in vivo. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Jun;90(6):790–795. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12461511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grøndahl-Hansen J., Ralfkiaer E., Nielsen L. S., Kristensen P., Frentz G., Danø K. Immunohistochemical localization of urokinase- and tissue-type plasminogen activators in psoriatic skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Jan;88(1):28–32. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12464827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidtmann H. H., Hofmann M., Jacob E., Erbil C., Havemann K., Schwartz-Albiez R. Synthesis and secretion of plasminogen activators and plasminogen activator inhibitors in cell lines of different groups of human lung tumors. Cancer Res. 1989 Dec 15;49(24 Pt 1):6960–6965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King L. E., Jr, Gates R. E., Stoscheck C. M., Nanney L. B. The EGF/TGF alpha receptor in skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Jun;94(6 Suppl):164S–170S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12876141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecander I., Astedt B. Isolation of a new specific plasminogen activator inhibitor from pregnancy plasma. Br J Haematol. 1986 Feb;62(2):221–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1986.tb02925.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G. Latent tissue plasminogen activator produced by human endothelial cells in culture: evidence for an enzyme-inhibitor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6804–6808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., van Mourik J. A., Erickson L. A., Lawrence D. Detection of an unusually stable fibrinolytic inhibitor produced by bovine endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2956–2960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Robbins E., Rifkin D. B. Tumor invasion through the human amniotic membrane: requirement for a proteinase cascade. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):487–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90613-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morioka S., Lazarus G. S., Baird J. L., Jensen P. J. Migrating keratinocytes express urokinase-type plasminogen activator. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Apr;88(4):418–423. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12469754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedbala M. J., Sartorelli A. C. Regulation by epidermal growth factor of human squamous cell carcinoma plasminogen activator-mediated proteolysis of extracellular matrix. Cancer Res. 1989 Jun 15;49(12):3302–3309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L. In vivo invasion of modified chorioallantoic membrane by tumor cells: the role of cell surface-bound urokinase. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2437–2445. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L. Plasminogen activator dependent pathways in the dissemination of human tumor cells in the chick embryo. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):321–328. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Reich E. Antibodies to plasminogen activator inhibit human tumor metastasis. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):611–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Busso N., Belin D., Vassalli J. D. Increase of urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene expression in human lung and breast carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1987 Aug 1;47(15):4043–4046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Huarte J., Belin D., Vassalli J. D. Plasminogen activators in tissue remodeling and invasion: mRNA localization in mouse ovaries and implanting embryos. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2471–2479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Huarte J., Vassalli J. D., Belin D. Sites of synthesis of urokinase and tissue-type plasminogen activators in the murine kidney. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):962–970. doi: 10.1172/JCI115104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Rifkin D. B. Inhibition of endothelial cell movement by pericytes and smooth muscle cells: activation of a latent transforming growth factor-beta 1-like molecule by plasmin during co-culture. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):309–315. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spyratos F., Maudelonde T., Brouillet J. P., Brunet M., Defrenne A., Andrieu C., Hacene K., Desplaces A., Rouëssé J., Rochefort H. Cathepsin D: an independent prognostic factor for metastasis of breast cancer. Lancet. 1989 Nov 11;2(8672):1115–1118. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91487-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppelli M. P., Corti A., Soffientini A., Cassani G., Blasi F., Assoian R. K. Differentiation-enhanced binding of the amino-terminal fragment of human urokinase plasminogen activator to a specific receptor on U937 monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4939–4943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppelli M. P., Verde P., Grimaldi G., Locatelli E. K., Blasi F. Increase in urokinase plasminogen activator mRNA synthesis in human carcinoma cells is a primary effect of the potent tumor promoter, phorbol myristate acetate. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1235–1241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Mahdavi V. The induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells by retinoic acid. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Baccino D., Belin D. A cellular binding site for the Mr 55,000 form of the human plasminogen activator, urokinase. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):86–92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Belin D. Amiloride selectively inhibits the urokinase-type plasminogen activator. FEBS Lett. 1987 Apr 6;214(1):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verde P., Stoppelli M. P., Galeffi P., Di Nocera P., Blasi F. Identification and primary sequence of an unspliced human urokinase poly(A)+ RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4727–4731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu H. R., Schultz R. M. Relationship between secreted urokinase plasminogen activator activity and metastatic potential in murine B16 cells transfected with human urokinase sense and antisense genes. Cancer Res. 1990 Dec 1;50(23):7623–7633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]